Abstract
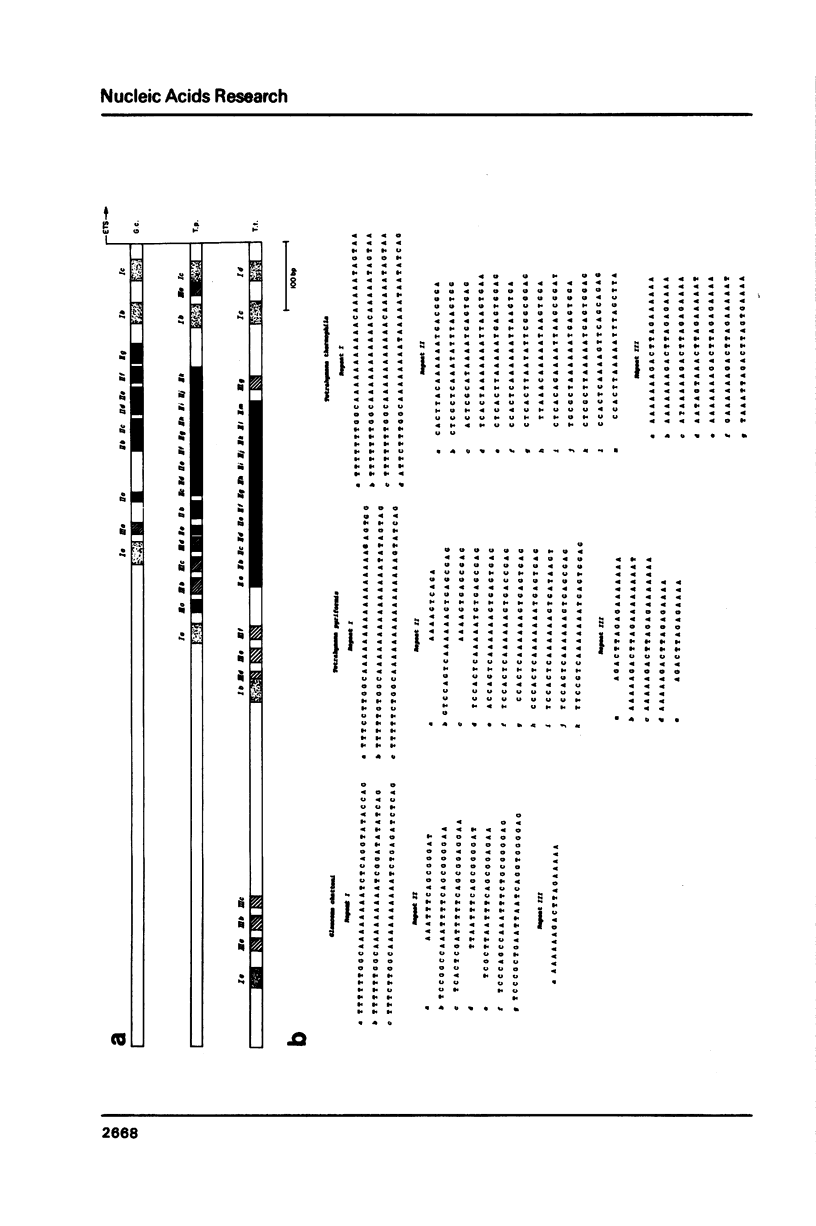
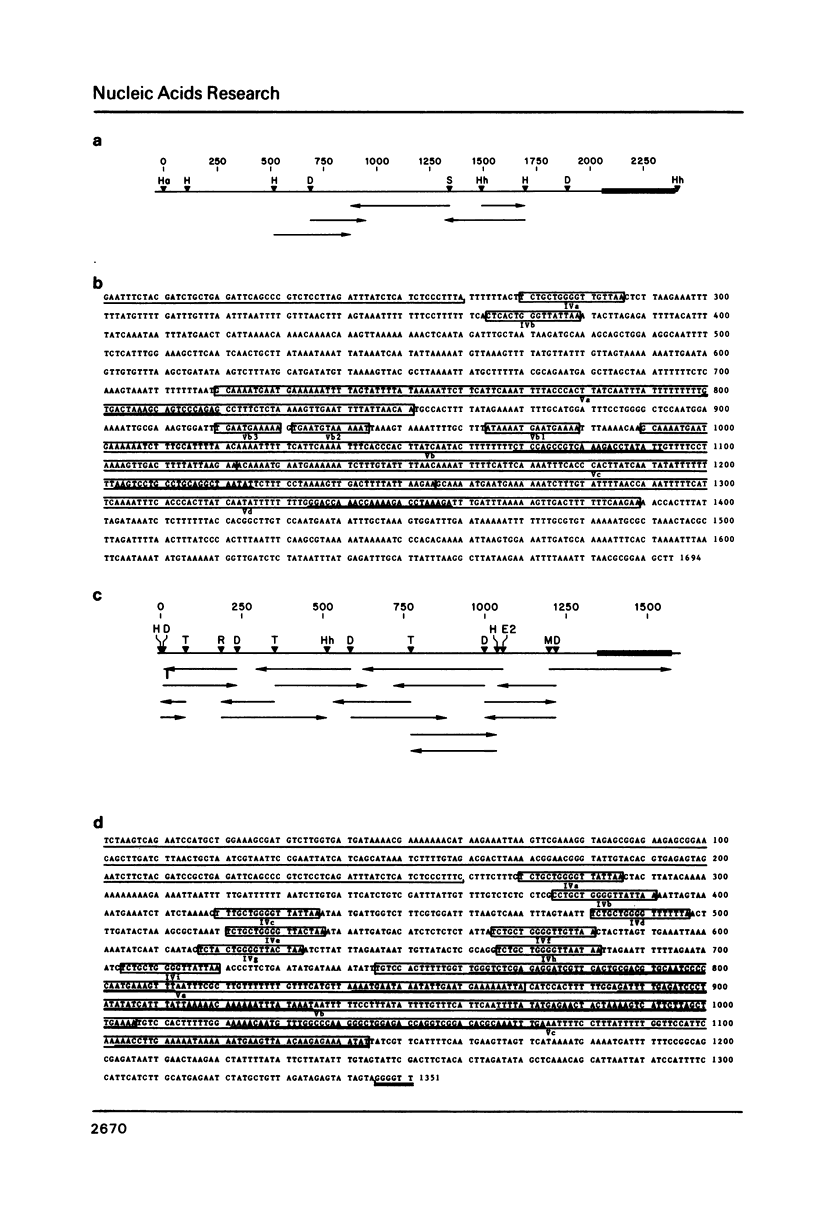
We have analyzed the nucleotide sequences of the nontranscribed spacer (NTS) and transcription initiation and termination regions of the extrachromosomal rDNAs of the ciliated protozoans Tetrahymena thermophila and Glaucoma chattoni. The sequences surrounding the sites of transcription initiation and termination are highly conserved. The only extensive homologies of the NTS regions occur in five sets of dispersed repetitive sequences. Type I, II and III repeats in the 5' NTS are strongly conserved in sequence between Tetrahymena and Glaucoma in the case of the type I and III repeats, and in location relative to the transcription initiation site in the case of type I and II repeats. We identify two new repeat types, designated IV and V, in the 3' NTS. The sequence of type IV repeats, and the location relative to the transcription termination site of type IV and V repeats, are conserved. All five types of repeats are interspersed with nonconserved DNA sequences. These results suggest that the five repeat types in the 5' and 3' NTSs are important in rRNA gene function; the sequence organization, and the differing rates of divergence between species of the repeat types, provide strong evidence for their functional selection through the process of molecular coevolution.
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin A. A., Pearlman R. E. Autonomously replicating sequences from the non transcribed spacers of Tetrahymena thermophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2647–2659. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Challoner P. B. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Brehm S. L. Replication of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes of Tetrahymena thermophilia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3531–3543. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cizewski V., Sollner-Webb B. A stable transcription complex directs mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7043–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E. S., Dover G. A. Multiple Pol I initiation sequences in rDNA spacers of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):7017–7026. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E., Strachan T., Dover G. Dynamics of concerted evolution of ribosomal DNA and histone gene families in the melanogaster species subgroup of Drosophila. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):17–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney A. D. A DNA sequence handling program. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):61–67. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Din N., Engberg J. Extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena: structure and evolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 5;134(3):555–574. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90367-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Din N., Engberg J., Gall J. G. The nucleotide sequence at the transcription termination site of the ribosomal RNA gene in Tetrahymena thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1503–1513. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. A., Flavell R. B. Molecular coevolution: DNA divergence and the maintenance of function. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):622–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90255-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Din N., Saiga H., Higashinakagawa T. Nucleotide sequence of the 5'-terminal coding region for pre-rRNA and mature 17S rRNA in Tetrahymena thermophila rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):959–972. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N. V. On spacers. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):697–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke E., Bonven B. J., Westergaard O. A site and strand specific nuclease activity with analogies to topoisomerase I frames the rRNA gene of Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7661–7678. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Ljljana A., Sakaki Y. Direct repeats surrounding the ribosomal RNA genes of Physarum polycephalum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2047–2053. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen A. L., Cann G. M., Blackburn E. H. Sequence-specific fragmentation of macronuclear DNA in a holotrichous ciliate. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90321-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil R. L., Roeder G. S. Cis-acting, recombination-stimulating activity in a fragment of the ribosomal DNA of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss G. B., Amin A. A., Pearlman R. E. Two separate regions of the extrachromosomal ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid of Tetrahymena thermophila enable autonomous replication of plasmids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;1(6):535–543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.6.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss G. B., Pearlman R. E. Extrachromosomal rDNA of Tetrahymena thermophila is not a perfect palindrome. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. A component of Drosophila RNA polymerase I promoter lies within the rRNA transcription unit. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):179–181. doi: 10.1038/304179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Localization of DNA sequences promoting RNA polymerase I activity in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Nontranscribed spacer sequences promote in vitro transcription of Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6879–6886. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Tjian R. In vitro transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Identification of the in vivo and in vitro origin of transcription in human rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3933–3949. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Boseley P. G., Birnstiel M. L. More ribosomal spacer sequences from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 11;8(3):467–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Cunningham K., Jain R. Structure of the Tetrahymena pyriformis rRNA gene. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription termination region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12857–12860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G. Identification of multiple sites in the promoter region of the Tetrahymena pyriformis rRNA gene which bind the Escherichia coli catabolite regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):672–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Sutiphong J., Haque S. Structure of the Tetrahymena pyriformis rRNA gene. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12849–12856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan W. C., Blackburn E. H. Single extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA gene copies are synthesized during amplification of the rDNA in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Enhancers and ribosomal gene spacers. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiga H., Mizumoto K., Matsui T., Higashinakagawa T. Determination of the transcription initiation site of Tetrahymena pyriformis rDNA using in vitro capping of 35S pre-rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4223–4236. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Wilkinson J. A., Roan J., Reeder R. H. Nested control regions promote Xenopus ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Gall J. G. The replication of ribosomal DNA in the macronucleus of Tetrahymena. Chromosoma. 1977 Dec 6;64(4):295–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00294937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Kominami R., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of the putative transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6043–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Liu A. Y., Borst P. Structure of the growing telomeres of Trypanosomes. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt C., Grummt I. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes is a prerequisite for ribosomal DNA transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3795–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild M. A., Gall J. G. An intervening sequence in the gene coding for 25S ribosomal RNA of Tetrahymena pigmentosa. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Gall J. G. A single integrated gene for ribosomal RNA in a eucaryote, Tetrahymena pyriformis. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


