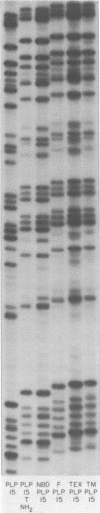
Abstract
A rapid and versatile method has been developed for the synthesis of oligonucleotides which contain an aliphatic amino group at their 5' terminus. This amino group reacts specifically with a variety of electrophiles, thereby allowing other chemical species to be attached to the oligonucleotide. This chemistry has been utilized to synthesize several fluorescent derivatives of an oligonucleotide primer used in DNA sequence analysis by the dideoxy (enzymatic) method. The modified primers are highly fluorescent and retain their ability to specifically prime DNA synthesis. The use of these fluorescent primers in DNA sequence analysis will enable DNA sequence analysis to be automated.
Full text
PDF


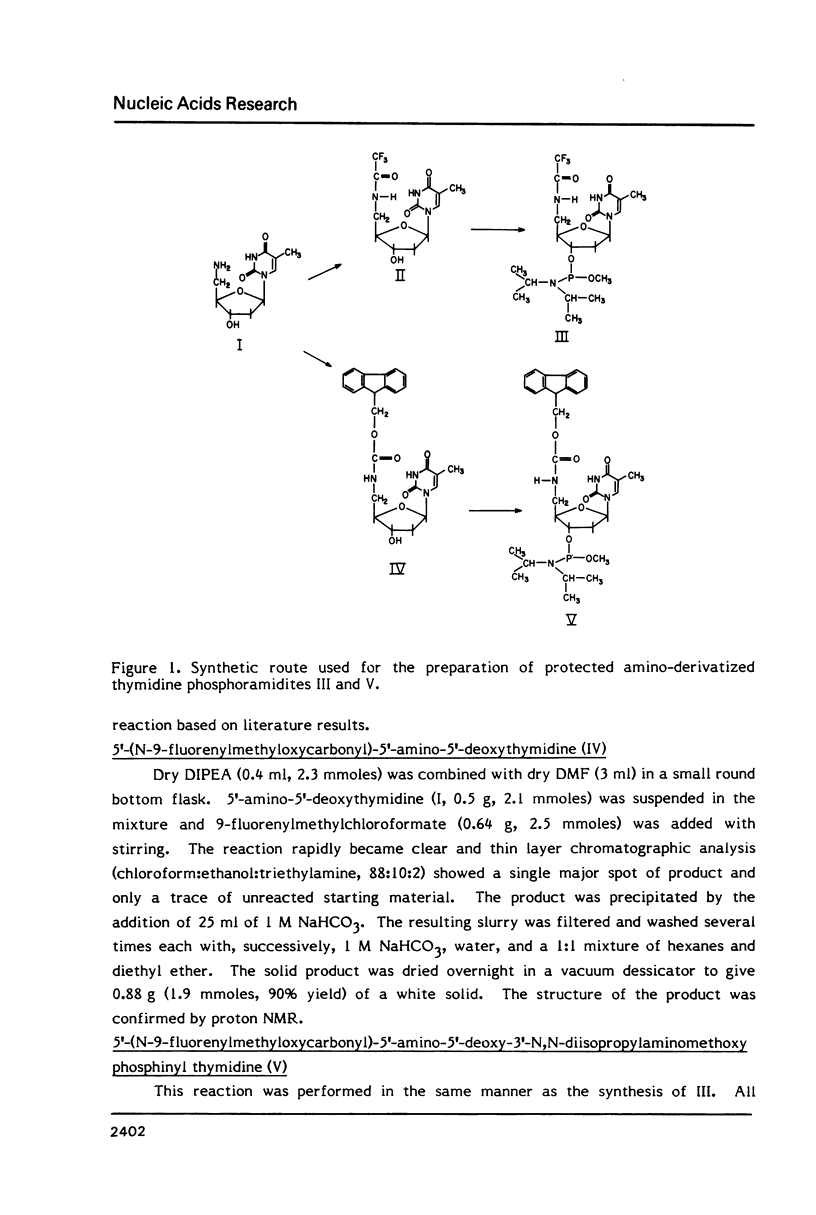




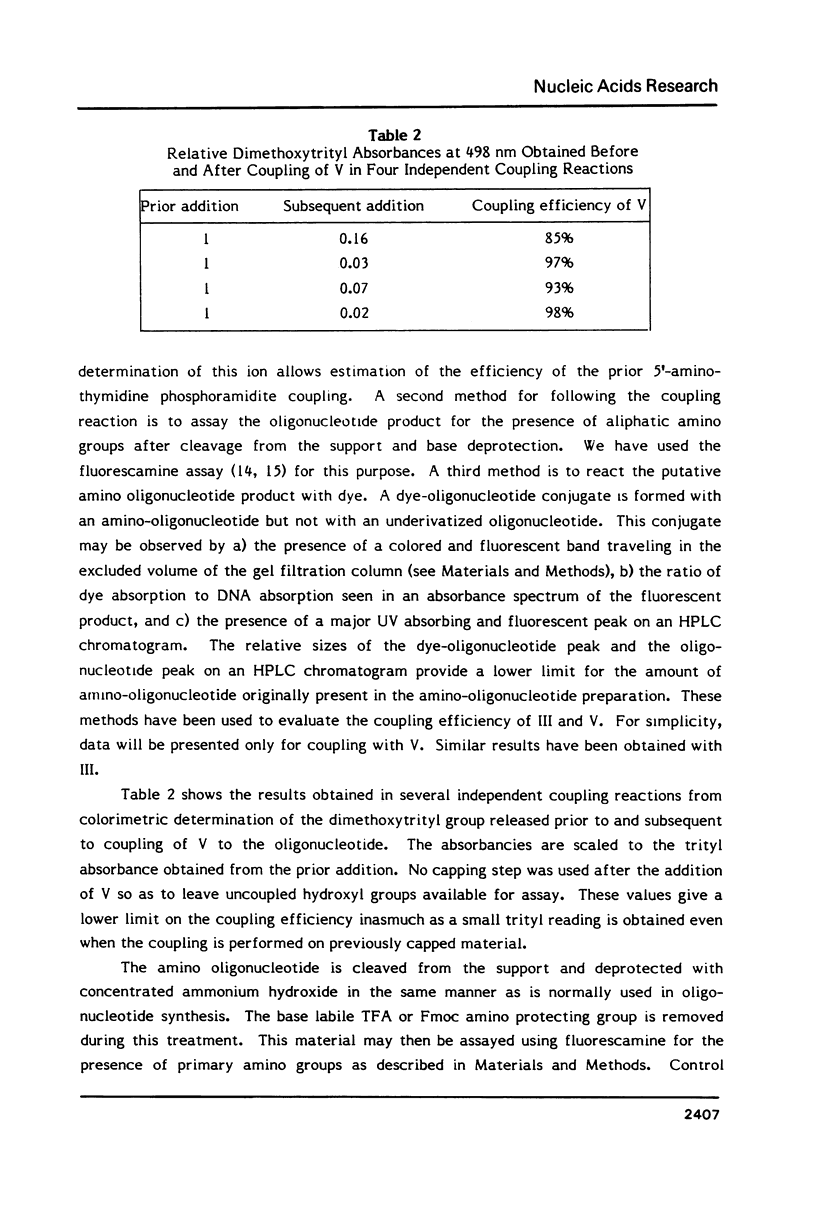

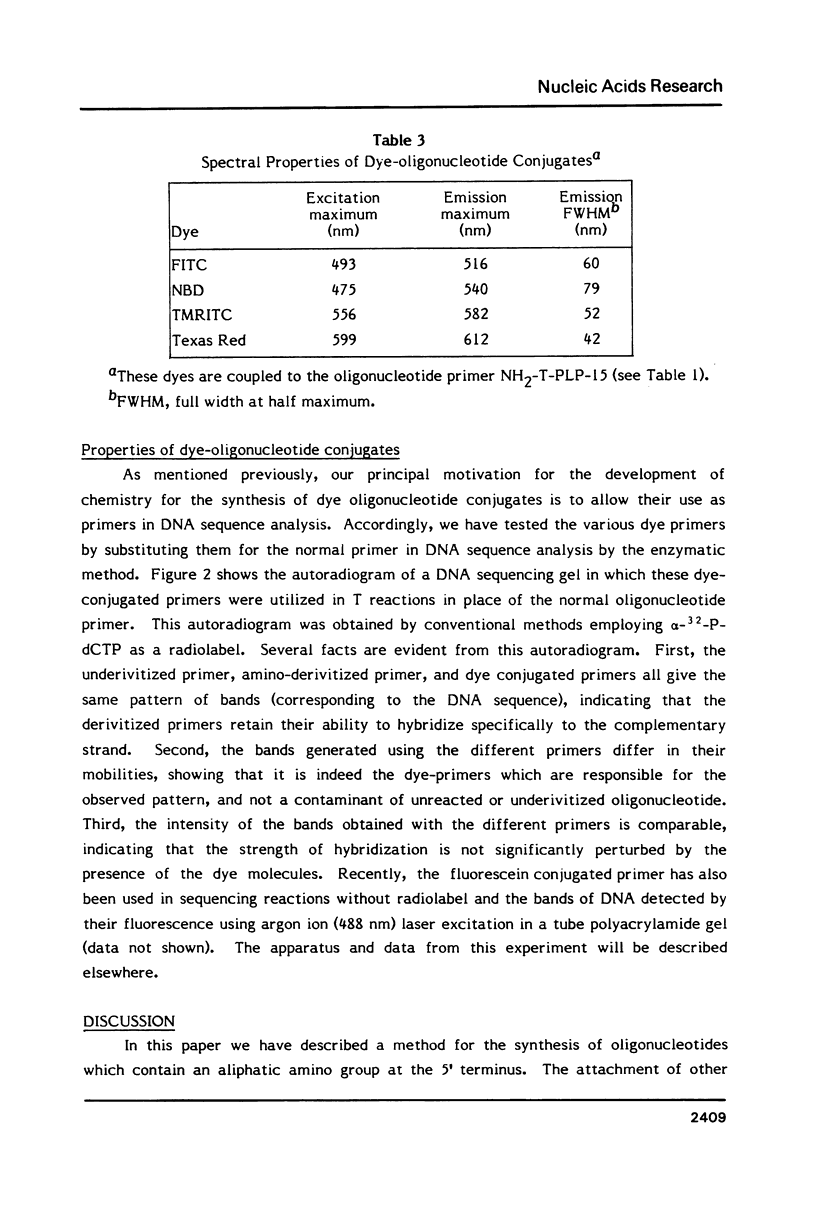



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barone A. D., Tang J. Y., Caruthers M. H. In situ activation of bis-dialkylaminophosphines--a new method for synthesizing deoxyoligonucleotides on polymer supports. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4051–4061. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu B. C., Wahl G. M., Orgel L. E. Derivatization of unprotected polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6513–6529. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B., Messing J. Methylation of single-stranded DNA in vitro introduces new restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):375–377. doi: 10.1038/272375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Ikeda K. Synthesis of oligonucleotides containing the hypermodified base, alpha-putrescinylthymine. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1983;(12):75–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]