Abstract
Vaccination of one person may prevent the infection of another either because the vaccine prevents the first from being infected and from infecting the second, or because, even if the first person is infected, the vaccine may render the infection less infectious. We might refer to the first of these mechanisms as a contagion effect and the second as an infectiousness effect. In the simple setting of a randomized vaccine trial with households of size two, we use counterfactual theory under interference to provide formal definitions of a contagion effect and an unconditional infectiousness effect. Using ideas analogous to mediation analysis, we show that the indirect effect (the effect of one person’s vaccine on another’s outcome) can be decomposed into a contagion effect and an unconditional infectiousness effect on the risk-difference, risk-ratio, odds-ratio and vaccine-efficacy scales. We provide identification assumptions for such contagion and unconditional infectiousness effects, and describe a simple statistical technique to estimate these effects when they are identified. We also give a sensitivity-analysis technique to assess how inferences would change under violations of the identification assumptions. The concepts and results of this paper are illustrated with hypothetical vaccine-trial data.
Administering a vaccine to one or several persons in a population may protect not only those vaccinated but also others as well. In the causal inference vaccine literature, the protection afforded unvaccinated people has been called the indirect effect of vaccination. A number of papers have considered the methodology of estimating such indirect effects.1–5 Two distinct mechanisms may contribute to such an indirect effect. Suppose there are two persons in a household and we vaccinate the first. Vaccinating the first person may prevent the infection in the first, thus preventing the first from infecting the second. Alternatively, vaccinating the first person may protect the second because, even if infected, the vaccinated first person may be less infectious, and not infect the second. This is referred to as an “infectiousness effect.”6–8 We will refer to the former as a “contagion effect”, following terminology in the social network literature,9 though we acknowledge that “infectiousness” and “contagion” are sometimes used interchangeably in the infectious disease literature. Establishing that vaccination can have indirect effects and estimating the effects of vaccination on reducing infectiousness for others can have important implications for global vaccine policy.
As an example, consider the individually randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of an acellular pertussis vaccine among infants in Sweden in the early 1990s.10 In addition to the usual protective effects, the investigators were interested in estimating the indirect protection of vaccination on siblings and parents in the households of the randomized infants. Based on person-time at risk, under one case definition, the estimated indirect effects in younger siblings was 0.61 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.15–0.83) and in parents 0.58 (95% CI 0.20–0.80). Similar “minicommunity” designs have been used to estimate indirect effects of vaccination for settings including influenza, cholera, and pneumococcus vaccination.5
Consider now a slightly different vaccine trial setting in which one-year-olds at a day-care center are randomized to receive pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against a given pneumococcus serotype. The colonization status with respect to the given serotype of the one-year-old and one of its parents (the mother, say) is also monitored. Because pneumococcus is highly prevalent in young children who attend day care, the mother is much more likely to acquire the pneumococcus from the child than through other transmission routes. In settings in which it can effectively be assumed that, at least for the study period, the second person (e.g. the mother) can be infected only from the first (e.g. the one-year-old), the indirect effect itself can be decomposed into a contagion effect and what will be defined below as an unconditional infectiousness effect. Understanding what proportion of an indirect effect is due to decreasing infectiousness can give insight into the mechanism by which the vaccine protects others.
We draw on theory for causal inference under interference3,4,7,11 and on mediation analysis12–15 to provide formal counterfactual decompositions for each of these effects. We show that these decompositions hold for the risk-difference, risk-ratio, odds-ratio and vaccine-efficacy scales. We discuss assumptions that suffice to identify these effects from vaccine trial data and propose a simple statistical modeling strategy to estimate these effects. We describe a sensitivity analysis technique that can be employed to assess the sensitivity of the estimates to violations in the assumptions.
Many of the methodological developments in this paper are accomplished using ideas from mediation analysis. Mediation analysis is a set of tools and techniques for assessing the extent to which an exposure affects an outcome through particular pathways. For example, one might assess the extent to which the effect of an exposure on an outcome is mediated by a particular intermediate variable and the extent to which it is “direct” or through other pathways. Within the context of a vaccine trial, we take the vaccine status of one person as the exposure variable, the infection status of that person as the intermediate variable, and the infection status of a second person in the same household as the outcome variable. We consider effect measures and assumptions to interpret estimates causally within this context. We illustrate the methodology by analyzing data that might arise from a hypothetical vaccine trial (cf. Table 1) such as the pneumococcal vaccine trial among one-year-olds considered above. In the discussion we further consider implications of the methodology for infectious disease epidemiology.
Table 1.
Numbers infected, (Yi1, Yi2), from a hypothetical randomized trial of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine with 2000 households, where person 1 (one-year-old) was randomized to 1:1 to vaccine or control, and person 2 (the mother) was not vaccinated (vaccination status (Ai1, Ai2)) and half the households have either low or high socioeconomic status (SES)
| Yi1 = 0, Yi2 = 0 (n=1200) | Yi1 = 1, Yi2= 0 (n=416) | Yi1 = 1, Yi2= 1 (n=384) | Total (n=2000) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low SES: Ai1 = 0, Ai2 = 0 | 200 | 120 | 180 | 500 |
| Ai1 = 1, Ai2 = 0 | 350 | 96 | 54 | 500 |
| High SES: Ai1 = 0, Ai2 = 0 | 250 | 125 | 125 | 500 |
| Ai1 = 1, Ai2 = 0 | 400 | 75 | 25 | 500 |
Concepts and Definitions
To begin, we consider a setting similar to previous literature7,8 in which there are N households indexed by i = 1, …, N such that each household consists of two persons indexed by j = 1, 2. We let Aij denote the vaccine status for individual j in household i, where Aij = 1 denotes vaccinated and Aij = 0 denotes not vaccinated. We let Yij denote the infection status of individual j in household i after some fixed follow-up period, with Yij = 1 denoting infection and Yij = 0 denoting no infection.
The counterfactual framework defines causal effects in terms of contrasts of hypothetical scenarios or interventions, some of which may be contrary to fact. For example, Yij(ai1, ai2) denotes the potential infection outcome for person j in household i if the two persons in that household had, possibly contrary to fact, vaccination status of (ai1, ai2). Thus, Yi2(1, 0) denotes the potential outcome of person 2 if person 1 receives vaccine and person 2 does not; and Yi1(0, 0) denotes the potential infection outcome of person 1 if neither person 1 nor person 2 received the vaccine. For a particular person, say person 1, we have four potential outcomes in this setting: Yi1(0, 0), Yi1(0, 1), Yi1(1, 0), Yi1(1, 1). We could then consider various contrasts of these potential outcomes as causal effects. The potential outcomes are related to the observed data by a consistency assumption that, when the actual vaccine status (Ai1, Ai2) = (ai1, ai2), the actual observed outcomes Yij = Yij(ai1, ai2). Thus, for a particular household and particular person we actually observe only one of these four potential outcomes: the one corresponding to the vaccine status that actually occurred. We thus will not be able to estimate the causal effects for a particular person and a particular household. However, if vaccine is randomly assigned, we can hope to estimate a population average effect. In this paper, we define our average causal effects using this “potential outcomes” or counterfactual notation, as it allows for precise definitions for contagion and infectiousness effects.
Under the notation above, the potential outcome for individual 1, Yi1(ai1, ai2) depends on the vaccine status of both person 1 and person 2, and likewise the potential outcome for individual 2, Yi2(ai1, ai2) depends on the vaccine status of both persons. Thus, the exposure status of one person could affect the outcome of another. In the statistics literature, this is sometimes referred to as interference or spillover effect.3,4,16–19 Most literature in causal inference assumes there is no interference,16,20 so that one person’s outcome does not depend on the exposure of others. In the current context this would imply that Yi1(ai1, ai2) = Yi1(ai1) and Yi2(ai1, ai2) = Yi2(ai2) so that each person’s outcome depends only on his or her own exposure status. This assumption of no interference is implausible in the infectious disease context2, and so we do not make it here. We do, however, assume the exposure status of persons in one household in the study does not affect the outcomes of those in other study households, sometimes called an assumption of partial interference.3,17 This might be plausible if the various households are sufficiently geographically separated or do not interact with one another. In the case of a vaccine trial, where a few households are randomly sampled from a large city and the cluster is treated as the household, this assumption is perhaps not unreasonable - but it is unlikely to hold exactly. Importantly, this assumption pertains to household units in the study, not to all households that might have been in the study.
Throughout this paper we assume a simple randomized experiment in which one of the two persons is randomized to receive a vaccine or control and the second person is always unvaccinated. This could correspond to the hypothetical pneumococcal vaccine trial described above where we are interested in the effect on the mother of vaccinating the one-year-old. In the Discussion we consider relaxing these assumptions. We will let j = 1 denote the individual who may or may not be vaccinated and j = 2 the individual who is always unvaccinated. The methodology below and the definitions used will still be applicable even if some persons in the study are immune to infection.
Using the counterfactual notation, the average indirect effect is
i.e. the difference in infection status for person 2 if person 1 is vaccinated versus unvaccinated.8
If vaccine status is randomized, this can be estimated by7,8:
Halloran and Hudgens8 also refer to this as the “ITT (intention to treat) indirect effect.”
To proceed with decomposing this indirect effect into the two effects we need to consider counterfactuals of a different form. From this point onwards, we assume that only person 1, not person 2, can be infected from outside the household; person 2 can be infected only by person 1. Thus if Yi1(ai1, ai2) = 0 then Yi2(ai1, ai2) = 0. This could again correspond to a vaccine trial for pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for one-year-olds at the day-care center.
Suppose that in addition to potentially intervening to give person 1 the vaccine we could also, at least hypothetically, intervene to infect or not infect person 1. Then Yi2(ai1, ai2, yi1) would denote the infection status of person 2 if we would set the vaccine status of person 1 and person 2 to ai1 and ai2 and the infection status of person 1 to yi1. This in some sense formalizes, using counterfactual notation, ideas that were proposed by Halloran and Struchiner.2
The assumption that individual 2 is always unvaccinated allows a simplified notation. Counterfactuals Yi1(ai1, ai2) and Yi2(ai1, ai2) can be written as Yi1(ai1) := Yi1(ai1, 0) and Yi2(ai1) := Yi2(ai1, 0). We are still assuming interference/spillover in that the vaccine of person 1 affects the outcome of person 2. This simple setting in which person 2 always remains unvaccinated also allows us to rewrite the counterfactual Yi2(ai1, ai2, yi1) as Yi2(ai1, yi1) := Yi2(ai1, 0, yi1). We thus consider counterfactuals of the form Yi1(ai1), Yi2(ai1) and Yi2(ai1, yi1). The direct effect of person 1’s vaccine on person 1’s outcome is E[Yi1(1) − Yi1(0)]; the indirect effect of person 1’s vaccine on person 2’s outcome is simply E[Yi2(1) − Yi2(0)]. In the next section we will use these counterfactuals to define contagion and unconditional infectiousness effects.
Contagion and Infectiousness Effects
Consider now the counterfactual contrast
The term Yi2(0, Yi1(1)) considers what the potential infection outcome of person 2 is if person 1 is left unvaccinated but we set the infection status of person 1 to the level it would have been if person 1 was vaccinated. The contrast compares this counterfactual to Yi2(0, Yi1(0)), the potential infection outcome of person 2 if person 1 is not vaccinated, but we set the infection status of person 1 to the level it would be if person 1 was unvaccinated. For this contrast to be non-zero, Yi1(1) and Yi1(0) have to differ, i.e. vaccination of person 1 would have to affect the infection status of person 1, and that change in infection for person 1 would have to change the infection status for person 2, even if person 1 had been left unvaccinated. Essentially, the contrast is non-zero if the vaccine prevents infection in person 1, and that in turn prevents person 2 from being infected. We refer to this counterfactual contrast as a contagion effect.9
Consider now the contrast
This compares the potential infection outcome of person 2 if person 1 had been vaccinated versus unvaccinated and person 1 had the infection status that would occur if vaccinated. This contrast will be non-zero only if person 1 is infected when vaccinated (becasuse person 1’s vaccination status will not affect person 2’s outcome unless person 1 is infected). If the contrast is non-zero, this will be because even when person 1 is vaccinated and infected, the vaccine itself affects whether person 2 is infected by person 1. This is a novel measure. It is in some ways analogous to what in infectious disease epidemiology is called an infectiousness effect.6,21 However, this new measure differs in essential ways from the ordinary or “conditional infectiousness effect” in that it does not condition on person 1 actually being infected. The standard (conditional) infectiousness effect would, in contrast, compare outcomes for person 2 when person 1 is, versus is not, vaccinated but conditional on person 1 actually being infected. Counterfactual formalizations of the standard infectiousness effect have been proposed previously.7,8 We further discuss the relation of the conditional and unconditional infectiousness effects in the context of the hypothetical example and in the discussion section. Until then, however, our discussion will focus on this new “unconditional infectiousness effect” and we will thus omit the word “conditional” before “infectiousness effect” unless otherwise needed for clarity.
These counterfactual definitions of the contagion and infectiousness effects have the desirable feature that we can decompose an indirect effect into a contagion and an infectiousness effect by taking the indirect effect and adding and subtracting the term E[Yi2(0, Yi1(1)]]:
where the first term in the sum is the infectiousness effect and the second term in the sum is the contagion effect. This decomposition is analogous to what in the mediation analysis literature is sometimes referred to as “natural direct and indirect effects.”12,13 We exploit this analogy in our discussion of identification, estimation, and sensitivity analysis. The term “indirect effect” is used differently in mediation analysis than in causal inference with interference. In mediation analysis, “indirect effect” describes the effect of an exposure on an outcome for one person that operates through some intermediate or mediator in that same person, also called a mediated effect. In causal inference in the presence of interference, the indirect effect (also called a “spillover effect” in the social sciences) of, say, vaccinating some persons in a population, is a contrast of potential outcomes comparing the outcomes in those other persons who did not receive the vaccine to what their outcomes would have been if the vaccinated persons were not vaccinated. Further discussion is given in the Appendix and a glossary presented in Table 2 is to help guide the reader through the various terms used in the paper.
Table 2.
Glossary of main terms used in this paper. (Note that the relation of the terms used in this paper to what is standard in the mediation analysis is detailed in the “Note on Terminology” in the Appendix and also in the main text.)
| Indirect Effect /Spillover Effect: The effect the vaccine status of other people on a particular individual’s outcome |
| Contagion Effect: The effect of one person’s vaccine on another’s outcome by preventing the first from being infected; analytically somewhat analogous to the natural indirect effect of mediation analysis. |
| (Conditional) Infectiousness Effect: The effect of a vaccine on rendering the infection of an infected person less infectious |
| (Unconditional) Infectiousness Effect: An infectiousness effect that averages over also those households for whom person 1 is uninfected; analytically somewhat analogous to the natural direct effect of mediation analysis. |
| Direct Effect: The effect of a person’s vaccination status on his or her outcome |
| Interference: The phenomenon whereby the exposure (vaccination) of one person can affect the outcome of another. |
Thus far we have been considering measures of effect on a risk-difference scale. However, risk-ratio, odds-ratio, or vaccine-efficacy measures are more commonly employed in the vaccine literature. The effects and their decomposition described above have analogs for ratio and vaccine-efficacy measures. For example, the indirect effect on the risk ratio and odds-ratio scale could be defined as or . The decomposition for the risk ratio is
Here the first term in the product is the infectiousness effect on the risk-ratio scale and the second term is the contagion effect on the risk-ratio scale; the indirect effect is the product of the contagion and infectiousness effects on the risk-ratio scale, rather than their sum. A similar decomposition holds for odds-ratio measures.
Similar definitions and a somewhat analogous decomposition holds with a vaccine efficacy measure. As in Halloran and Hudgens,8 the vaccine efficacy measure for the indirect effect would be defined as:
We might likewise define vaccine efficacy for the contagion effect and infectiousness effect as:
Some algebra gives:
and we thus have:
In words, the vaccine efficacy measure for the indirect effect is the sum of the vaccine efficacy for the contagion effect and that of the infectiousness effect, where the vaccine efficacy of the infectiousness effect is adjusted by the factor to account for the fact that when the infectiousness effect operates, the contagion effect has essentially already occurred (the infectiousness effect makes the infection less infectious but this infectiousness effect will not operate if the vaccine in fact prevents person 1 from being infected).
Each of these effect measures could be defined conditional on covariates Ci. For example, the contagion and infectiousness effects on the risk ratio scale conditional on covariates Ci = c would be and .
Identification of Contagion and Infectiousness Effects
We have defined the contagion and unconditional infectiousness effects in terms of counterfactuals not immediately estimable from the data. Although these effects may be of substantive interest, we cannot estimate them without further assumptions. Suppose that data are available on some set of baseline covariates Ci that may be attributes of person 1 or of person 2 or of their household. Conditional on the set of covariates Ci we make the following assumptions:
The effect of Ai1 on Yi2 is unconfounded conditional on Ci
The effect of Yi1 on Yi2 is unconfounded conditional on (Ci, Ai1)
The effect of Ai1 on Yi1 is unconfounded conditional on Ci
Given that (ii) holds, there is no confounder of the relationship between Yi1 and Yi2 that is itself affected by Ai1
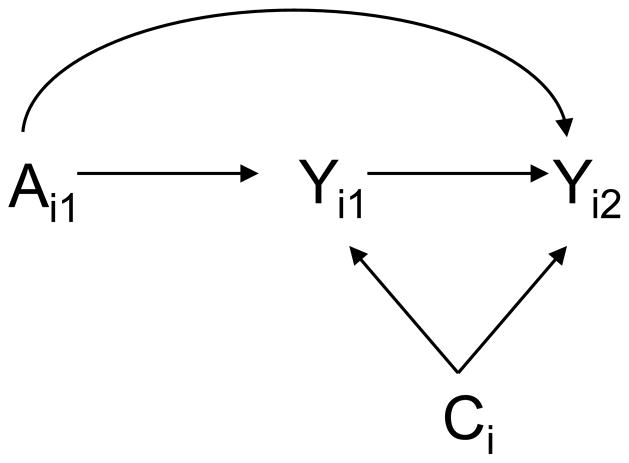
Under these four assumptions, the contagion and infectiousness effects are identified from the data. In the appendix we give formal counterfactual statements of these assumptions (equivalent to (i)–(iv) above on causal diagrams interpreted as in Pearl13), along with proof of identifiability and empirical formulas for identification. The assumptions can also be usefully illustrated, as below, using the diagram in the Figure, which assumes the vaccine status of person 1 is randomized.
Figure.
Vaccine trial in which person 1 is randomized to vaccine and person 2 does not receive the vaccine. Ai1 denotes the vaccine status of person 1; Yi1 denotes the infection status of person 1; Yi2 denotes the infection status of person 2; Ci denotes individual and household covariates for household i.
We now describe the four assumptions in a bit more detail. If, as assumed, vaccine status of person 1 is randomized, then assumptions (i) and (iii) will hold by randomization. In an observational setting, assumptions (i) and (iii) would hold only if a sufficiently rich set of covariates Ci were available such that vaccination was effectively randomized within strata of covariates Ci.
Assumption (ii) effectively requires that within the set of available covariates Ci we have all variables that are common causes of person 1’s infection status and person 2’s infection status (see the Figure). Such common causes might include, for example, environmental factors related to the sanitary, spatial and nutritional characteristics of the household. Assumption (ii) is a strong assumption. It can perhaps be made more plausible by attempting to control for such variables, but in general it will not be possible to verify assumption (ii). Assumption (iv) by contrast is arguably somewhat weaker: it requires that of all the common causes of person 1’s and person 2’s infection status, none is affected by the vaccine itself, i.e., there is no arrow from Ai1 to Ci in the Figure. Because most of these common causes are likely to be characteristics of the household environment, it seems reasonably plausible that such characteristics would not be changed by the vaccine.
The key to identifying the contagion and infectiousness effects thus arguably lies with trying to ensure the validity of assumption (ii): trying to adjust for covariates that may be common causes of person 1’s and person 2’s infection status.
Statistical Models to Estimate Contagion and Infectiousness Effects
Now we consider two logistic regression models to estimate these effects when they are in fact identified. Suppose the following two logistic regression models are fit to the observed data, (i) for the probability of infection for person 1 conditional on person 1’s vaccine status a1 and the covariates c and (ii) for the probability of infection for person 2, conditional on person 1’s vaccine status a1, person 1’s infection outcome and the covariates c:
The model for person 2’s infection status allows for potential statistical interaction between the effects of the vaccine status and infection status of person 1. Such interaction is likely because the vaccine status of person 1 is unlikely to have an effect on whether person 2 is infected unless person 1 is in fact infected.
The following results suppose that the infection outcome for person 2 is rare enough for the odds ratios to approximate risk ratios and the logistic link to approximate a log link. If the infection outcome for person 2 is not rare, then the results given below will hold if the logistic regression model for Y2 is replaced by a log-linear model while the model for Y1 is kept as a logistic model. No rare-outcome assumption or log-linear model is needed for Y1.
If covariates Ci satisfy assumptions (i)–(iv), and the models above are correctly specified, then, as shown in the Appendix, the contagion effect on the risk-ratio scale conditional on the covariates Ci = c is given by:
| (1) |
and the infectiousness effect on the risk-ratio scale conditional on the covariates is given by:
| (2) |
These expressions can be obtained directly from the estimates of the logistic regression parameters. In the Appendix we discuss adapting SAS and SPSS macros for mediation analysis15 to compute these contagion and infectiousness effects together with their standard errors and confidence intervals.
Sensitivity Analysis for Contagion and Infectiousness Effects
Identification and estimation of the contagion and infectiousness effects depend critically on assumptions (i)–(iv). Unfortunately, these are fairly strong assumptions, especially assumption (ii). In this section we give a relatively straightforward sensitivity analysis technique that can be employed to assess how vulnerable one’s estimates and conclusions are to violations of assumption (ii). The technique assumes there is an unmeasured binary confounding variable U that is a common cause of the infection status of person 1 and person 2, and that assumptions (i)–(iv) would hold conditional on (Ci, U ) but not on the measured covariates Ci alone. The investigator can then specify sensitivity parameters corresponding to (i) the effect of the unmeasured confounding U on the infection status of person 2 conditional on the vaccine status of person 1, the infection status of person 1, and the observed covariates Ci and (ii) the prevalence of U within each stratum defined by the vaccine status of person 1 and the infection status of person 1, conditional on the observed covariates Ci. The technique then uses the estimates obtained by controlling only for observed covariates Ci, along with these sensitivity parameters, to calculate the corrected estimates that would have been obtained had it been possible to control for the unmeasured confounding variable U as well. The sensitivity-analysis parameters can be varied across a range of plausible values to assess how sensitive the conclusions and estimates are to a potential unmeasured common cause of the infection status of person 1 and person 2.
The technique assumes that the effect of U on the infection status of person 2 is constant across the vaccine status of person 1 and the infection status of person 1, and is given by
The sensitivity analysis parameter γ thus captures the effect of U on the infection status of person 2. The investigator also specifies the prevalence of U in each stratum defined by the vaccine status of person 1 and the infection status of person 1 conditional on the observed covariates Ci:
From these sensitivity analysis parameters the following can be calculated
It follows from derivations in VanderWeele22 that if we let
and replace (θ1, θ2, θ3) with ( ) in formulas (1) and (2), this gives corrected contagion and infectiousness effect estimates corresponding to what would have been obtained had we been able to adjust for U and Ci rather than only the observed covariates Ci alone. In general we will not know the true values of the sensitivity-analysis parameters; however, varying the parameters γ and π00, π10, π01, π11 will give some sense as to how sensitive the results are to potential unmeasured common causes of the infection status of person 1 and person 2. The sensitivity technique is of course also limited by the assumptions made, which are (i) a single unmeasured binary confounder and (ii) the effect of U on the infection status of person 2 is constant across vaccine status of person 1 and infection status of person 1.
Illustration
Consider data from a hypothetical vaccine trial in Table 1 in which one-year-olds (j = 1) are randomized to pneumococcal conjugate vaccine with follow-up for both the one-year-olds and their mothers (j = 2). In this example, pneumococcus is assumed to be highly prevalent in children in day care, so that the mother is much more likely to acquire the pneumococcus from the child than through other transmission routes. It is assumed that during the study period the mother is infected only from the one-year-old. Suppose we fit a logistic model for the probability of infection for person 1 conditional on person 1’s vaccine status a1 and the covariates c and a log-linear model for the probability of infection for person 2, conditional on person 1’s vaccine status a1, person 1’s infection outcome and the covariates c. Using expressions (1) and (2) above for the contagion and infectiousness effects, and setting the covariate to its mean value, we obtain, on the risk-ratio scale, under assumptions (i)–(iv), an overall estimate of the indirect effect of 0.63 (95% CI: 0.56, 0.70), an estimate of the contagion effect of 0.80 (95% CI: 0.74, 0.85) and an estimate of the infectiousness effect of 0.79 (95% CI: 0.71, 0.87). The indirect effect on the risk-ratio scale decomposes into the product of the contagion and infectiousness effects: 0.63 = 0.80 × 0.79. On the vaccine-efficacy scale, we would have an overall indirect effect of 1 − 0.63 = 37%, a contagion effect of 1−0.80 = 20%, an infectiousness effect of 1−0.79 = 21%, and vaccine-efficacy component due to the infectiousness effect of (0.80)(21%) = 17% (essentially taking into account the fact that the infectiousness effect will operate only if the contagion effect has not). We can then decompose the indirect effect on the vaccine efficacy scale into the sum of the contagion effect and the component due to infectiousness: 37% = 20% + 17%. In this hypothetical example, roughly equal portions of the indirect effect of person 1’s vaccine on person 2’s infection status appear to be due to the contagion effect versus the infectiousness effect.
Discussion
In this paper we have considered how an indirect effect of vaccination of one person on the outcome of another can be decomposed into two components: one corresponding to the vaccine preventing the infection in person 1, which then protects person 2 (the contagion effect), and another corresponding to the fact that even if person 1 is infected the vaccine may render the infection less infectious (the unconditional infectiousness effect). A conditional infectiousness effect has been considered in other work in the vaccine literature.6,21,23 Within causal inference, Halloran and Hudgens8 and VanderWeele and Tchetgen Tchetgen7 define causal estimands for the conditional infectiousness effect by examining the effect of the vaccine of person 1 on the infection status of person 2 in the principal-stratum24 in which person 1 would be infected irrespective of vaccine status. Issues of inference for this conditional infectiousness effect are described elsewhere.7,8 This infectiousness effect based on principal strata is different than that considered here: essentially the “principal stratum” infectiousness effect is a conditional effect (it conditions on the subgroup for which person 1 would be infected irrespective of vaccine status), and the traditional infectiousness effect conditions on person 1 being infected regardless of principal stratum. However, the infectiousness effect considered here is an unconditional infectiousness effect - it averages over also those clusters for whom person 1 is uninfected (for which any potential infectiousness effect of the vaccine would not have the opportunity to operate).
These issues are important in the interpretation of these effects; both types of infectiousness effects (conditional and unconditional) could potentially be reported. Using the methodology and assumptions of VanderWeele and Tchetgen Tchetgen,7 an upper bound on the conditional infectiousness effect on the risk-ratio scale from the data in Table 2 would be 0.57 (a lower risk ratio implies a stronger protective effect). This is lower than the unconditional infectiousness effect risk ratio of 0.79 reported above. Again, this is in part because the conditional infectiousness effect already conditions on person 1 being infected, whereas the unconditional infectiousness effect essentially includes in the denominator those households in which person 1 is not infected. The advantage of the infectiousness effect given in this paper (the unconditional version) is that it can be used to decompose the overall effect into the contagion and infectiousness components.
Our work here could be extended in a number of directions and is also subject to various limitations. First, we have considered the setting in which there are two persons per cluster and only one person is randomized to vaccination. However, in settings in which both are randomized to vaccination, the analysis could be pursued separately for households in which person 2 is or is not vaccinated. Another simple extension to the work here might involve settings in which only one person in each household is randomized to vaccine but outcome data are collected on numerous additional persons per household. In such cases the outcome Yi2 in this paper could be replaced with the proportion in the household who are infected (other than the person randomized); the logistic regression would then have to be replaced with a linear or log-linear regression, but similar methods from the mediation-analysis literature could potentially be adapted and applied.15 If the numbers in each household vary across households, this number could also be controlled for in the analysis.
One limitation of the approach described here is that the analysis assumes that the regression models have been correctly specified. In settings with a large number of covariates this may be a difficult assumption to make plausible. Future research could consider adapting robust statistical methods from the mediation analysis literature25 to help deal with this issue of model specification. Another limitation is that we have assumed that only person 1, not person 2, can be infected from outside of the household. While this may be plausible in some situations, in many other settings the assumption would likely not hold. Future research could consider extending the current methodology to settings in which both persons can be infected outside the household by using data on the timing of infections, as in Halloran and Hudgens.8
In some individually randomized, controlled vaccine trials, it may be straightforward to enroll households of trial participants for follow-up. A similar suggestion, called the augmented study design,26,27 was made to estimate vaccine efficacy for infectiousness in HIV vaccine trials. Such studies would be relatively cost-effective and allow for estimating indirect effects and infectiousness effects. In some settings they would allow one to carry out the decomposition described in this paper. Estimates of indirect effects and vaccine effects on infectiousness can influence global vaccine policy decisions. Moreover, understanding what proportion of an indirect effect is due to decreasing infectiousness can give insight into the mechanism by which the vaccine protects others, and could perhaps also allow for further vaccine refinement and development. It is thus important to consider collecting outcome data on other household members in vaccine trials. Such studies would allow estimation of a number of the effects described in this paper.
Acknowledgments
Financial Support : National Institutes of Health grants ES017876, HD 060696, AI085073, and AI032042
Appendix
Formalizations and Derivations
In this appendix we give a formal statement of the identification assumption (i)–(iv) in the text, provide non-parametric empirical expressions for the contagion and unconditional infectiousness effects when they are identified, and derive closed form expressions for these when logistic or log-linear regression models are used to model the probabilities of infection and provide a sensitivity analysis technique when the identification assumptions are violated. Most of this is accomplished by noting an analytic relation between the contagion and infectiousness effects defined in the text and what are sometimes called “natural direct and indirect effects” in mediation analysis12–15,22. In mediation analysis, interest lies in assessing the extent to which the effect of an exposure A on outcome Y is mediated by some intermediate M. If we take the exposure as person 1’s vaccine status, the mediator as person 1’s infection status, and the outcome as person 2’s infection status, then the contagion and unconditional infectiousness effects defined in this paper correspond to the “total” natural direct effect and the “pure” natural indirect effect in mediation.12,14,28
We use X ⫫ Y |Z to denote that X is conditionally independent of Y given Z. In counterfactual notation, identification assumptions (i)–(iv) in the text can be formally stated as:
Yi2(ai1, yi1) ⫫ Ai1|Ci
Yi2(ai1, yi1) ⫫ Yi1|(Ci, Ai1)
Yi1(ai1) ⫫ Ai1|Ci
where is simply a different value of Ai1 than ai1. Drawing the analogy mediation analysis, the interpretation of (i)–(iv) above is essentially (i)–(iv) in the text13,14.
Assumptions (i) and (iii) will hold if Ai1, the vaccine status of person 1, is randomized. Assumptions (ii) and (iv) are substantial and would have be to determined on subject matter grounds. Under assumptions (i)–(iv), the contagion and infectiousness effects are identified from the vaccine trial data. To see this, note that:
where the first equality holds by iterated expectations, the second by assumption (iv), the third by assumptions (i) and (iii), the fourth by assumption (ii) and the final equality holds by a consistency assumption. The final expression is given in terms of the observed data. If we first let ai1 = 0, and then ai1 = 0, , the contagion effect conditional on Ci is given by E[Yi2(0, Yi1(1)) − Yi2(0, Yi1(0))|c] =
If we first let ai1 = 1, and then ai1 = 0, the infectiousness effect is given by E[Yi2(1, Yi1(1)) − Yi2(0, Yi1(1)|c] =
The contagion effect then contrasts the observed expectation E[Yi2|Ai1 = 0, y1, c] as standardized by the distribution of the infection status of person 1 among the households with person 1 vaccinated versus unvaccinated. The infectiousness effect is the observed expectation contrast E[Yi2|Ai1 = 1, y1, c] − E[Yi2|Ai1 = 0, y1, c] standardized by the distribution of the infection status of person 1 among the households with person 1 vaccinated.
Likewise on a risk ratio scale the contagion effect is given by:
and the infectiousness effect is given by:
Suppose the following two models were fit to the data:
and that the infection outcome Y2 for person 2 is sufficiently rare so that odds ratios approximated risk ratios (and the logit link approximated a log-link). Using these models for the conditional predicted probabilities for Y1 and Y2 gives, for the contagion effect:
and for the infectiousness effect:
If the infection outcome for person 2 is not rare then the results above will hold if the logistic regression model for Y2 is replaced by a log-linear model but the model for Y1 is kept as a logistic model. No rare outcome assumption or log-linear model is needed for Y1. Standard errors and confidence intervals for these expressions can be obtained via the delta method as in Valeri and VanderWeele.15 In fact, the SAS and SPSS macros in Valeri and VanderWeele15 can be directly adapted to estimate these effects and their standard errors and confidence intervals by: specifying the exposure as the vaccine status of person 1, the mediator as the infection status of person 1, the outcome as the infection status of person 2, the outcome model as logistic (or log-linear if the infection outcome for person 2 is not rare), the mediator model as logistic and requesting the option that the full output be given. The estimates reported for the “pure natural indirect effect” can then be taken as a measure of the contagion effect on the conditional risk ratio scale and that reported for the “total natural direct effect” can be taken as the measure of the unconditional infectiousness effect on the conditional risk ratio scale. The macro provides standard errors and confidence intervals for these estimates. The formal analytic relation between natural direct and indirect effects and the contagion and unconditional infectiousness effects also allows us to adapt sensitivity analysis techniques for natural direct and indirect effects22 to apply to contagion and infectiousness effects as in the text.
A few further technical comments merit attention. VanderWeele and Tchetgen Tchetgen7 provided an alternative definition of the infectiousness effect on a ratio scale as E[Yi2(1, Yi1(1))|Yi1(1) = Yi1(0) = 1]/E[Yi2(0, Yi1(0))|Yi1(1) = Yi1(0) = 1] i.e. the effect of the vaccine of person 1 on the infection status of person 2 in the principal stratum24 in which person 1 would be infected irrespective of vaccine status. This infectiousness effect is “conditional” in the sense that it is conditional on the subgroup for which person 1 would be infected irrespective of vaccine status, whereas the infectiousness effect in the text is an unconditional infectiousness effect - it averages over also those households for whom person 1 is uninfected. Yet another definition of an infectiousness effect could be given as E[Yi2(1, 1)|c]/E[Yi2(0, 1)|c] i.e. the effect of the vaccine of person 1 on the outcome of person 2, intervening to set person 1’s infection status to positive. This effect is analogous to the “controlled direct effect”12,13 in the mediation literature. Under assumptions (i) and (ii) above it is identified by E[Yi2|Ai1 = 1, Yi1 = 1, Ci = c]/E[Yi2|Ai1 = 0, Yi1 = 1, Ci = c]. It is a marginal effect insofar as it is for the entire population for which Ci = c; however it is “conditional on infection” in the sense that it considers a hypothetical contrast in which, in all house-holds, person 1 is infected. Under the logistic regression models given above (assuming rare outcome or using a log-linear model rather than logistic model for Yi2), this would be eθ1+θ3. It should also be noted that under the exclusion restriction that the vaccine of person 1 does not affect the infection status of person 2 unless person 1 is infected we would have E[Yi2(1, 0)|c]/E[Yi2(0, 0)|c] = 1. Under assumptions (i) and (ii) and the two regression models we then have 1 = E[Yi2(1, 0)|c]/E[Yi2(0, 0)|c] = E[Yi2|Ai1 = 1, Yi1 = 0, Ci = c]/E[Yi2|Ai1 = 0, Yi1 = 0, Ci = c] = eθ1 i.e. θ1 = 0. This implication of the exclusion restriction can be tested empirically.
A Note on Terminology
In this paper we have exploited relations between what we have defined as the “contagion and unconditional infectiousness effects” on the one hand and “natural direct and indirect effects” on the other. Because of the terminological overlap, the language employed can be somewhat confusing. In mediation analysis13, “indirect effect” is used to describe situations in which the effect of an exposure on an outcome for one person operates through some intermediate or mediator for that individual. The “contagion effect” and “infectiousness effect” in this paper are, analytically somewhat analogous to the “natural indirect effect” and “natural direct effect”, respectively, in mediation analysis. The “contagion effect” is essentially the effect of person 1’s vaccine on person 2’s infection outcome mediated by person 1’s infection outcome. The “ unconditional infectiousness effect” is essentially the effect of person 1’s vaccine on person 2’s infection outcome not mediated by person 1’s infection outcome.
In the infectious disease and vaccine literature, the “indirect effect of vaccination” has one more general usage and also a more technical meaning.1 In general, an “indirect effect of vaccination” is used to describe settings in which vaccination of one person affects the outcome of another individual. This is a specific case of the dependent happenings described by Sir Ronald Ross29 wherein the number of events depends on how many others are already affected. However, in the causal inference literature for vaccine effects, there are several effects of vaccination strategies due to the interference between individuals2, wherein the treatment assignment of one person affects the potential outcomes of other persons.16,19,20 In this literature, the indirect effect of vaccination is the effect of a vaccination strategy in a population in those individuals, or a subpopulation of those individuals, who were not vaccinated. The total effect of vaccination is the effect of a vaccination strategy in a population in those individuals, or a subpopulation of those individuals, who were vaccinated. There have been a number of more recent formal papers on these indirect and total effects in the presence of interference3,4,11. In other statistical and causal inference literature effects due to interference are sometimes called “spillover effects”.17
In this paper, we have decomposed the “indirect effect of a vaccination” in the literature on causal inference in the presence of interference into the “natural indirect effect” and “natural direct effect” of mediation analysis. Because these two literatures, causal inference in the presence of interference on the one hand and causal inference mediation analysis on the other hand - use the same terms for different concepts, and moreover because, as we have seen in this paper, these concepts are not entirely unrelated, it is important to clarify in each instance specifically the various terms being employed.
Contributor Information
Tyler J. VanderWeele, Departments of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Harvard School of Public Health
Eric J. Tchetgen Tchetgen, Departments of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Harvard School of Public Health
M. Elizabeth Halloran, Departments of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Harvard School of Public Health.
References
- 1.Halloran ME, Struchiner CJ. Study designs for dependent happenings. Epidemiology. 1991;2:331–338. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199109000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Halloran ME, Struchiner CJ. Causal inference for infectious diseases. Epidemiology. 1995;6:142–51. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199503000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hudgens MG, Halloran ME. Towards causal inference with interference. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 2008;103:832–842. doi: 10.1198/016214508000000292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tchetgen Tchetgen EJ, VanderWeele TJ. Estimation of causal effects in the presence of interference. Statistical Methods in Medical Research - Special Issue on Causal Inference. doi: 10.1177/0962280210386779. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Halloran ME. The minicommunity for assessing indirect effects of vaccination. Epidemiologic Methods. doi: 10.1515/2161-962X.1008. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Datta S, Halloran ME, Longini IM. Efficiency of estimating vaccine efficacy for susceptibility and infectiousness: randomization by individual versus household. Biometrics. 1999;55:792–798. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.1999.00792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.VanderWeele TJ, Tchetgen Tchetgen EJ. Bounding the infectiousness effect in vaccine trials. Epidemiology. 2011;22:686–693. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e31822708d5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Halloran ME, Hudgens MG. Causal inference for vaccine effects on infectiousness. International Journal of Biostatistics. 2012;8(2):Article 6. doi: 10.2202/1557-4679.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Christakis NA. Fowler, Social contagion theory: examining dynamic social networks and human behavior. Statistics in Medicine. doi: 10.1002/sim.5408. to appear. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Trollfors B, Taranger J, Lagergard T, Sundh V, Bryla DA, Schneerson R, Robbins JB. Immunization of children with pertussis toxoid decreases spread of pertussis within the family. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:196–199. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199803000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.VanderWeele TJ, Tchetgen Tchetgen EJ. Effect partitioning under interference for two-stage randomized vaccine trials. Statistics and Probability Letters. 2011;81:861–869. doi: 10.1016/j.spl.2011.02.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Robins JM, Greenland S. Identifiability and exchangeability for direct and indirect effects. Epidemiology. 1992;3:143–155. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199203000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pearl J. Direct and indirect effects. Proceedings of the Seventeenth Conference on Uncertainty and Artificial Intelligence; San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann; 2001. pp. 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- 14.VanderWeele TJ, Vansteelandt S. Odds ratios for mediation analysis with a dichotomous outcome. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2010;172:1339–1348. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwq332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Valeri L, VanderWeele TJ. Mediation analysis allowing for exposure-mediator interactions and causal interpretation: theoretical assumptions and implementation with SAS and SPSS macros. Psychological Methods. doi: 10.1037/a0031034. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rubin DB. Comment on: Neyman (1923) and Causal Inference in Experiments and Observational Studies. Statistical Science. 1990;5:472–480. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sobel ME. What do randomized studies of housing mobility demonstrate? Causal Inference in the face of interference. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 2006;101:1398–1407. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hong G, Raudenbush SW. Evaluating kindergarten retention policy: A case study of causal inference for multilevel observational data. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 2006;101:901–910. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rosenbaum PR. Interference between units in randomized experiments. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 2007;102:191–200. doi: 10.1080/01621459.2012.655954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cox DR. The Planning of Experiments. New York: Wiley; 1958. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Préziosi M-P, Halloran ME. Effects of pertussis vaccination on transmission: vaccine efficacy for infectiousness. Vaccine. 2003;21:1853–1861. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(03)00007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.VanderWeele TJ. Bias formulas for sensitivity analysis for direct and indirect effects. Epidemiology. 2010;21:540–551. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181df191c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Becker NG, Britton T, O’Neill PD. Estimating vaccine effects from studies of outbreaks in household pairs. Statistics in Medicine. 2006;25:1079–1093. doi: 10.1002/sim.2236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Frangakis CE, Rubin DB. Principal stratification in causal inference. Biometrics. 2002;58:21–29. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2002.00021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tchetgen Tchetgen EJ, Spitser I. Semiparametric theory for causal mediation analysis: efficiency bounds, multiple robustness, and sensitivity analysis. Ann Statist. doi: 10.1214/12-AOS990. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Longini IM, Datta S, Halloran ME. Measuring vaccine efficacy for both susceptibility to infection and reduction in infectiousness for prophylactic HIV-1 vaccines. J Acq Immun Def Synd. 1996;13:440–447. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199612150-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Datta S, Halloran ME, Longini IM. Augmented HIV vaccine trial designs for estimating reduction in infectiousness and protective efficacy. Stat Med. 1998;17:185–200. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19980130)17:2<185::aid-sim732>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Robins JM. Semantics of causal DAG models and the identification of direct and indirect effects. In: Green P, Hjort NL, Richardson S, editors. Highly Structured Stochastic Systems. Oxford University Press; New York: 2003. pp. 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ross R. An application of the theory of probabilities to the study of a priori pathometry, Part 1. Proc R Soc Series A. 1916;92:204–230. [Google Scholar]