Abstract
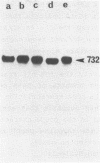
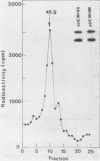
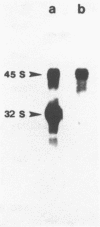
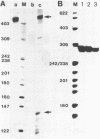
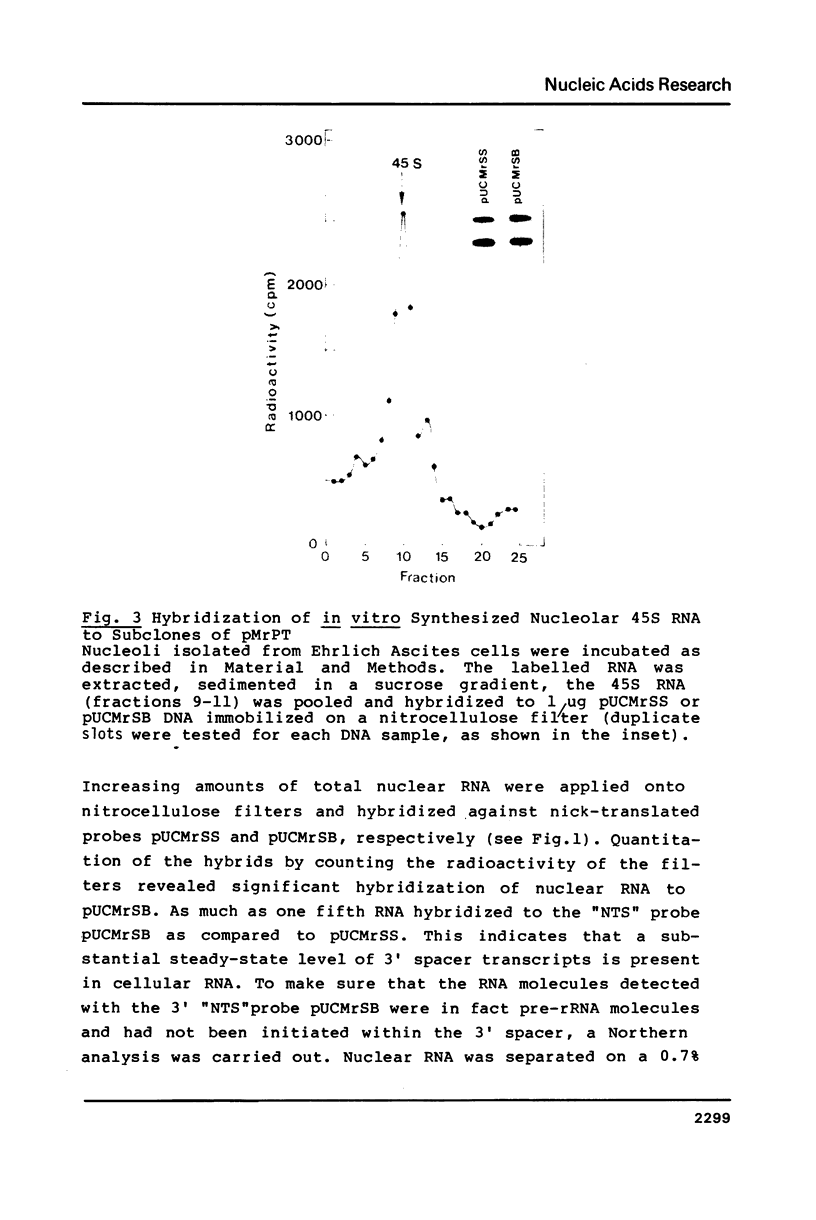
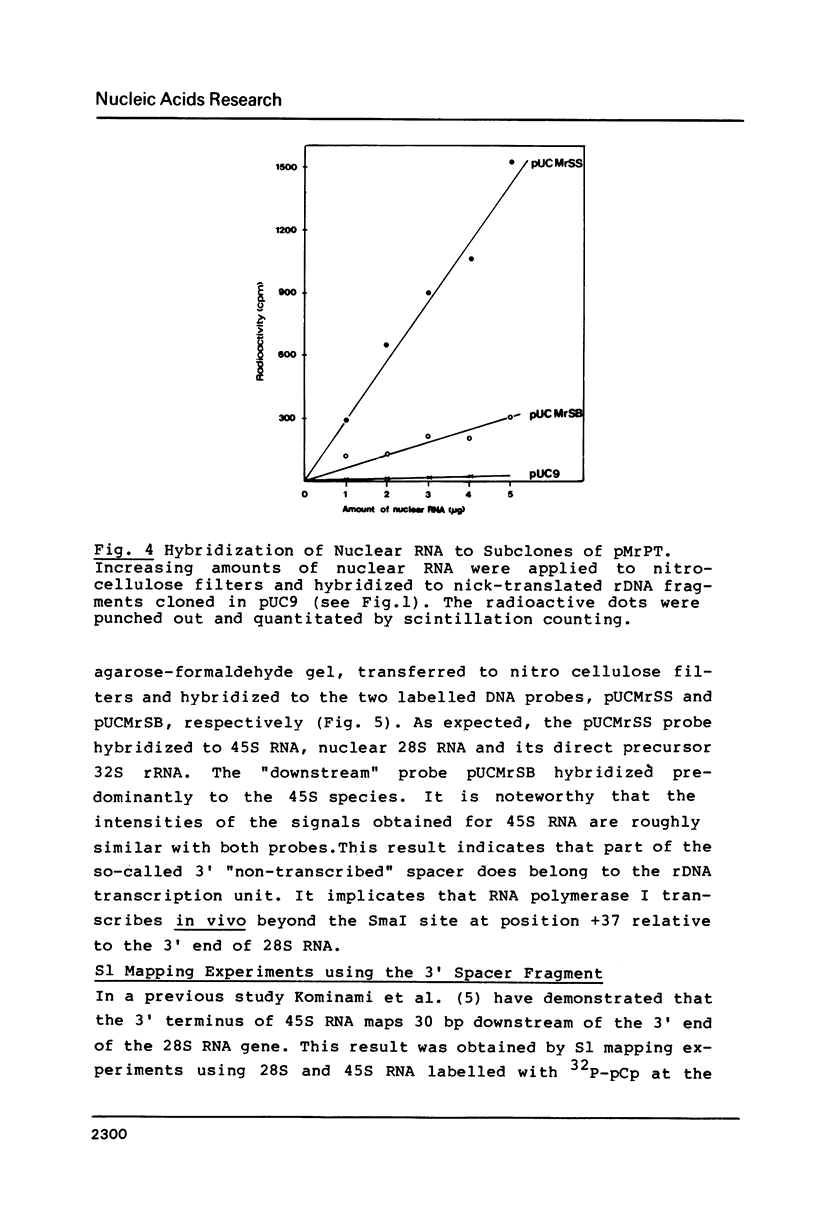
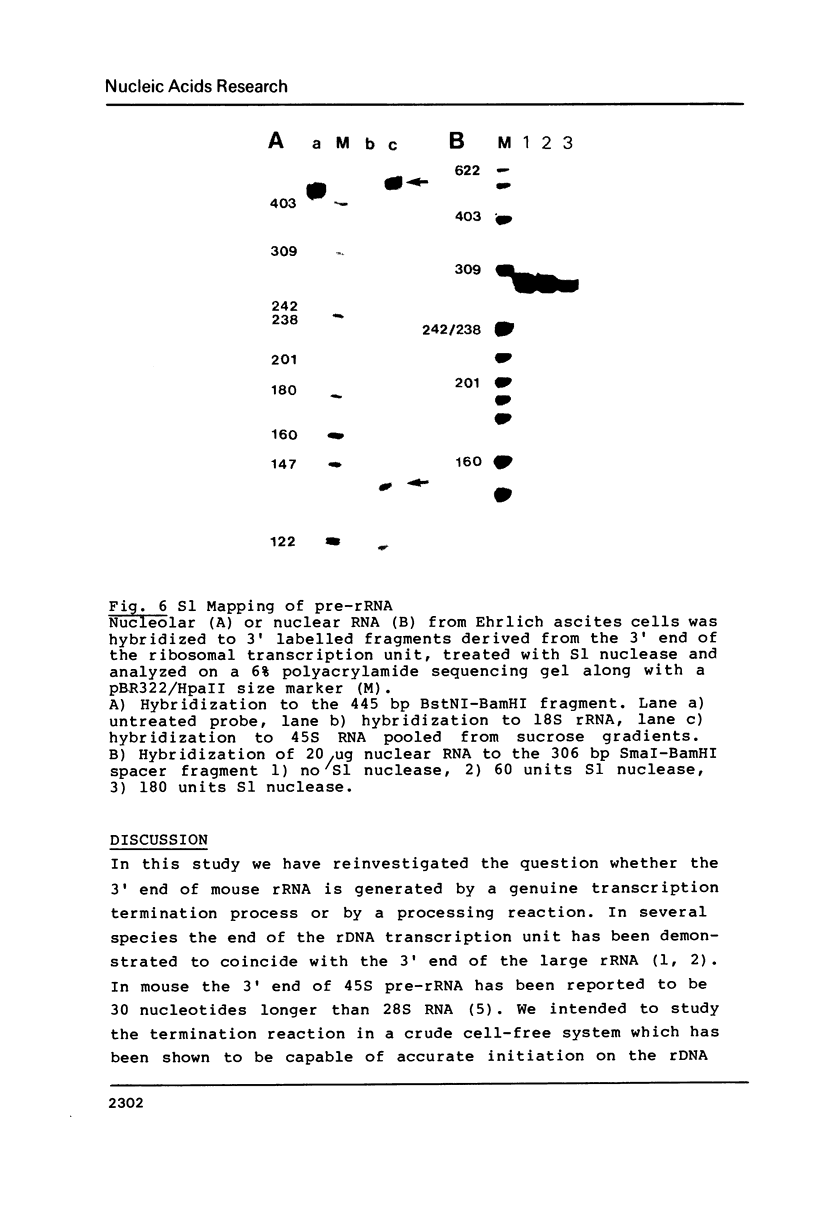
Evidence is presented that more than 300 bp of spacer sequences downstream of the 28S RNA coding sequence are part of the mouse rDNA transcription unit. Studies in two cell-free transcription systems as well as analysis of cellular RNA indicate that RNA polymerase I does not terminate within the 334 bp 3' terminal spacer sequences contained in the rDNA clone used. Quantitative hybridization data, S1 mapping experiments and Northern analysis of nuclear RNA showed that the 14 kb pre-rRNA molecules hybridize with the same efficiency to both the 28S and the 3' NTS specific DNA probe. This indicates that the rRNA precursor contains both at the 5' and 3' end several hundreds bases of external transcribed spacer sequences which are eliminated in subsequent processing reactions.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Din N., Engberg J., Gall J. G. The nucleotide sequence at the transcription termination site of the ribosomal RNA gene in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1503–1513. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Mapping of a mouse ribosomal DNA promoter by in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6093–6102. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Smith V. A., Grummt F. Amino acid starvation affects the initiation frequency of nucleolar RNA polymerase. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., van Heerikhuizen H., Musters W., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Transcription of an artificial ribosomal RNA gene in yeast. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1377–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami R., Mishima Y., Urano Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Cloning and determination of the transcription termination site of ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1963–1979. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal R. K., Dawid I. B. The nucleotide sequence at the transcription termination site of ribosomal RNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1801–1811. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Galibert F., Boiron M. Evidence for the existence of several molecular species in the "45S fraction" of mammalian ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1117–1120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Kominami R., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of the putative transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6043–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Jonge P., Leer R. J., Planta R. J. The transcription termination site of the ribosomal RNA operon in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5179–5192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]