Abstract
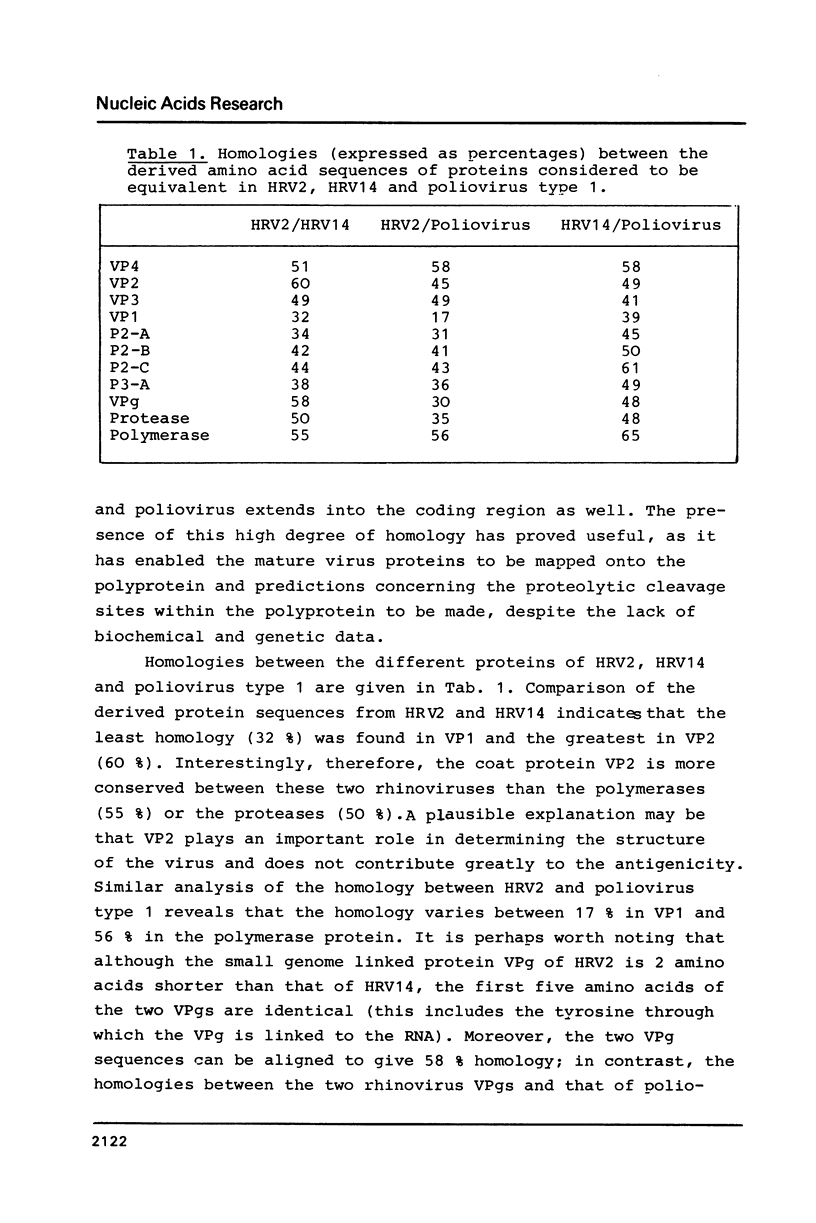
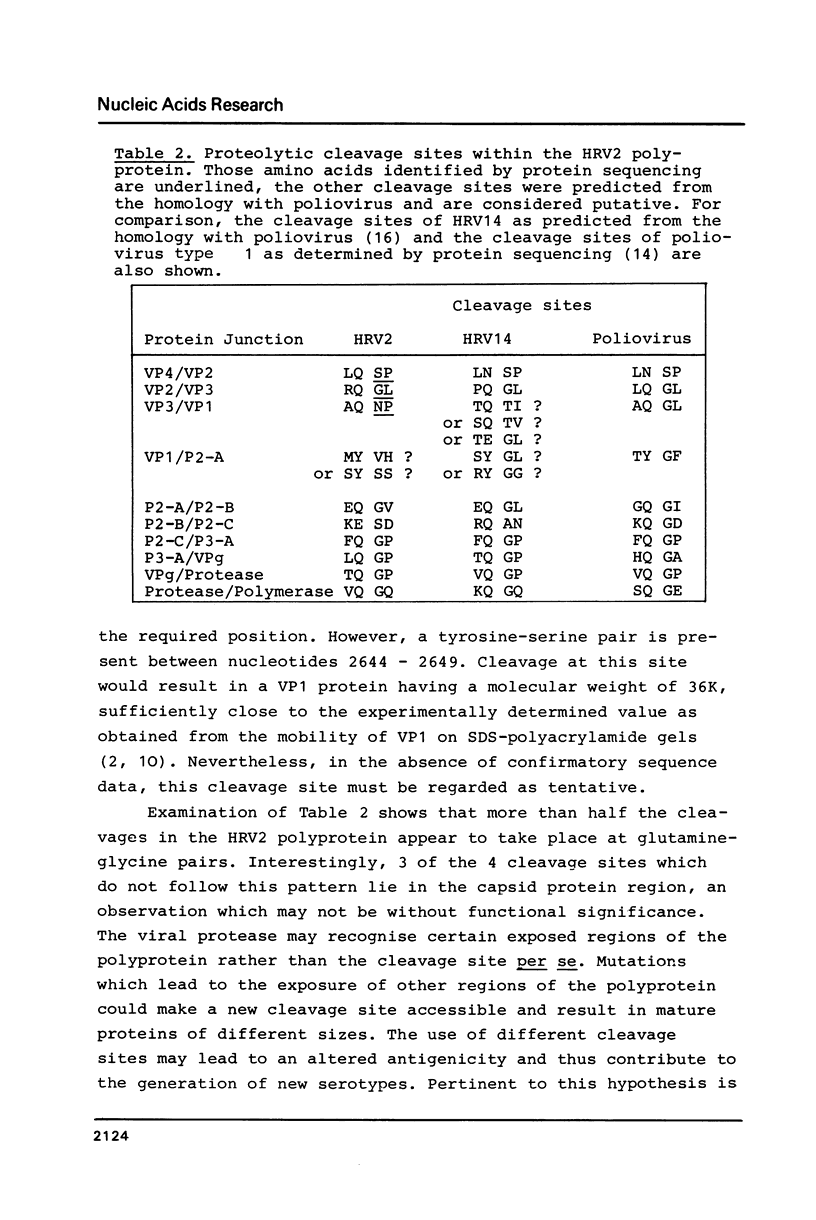
cDNA clones representing the entire genome of human rhinovirus 2 have been obtained and used to determine the complete nucleotide sequence. The genome consists of 7102 nucleotides and possesses a long open reading frame of 6450 nucleotides; this reading frame is initiated 611 nucleotides from the 5' end and stops 42 nucleotides from the polyA tract. The N-terminal sequences of three of the viral capsid proteins have been elucidated, thus defining the positions of three cleavage sites on the polyprotein. The extensive amino acid sequence homology with poliovirus and human rhinovirus 14 enabled the other cleavage sites to be predicted. Cleavages in the 3' half of the molecule appear to take place predominantly at Gln-Gly pairs, whereas those in the 5' half (including the capsid proteins) are more heterogeneous.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Many rhinovirus serotypes share the same cellular receptor. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.340-345.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlquist P., Kaesberg P. Determination of the length distribution of poly(A) at the 3' terminus of the virion RNAs of EMC virus, poliovirus, rhinovirus, RAV-61 and CPMV and of mouse globin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1195–1204. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Korant B. D. Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):282–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.282-291.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M. K., Fox J. P., Kenny G. E. Antigenic groupings of 90 rhinovirus serotypes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):642–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.642-647.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Colonno R. J., Wimmer E. Antigenic conservation and divergence between the viral-specific proteins of poliovirus type 1 and various picornaviruses. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P. Is a rhinovirus vaccine possible? Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Apr;103(4):345–354. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J. Fragility of the rhinovirus type 14 genome to incubation at 60 degrees. Intervirology. 1980;13(1):7–15. doi: 10.1159/000149150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. The genome-linked protein of picornaviruses. IV. Difference in the VPg's of encephalomyocarditis virus and poliovirus as evidence that the genome-linked proteins are virus-coded. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr Rhinoviruses. Yale J Biol Med. 1975 Mar;48(1):17–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfpap L. M., Cooney M. K. Isolation of rhinovirus intertypes related to either rhinoviruses 12 and 78 or 36 and 58. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):213–218. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.213-218.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Protein sequence analysis: automated microsequencing. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):650–659. doi: 10.1126/science.6687410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isono K. Computer programs to analyze DNA and amino acid sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):85–89. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Crowell R. L., Philipson L. Unrelated animal viruses share receptors. Nature. 1976 Feb 26;259(5545):679–681. doi: 10.1038/259679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medappa K. C., McLean C., Rueckert R. R. On the structure of rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L. Taxonomy of viruses, 1980. Prog Med Virol. 1980;26:214–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Sommergruber W., Blaas D., Pieler C., Kuechler E. Relationship of human rhinovirus strain 2 and poliovirus as indicated by comparison of the polymerase gene regions. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R., Hughes P., Clarke L. D., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. The nucleotide sequence of poliovirus type 3 leon 12 a1b: comparison with poliovirus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5629–5643. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of a common cold virus: human rhinovirus 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7859–7875. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Killington R. A. Rhinoviruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:503–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Agol V. I. Complete translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA and faithful cleavage of virus-specific proteins in a cell-free system from Krebs-2 cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


