Abstract
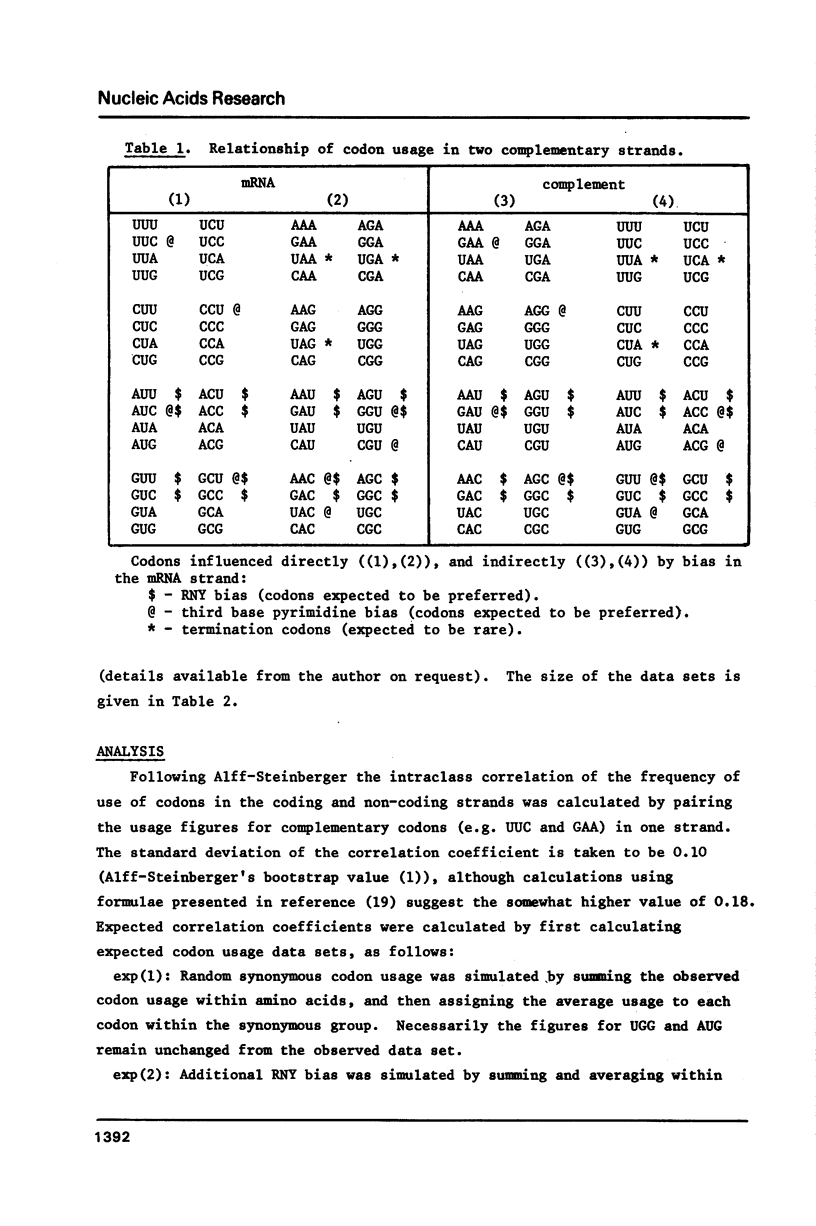
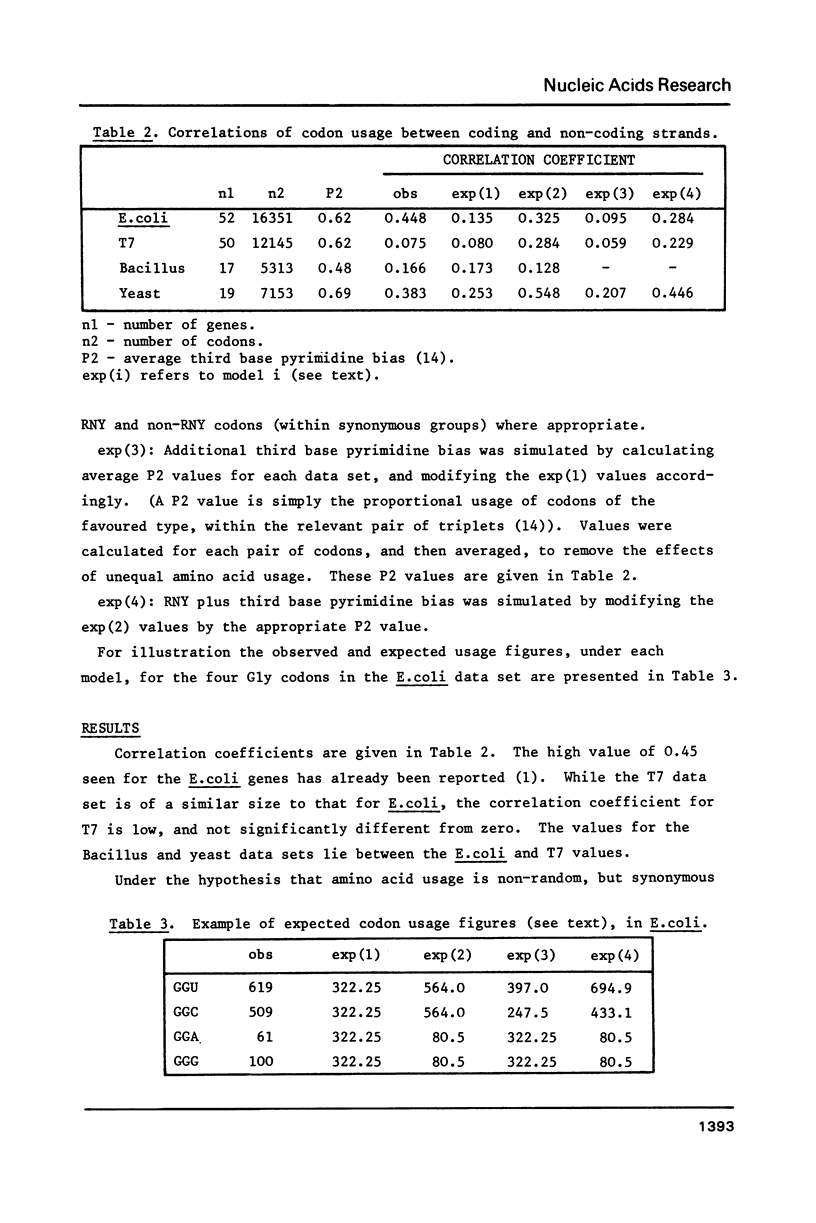
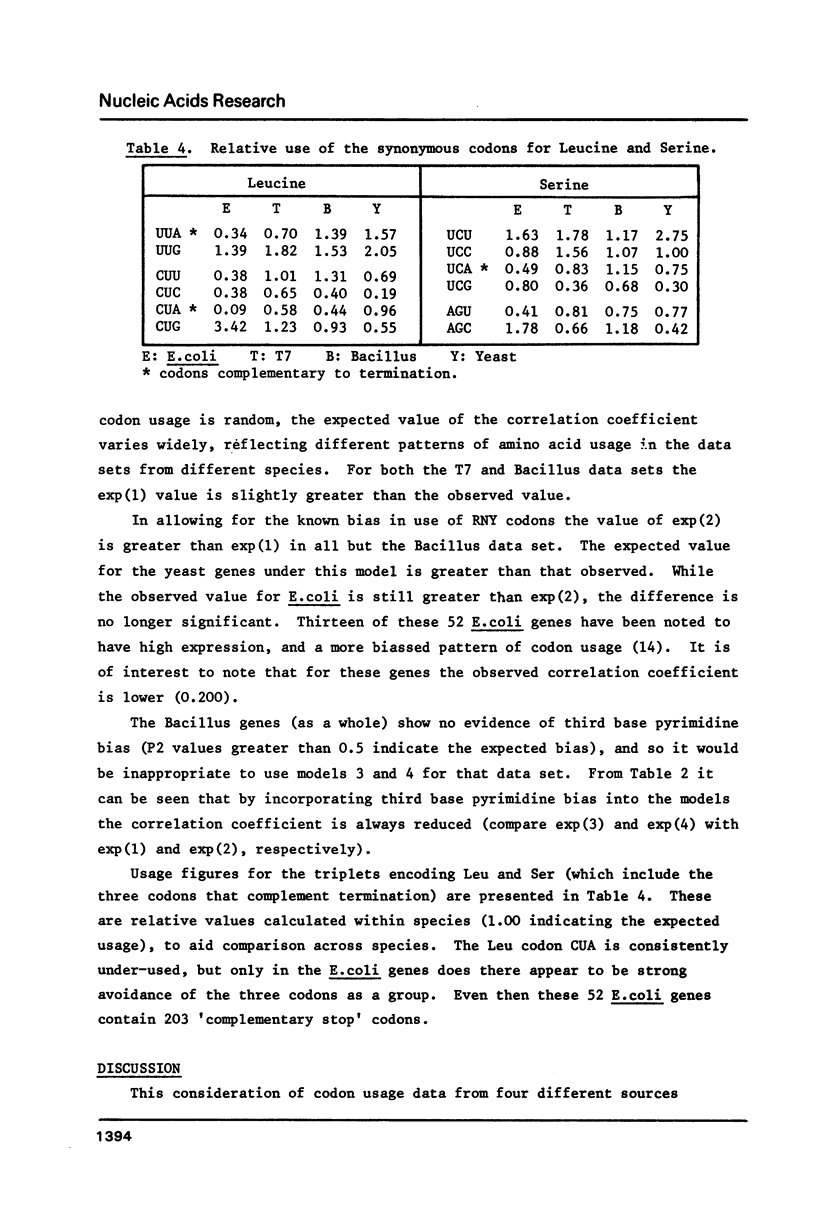
The hypothesis that DNA strands complementary to the coding strand contain in phase coding sequences has been investigated. Statistical analysis of the 50 genes of bacteriophage T7 shows no significant correlation between patterns of codon usage on the coding and non-coding strands. In Bacillus and yeast genes the correlation observed is not different from that expected with random synonymous codon usage, while a high correlation seen in 52 E. coli genes can be explained in terms of an excess of RNY codons. A deficiency of UUA, CUA and UCA codons (complementary to termination) seems to be restricted to the E. coli genes, and may be due to low abundance of the relevant cognate tRNA species. Thus the analysis shows that the non-coding strand has the properties expected of a sequence complementary to a coding strand, with no indications that it encodes, or may have encoded, proteins.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alff-Steinberger C. Evidence for a coding pattern on the non-coding strand of the E. coli genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2235–2241. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casino A., Cipollaro M., Guerrini A. M., Mastrocinque G., Spena A., Scarlato V. Coding capacity of complementary DNA strands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1499–1518. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. Darwinian evolution of proteins. Science. 1970 May 22;168(3934):1009–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3934.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. Estimating the total number of nucleotide substitutions since the common ancestor of a pair of homologous genes: comparison of several methods and three beta hemoglobin messenger RNA's. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(3-4):153–209. doi: 10.1007/BF01804976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Markowitz E. An improved method for determining codon variability in a gene and its application to the rate of fixation of mutations in evolution. Biochem Genet. 1970 Oct;4(5):579–593. doi: 10.1007/BF00486096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding G. B., Strobeck C. Expected frequencies of codon use as a function of mutation rates and codon fitnesses. J Mol Evol. 1982;18(6):379–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01840886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C. Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7055–7074. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Mercier R., Pavé A. Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r49–r62. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Ozeki H. Codon usage and transfer RNA contents: organism-specific codon-choice patterns in reference to the isoacceptor contents. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1087–1097. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Gojobori T., Nei M. Pseudogenes as a paradigm of neutral evolution. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):237–239. doi: 10.1038/292237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Hayashida H. Extraordinarily high evolutionary rate of pseudogenes: evidence for the presence of selective pressure against changes between synonymous codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5739–5743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modiano G., Battistuzzi G., Motulsky A. G. Nonrandom patterns of codon usage and of nucleotide substitutions in human alpha- and beta-globin genes: an evolutionary strategy reducing the rate of mutations with drastic effects? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1110–1114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieczenik G. Predicting coding function from nucleotide sequence or survival of "fitness" of tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3539–3543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond R. C. Non-Darwinian evolution: a critique. Nature. 1970 Mar 14;225(5237):1025–1028. doi: 10.1038/2251025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C. From primeval message to present-day gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1099–1108. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C. Periodic correlations in DNA sequences and evidence suggesting their evolutionary origin in a comma-less genetic code. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(2):94–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01732679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneath P. H. Relations between chemical structure and biological activity in peptides. J Theor Biol. 1966 Nov;12(2):157–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



