Abstract
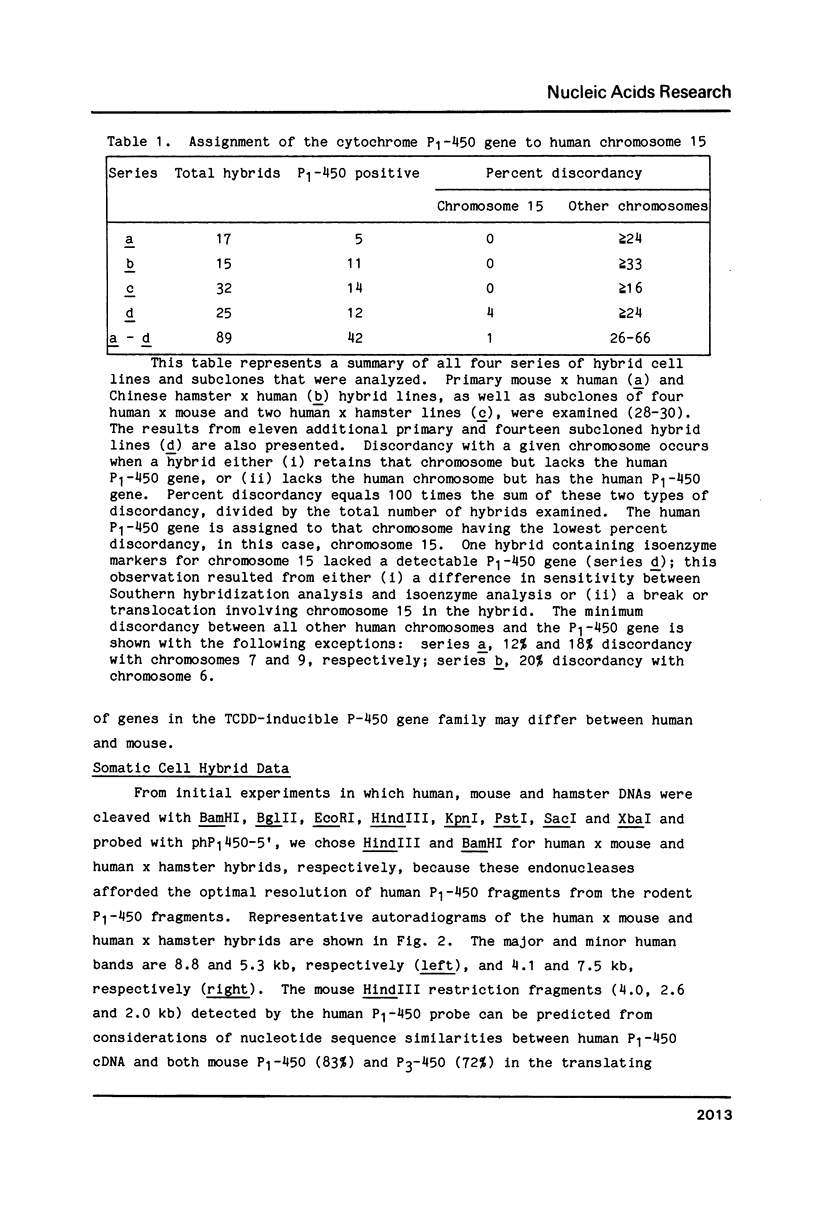
The human 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible cytochrome P1-450 full-length cDNA has been recently isolated and sequenced [Jaiswal, A.K., Gonzalez, F.J. and Nebert, D.W. (1985) Science, in press]. A 1521-bp 5' DNA fragment representing almost all of the translating region was used to probe DNA from human, mouse, hamster, 53 human X mouse somatic cell hybrids, and 36 human X hamster somatic cell hybrids. These data indicate that the P1-450 gene resides on human chromosome 15. Knowledge of the chromosomal assignment of this gene should help in our understanding of its regulation and role in development and disease.
Full text
PDF


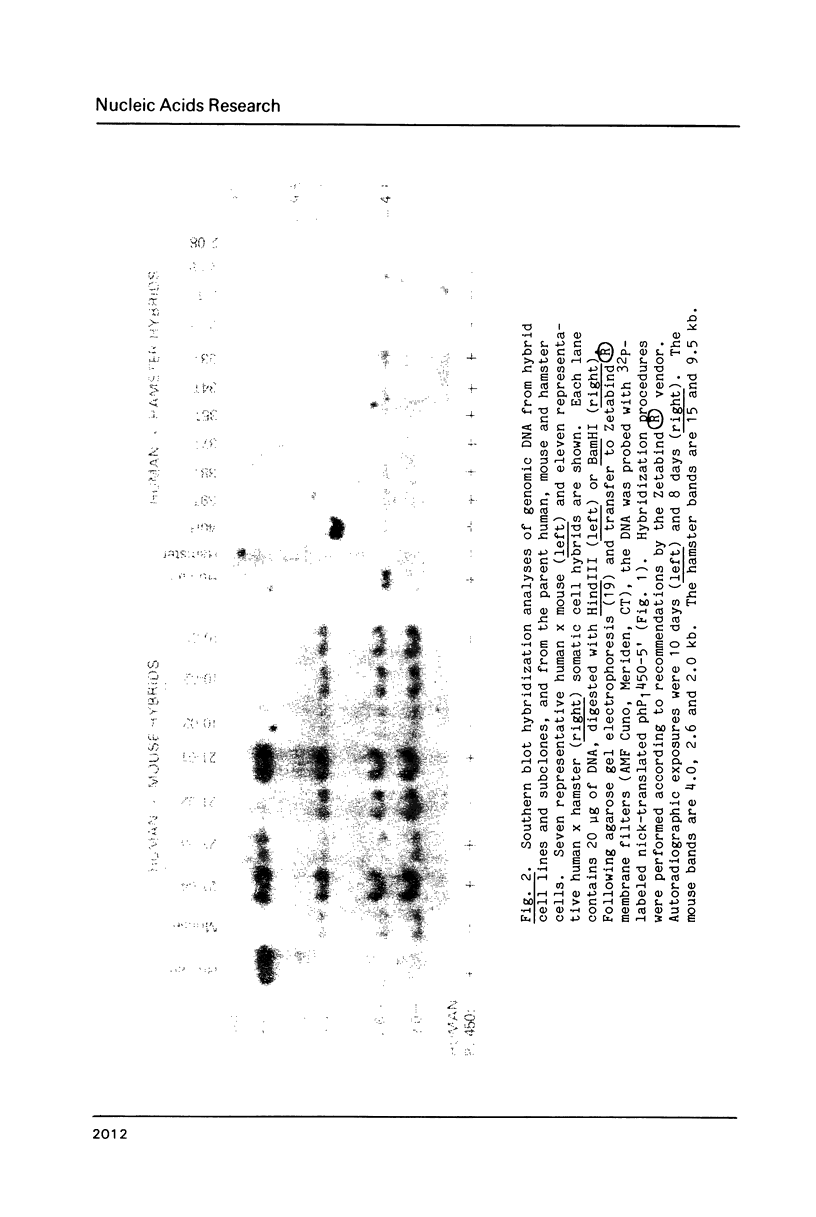



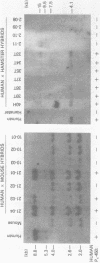
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedict W. F., Nebert D. W., Thompson E. B. Expression of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction and suppression of tyrosine aminotransferase induction in somatic-cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2179–2183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Wiebel F. J., Gelboin H. V., Minna J. D. Assignment of a locus required for flavoprotein-linked monooxygenase expression to human chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4628–4632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke J. M., Elfström G., Högberg B., Gustafsson J. A. Ontogeny of the rat hepatic receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and its endocrine indepence. Cancer Res. 1979 Nov;39(11):4653–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Langley C. H. Protein evolution and the molecular clock. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2092–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger L. E., Neal R. A. Mutagenicity testing of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlordibenzo-p-dioxin in histidine auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 15;59(1):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Tukey R. H., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the Ah locus. Transcriptional regulation of cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 mRNA levels by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Regulation of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5400–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Mouse cytochrome P3-450: complete cDNA and amino acid sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2917–2928. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. The murine Ah locus. Comparison of the complete cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 cDNA nucleotide and amino acid sequences. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10705–10713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C., Poland A. Keratinization of mouse teratoma cell line XB produced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: an in vitro model of toxicity. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouri R. E., McKinney C. E., Slomiany D. J., Snodgrass D. R., Wray N. P., McLemore T. L. Positive correlation between high aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity and primary lung cancer as analyzed in cryopreserved lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):5030–5037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legraverend C., Kärenlampi S. O., Bigelow S. W., Lalley P. A., Kozak C. A., Womack J. E., Nebert D. W. Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction by benzo[a]anthracene: regulatory gene localized to the distal portion of mouse chromosome 17. Genetics. 1984 Jul;107(3):447–461. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Battey J., Hollis G. F., Swan D. C., Siebenlist U., Leder P. Localization of human variable and constant region immunoglobulin heavy chain genes on subtelomeric band q32 of chromosome 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8155–8170. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Swan D. C., Santos E., Barbacid M., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Localization of the normal allele of T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene to chromosome 11. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):773–774. doi: 10.1038/300773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray F. J., Smith F. A., Nitschke K. D., Humiston C. G., Kociba R. J., Schwetz B. A. Three-generation reproduction study of rats given 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in the diet. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 15;50(2):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Taylor B. A. Lengths of chromosomal segments conserved since divergence of man and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):814–818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarkatti P. S., Sweeney G. D., Gauldie J., Clark D. A. Sensitivity to suppression of cytotoxic T cell generation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is dependent on the Ah genotype of the murine host. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;72(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W. Genetic differences in susceptibility to chemically induced myelotoxicity and leukemia. Environ Health Perspect. 1981 Jun;39:11–22. doi: 10.1289/ehp.813911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Negishi M. Multiple forms of cytochrome P-450 and the importance of molecular biology and evolution. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 15;31(14):2311–2317. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90523-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Bondy G. P., Mason M. E., Kahl G. F., Eisen H. J., Guenthner T. M., Nebert D. W. Regulatory gene product of the Ah locus. Characterization of the cytosolic inducer-receptor complex and evidence for its nuclear translocation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11636–11648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. 2,3,7,8,-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: segregation of toxocity with the Ah locus. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):86–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E., Kende A. S. Stereospecific, high affinity binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by hepatic cytosol. Evidence that the binding species is receptor for induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4936–4946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Knutson J. C. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:517–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Palen D., Glover E. Tumour promotion by TCDD in skin of HRS/J hairless mice. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):271–273. doi: 10.1038/300271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roderick T. H., Lalley P. A., Davisson M. T., O'Brien S. J., Womack J. E., Créau-Goldberg N., Echard G., Moore K. L. Report of the Committee on Comparative Mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):312–339. doi: 10.1159/000132013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. Mapping the human genome, cloned genes, DNA polymorphisms, and inherited disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1982;12:341–452. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8315-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. A., Schwetz B. A., Nitschke K. D. Teratogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in CF-1 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;38(3):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Parthasarathy S., Leake D. S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Modification of low density lipoprotein by endothelial cells involves lipid peroxidation and degradation of low density lipoprotein phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tukey R. H., Lalley P. A., Nebert D. W. Localization of cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 genes to mouse chromosome 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3163–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebel F. J., Hlavica P., Grzeschik K. H. Expression of aromatic polycyclic hydrocarbon-induced monooxygenase (aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase) in man x mouse hybrids is associated with human chromosome 2. Hum Genet. 1981;59(4):277–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00295458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. C., Carlson S. S., White T. J. Biochemical evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:573–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]