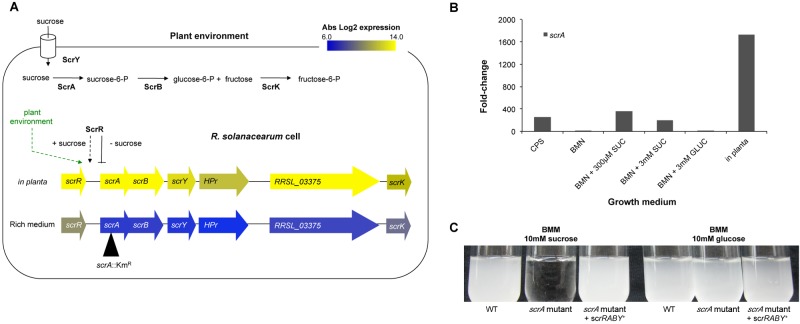
FIG 3 .
The scrRABY sucrose metabolic cluster is induced in planta and encodes a sucrose-specific PTS. (A) R. solanacearum converts sucrose to glucose-6-phosphate (glucose-6-P) and fructose-6-P with the components of a sucrose-specific PTS encoded by the scr cluster, which was highly expressed in planta. The absolute log2 gene expression from bacteria growing in planta or in rich medium is shown in a heat map layered on the scr gene cluster. The location of the insertional mutation in scrA (scrA::Kmr or scrA) is indicated by a black triangle. (B) Relative fold change of scrA expression in R. solanacearum UW551 cells growing in culture media (CPS, broth containing Casamino Acids, peptone, and 55 mM sucrose; BMM, Boucher’s minimal medium; SUC, sucrose; GLUC, glucose) or in Bonny Best tomato stems. Gene expression was measured at a cell density of 1 × 109 CFU/ml broth or 1 × 109 CFU/g tomato stem and determined on a per-cell basis. The black bars represent the mean scrA expression fold change for each growth condition compared to the level in CPG medium, with three biological replicates for culture and four biological replicates for in planta expression. R. solanacearum UW551 scrA expression fold changes in planta were significantly different from expression levels in all culture media tested (P < 0.03 by Mann-Whitney test). (C) A UW551 scrA mutant grew as well as the wild type (WT) on minimal medium (BMM) plus glucose but failed to grow on sucrose as the sole carbon source. Growth on sucrose was restored by scrRABY in trans on plasmid pUFJ10.