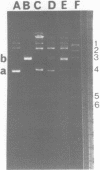
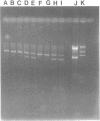
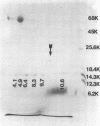
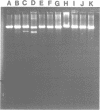
Abstract
The bacteriophage lambda terminase enzyme cleaves the cohesive-end sites of lambda DNA to yield the protruding 5'-termini of the mature molecule. In vitro, this endonucleolytic event requires a protein factor which has been isolated and purified from extracts of uninfected E. coli. The terminase host factor (THF) is a heat stable basic protein of M.W. approximately 22,000. The integration host factor (IHF) protein of E. coli can efficiently substitute for THF in the terminase reaction; however, THF can be demonstrated to be physically present in, and isolated with full biological activity from extracts of cells defective or deficient in IHF.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K., Gottesman S. Purification of the bacteriophage lambda xis gene product required for lambda excisive recombination. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9658–9662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear S. E., Court D. L., Friedman D. I. An accessory role for Escherichia coli integration host factor: characterization of a lambda mutant dependent upon integration host factor for DNA packaging. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):966–972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.966-972.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker A., Gold M. Enzymatic breakage of the cohesive end site of phage lambda DNA: terminase (ter) reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker A., Marko M., Gold M. Early events in the in vitro packaging of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):291–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold V., Geider K. Interaction of DNA with DNA-binding proteins. The characterization of protein HD from Escherichia coli and its nucleic acid complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):443–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Mizuuchi K. A defined system for the DNA strand-transfer reaction at the initiation of bacteriophage Mu transposition: protein and DNA substrate requirements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7570–7574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Frackman S., Sippy J. Essential interaction between lambdoid phage 21 terminase and the Escherichia coli integrative host factor. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90216-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M., Becker A. The bacteriophage lambda terminase. Partial purification and preliminary characterization of properties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14619–14625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M., Hawkins D., Murialdo H., Fife W. L., Bradley B. Circular monomers of bacteriophage lambda DNA as substrates for in vitro packaging. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Lutz H., Kornberg A. Novel histone H2A-like protein of escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5097–5101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Rudt F., Koch C., Mertens G. G inversion in bacteriophage Mu DNA is stimulated by a site within the invertase gene and a host factor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):771–780. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi F., Ebina Y., Miki T., Nakazawa T., Nakazawa A. Purification and characterization of a protein from Escherichia coli which forms complexes with superhelical and single-stranded DNAs. J Biochem. 1982 Oct;92(4):1059–1068. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Friedman D. I. An E. coli gene product required for lambda site-specific recombination. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. I., Mozola M. A., Friedman D. I. int-h: An int mutation of phage lambda that enhances site-specific recombination. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: the mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli protein factor required for lambda integrative recombination. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9246–9253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A. B., Gottesman S., Gottesman M. Regulation of bacteriophage lambda int gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):327–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Gros F. Characterization of a novel, low-molecular-weight DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Becker A., Gold M. DNA packaging in the lambdoid phages: the role of lambda genes Nu1 and A. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):642–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90363-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Nedospasov S. A., Bakayev V. V., Bakayeva T. G., Georgiev G. P. Histone-like proteins in the purified Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleoprotein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2725–2745. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. G., Blattner F. R., Jaskunas S. R., Nomura M. Insertion of DNA carrying ribosomal protein genes of Escherichia coli into Charon vector phages. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7344–7354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K., Nagata A., Kano Y., Imamoto F. Isolation and characterization of nucleoid proteins from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(2):217–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00328053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]