Abstract
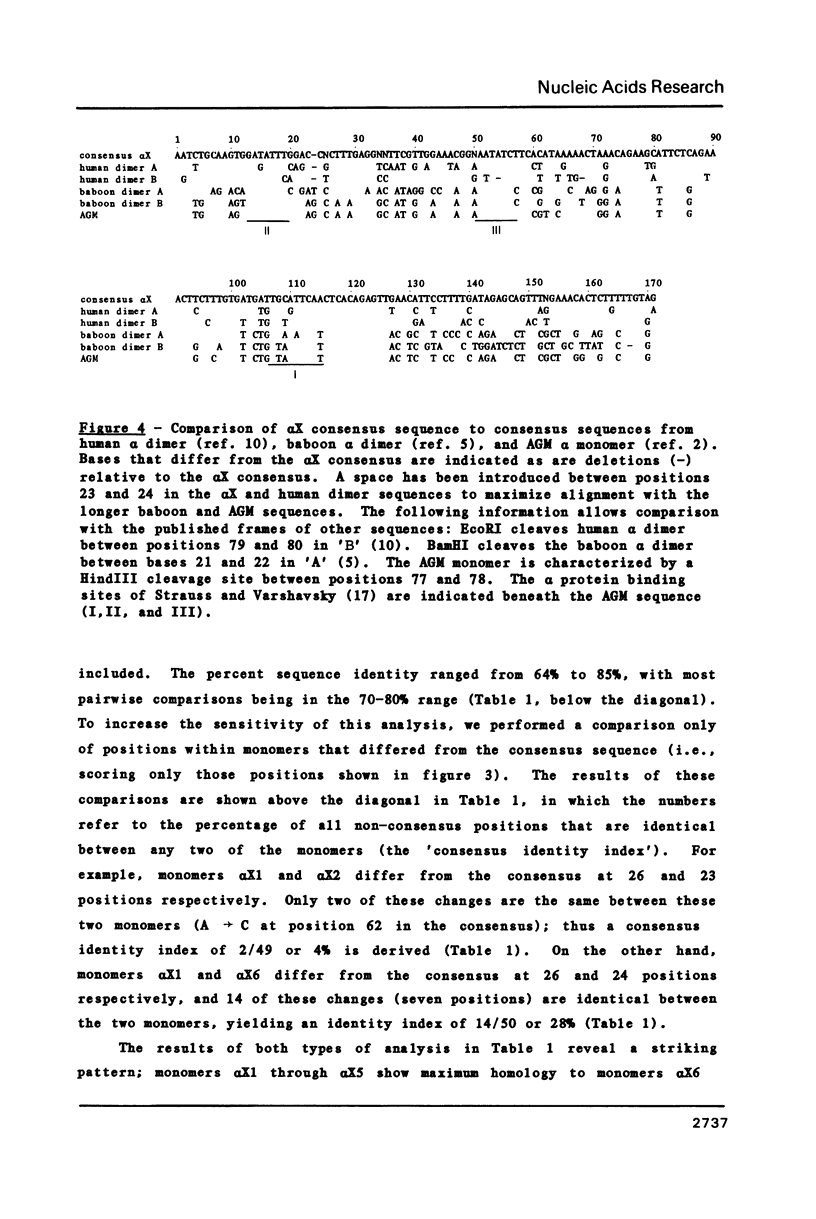
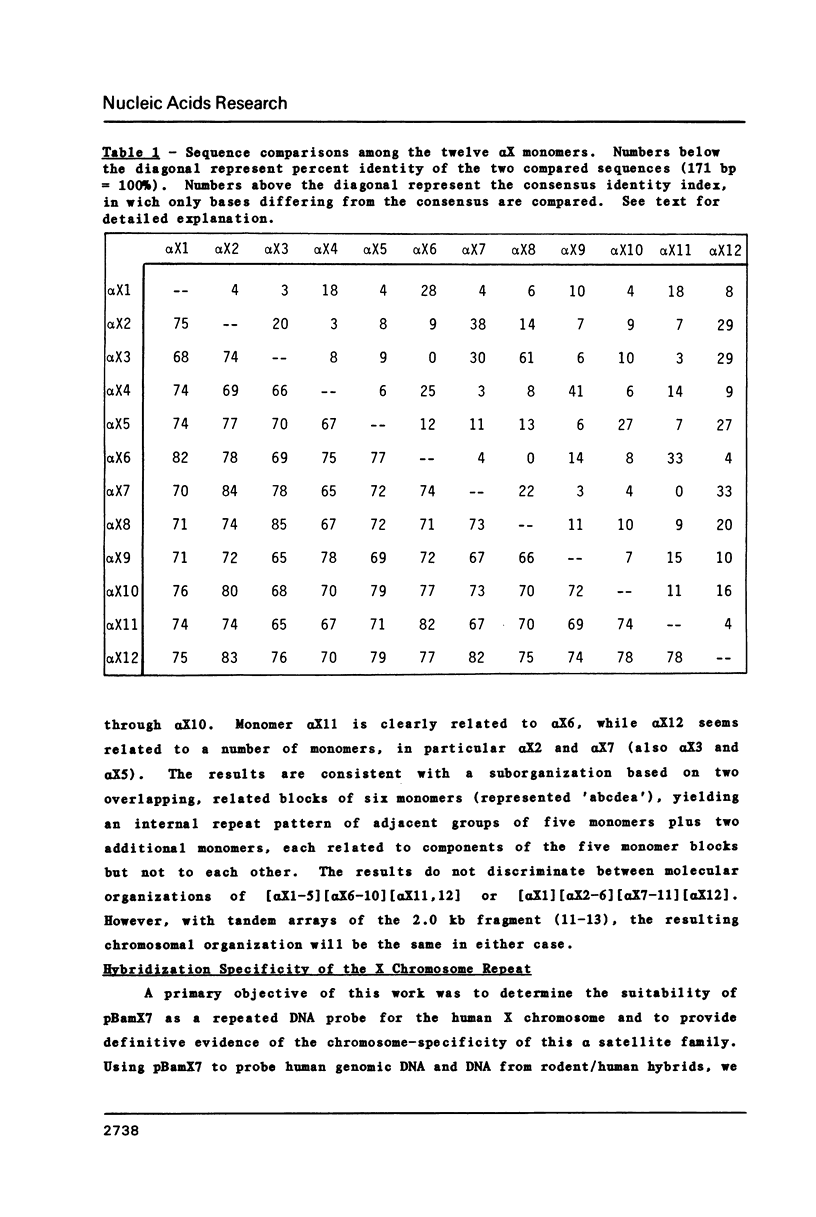
The pericentromeric region of the human X chromosome is characterized by a tandemly repeated family of 2.0 kilobasepair (kb) DNA fragments, initially revealed by cleavage of human DNA with the restriction enzyme BamHI. We report here the complete nucleotide sequence of a cloned member of the repeat family and establish that this X-linked DNA family consists entirely of alpha satellite DNA. Our data indicate that the 2.0 kb repeat consists of twelve alpha satellite monomers arranged in imperfect, direct repeats. Each of the alpha X monomers is approximately 171 basepairs (bp) in length and is 60-75% identical in sequence to previously described primate alpha satellite DNAs. The twelve alpha X monomers are 65-85% identical in sequence to each other and are organized as two adjacent, related blocks of five monomers, plus an additional two monomers also related to monomers within the pentamer blocks. Partial nucleotide sequence of a second, independent copy of the 2.0 kb BamHI fragment established that the 2.0 kb repeat is, in fact, the unit of amplification on the X. Comparison of the sequences of the twelve alpha X monomers allowed derivation of a 171 bp consensus sequence for alpha satellite DNA on the human X chromosome. These sequence data, combined with the results of filter hybridization experiments of total human DNA and X chromosome DNA, using subregions within the 2.0 kb repeat as probes, provide strong support for the hypothesis that individual human chromosomes are characterized by different alpha satellite families, defined both by restriction enzyme periodicity and by chromosome-specific primary sequence.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Donehower L., Gillespie D. Restriction site periodicities in highly repetitive DNA of primates. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):805–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90487-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss S. J., Harris H. Gene transfer by means of cell fusion I. Statistical mapping of the human X-chromosome by analysis of radiation-induced gene segregation. J Cell Sci. 1977 Jun;25:17–37. doi: 10.1242/jcs.25.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Characterization of a cloned DNA sequence that is present at centromeres of all human autosomes and the X chromosome and shows polymorphic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4884–4888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. N., Singer M. F. Structural organization of alpha-satellite DNA in a single monkey chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):323–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Toward a molecular paleontology of primate genomes. I. The HindIII and EcoRI dimer families of alphoid DNAs. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):103–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00286019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma. 1978 Mar 22;66(1):23–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00285813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Repeating restriction fragments of human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3063–3076. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Wu J. C. Homology between human and simian repeated DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):92–94. doi: 10.1038/276092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maresca A., Singer M. F., Lee T. N. Continuous reorganization leads to extensive polymorphism in a monkey centromeric satellite. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):629–649. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Brown F. L., Maio J. J. Highly repetitive component alpha and related alphoid DNAs in man and monkeys. Chromosoma. 1980;80(3):331–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00292688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T., Fink G. R. Gene conversion between repeated genes. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):216–217. doi: 10.1038/300216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Smith K. D., Sutherland J. Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2017–2033. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Manuelidis L. Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Hansen S. K., Oishi K. K., Ryder O. A., Hamkalo B. A. Characterization of a cloned repetitive DNA sequence concentrated on the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6593–6597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]