Abstract
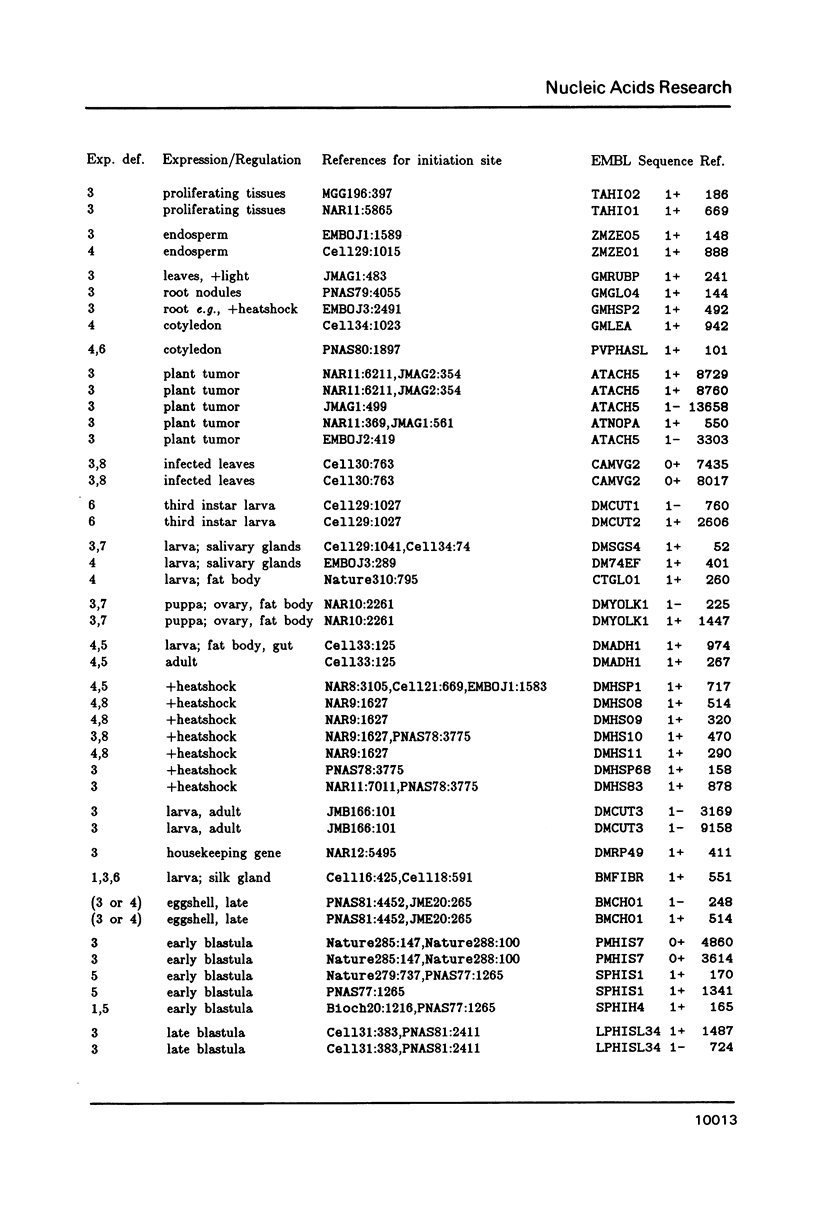
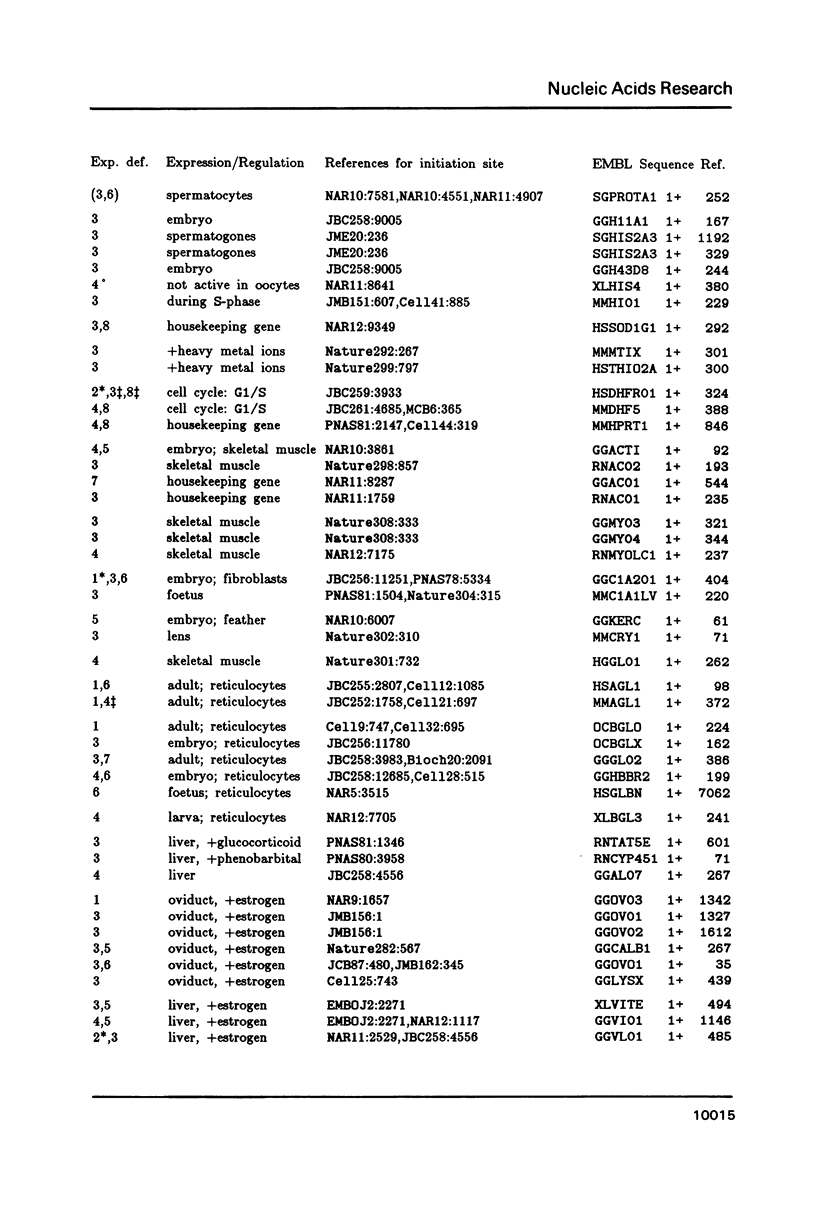
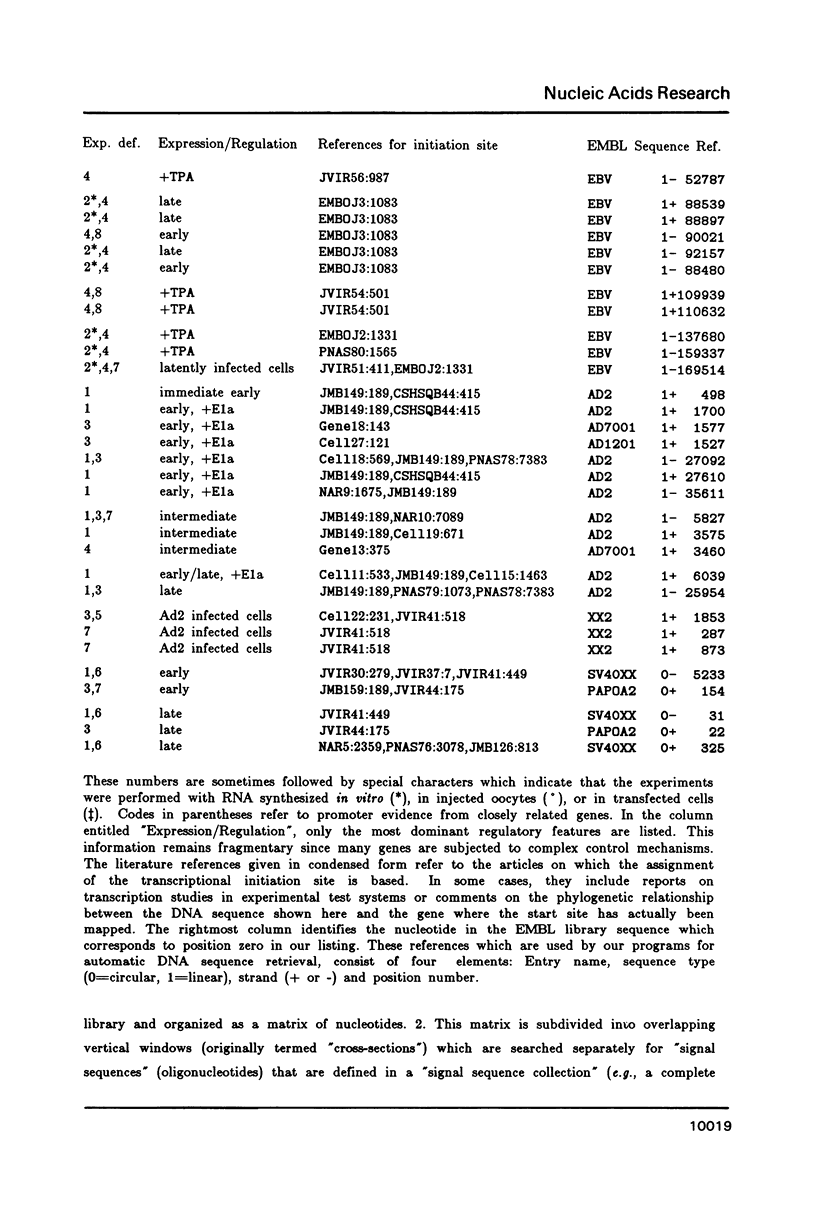
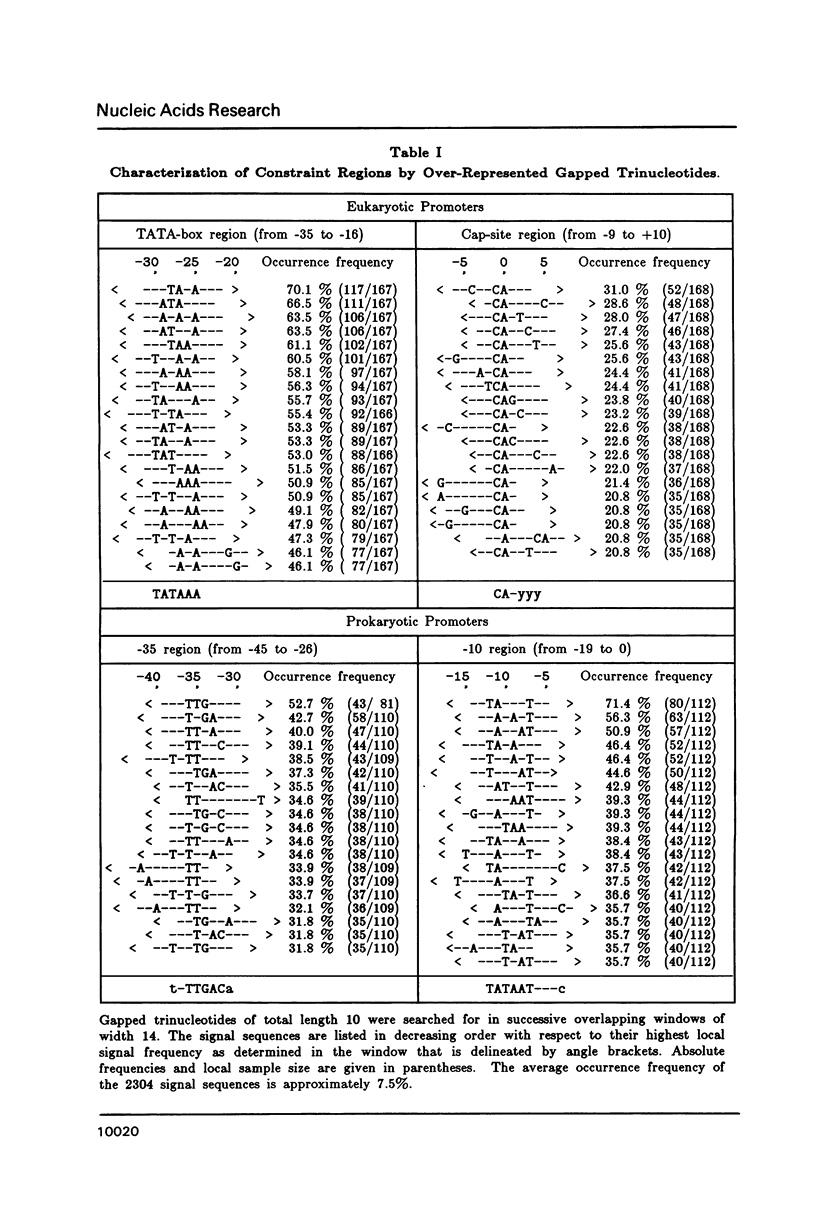
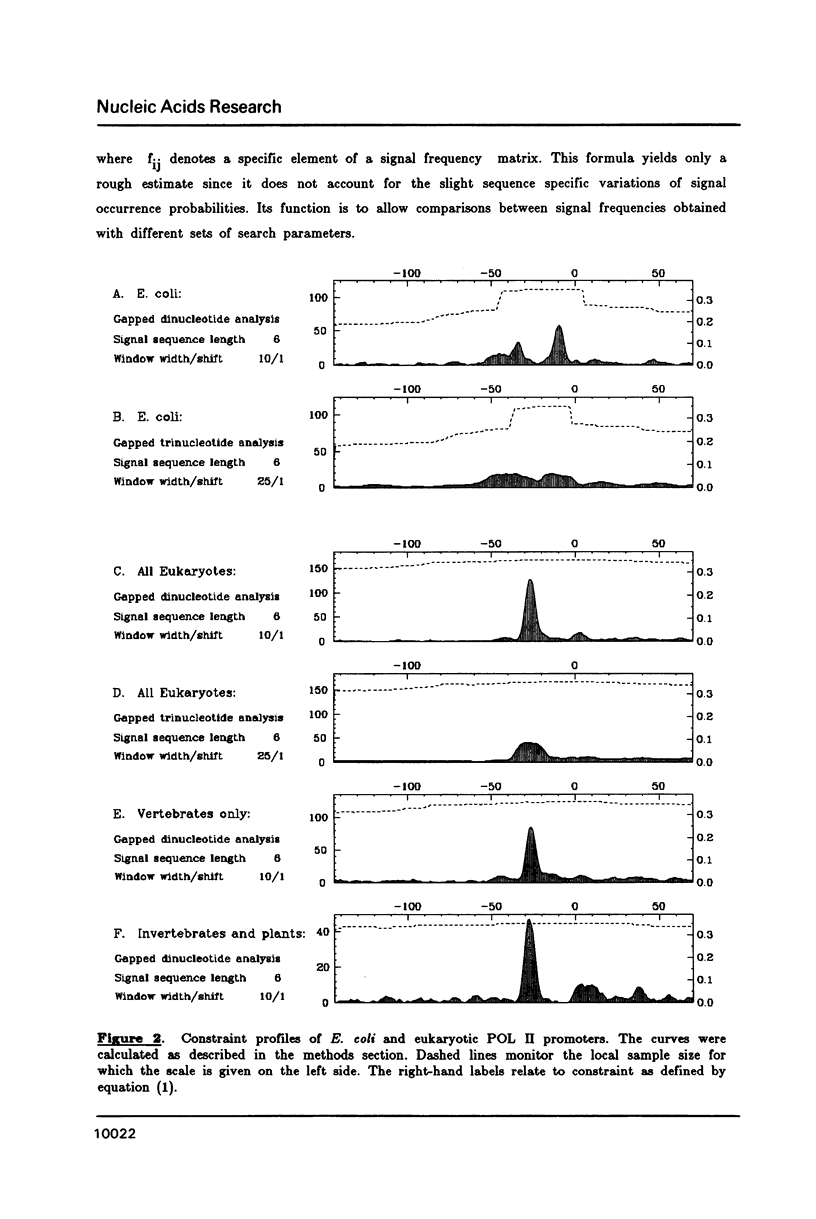
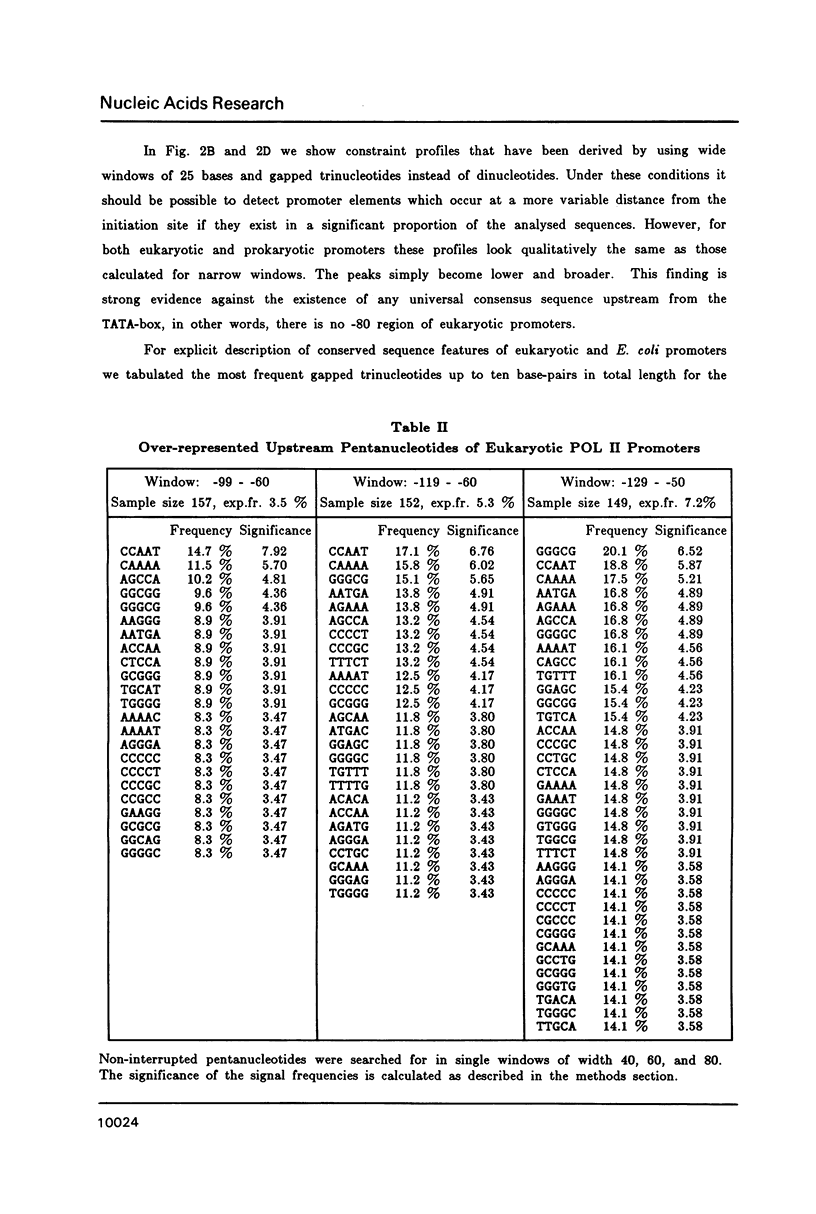
A representative set of 168 eukaryotic POL II promoters has been compiled from the EMBL library and subjected to computer signal search analysis. Application of this technique to E. coli promoters as a control ensemble revealed the well known consensus sequences at -35 and -10 which indicates that the methods are adequate to approach problems of this kind. The results obtained from the eukaryotic promoter set can be summarized as follows: Common sequence features are confined to a region between -50 and +10 relative to the transcriptional initiation site. The only well conserved consensus sequence is TATAAA, centered at -28. A weak motif, CA followed preferentially by pyrimidines, surrounds the cap-site. Two pentanucleotides which have been shown by experiments to stimulate transcription of certain genes, GGGCG and CCAAT, are moderately over-represented in the upstream region (between -129 and -50). However, they occur at highly variable distances from the initiation site.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P., Bryan B. Signal search analysis: a new method to localize and characterize functionally important DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):287–305. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Tyndall C., Kamen R. Sequences at the capped 5'-ends of polyoma virus late region mRNAs: an example of extreme terminal heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6305–6322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepin M., Triadou P., Lelong J. C., Gros F. Identification of transcription initiation sites for bacterial RNA polymerase and eukaryotic RNA polymerase B on the 5' end of the mouse beta-Globin gene. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):371–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Eggert M., Waterman M. S. Rigorous pattern-recognition methods for DNA sequences. Analysis of promoter sequences from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge P., Feix G. A zein gene of maize is transcribed from two widely separated promoter regions. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90559-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ream L. W., Gordon M. P. Crown gall disease and prospects for genetic manipulation of plants. Science. 1982 Nov 26;218(4575):854–859. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4575.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Yarus M. A., Gold L. Delila system tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):129–140. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. S., Arratia R., Galas D. J. Pattern recognition in several sequences: consensus and alignment. Bull Math Biol. 1984;46(4):515–527. doi: 10.1007/BF02459500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M. Regulation of eukaryotic gene expression by transactivating proteins and cis acting DNA elements. Biol Cell. 1984;50(3):203–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



