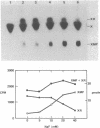
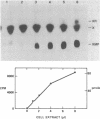
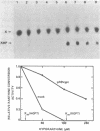
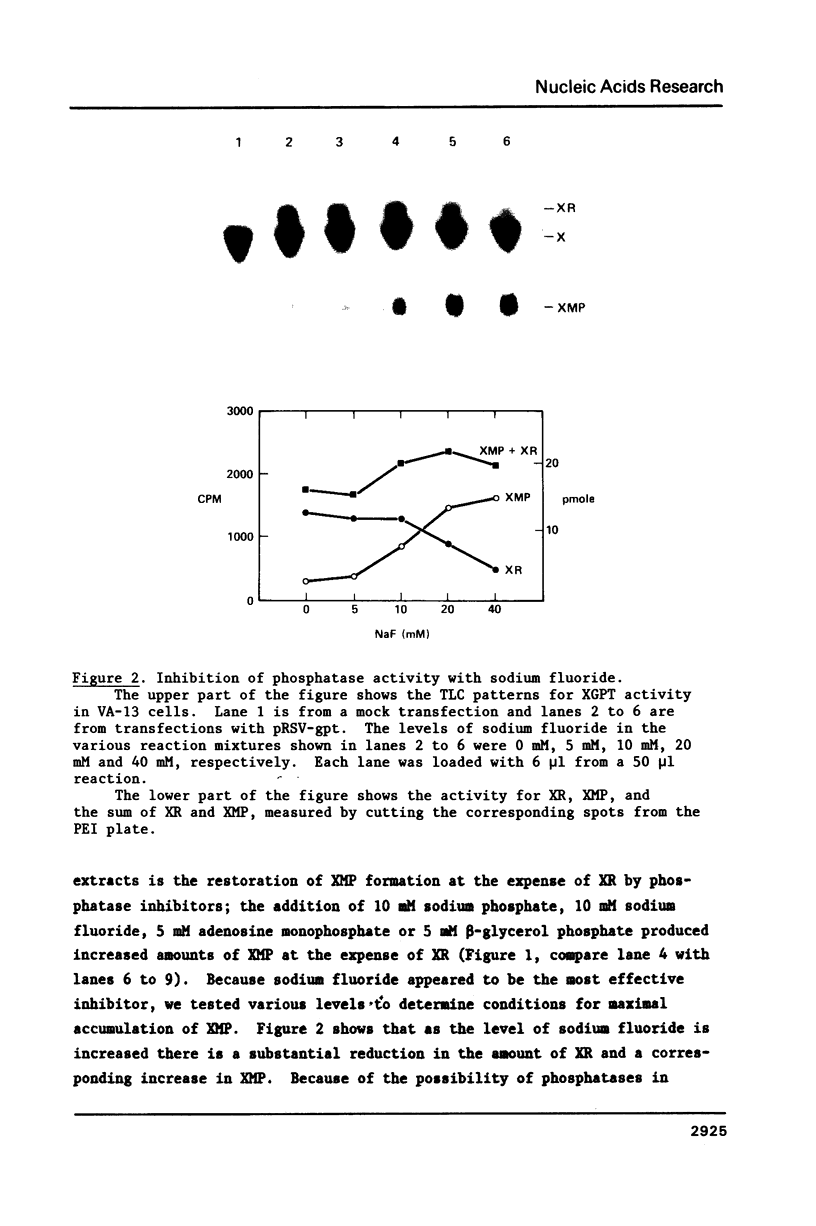
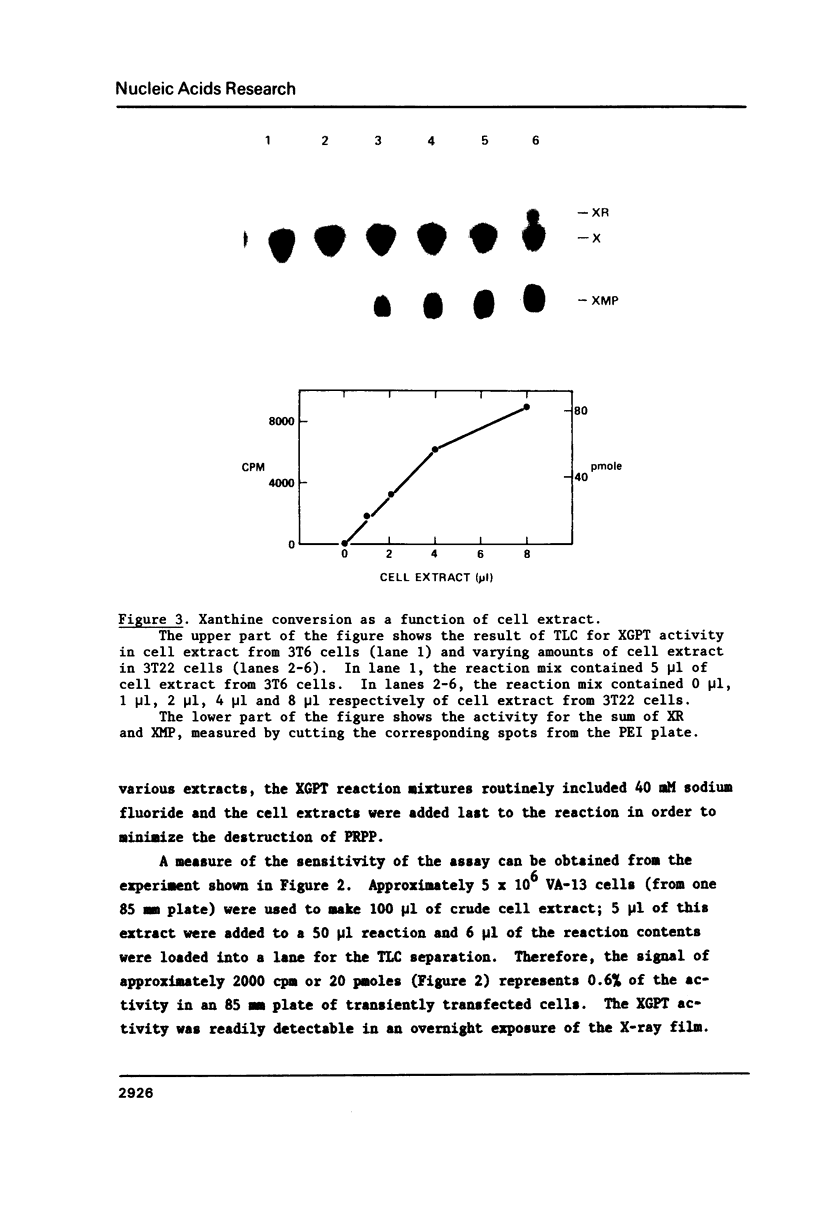
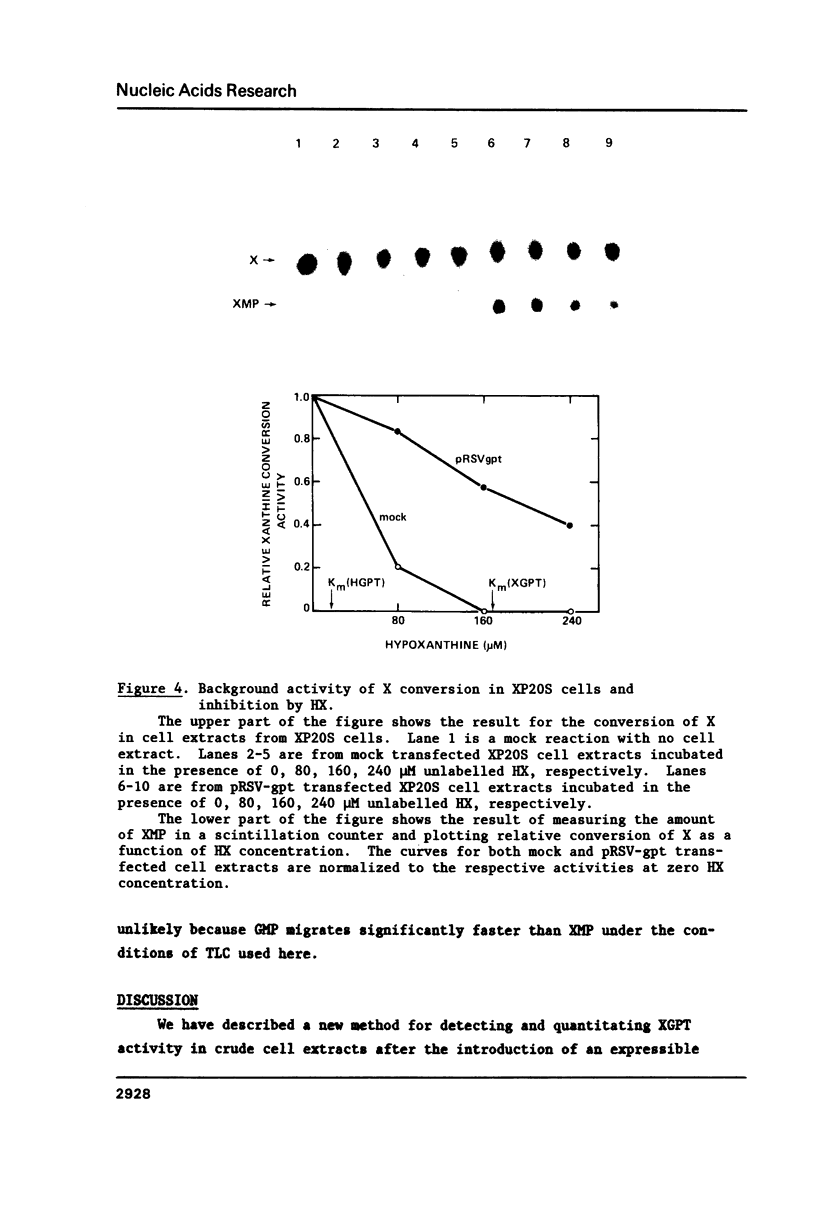
Abstract
Cultured mammalian cells transduced with the Escherichia coli gene, Ecogpt, synthesize the bacterial enzyme xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (XGPT) (1). This paper describes a method for measuring XGPT activity in crude cell extracts by following the conversion of 14C-xanthine (X) to 14C-xanthine monophosphate (XMP) and 14C-xanthosine (XR) by thin layer chromatography. The method is rapid, easy to use, sensitive and linear over a wide range of XGPT activity and has been useful for detecting XGPT in cells that were transiently transfected or stably transformed with Ecogpt. During our studies, we have found that a human cell line (XP20S) converts xanthine to XMP. This activity is probably catalyzed by a variant hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPT) since the low activity is readily inhibited by hypoxanthine. A low level of conversion of X to XMP may explain why some cell lines are not killed in a medium containing mycophenolic acid and X.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. Complete analysis of cellular nucleotides by two-dimensional thin layer chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9759–9769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J., Cook J. M. The inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis by mycophenolic acid. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):515–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1130515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A., Papaioannou R., Elion G. B. Human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. I. Purification, properties, and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1263–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. W., Milman G. Purification and characterization of Escherichia coli guanine-xanthine phosphoribosyltransferase produced by a high efficiency expression plasmid utilizing a lambda PL promoter and CI857 temperature-sensitive repressor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7469–7475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Kelley W. N. Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: altered kinetic properties of mutant enzyme. Science. 1971 Feb 19;171(3972):689–691. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3972.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Ramsey G. A., Krenitsky T. A., Elion G. B. Guanine phosphoribosyltransferase from Escherichia coli, specificity and properties. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4723–4731. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe H., Nii S., Ishii M. I., Utsumi H. Comparative studies of host-cell reactivation, colony forming ability and excision repair after UV irradiation of xeroderma pigmentosum, normal human and some other mammalian cells. Mutat Res. 1974 Dec;25(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Takebe H. Establishment by SV40 transformation and characteristics of a cell line of xeroderma pigmentosum belonging to complementation group F. Mutat Res. 1983 Feb;112(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(83)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]