Abstract
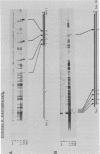
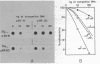
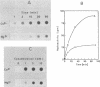
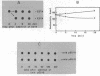
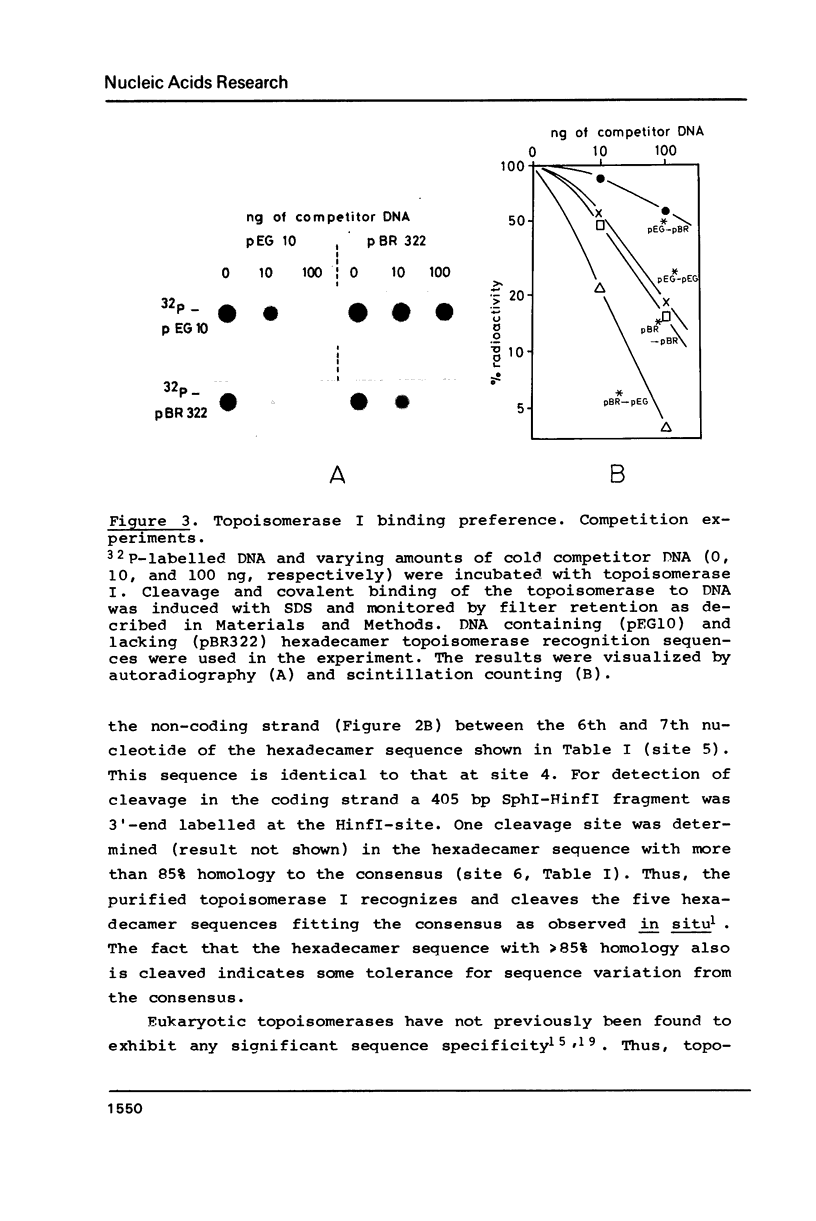
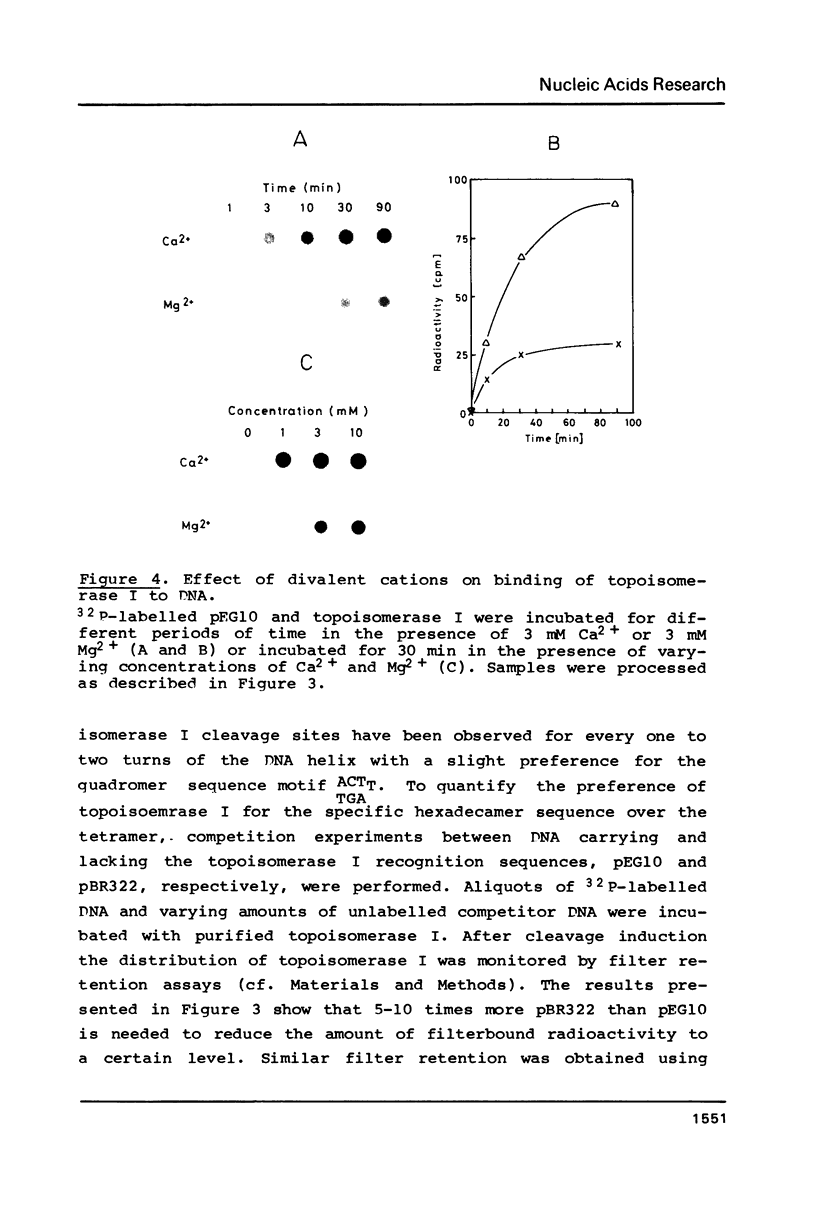
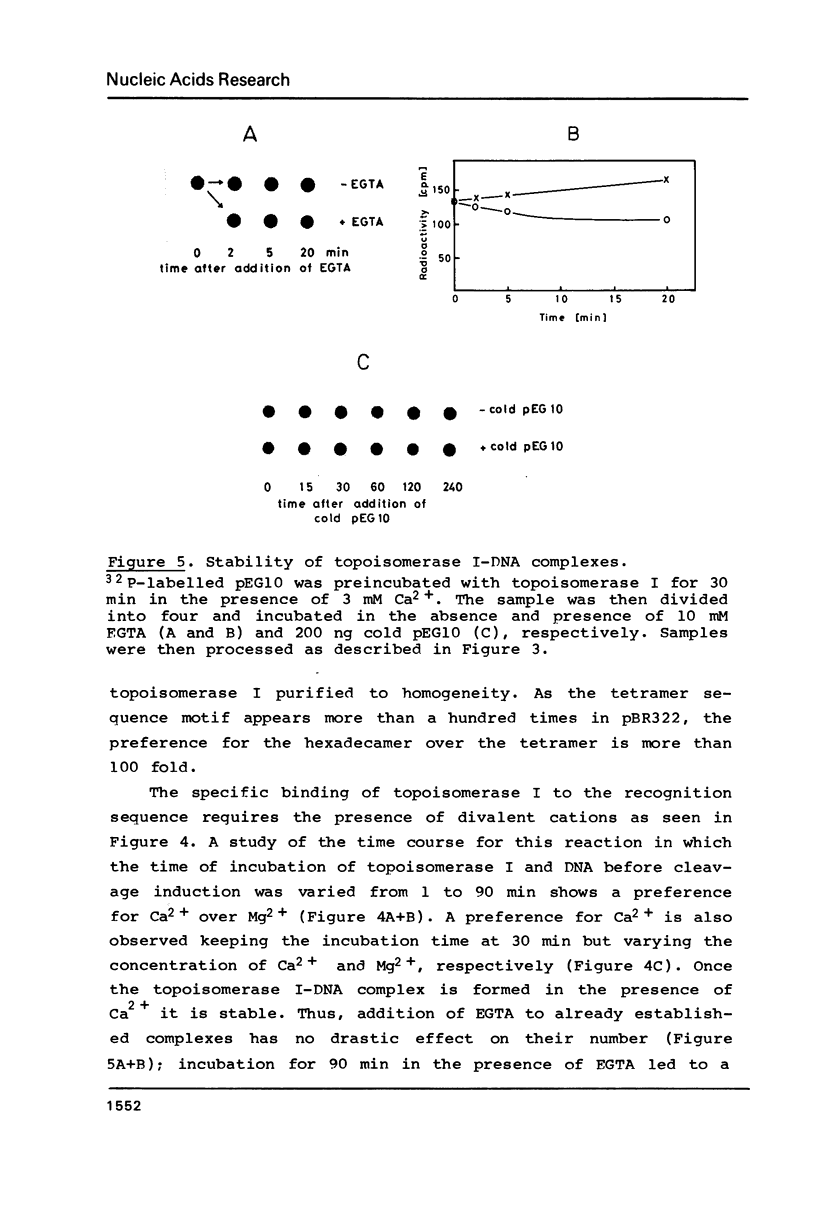
Topoisomerase I is in situ associated with DNaseI hypersensitive sites located in the promotor and terminator regions of the extrachromosomal rDNA in Tetrahymena thermophila at sites with sequences fitting the motif (sequence in text) Reconstitution experiments with purified topoisomerase I and cloned fragments of rDNA demonstrate that the enzyme exhibits the same binding and cleavage properties on naked DNA. These observations are striking as topoisomerase I previously has been found to exhibit low sequence specificity. The specific binding of the enzyme has an absolute requirement for divalent cations with a preference for Ca2+. The strong binding to the hexadecamer has been characterized by competition experiments, and it has been used to determine the molecular weight of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Burgess R. R., Champoux J. J. Nucleotide sequence preference at rat liver and wheat germ type 1 DNA topoisomerase breakage sites in duplex SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3097–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonven B., Westergaard O. DNase I hypersensitive regions correlate with a site-specific endogenous nuclease activity on the r-chromatin of Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7593–7608. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
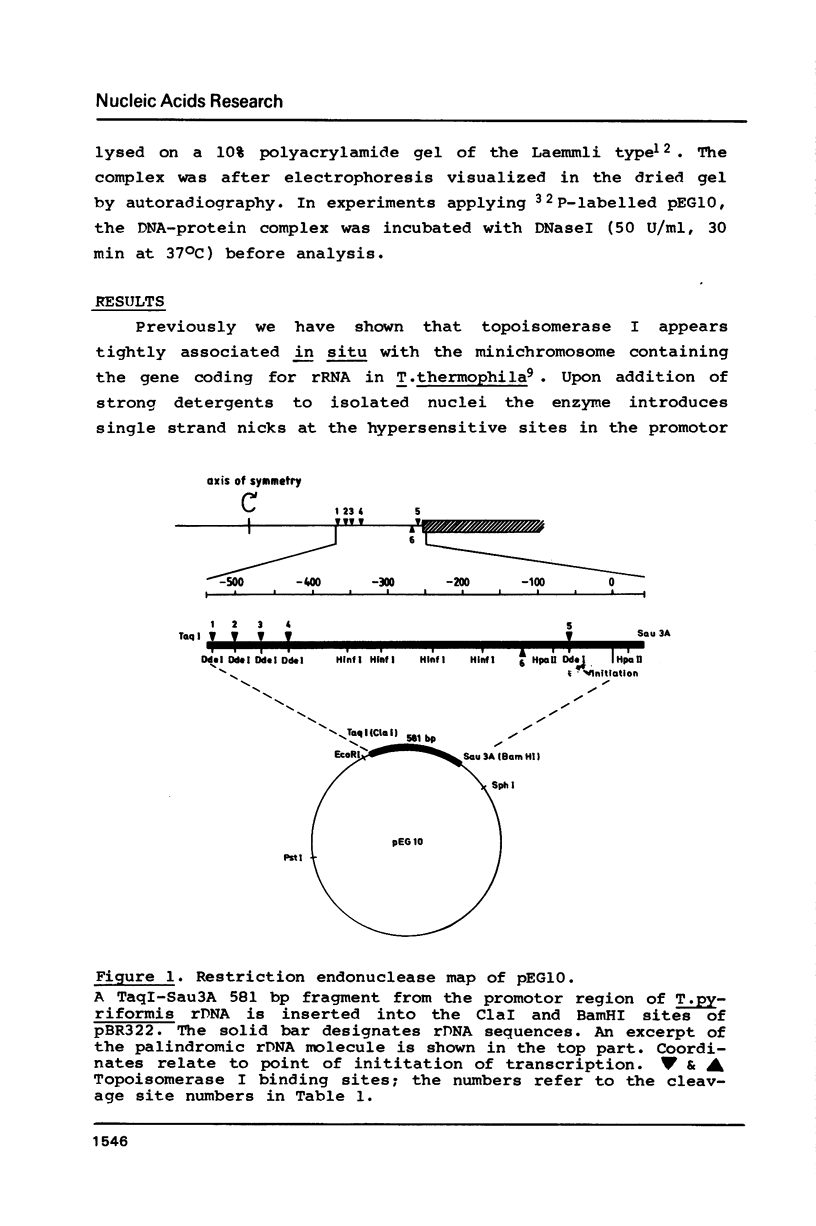
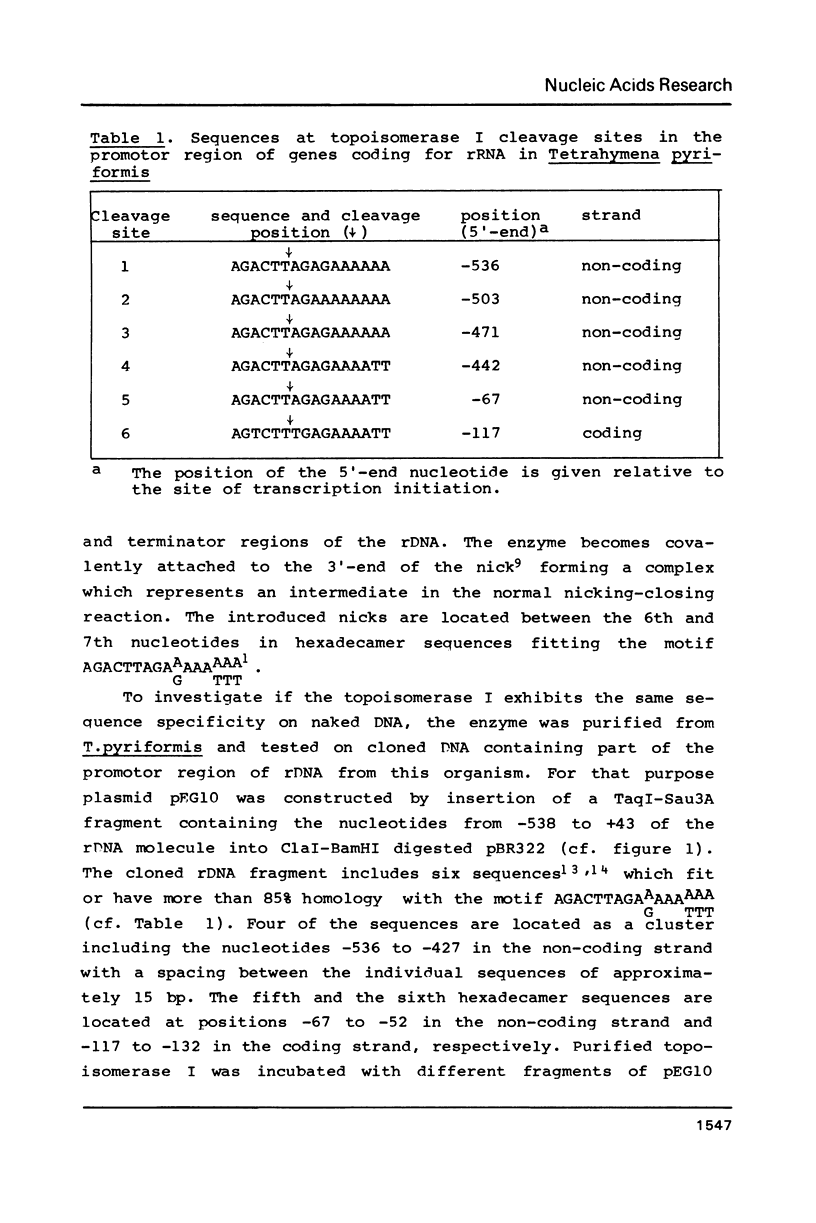
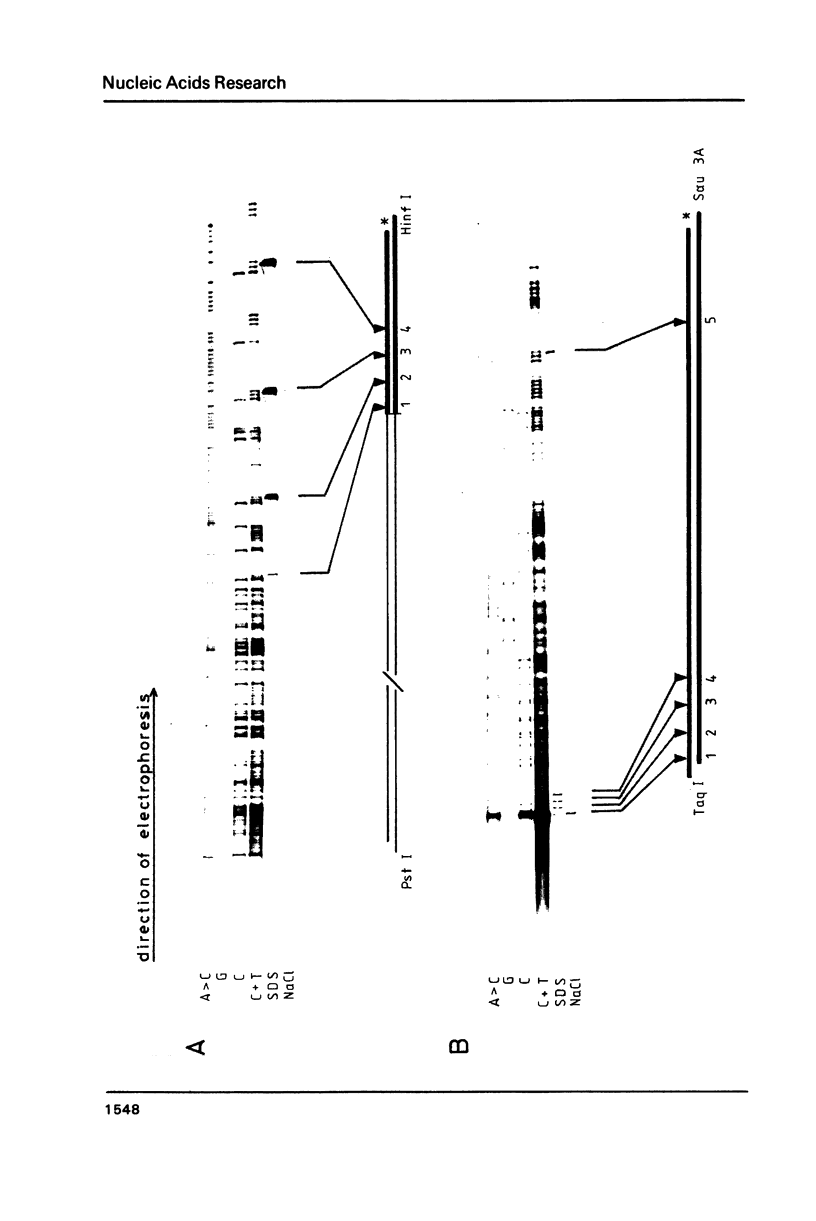
- Borchsenius S., Bonven B., Leer J. C., Westergaard O. Nuclease-sensitive regions on the extrachromosomal r-chromatin from Tetrahymena pyriformis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):245–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K. A., Halligan B. D., Davis J. L., Nivera N. L., Liu L. F. Recognition sites of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I: DNA nucleotide sequencing analysis of topo I cleavage sites on SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2565–2576. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Anatomy of hypersensitive sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):213–214. doi: 10.1038/309213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Din N., Saiga H., Higashinakagawa T. Nucleotide sequence of the 5'-terminal coding region for pre-rRNA and mature 17S rRNA in Tetrahymena thermophila rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):959–972. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann G., Pflugfelder G., Steiner E. K., Javaherian K., Howard G. C., Wang J. C., Elgin S. C. Drosophila DNA topoisomerase I is associated with transcriptionally active regions of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6958–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Ruberti I., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vitro studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke E., Bonven B. J., Westergaard O. A site and strand specific nuclease activity with analogies to topoisomerase I frames the rRNA gene of Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7661–7678. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Wahn H., Reeder R. H. Isolation of ribosomal gene chromatin. Dev Biol. 1977 Feb;55(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Liu L. F. Association of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I with nucleosomes and chromosomal proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):461–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
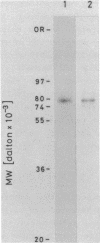
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Miller K. G. Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerases: two forms of type I DNA topoisomerases from HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3487–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchnik A. N., Bakayev V. V., Zbarsky I. B., Georgiev G. P. Elastic torsional strain in DNA within a fraction of SV40 minichromosomes: relation to transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1353–1358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01322.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prell B., Vosberg H. P. Analysis of covalent complexes formed between calf thymus DNA topoisomerase and single-stranded DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):389–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Clayton D. A. Altered mobility of polydeoxyribonucleotides in high resolution polyacrylamide gels due to removal of terminal phosphates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6787–6794. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. T. Properties of active nucleosomes as revealed by HMG 14 and 17 chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2017–2042. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]