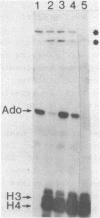
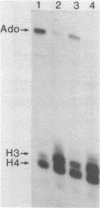
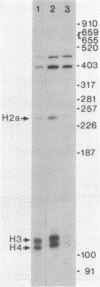
Abstract
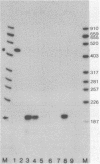
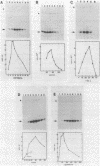
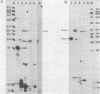
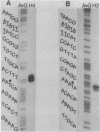
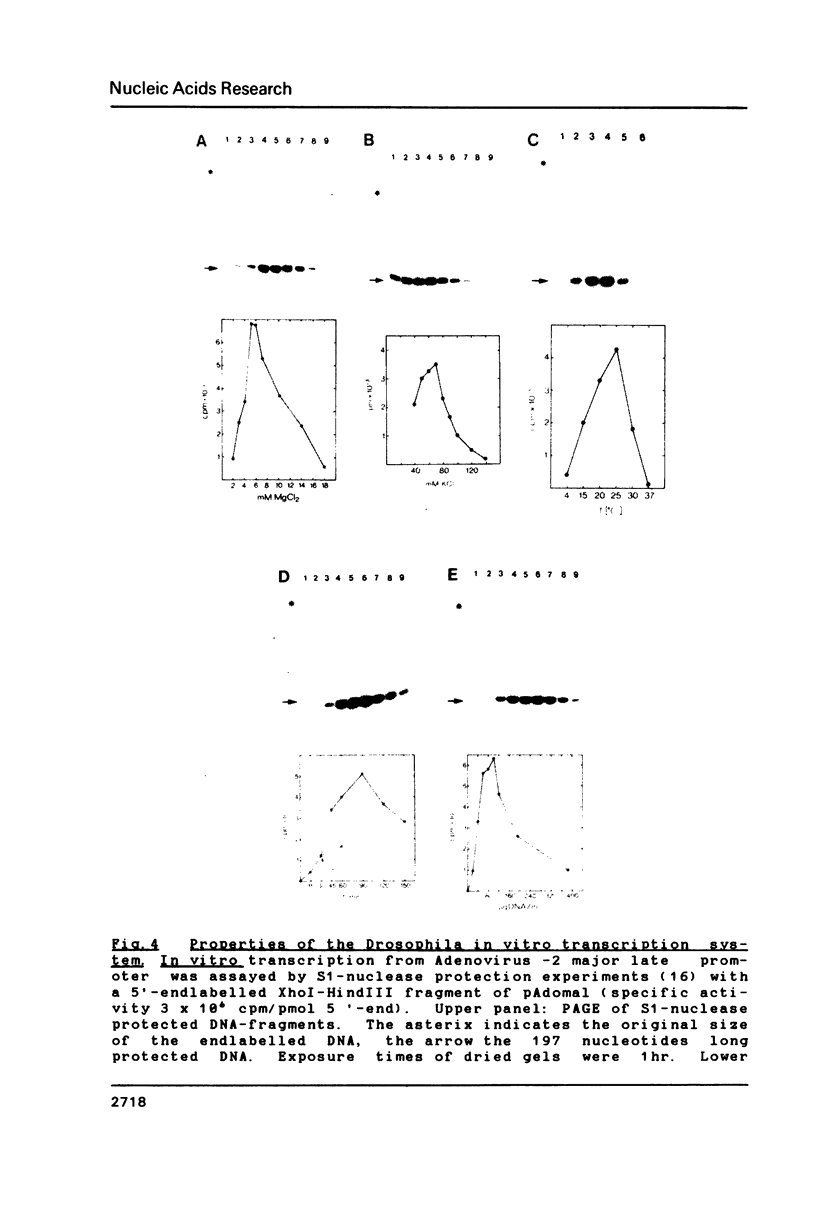
An in vitro transcription system has been developed from 0.3M NaCl extracts of nuclei of Drosophila embryos. Optimal transcription in the Drosophila embryo extract (DEX) was at 5mM MgCl2, 70mM KCl, 25 degrees C and with promoter concentrations of 0,75-1.0 pmol/assay. In vitro transcription from the Adenovirus-2 major late and the Drosophila histone gene promoters was studied in particular. S1-nuclease protection experiments showed that in vitro transcription from these promoters was accurate. In vitro transcription from the Adenovirus-2 major late promoter was less efficient than from histone gene H3 and H4 promoters in DEX. Vicecersa, in vitro transcription from Adenovirus-2 major late promoter was more efficient in HeLa whole cell extracts. The efficiencies of transcription from histone gene promoters decreased in DEX in the order H4 greater than or equal to H3 greater than H2a. Transcription from H2b and H1 promoters was not detected in DEX. The transcription from the Adenovirus-2 major late promoter was completely inhibited by histone H3 and H4 promoters. Preincubation of DEX with the adenoviral template, however, did not inhibit transcription from histone H3 and H4 promoters. The transcription start sites of histone genes H3 and H4 are separated by 160 base pairs. The H3 and H4 transcription start sites were subcloned separately. Now, a competition of transcription from the H3/H4 promoters with the Adenovirus-2 major late promoter was observed. The competition studies suggest that preincubation of DEX with the adenoviral template inhibited transcription from the H3 promoter more strongly than from the H4 promoter.
Full text
PDF




















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P., Dierich A., Gaub M. P., Jakowlev S., Jongstra J., Krust A., LePennec J. P., Oudet P., Reudelhuber T. Promoter elements of genes coding for proteins and modulation of transcription by estrogens and progesterone. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:1–42. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cizewski V., Sollner-Webb B. A stable transcription complex directs mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7043–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J., Bloomer L. S. Assembly of transcriptionally active 5S RNA gene chromatin in vitro. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Bautz E. K. RNA polymerase B from Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Purification and partial characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):169–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb20989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Delimitation of far upstream sequences required for maximal in vitro transcription of an H2A histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Sharp P. A. Sequences controlling in vitro transcription of SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2293–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Manley J. L. In vitro transcription from the adenovirus 2 major late promoter utilizing templates truncated at promoter-proximal sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8513–8521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Analysis of the expression of genes encoding animal mRNA by in vitro techniques. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:195–244. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60687-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Cohn R., Kedes L., Mohun T. Expression and organization of histone genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:239–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace B., Pace N. R. The chromatography of RNA and oligoribonucleotides on boronate-substituted agarose and polyacrylamide. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):128–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Transcription modulation in vitro of the fibroin gene exerted by a 200-base-pair region upstream from the "TATA" box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7442–7446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigneron M., Barrera-Saldana H. A., Baty D., Everett R. E., Chambon P. Effect of the 21-bp repeat upstream element on in vitro transcription from the early and late SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2373–2382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk H. E., Kecskemethy N., Schäfer K. P. m-Aminophenylboronate agarose specifically binds capped snRNA and mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7621–7633. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zan-Kowalczewska M., Bretner M., Sierakowska H., Szczesna E., Filipowicz W., Shatkin A. J. Removal of 5'-terminal m7G from eukaryotic mRNAs by potato nucleotide pyrophosphatase and its effect on translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3065–3081. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]