Abstract
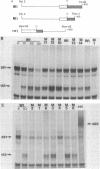
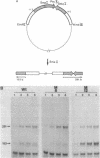
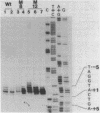
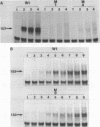
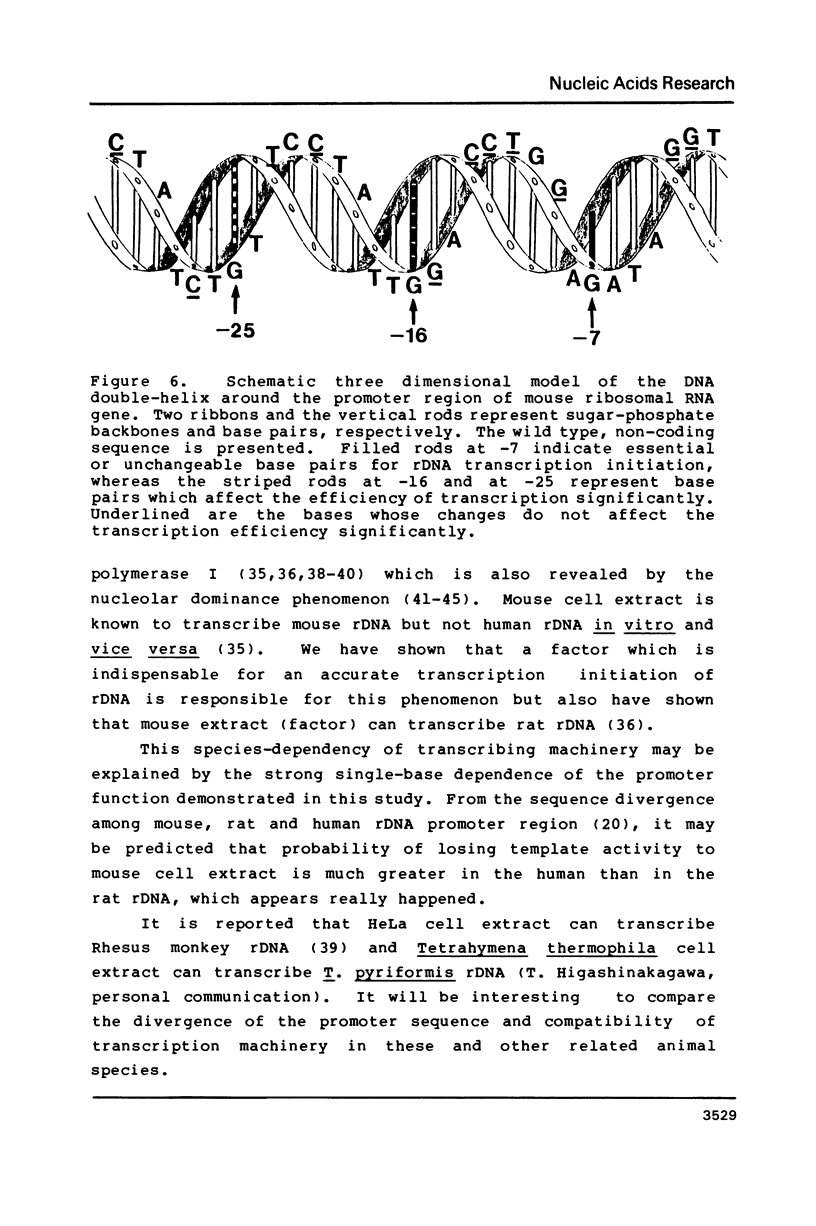
Point mutations are introduced into a mouse rDNA fragment containing the promoter region by a sodium bisulfite method and the mutants are tested for the ability of accurate transcription initiation in vitro. The results indicate that the change, G to A, at -7 completely eliminates the promoter activity, and those at -16 and at -25 decrease it to about 10% and 50%, respectively. On the other hand, the substitutions at +9, +4, -2, -9 and -39 do not alter the template activity significantly. It is concluded that there are limited but distinct nucleotides that are essential for the transcription initiation of this gene. This sort of absolute requirement for single specific bases is not reported in protein coding genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II. We propose that these rigid recognition signals which we have found are the molecular basis for the strong species-dependency of the transcription machinery of RNA polymerase I system. A model is presented in which a transcription factor interacts with the rDNA promoter from one side of the DNA double-helix with essential contacts at these bases.
Full text
PDF




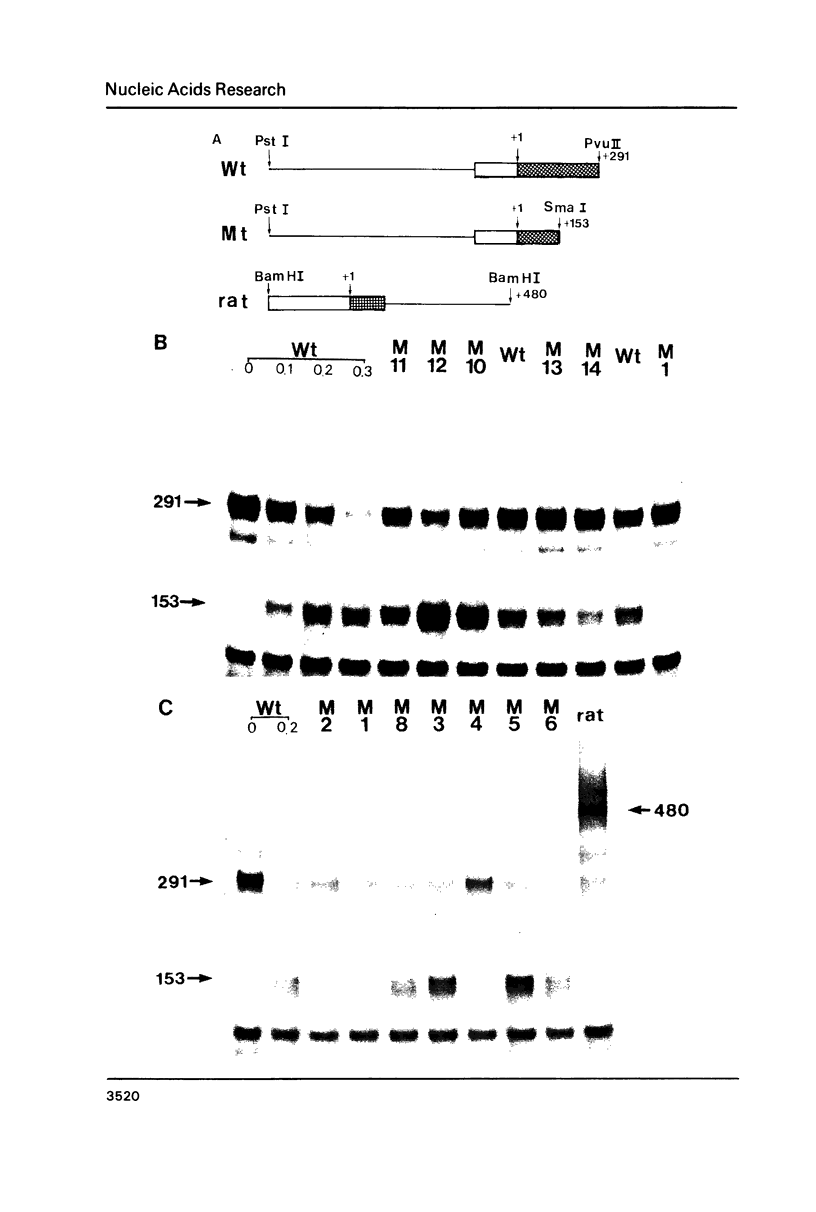

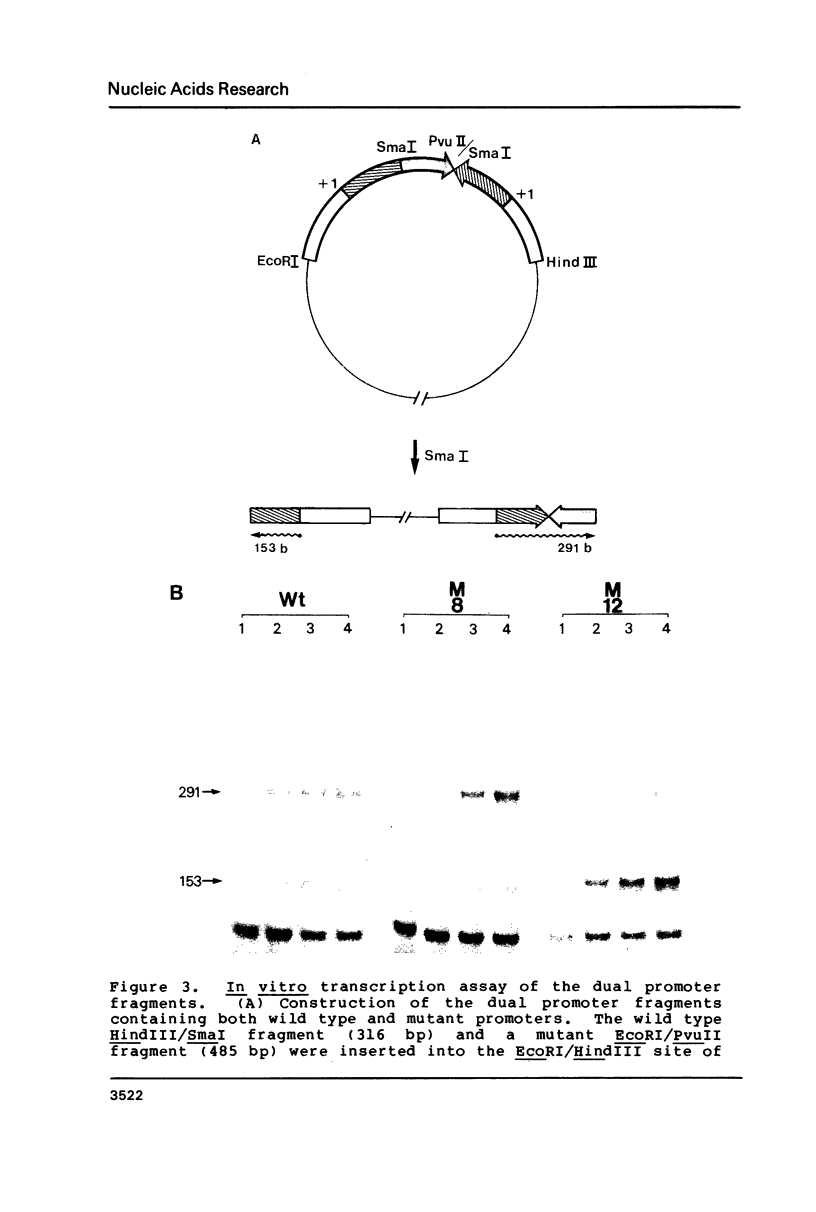

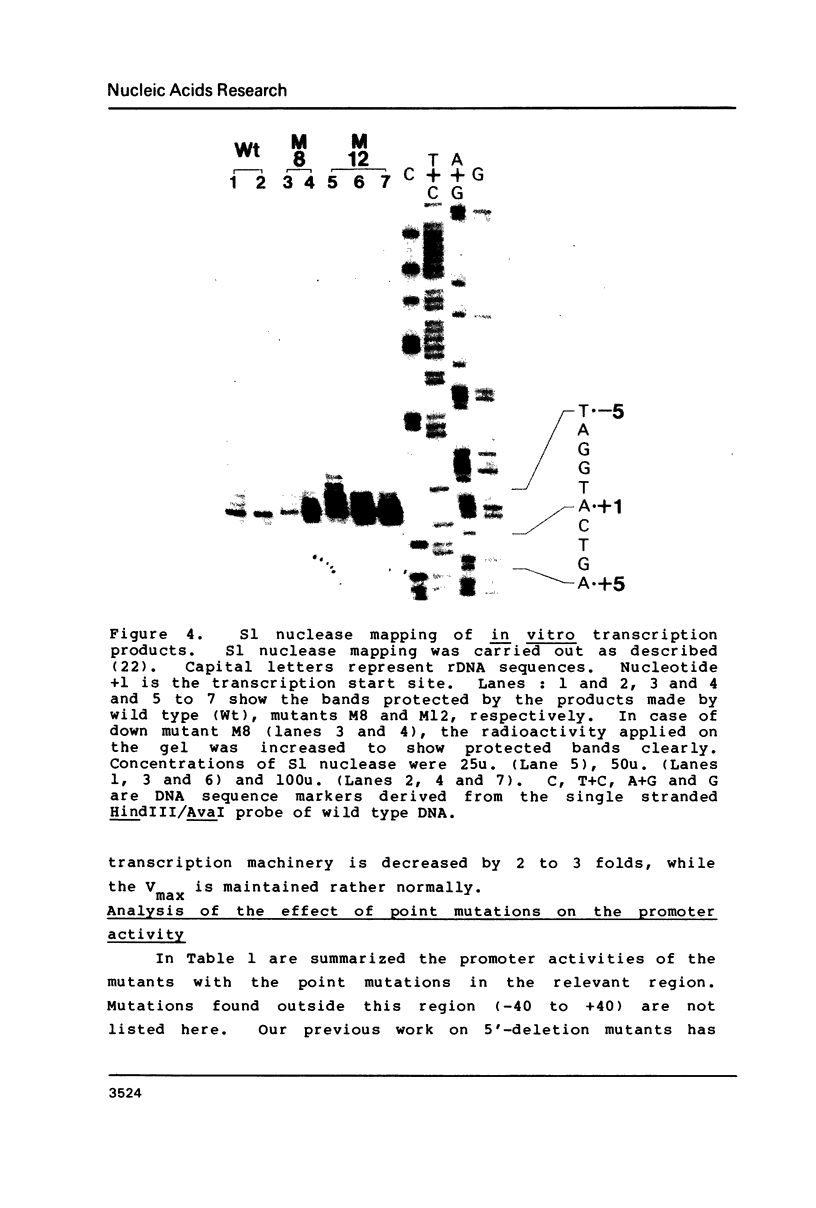
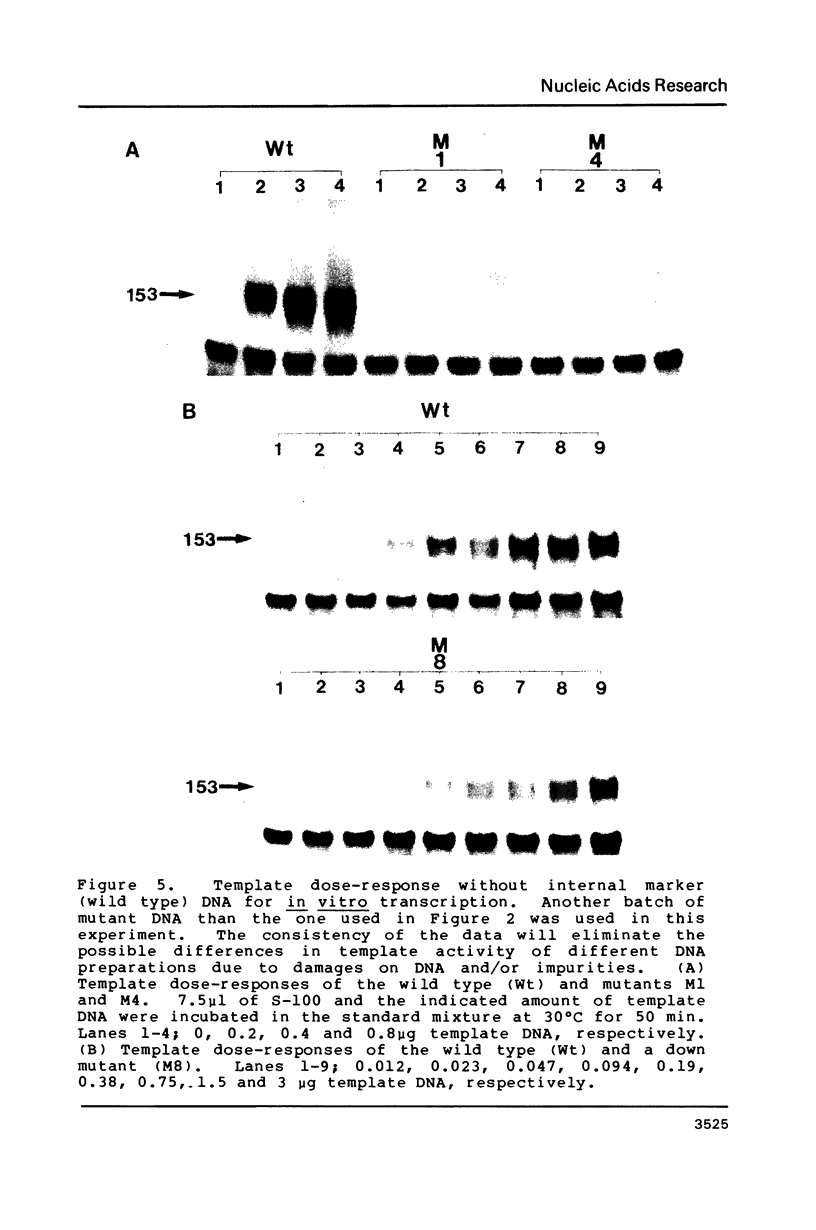






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Grummt I., Allet B. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation region of the ribosomal transcription unit from mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1559–1569. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Talavera A., Basilico C., Miller O. J. Suppression of production of mouse 28S ribosomal RNA in mouse-human hybrids segregating mouse chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):694–697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Mantei N., Weissmann C. DNA sequences preceding the rabbit beta-globin gene are required for formation in mouse L cells of beta-globin RNA with the correct 5' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri G. L., Green H. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in human-mouse hybrid cells. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr;41(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Muramatsu M. Nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region of a rat ribosomal RNA gene. Gene. 1982 May;18(2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Hofstetter H. A detailed mutational analysis of the eucaryotic tRNAmet1 gene promoter. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Takeuchi K., Hori H., Hirose T., Inayama S., Suzuki Y. Contact points between transcription machinery and the fibroin gene promoter deduced by functional tests of single-base substitution mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1394–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Reeder R. H. Preferential transcription of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA in interspecies hybrids between Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Oostra B. A., Ely B. K., Smith A. E. Deletion loop mutagenesis: a novel method for the construction of point mutations using deletion mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5161–5171. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. A component of Drosophila RNA polymerase I promoter lies within the rRNA transcription unit. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):179–181. doi: 10.1038/304179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Accurate transcription of truncated ribosomal DNA templates in a Drosophila cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1501–1505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Localization of DNA sequences promoting RNA polymerase I activity in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Smale S. T., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. Regulation of human ribosomal RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3558–3562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Tjian R. In vitro transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Rebbert M. L., Dawid I. B. Nucleotide sequence of the initiation site for ribosomal RNA transcription in Drosophila melanogaster: comparison of genes with and without insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1513–1517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Sollner-Webb B., Croce C., Arnheim N. The absence of a human-specific ribosomal DNA transcription factor leads to nucleolar dominance in mouse greater than human hybrid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1306–1312. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Yamamoto O., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. In vitro transcription of a cloned mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6773–6785. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. Directed semisynthetic point mutational analysis of an RNA polymerase III promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7695–7700. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka A., Sugimoto K., Sasaki H., Takanami M. An in vitro method generating base substitutions in preselected regions of plasmid DNA: application to structural analysis of the replication origin of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90189-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi T., Berglund C., Reeder R. H. On the mechanism of nucleolar dominance in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):484–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiga H., Mizumoto K., Matsui T., Higashinakagawa T. Determination of the transcription initiation site of Tetrahymena pyriformis rDNA using in vitro capping of 35S pre-rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 24;10(14):4223–4236. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.14.4223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Nathans D. Local mutagenesis: a method for generating viral mutants with base substitutions in preselected regions of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. In vitro mutagenesis and transcriptional analysis of a mouse ribosomal promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. A novel method for site-directed mutagenesis: its application to an eukaryotic tRNAPro gene promoter. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):415–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Hirose S., Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Promoter sequence of fibroin gene assigned by in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Kominami R., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. The nucleotide sequence of the putative transcription initiation site of a cloned ribosomal RNA gene of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6043–6058. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeet M. P., Klootwijk J., van Heerikhuizen H., Fontijn R. D., Vreugdenhil E., Planta R. J. A conserved sequence element is present around the transcription initiation site for RNA polymerase A in Saccharomycetoideae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1137–1148. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Derbyshire R., Guy A., Molko D., Roget A., Téoule R., Chambon P. Specific in vitro transcription of conalbumin gene is drastically decreased by single-point mutation in T-A-T-A box homology sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7024–7028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O., Takakusa N., Mishima Y., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Determination of the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene by an in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):299–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarucki-Schulz T., Tsai S. Y., Itakura K., Soberon X., Wallace R. B., Tsai M. J., Woo S. L., O'Malley B. W. Point mutagenesis of the ovalbumin gene promoter sequence and its effect on in vitro transcription. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11070–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]