Abstract
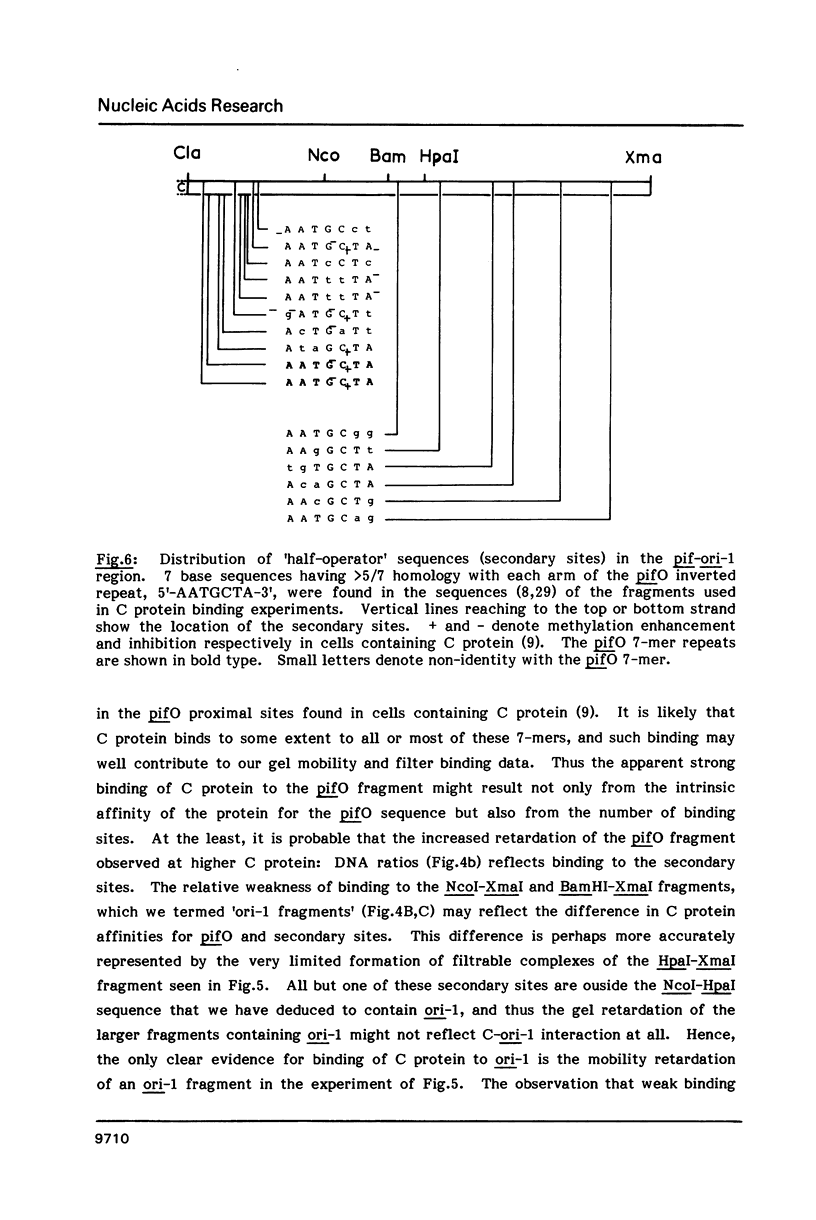
The C (pifC) protein of miniF represses transcription of its own gene by binding to the pif operator (pifO); it is also needed for replication initiated from the miniF primary origin (ori-1). We have determined the nucleotide sequence of the C gene. The gene has been inserted into an expression vector under Ptrp control where it is expressed at high levels. The C protein has been purified from cells carrying the Ptrp-C plasmid, and a preliminary study of C protein-DNA binding properties has been carried out. C protein binds strongly to pifO, and weakly to sequences in the ori-1 region.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. M., Bevan M., Son P. H. Kilo-sequencing: creation of an ordered nest of asymmetric deletions across a large target sequence carried on phage M13. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:98–122. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist P. L., Adelberg E. A. Abnormal excision and transfer of chromosomal segments by a strain of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):119–128. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.119-128.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram H. K., Cram D., Skurray R. F plasmid pif region: Tn1725 mutagenesis and polypeptide analysis. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelaub R., Wehlmann H. Amber-mutants of plasmid mini-F defective in replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):201–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00267370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichenlaub R., Figurski D., Helinski D. R. Bidirection replication from a unique origin in a mini-F plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1138–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F. A systemic DNA sequencing strategy. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R., Cram D., Ray A., DiBerardino D., Skurray R. Cloning and analysis of pif, replication and leading regions of the F plasmid. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(1):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00327933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komai N., Nishizawa T., Hayakawa Y., Murotsu T., Matsubara K. Detection and mapping of six miniF-encoded proteins by cloning analysis of dissected miniF segments. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):193–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00331850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D., Hill D., Caughey P., Gunn P. The mini-F primary origin. Sequence analysis and multiple activities. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):267–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manis J. J., Kline B. C. Restriction endonuclease mapping and mutagenesis of the F sex factor replication region. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):175–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00268815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Yoshioka K., Horiuchi T. Control of cell division by sex factor F in Escherichia coli. I. The 42.84-43.6 F segment couples cell division of the host bacteria with replication of plasmid DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):605–625. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Lanka E., Malamy M. H. F factor inhibition of conjugal transfer of broad-host-range plasmid RP4: requirement for the protein product of pif operon regulatory gene pifC. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1067–1073. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1067-1073.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Malamy M. H. Identification of the pifC gene and its role in negative control of F factor pif gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):338–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.338-347.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Malamy M. H. Mutational and in vivo methylation analysis of F-factor PifC protein binding to the pif operator and the region containing the primary origin of mini-F replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1433–1437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Malamy M. H. Regulation of the F-factor pif operon: pifO, a site required in cis for autoregulation, titrates the pifC product in trans. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):192–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.192-198.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman G. S., Cooney R., Malamy M. H. Cloning of the pif region of the F sex factor and identification of a pif protein product. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.254-264.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Krovatin W., DeAnda J., Youderian P., Susskind M. M. Primary structure of the immI immunity region of bacteriophage P22. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):699–713. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Iino T. An essential gene for replication of the mini-F plasmid from origin I. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00334092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto K., Iino T. Transfer inhibition of RP4 by F factor. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;192(1-2):104–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00327654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokino T., Murotsu T., Matsubara K. Purification and properties of the mini-F plasmid-encoded E protein needed for autonomous replication control of the plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4109–4113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Purification of bacteriophage lambda O protein that specifically binds to the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(3):325–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00425606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehlmann H., Eichenlaub R. Plasmid mini-F encoded proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):205–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00267371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]