Abstract
The sequence requirements for splicing of the Tetrahymena pre-rRNA have been examined by altering the rRNA gene to produce versions that contain insertions and deletions within the intervening sequence (IVS). The altered genes were transcribed and the RNA tested for self-splicing in vitro. A number of insertions (8-54 nucleotides) at three locations had no effect on self-splicing activity. Two of these insertions, located at a site 5 nucleotides preceding the 3'-end of the IVS, did not alter the choice of the 3' splice site. Thus the 3' splice site is not chosen by its distance from a fixed point within the IVS. Analysis of deletions constructed at two sites revealed two structures, a hairpin loop and a stem-loop, that are entirely dispensable for IVS excision in vitro. Three other regions were found to be necessary. The regions that are important for self-splicing are not restricted to the conserved sequence elements that define this class of intervening sequences. The requirement for structures within the IVS for pre-rRNA splicing is in sharp contrast to the very limited role of IVS structure in nuclear pre-mRNA splicing.
Full text
PDF

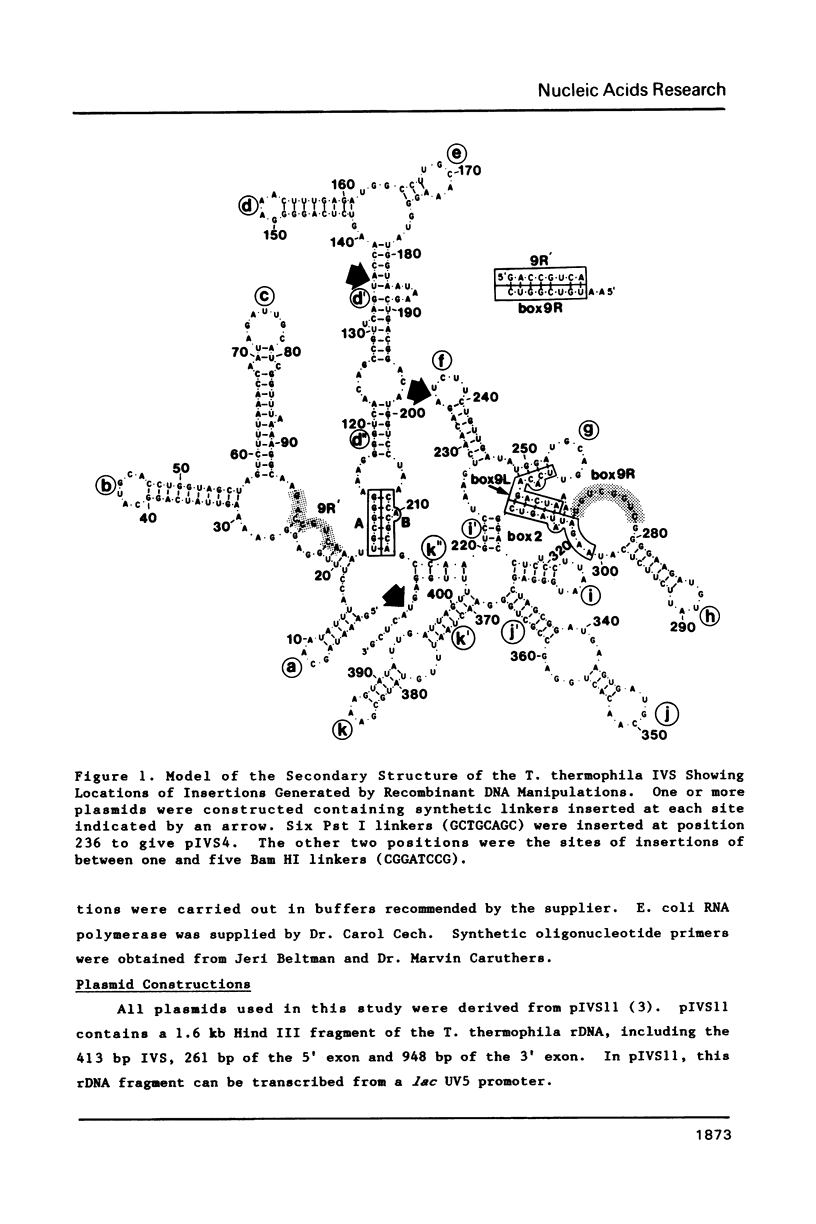




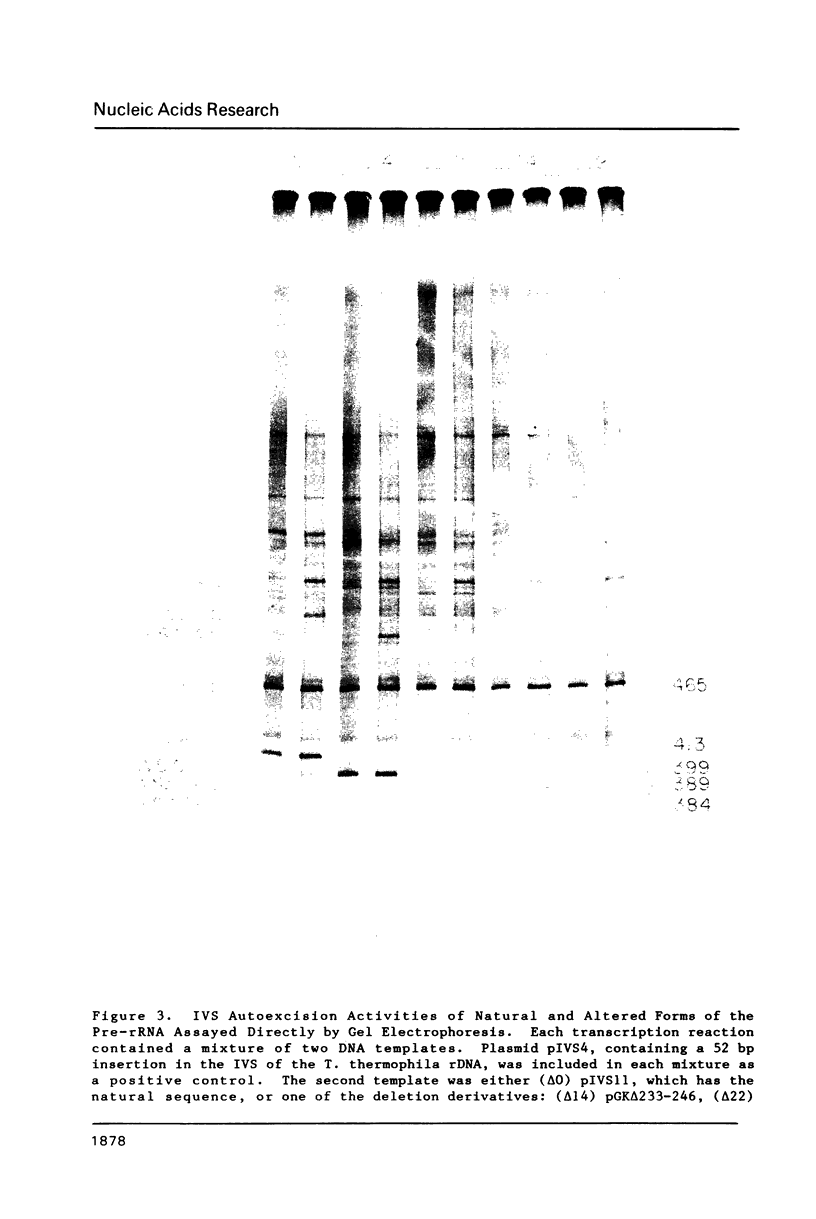











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass B. L., Cech T. R. Specific interaction between the self-splicing RNA of Tetrahymena and its guanosine substrate: implications for biological catalysis by RNA. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):820–826. doi: 10.1038/308820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., RajBhandary U. L. Intron within the large rRNA gene of N. crassa mitochondria: a long open reading frame and a consensus sequence possibly important in splicing. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Tanner N. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Weir B. R., Zuker M., Perlman P. S. Secondary structure of the Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA intervening sequence: structural homology with fungal mitochondrial intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J. In vitro splicing of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena: involvement of a guanosine nucleotide in the excision of the intervening sequence. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in Neurospora mitochondria. The large rRNA intron contains a noncoded, 5'-terminal guanosine residue. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14745–14748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in neurospora mitochondria: self-splicing of a mitochondrial intron in vitro. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence of the ribosomal RNA precursor is converted to a circular RNA in isolated nuclei of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan N. C., Gall J. G. The intervening sequence of the ribosomal RNA gene is highly conserved between two Tetrahymena species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2809–2822. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Evidence for the biochemical role of an internal sequence in yeast nuclear mRNA introns: implications for U1 RNA and metazoan mRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Scazzocchio C., Brown T. A., Davies R. W. Close relationship between certain nuclear and mitochondrial introns. Implications for the mechanism of RNA splicing. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):595–605. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Brummer B., Holl J., Schweyen R. J., Rödel G., Kaudewitz F. Processing of yeast mitochondrial RNA: involvement of intramolecular hybrids in splicing of cob intron 4 RNA by mutation and reversion. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild M. A., Sommer R. Sequence of a ribosomal RNA gene intron from Tetrahymena. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):693–694. doi: 10.1038/283693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J., Cech T. R. Autocatalytic cyclization of an excised intervening sequence RNA is a cleavage-ligation reaction. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):578–583. doi: 10.1038/301578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. A labile phosphodiester bond at the ligation junction in a circular intervening sequence RNA. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):574–578. doi: 10.1126/science.6200938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









