Abstract
In-cell NMR in the yeast P. pastoris was used to study the influence of metabolic changes on protein structure and dynamics at atomic resolution. Induction of Ubiquitin overexpression from the methanol induced AOX1 promoter results in the protein being localized in the cytosol and yields a well-resolved in-cell NMR spectrum. When P. pastoris is grown on a mixed carbon source containing both dextrose and methanol, Ubiquitin is found in small storage vesicles distributed in the cytosol and the resulting in-cell NMR spectrum is broadened. The sequestration of overexpressed proteins into storage vesicles, which are inaccessible to small molecules, was demonstrated for two unrelated proteins and two different strains of P. pastoris, suggesting its general nature.
Introduction
Elucidating the physico-chemical properties of proteins inside living cells is the ultimate goal of biochemists. The dynamics of living cells are complex and their reactions lie far from equilibrium; as a result, many in vivo processes are not adequately represented when the system is reconstituted in vitro 1. In-cell NMR is one technique that allows us to observe selected (target) proteins in the crowded environment of the cytosol and to follow the changes in protein structure and dynamics during different stages of cellular physiology2–4.
In-cell NMR spectroscopy in bacterial cells is a well-established methodology4 made possible by using powerful bacterial promoters that essentially shut down expression of endogenous proteins in favor of heterologous expression. By employing stable isotope labeling and NMR editing techniques, in-cell NMR results in signals from overexpressed proteins that are much stronger than background signals from endogenous proteins5,6. Protein over-expression does not work in higher eukaryotes because of the lack of strong promoters capable of producing adequate amounts of isotope labeled proteins for detecting by in-cell NMR. Yeast, which can be used as a model system for eukaryotic cells 7,8, do possess strong promoters, comparable to those found in bacterial cells9, that can be used for protein over-expression10.
Eukaryotic cells are much larger and more complex than bacterial cells. This complexity stems from the increased demand for specialization and stability in higher eukaryotes. Until now, in-cell NMR in eukaryotic cells has relied exclusively on exogenous sources for isotope labeled protein. For example, protein microinjection is used to introduce isotope labeled proteins into large Xenopus laevis oocytes11,12. More recently, phagocytosis of labeled proteins was used to deliver purified target protein into various human cells2,13,14. These techniques provide virtually background free NMR spectra of proteins inside different types of eukaryotic cells, but although powerful, they are not well suited for studying the influence of intracellular biochemical processes on protein structure since the target proteins do not undergo proper cellular processing.
Chemical reactions are impeded by the comparatively large volume of eukaryotic cells, which reduces the effective concentration of the reacting species. One natural solution to increase local concentrations is compartmentalization, which is not observed in prokaryotic cells1. For example, metabolic changes result in the sequestration of proteins to specialized compartments where metabolites are processed and substrates are channeled from one enzymatic activity to another15–18. Recent reports suggest that proteins that are not involved in active metabolic pathways are targeted to protein storage bodies, possibly facilitating catabolite repression on the protein level15,17,19. Proteins may be closely packed in these compartments or in an aggregated state. The protein structure will necessarily be affected by close packing. Indeed, reports of hormonal proteins in an amyloid state suggest that proteins acquire different conformations under storage. The stored proteins are released and folded into functional form when conditions require20–22.
It is important to understand the protein conformations that can exist inside the cell 3,23. For example, in drug design, drugs that target in vitro conformations may not interact with proteins confined to separate compartments or closely packed in protein storage bodies. Furthermore, proteins confined to cellular compartments may not be accessible to small effector molecules, thus thwarting cellular-based screening of otherwise effective drug candidates. In-cell NMR has the potential to reveal the hidden conformations that depend on various intracellular environments2,23 and thereby help design experiments that are more effective at identifying potential drug candidates.
We developed a protocol for isotopic labeling and protein overexpression in the budding yeast P. pastoris that allows us to obtain high resolution in-cell NMR spectra of yeast Ubiquitin. By changing the metabolic state of the cells we are able to alter the intracellular location of overexpressed protein from cytosol to vesicles. We characterized changes in protein structure due to vesicular localization using immunomicroscopy, cellular fractionation and in-cell NMR. The general nature of the observed phenomenon was demonstrated by overexpressing β-galactosidase, which was also packed into vesicles when the metabolic state was changed. The work suggests that in-cell NMR of proteins in yeast can be widely used for metabolic profiling experiments24,25.
Results
1. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ubiquitin is over-expressed in P. pastoris
We cloned S. cerevisiae and human ubiquitins into plasmid pPIC6. These constructs integrate into the AOX1 locus of the P. pastoris strain X-33 genome9 and places the heterologous gene under the control of the strong, methanol-induced AOX1 promoter (Figure 1A). To overexpress Ubiquitin, the integrant was grown in Buffered Minimal Dextrose (BMD). Dextrose is the preferred carbon source for yeast growth and is also a known suppressor of heterologous protein expression26,27. Protein overexpression was induced by switching the carbon source in the medium from dextrose to methanol by either adding methanol to BMD medium (BMDM) or washing the cells and re-suspending them in Buffered Minimal Methanol (BMM) medium. Protein overexpression proceeded for two days; additional methanol was added to the induced cultures after the first day of expression.
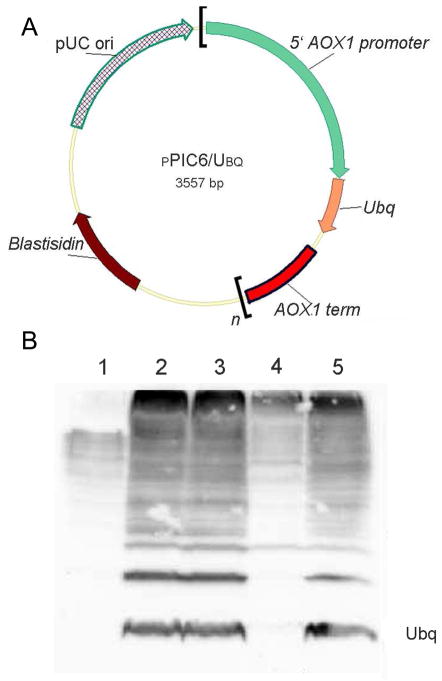
Figure 1.
In-cell NMR in yeast. A. pPic6-Ubq plasmid used to integrate ubiquitin into P. pichia strain X-33. n=1,2 is the number of ubiquitin multimers. B. Western blot showing Ubiquitin expression in BMM and BMDM. Lane 1- Uninduced; Lane 2- 24 h induction in BMM; Lane 3- 48 h induction in BMM; Lane 4- 24 h induction in BMDM; Lane 5- 48 h induction in BMDM.
S. cerevisiae Ubiquitin was strongly overexpressed in both BMM and BMDM media and was visible on Western blots (Figure 1B). Due to the large number of proteins in eukaryotic hosts, the Ubiquitin band could not be easily identified by using SDS-PAGE. We did not observe any improvement in protein overexpression by using multiple integrants of the construct. In spite of 96% sequence identity between S. cerevisiae and human Ubiquitin, human Ubiquitin was only weakly expressed and barely detectible on a Western blot. It is known that some heterologous sequences are not well-expressed in yeast28. Subsequently, all experiments were performed using S. cerevisiae Ubiquitin.
A long term stability study of the cells over-expressing Ubiquitin revealed that over a period of one month the expression became much lower than that from fresh integrants. We attributed this loss of expression to recombination events in which the heterologous gene is spliced out of the genome. To restore expression levels, the yeast containing heterologous S. cerevisiae ubiquitin was re-selected on blasticidin plates. Only the clones that produced maximum expression were chosen for further analysis.
2. Ubiquitin is well folded and localized in the P. pastoris cytosol
The yeast cytosol occupies a majority of the intracellular space and has a relatively low viscosity; Ubiquitin tumbling is not impaired by hydrodynamic drag or interactions with plasma cell membranes, thus allowing us to obtain high quality in-cell NMR spectra. The in-cell 1H{15N}-HSQC NMR spectrum of Ubiquitin is evident after 4 hours of NMR data acquisition. The in-cell NMR spectrum acquired 24 h post-induction shows only a few well-resolved peaks (Figure 2A). Control experiments indicated that the signals arise exclusively from intracellular protein (Supplementary Figure 1). The dispersion of the backbone amide protons from 6.5 ppm to 10 ppm indicates that Ubiquitin is well folded inside P. pastoris cells. Background signals from small 15N labeled metabolites dominate the spectra in the region from 8 ppm to 8.5 ppm and impede high-resolution analysis of Ubiquitin peaks. Most of the peaks are broadened or missing, suggesting that Ubiquitin interacts with large intracellular complexes. Indeed, eukaryotic host cells contain many proteins that contain ubiquitin binding domains. These proteins are often localized within large signal transduction complexes and can potentially provide binding sites for overexpressed Ubiquitin. The in-cell NMR spectrum of Ubiquitin acquired from X. laevis cells was similarly broadened 2,12.
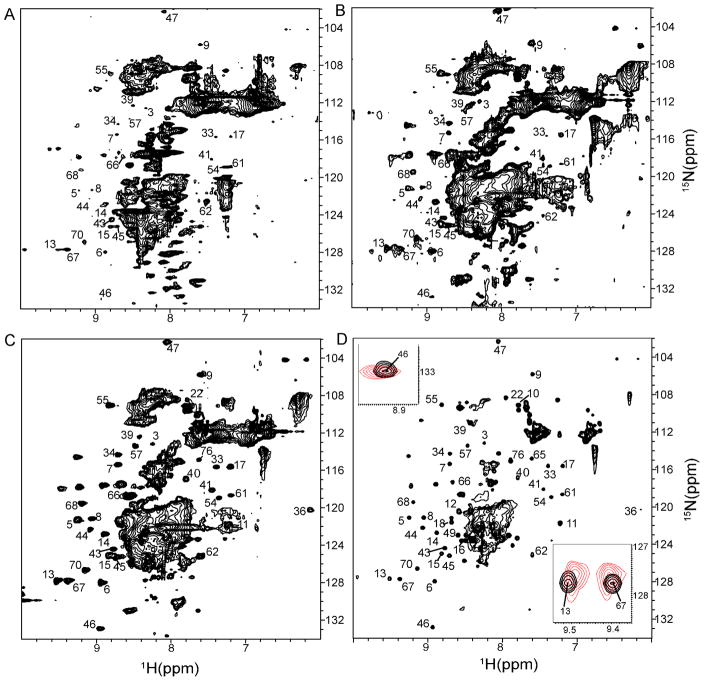
Figure 2.
In-cell 1H{15N}-HSQC NMR spectra of Ubiquitin overexpressed in P. pastoris. A. 24 h post-methanol induction without nitrogen starvation. B. 48 h post-methanol induction without nitrogen starvation. C. 48 h post-methanol induction with 6 h nitrogen starvation. D. Lysate of 48 h sample with nitrogen starvation. Inserts are overlaps of selected peaks from C (red) and D (black).
The in-cell NMR spectrum of Ubiquitin acquired 48 h post-induction (Figure 2B) contains most of the peaks expected for folded protein suggesting that a significant portion of Ubiquitin is free to tumble inside the yeast. By overexpressing Ubiquitin for two days most of the Ubiquitin binding sites were saturated, allowing free Ubiquitin to be observed. Nevertheless, residues, Leu8, Ile44, and Ala46, located in the hydrophobic patch involved in Ubiquitin-protein interactions, were substantially broadened. An overlay of in-cell and lysate NMR spectra shows that in-cell Ubiquitin amide protons exhibit small but characteristic chemical shift changes relative to those of the yeast lysate (Figure 2D, insets). The pH of the P. Pastoris cytosol is 7.229 which is slightly higher than that of the NMR buffer, 7.0. We assumed that the observed changes in chemical shifts are related to the difference between intra- and extracellular pH.
Because NMR peaks from small metabolites overlap Ubiquitin peaks and hamper its structural analysis, we attempted to reduce metabolite peak intensities. We reasoned that NMR peaks from 15N-labeled background metabolites might be reduced by briefly starving the cells of nitrogen so that small metabolites are incorporated into large protein or nucleic acid structures and disappear from the 15N edited NMR spectra. To achieve nitrogen starvation, the cells were washed after 24 h or 48 h of methanol induction and re-suspended into modified BMM medium, in which ammonium sulfate/chloride is replaced by sodium sulfate. After 6 h of nitrogen starvation, cells were prepared for in-cell NMR. The in-cell NMR spectrum of Ubiquitin in nitrogen starved cells reveals a dramatically improved NMR spectrum (Figure 2C). The background signal is diminished and Ubiquitin peaks are clearly seen in between 8.5 ppm and 8.0 ppm, a region previously dominated by small metabolite peaks. No changes in chemical shifts are observed between the cells with and without nitrogen starvation suggesting that this step does not significantly change the interior of the yeast.
Immunofluorescence was used to determine the intracellular localization of overexpressed Ubiquitin (Figure 3). The P. pastoris cell wall had to be completely removed to facilitate optimal antibody penetration during immunostaining. Due to its small size, Ubiquitin tends to wash out of the spheroplasts during and after staining. To eliminate this problem, Ubiquitin was immobilized inside the cells with formaldehyde before the cell wall was digested.
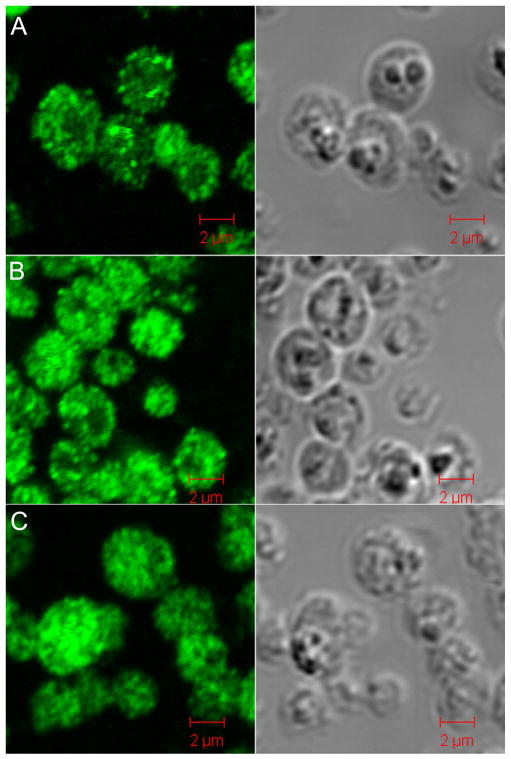
Figure 3.
Immunofluorescence and differential interference (DI) contrast microscopy of P. pastoris overexpressing Ubiquitin. A. 24 h post-methanol induction without nitrogen starvation. B. 48 h post-methanol induction without nitrogen starvation. C. 48 h post-mixed dextrose/methanol induction. Immunofluoresent staining reveals a distribution of Ubiquitin throughout the cytosol and in protein storage bodies. Vacuoles are evident as dark regions in DI contrast images.
The yeast cells used for in-cell NMR are in the active growth stage since 40% of the imaged cells exhibit new buds. Ubiquitin is localized in the yeast cytosol as well as in brightly stained intracellular vesicles (Figure 3, left), which were identified as previously described protein storage bodies15. Yeast vacuoles, which are large, dark and generally well resolved in differential interference contrast images (Figure 3, right), play a role in osmoregulation, homeostasis and degradative processes. Overexpressed Ubiquitin is excluded from vacuoles suggesting that it does not function in protein degradation. There are no obvious differences in the localization of Ubiquitin observed in cells grown in either methanol or dextrose/methanol. Control immunofluorescence experiments showed that nitrogen starvation did not affect the cellular localization of Ubiquitin (Supplementary Figure 2). We could not differentiate between the in-cell NMR spectra of cytosolic Ubiquitin and that of Ubiquitin trapped in cytosolic vesicles.
3. Yeast growth on dextrose packs Ubiquitin into protein storage bodies
Nutrients play a critical role in re-organizing the yeast cytosol. Different carbon sources influence protein expression by enhancing the production of metabolic enzymes necessary for optimal growth and suppressing proteins not involved in the metabolism of specific carbon sources. This phenomenon, described as catabolite inactivation, can influence protein expression on the transcriptional, translational, and post-translational level. We took advantage of catabolite inactivation to study Ubiquitin compartmentalization in small protein storage bodies15,16.
By growing P. pichia on mixed dextrose/methanol carbon sources, the yeast are subject to the conditions of catabolite inactivation. At the same time, transcriptional repression of Ubiquitin expression is overcome by methanol26,30. Similar experiments using mixed carbon sources were described by Egli et al31. We expected that Ubiquitin produced under these conditions would be packed into intracellular vesicles, such as protein storage bodies15, rather then be released free in the cytosol where it may interfere with optimal metabolism of dextrose. Yeast were grown in 15N labeled minimal medium containing both dextrose and methanol. In-cell NMR samples were collected 24 h and 48 h after induction with a 6 h nitrogen starvation at the end of the Ubiquitin expression period. Western blots revealed that Ubiquitin was overexpressed at the same level as when grown in methanol.
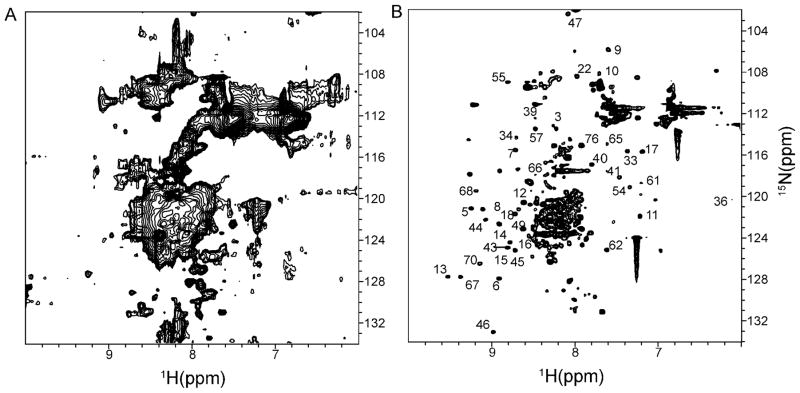
Only a few NMR peaks are visible in the in-cell NMR spectra of Ubiquitin samples collected after 24 h or 48 h inductions suggesting that protein tumbling is restricted (Figure 4A). Overexpressed Ubiquitin is packed into protein storage bodies in the fully or partially unfolded form, similar to proteins packed into bacterial inclusion bodies20. To investigate the structure of Ubiquitin in the protein storage bodies, the cells, including their intracellular organelles, were lysed and the NMR spectrum of the supernatant was collected. The supernatant contained sharp Ubiquitin peaks (Figure 4B) that are similar to the peaks of yeast-expressed Ubiquitin suggesting that Ubiquitin is packed into the vesicles in the folded form.
Figure 4.
1H{15N}-HSQC NMR spectra of Ubiquitin overexpressed on mixed dextrose/methanol medium. A. In-cell 48 h post-dextrose/methanol induction with nitrogen starvation. B. Lysate of A.
To further prove that Ubiquitin is packed in storage bodies, we gently removed the cell walls, ruptured the plasma membranes and fractionated the cells by using differential velocity centrifugation 32 (Figure 5). This procedure separates cytosolic proteins, the S fraction, from subcellular organelles, such as mitochondria, lysosomes, and microbodies, by sedimenting at 10,000g, to yield the membrane bound P1 fraction, and from smaller, lighter particles, such as ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum fragments, cell membranes, and microsomes, by sedimenting at 100,000g, to yield the P2 fraction. Ubiquitin expressed by growing yeast in methanol is found in both membrane bound (P1) and the cytosolic (S) fractions, whereas Ubiquitin expressed in yeast grown on mixed dextrose/methanol carbon sources is found only in the membrane bound fraction (P1) after 24 h, confirming its vesicular distribution. Control fractionation experiments showed that nitrogen starvation did not affect the cellular distribution of Ubiquitin (Supplementary Figure 3).
Figure 5.
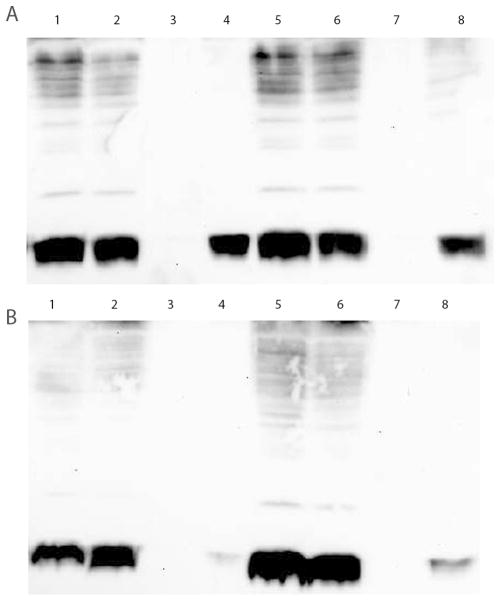
Cellular localization of Ubiquitin depends on growth conditions. A. Ubiquitin is localized to the cytosol following methanol induction. Lane 1- 24 h Total Sample (TL); Lane 2- 24 h Low Speed Precipitate (P1); Lane 3- 24 h High Speed Precipitate (P2); Lane 4- 24 h Supernatant (S); Lane 5- 48 h TL; Lane 6- 48 h P1; Lane 7- 48 h P2; Lane 8- 48 h S. B. Ubiquitin is localized to storage vesicles following mixed dextrose/methanol induction. Lane 1- 24 h TL; Lane 2- 24 h P1; Lane 3- 24 h P2; Lane 4- 24 h S; Lane 5- 48 h TL; Lane 6- 48 h P1; Lane 7- 48 h P2; Lane 8- 48 h S. Ubiquitin is localized in the P1 and cytosolic (S) fractions in methanol-induced cultures (Lanes 4A & 8A), but is not present in the cytosol of mixed dextrose/methanol-induced cultures (Lanes 4B & 8B). Anti-ubiquitin antibody was used to develop Ubiquitin Western blots.
4. Overexpressed β-galactosidase is also found in storage vesicles
Packing protein into protein storage bodies is a novel feature of catabolite inactivation30. However, due to its function, Ubiquitin is associated with many vesicular structures. To rule out the possibility that the observed phenomenon was specific to Ubiquitin, we used a different strain of P. pastoris (GS115) that expresses the bacterial enzyme, β-galactosidase, and assessed its localization and activity in yeast grown using either methanol or mixed dextrose/methanol as carbon sources.
Immunofluorescence and fractionation studies showed that β-galactosidase is localized in protein storage bodies when yeast is grown in mixed dextrose/methanol medium (Supplementary Figures 4 and 5). B-galactosidase expressed in yeast grown in methanol remains cytosolic. These observations confirm the general nature of the observed phenomenon of utilizing storage bodies during catabolite inactivation.
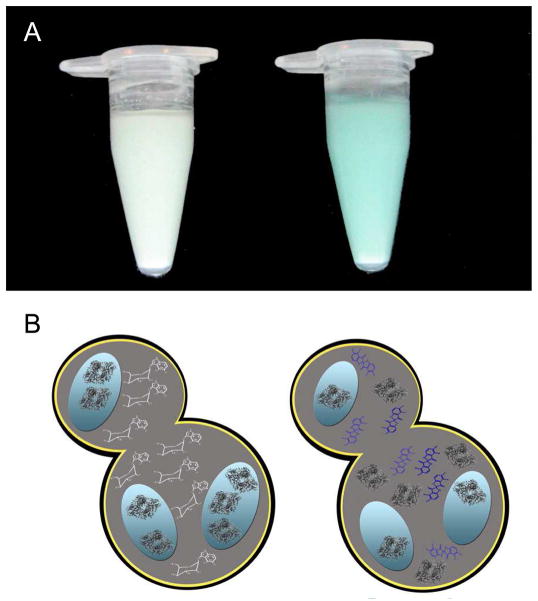
The enzymatic activity of β-galactosidase was assessed by adding its substrate, X-gal, directly to the yeast culture (Figure 6). Soluble X-gal diffuses across the plasma membrane into the yeast cytosol and is cleaved by β-galactosidase to yield the insoluble chromogenic product. Yeast containing β-galactosidase overexpressed in methanol exhibit a characteristic blue color after 4 h of incubation with X-gal. Yeast containing β-galactosidase overexpressed in mixed dextrose/methanol do not exhibit any color change after 4 h of incubation, although after 6 h a slight blue color is evident. The results of these experiments show that β-galactosidase is active in the cytosol. Interestingly, the absence of β-galactosidase activity when localized to protein storage bodies may be due to the inability of the substrate to penetrate into these compartments since the enzyme is active when released from the vesicles (Supplementary Figure 6).
Figure 6.
B-galactosidase sequestered in the storage vesicles cannot cleave substrate. A. P. pastoris with β-galactosidase over-expressed in methanol (right) or mixed dextrose/methanol (left) was exposed to X-gal for 4 h. B. β-galactosidase inactivation. When overexpressed in methanol (right), β-galactosidase is largely cytosolic and reacts with X-gal, to generate the blue chromo-genic reaction product. When overexpressed in mixed dextrose/methanol, β-galactosidase is sequestered into vesicles where it cannot react with X-gal.
Discussion
Yeast have been successfully used as a model organism to study basic biological processes inside eukaryotic cells33. The yeast two hybrid technique is widely used in proteomics to study protein-protein interactions34. These studies are limited since they are performed at the molecular level. In-cell NMR of proteins in yeast allows us to take the next step and visualize proteins and their interactions within the intracellular spaces inside living eukaryotic cells at atomic resolution.
In-cell NMR of eukaryotic cells has been demonstrated for proteins either injected or transported by active diffusion into a human or Xenopus cells2,11,12. While powerful, these techniques suffer from non-physiological delivery of labeled proteins, thus limiting applications of in-cell NMR in these cells. We showed that in-cell NMR spectra of isotope labeled proteins in yeast can be obtained by using the strong AOX induction/expression system in P. pastoris. Under our experimental conditions, in-cell NMR spectra can be collected within 6 hours with a signal to noise ratio of 4:1. Since overexpressed proteins pass through the eukaryotic translational system, they can be properly targeted to physiologically relevant compartments and used to study changes in protein structure under different physiological conditions.
Yeast in-cell NMR has multiple advantages compared to in-cell NMR of bacterial and even other eukaryotic cells: The stability of the yeast cell wall essentially eliminates cell leakage problems that plague bacterial and eukaryotic in-cell NMR studies35,36; also, an array of genetic tools are available to control protein overexpression and the well understood genetics of yeast facilitate experimental designs to study protein structures under different physiological conditions.
A straightforward application of in-cell NMR in yeast revealed a high background level of signals that obscures a significant portion of the amide proton spectral range, from 7.5 ppm to 8.5 ppm, a range essential to study protein structures. To resolve this problem we modified the standard sample preparation protocol by including a six hour nitrogen starvation period following over-expression of the target protein. During this time, small metabolites that contain 15N isotope are incorporated into either the target protein, thus, enhancing the desired NMR signal or into large cellular structures invisible to in-cell NMR. This dramatic improvement of the NMR signal allowed us to observe all but four NMR resonances of Ubiquitin inside yeast cells.
Yeast is known to extensively reorganize its cytosol upon changes of environmental conditions, such as sources of nutrients15. Catabolic inactivation results in the inactivation of metabolic pathways of non-preferred nutrients in favor of preferred ones30. We wanted to study changes in protein structure resulting from the metabolic changes of yeast grown in batch culture using different carbon sources. Growing yeast in mixed nutrients, dextrose and methanol, led to dramatic changes in the NMR spectrum of Ubiquitin as compared to those obtained when grown in methanol. When grown using mixed nutrients, Ubiquitin NMR peaks largely disappear from the spectrum due to broadening. Our immunomicroscopy and fractionation analyses show that Ubiquitin is sequestered into cytosolic vesicles, similar to the previously described protein storage depots 15,16. Protein sequestration is non-specific since the unrelated β-galactosidase protein is also sequestered in vesicles when yeast are grown in both dextrose and methanol. This process is unrelated to autophagy since vacuoles are largely devoid of the overexpressed protein.
The NMR spectrum of Ubiquitin released from the vesicles by cell lysis is identical to that of folded Ubiquitin suggesting that proteins are maintained in their functional forms within the vesicles. This is different from hormonal proteins in neuronal cells or proteins in bacterial inclusion bodies that possess an amyloid-like structure20,22. What is impeding the tumbling of the proteins inside vesicles and broadening the NMR signal? NMR of proteins in small artificially made vesicles is well-studied and provides valuable data to test the effect of molecular confinement on protein structure37. The size of the storage vesicles, which was determined to be 20 nm16, provides enough space for free Ubiquitin to tumble. We propose that the inner surface of the vesicles formed during metabolic changes has a non-specific affinity for proteins that increases the concentration of the proteins inside the vesicles and slows protein tumbling.
The most important implication of our observation of proteins stored inside cytoplasmic vesicles relates to drug screening and therapy38. We showed that β-galactosidase inside the vesicles does not enzymatically cleave the colorimetric substrate (Figure 6, Supplementary Figure 6). There can be two explanations for this result: The enzyme inside the vesicle is in an inactive form or the substrate cannot penetrate through the vesicular wall. The former is unlikely since we concluded that proteins inside the vesicles maintain proper folding. Therefore the latter is likely to hold true. If the phenomenon of sequestration of cytosolic proteins into storage vesicles is of a general nature, then the specific nutritional conditions present during drug administration may cause drug targets to be unavailable for effective interference, the so called food-drug interactions39. The ability to monitor the cytosolic distribution of protein targets by using in-cell NMR will help optimize conditions for drug-target interactions in drug screening. In-cell NMR in yeast, which allows us to study physiological biomolecular structures and interactions in eukaryotic cells, brings structural analyses one step closer to the coveted goal of understanding life processes at atomic resolution40.
Conclusions
We described a new mechanism to deliver endogenous, physiologically processed target proteins into eukaryotic cells, which allowed us to visualize atomic resolution protein structures by using in-cell NMR. We used this technique to observe a novel process in which changes in the metabolic state of the cells resulted in target proteins being directed to subcellular compartments allowing changes in protein structure to be assessed as a function of cellular localization. Finally, a critical observation that small molecular substrates are unable to penetrate subcellular vesicles and interact with the target molecule has implications for drug screening.
Experimental Section
Chemicals and Reagents
Restriction enzymes were from NEB. All other chemicals used were reagent grade or better.
Plasmid Construction
UBI3 coding for yeast Ubiquitin was amplified from S. cerevisiae strain BY4741 using the oligonucleotides 5′-TTTTTTCACGTGAAAATGCAGATTTTCGTC AAGACTTTGACC-3′ and 5′-TTTTTTCCGCGGTCAACCACCTCTTAGCCT TAGCACAAG-3′. The DNA was ligated into pPIC6A (Invitrogen) using the PmlI and SacII linker sites. pPIC confers blasticidin resistance and contains a pUC replication origin for selection using bacterial cells. Transformants were selected on low-salt LB plates [pH 8] containing 100 μg/mL blasticidin. The resulting recombinant plasmid, pPIC-ScUbq, places ubiquitin transcription under the control of the alcohol oxidase (AOX1) promoter, which is induced by methanol.
To prepare a dimeric insert, DNA coding for ScUbq was digested from pPIC-ScUbq using the BglII and BamHI sites. The insert was simultaneously digested with BglII and BamHI and ligated using T4 ligase in the presence of 300 mM ATP for 2 h at 37 °C (Invitrogen protocol). Ligation between BglII and BamHI will result in the loss of both restriction sites, while ligation between BglII sites (tail-to-tail) and between BamHI sites (head-to-head) will maintain the restriction sites; as a result only head-to-tail multimers will remain intact. Dimerized insert was gel purified and ligated into the BglII and BamHI sites of pPIC (Invitogen), which had been restriction digested and treated with antarctic phosphatase to prevent recircularization of the vector during ligation. Clones were selected on low-salt LB plates [pH 8] containing 100 μg/mL blasticidin. The resulting recombinant plasmid, pPIC-2xUbq, places two expression cassettes for Ubiquitin, each under the control of the alcohol oxidase (AOX1) promoter, which is induced by methanol.
Preparation of electroporation-competent X-33 cells
P. pastoris X-33 yeast were grown overnight in YPD at 30 °C. 250 mL of YPD were inoculated with the overnight culture and grown over-night at 30 °C to an OD600 of ~1. The cells were centrifuged at 1500g for 10 min at room temperature, RT, re-suspended in 10 mL of pre-warmed (30 °C) YPD containing 2 mL of 1 M Hepes [pH 8.0] and 250 μL of 1 M DTT. The cells were incubated for 30 min at 30 °C with no shaking. 40 mL of ice cold (sterile) water was added and the cells were centrifuged at 1500g for 10 min at 4 °C. The cells were washed once with 25 mL of ice cold water and washed a second time with ice cold 1 M sorbitol. The cells were finally re-suspended with 500 μL of ice cold 1 M sorbitol containing 10% glycerol, aliquoted and stored at −80 °C or used immediately.
Transformation of P. pastoris
0.5–1 mg of pPIC-ScUbq linearized by SacI digestion, or 10–12 mg of non-linearized pPIC-2xUbq, was added to frozen competent cells and thawed on ice. The cells were transferred to a chilled (4 °C)electroporation cuvette and electro-porated at 1500 V using a BTX Model ECM399 electroporator. 1 mL of ice-cold 1 M sorbitol was added immediately and the cells were incubated at 30 °C with shaking at 200 rpm for 1 h. 1 mL of pre-warmed (30 °C) YPD was added and the incubation continued for 1 h. 200 μl aliquots were plated onto YPD/sorbitol (YPDS) agar supplemented with 300 μg/mL of blasticidin. The cells were incubated for 2 more hours, after which 2 additional plates were spread with 200 μL of cells. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3–5 days. When ≤1 mg of DNA was used in the transformation, a lawn of “dead” cells appeared, punctuated with large white colonies, which were further tested for the ability to express ScUbq. When larger amounts of DNA were used to transform the yeast, large white colonies were not clearly evident. In these cases, randomly sampled portions of the lawn were streaked onto YPD/blasticidin plates containing 300 μg/mL, 600 μg/mL and 900 μg/mL to isolate recombinant clones. N.b. plasmids containing two or more expression cassettes cannot be linearized with SacI since this enzyme will cut within each cassette, thereby yielding multiple linearized expression fragments.
Isolating Ubiquitin over-expressing recombinants
Single colonies were grown in Buffered Minimal Methanol (BMM; 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0], 34 g/L yeast nitrogen base, 76 mM (NH4)2SO4, 1% methanol, 0.4 μg/mL biotin) medium with methanol as the sole carbon source. Biotin was added from a 0.2 mg/mL stock in 10 mM NaOH. Cell lysates were prepared and Western blots performed (see SDS-PAGE-Western analyses) to verify overexpression of Ubiquitin. The resulting recombinant yeasts, pPIC-ScUbq/X-33 and pPIC-2xUbq/X-33, overexpress Ubiquitin from the AOX1 promoter, which is induced by methanol.
Protein Expression
Cells were grown overnight at 30 °C in Buffered Minimal Dextrose (BMD; 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0], 34 g/L yeast nitrogen base, 76 mM (NH4)2SO4, 0.5% dextrose, 0.4 μg/mL biotin). The cells were centrifuged at 2000g for 10 minutes at RT, washed with 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0], re-centrifuged and suspended in BMM or Buffered Minimal Dextrose Methanol (BMDM; 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0], 34 g/L yeast nitrogen base, 76 mM (NH4)2SO4, 0.5% dextrose, 1% methanol, 0.4 μg/mL biotin) at an OD600 of 0.6. Methanol-induced protein overexpression proceeded for up to 48 h at 30 °C. Samples were taken at 24 h and 48 h post-induction. Additional methanol was added to a concentration of 0.5 % from a 10% stock solution after 24 h. For isotopic labeling, the ammonium sulfate in BMM or BMDM was replaced with 76 mM Na2SO4 and 2 g/L 15N-(NH4)2Cl. The OD600 of cell cultures was ~4 and ~6.5 after 24 h and 48 h of protein over-expression, respectively, for cultures containing dextrose, and ~2.5 and ~4 after 24 h and 48 h, respectively, for cultures grown in methanol. Some samples were subjected to nitrogen starvation prior to harvesting: Cell samples were centrifuged at 2000g for 10 min at RT, and re-suspended in an equal volume of modified BMM or BMDM, in which ammonium sulfate/chloride was replaced with 76 mM sodium sulfate, and incubated for an additional 6 h at 30 °C.
To overexpress β-galactosidase, P. pichia strain GS115/pPICZ/lacZ (Invitrogen), was used. This strain expresses β-galactosidase from the methanol-induced AOX1 promoter. The overexpressed protein is fused at the C-terminus to a myc epitope and a polyhistidine tag. Cells were grown as above.
β-Galactosidase Activity Assay
Cells were grown overnight at 30 °C in BMD. The cells were centrifuged at 2000g for 10 minutes at RT, washed with 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0], re-centrifuged and suspended in BMM or BMDM at an OD600 of 0.6. After 24 h of protein expression, X-gal and methanol were added to the cultures to a final concentration of 80 μg/mL and 2%, respectively, and allowed to incubate for up to 6 hours. Cell cultures in which β-galactosidase was over-expressed turned blue. Cell cultures in which β-galactosidase was not over-expressed remained white.
In-Cell NMR Spectroscopy
15N-isotope labeled ScUbq was prepared by growing X-33/ScUbq in BMM containing 15N ammonium chloride and methanol as the sole nitrogen and carbon sources, respectively. 100 mL samples from 24 h and 48 h cell cultures, both with and without nitrogen starvation, were centrifuged at 2000g for 10 min at RT and washed once with 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0] and once with 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0] containing 10% glycerol. The final sample was centrifuged and the pellet stored at −80 °C and used within 2 days. To prepare cells for in-cell NMR spectroscopy, the pellet was washed with 10 mM KPO4 [pH 7.0] buffer and re-suspended in 250 μL of 10 mM KPO4 [pH 7.0] buffer, 100 μL of D2O and 50 μL of glycerol. The resultant slurry was transferred to an NMR tube and the cells were packed down by centrifuging the NMR tube for 20 min at 21g. 1H{15N}-HSQC NMR experiments were performed to provide superior sensitivity due to the favorable relaxation characteristics of 15N nuclei41. NMR data were collected at 303 K on an 700 MHz Avance II Bruker NMR spectrometer equipped with a cryoprobe. After NMR experiments, cell viability, checked by plating and colony counting, was estimated to be >90%.
To prepare lysate samples, the cells were physically lysed: First, the cells were freeze-thawed five times by using a dry ice/ethanol bath. Second, the cells were sonicated three times for 1 min each using 0.3 sec pulses from a Branson Digital Sonifier at 60% maximum power. The lysed cells were centrifuged at 12,100g for 20 min at RT and D2O was added to the supernatant to a final concentration of 20%. The 1H{15N}-HSQC spectrum of each sample was acquired at 303 K using a Bruker 700 MHz spectrophotometer.
SDS-PAGE-Western analyses
Ubiquitin or β-galactosidase was expressed in P. pastoris yeast cells, as described in the Protein Expression section. After 24 h and 48 h of protein expression, 1 mL samples were obtained, the cells were pelleted and stored at −20 °C. Cells were suspended in 200 μL of yeast cracking buffer, 40 mM Tris-HCl [pH 6.8], 8 M Urea, 5% SDS, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.4 mg/mL bromphenol blue, containing 0.1% β-ME and 1 tablet of protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Molecular) per 50 mL, and incubated at 70 °C for 10 min. The solution was vortexed vigorously and then centrifuged at 12,000g for 1 min at RT. The samples were electrophoresed at 100 V for 1 h on a 16% (Ubiquitin) or 10% (β-galactosidase) gel in Tris-Glycine-SDS buffer using a Mini-PROTEAN 3 (Bio-Rad) apparatus. The gel was washed with Tris-Glycine buffer containing 20% methanol and transferred to a 0.2 μm nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad) in Tris-Glycine buffer containing 20% methanol using the Mini-PROTEAN 3 (Bio-Rad). The membrane was blocked for 2 h at RT with 1% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) in TBS-T (Tris Buffered Saline containing 0.05% Tween 20), and incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibody. For Ubiquitin, the primary antibody was rabbit polyclonal anti-ubiquitin IgG (Millipore). For β-galactosidase, the primary antibody was rabbit polyclonal anti-c-myc (QED Bioscience). The membrane was washed with TBS-T, and incubated for 1 h at RT with goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) HRP conjugate secondary antibody (Millipore). The membrane was washed once with TBS-T, then with TBS. Western blots were developed by incubating the membrane in Super-Signal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Thermo) for 5 min at RT and the resulting chemiluminescence imaged by using a Bio-Rad Chem-iDoc XRS equipped with Quantity One software.
Cell Fractionation
Ubiquitin or β-galactosidase was expressed in P. pastoris yeast cells, as described in the Protein Expression section. After 24 h and 48 h of protein expression, 500 mL samples were obtained, the cells were washed once with 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0] and once with 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0] containing 10% glycerol. The cells were pelleted and stored at −80 °C and used within 2 days. Thawed cells were sequentially washed (40 mL) with 85 mM KPO4 [pH 6.0], glass distilled water (GDW) and Spheroplast Buffer (SB), 40 mM KPO4 [pH 7.4], 1.4 M sorbitol. The cells were spheroplasted in 20 mL of SB containing 1% β-ME and 20 μL of zymolyase (MPBiomedicals), from a 250 U/g stock prepared in SB buffer, at RT for ~1 h, or until the OD600 of the solution decreased by 75%. The spheroplasts were centrifuged at 3270g for 5 min, washed 4 times with 20 mL of SB, and re-suspended in 10 mL of HB Buffer, 30 mM triethanolamine [pH 7.2], 1.2 M sorbitol, 1.3 mM EDTA, 240 mg/L AEBSF containing 1 tablet of protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Molecular) per 50 mL. The suspended cells were transferred to a dounce homogenizer, homogenized with ten strokes and re-centrifuged. The pellet was re-suspended in 10 mL of HB buffer and homogenized with 20 strokes and recombined with supernatant from the first douncing to produce 20 mL of total solution (TL). 18 mL of TL were centrifuged at 19,520g for 10 min at 4 °C to yield sample pellet P1. The resulting supernatant was centrifuged at 141,000g for 1 h at 4 °C to yield two samples, pellet P2 and supernatant S. The P1 and P2 samples were each re-suspended in 20 mL of lysis buffer, 30 mM triethanolamine [pH 7.2], 1.2 M sorbitol, 1.3 mM EDTA.
Western blots were used to detect Ubiquitin present in the TL, P1, P2 and S samples. The samples were mixed with an equal volume of Laemmli buffer42 and 5 μL were loaded into each lane. The solutions were denatured at 70 °C for 10 min prior to electrophoresis. Western blotting was performed as described in the SDS-PAGE-Western section.
Immunofluorescence microscopy
Ubiquitin or β-galactosidase was expressed in P. pastoris as described in the Protein Expression section. After 24 h and 48 h of protein expression, 30 mL samples were mixed with 4 mL of 37% of formaldehyde for 1 h at 28 °C. 5 mL were centrifuged at 12,000g at RT for 1 min. The cells were washed with 1 mL of Tris-EDTA buffer (TE), 100 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.0], 100 mM EDTA. The cells were re-suspended at an OD600 of ~3 in TE containing 0.3% β-ME and incubated for 45 min at 28 °C. The cells were centrifuged and re-suspended in 1 mL of buffer S, 10 mM PIPES [pH 6.5], 1 M sorbitol, containing 0.3% β-ME. 25 U of zymolyase was added and the cells were incubated for 60 min at 28 °C. The cells were washed 4 times in 1 mL of S buffer and suspended in 500 μL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS), 2 mM KH2PO4/10 mM Na2HPO4 [pH 7.4], 2.7 mM KCl, 137 mM NaCl.
Each well of a 6 mm, 10 well slide was treated with 15 μL of 1 mg/mL poly-D-lysine in 0.15 M sodium borate [pH 8.3] and incubated over-night at RT in a moist incubation chamber to prevent drying. The slides were rinsed with water and dried thoroughly before using. 20 μL of spheroplasted cells were spotted into each well and allowed to settle for 10 min. The slides were rinsed with PBS and dried thoroughly. Each well was incubated with 20 μL of 0.01% Triton X for 6 min, rinsed with PBS, incubated with 20 μL of blocking solution, 1% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) in PBS, for 2 h at RT and rinsed with PBS. The wells were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibody, diluted 1:500 in 0.1% BSA/PBS. The primary antibodies used were rabbit polyclonal IgG anti-ubiquitin (Millipore) and rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-c-myc (QED Bioscience). The slides were washed with PBS and incubated for 2 h at RT with the secondary antibody, goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) conjugated with Alexafluor 488, in 0.1% BSA/PBS.
The slides were rinsed with PBS and 5 μL of SlowFade Gold antifade reagent (Invitrogen) were added to each well. The wells were covered and sealed. The finished slides were imaged using a Zeiss LSM 510 laser scanning confocal microscope with a 63X oil-immersion objective. Fluorescence images were obtained by using an Argon laser emitting at 488 nm. Differential Interference Contrast images were obtained by using a mercury lamp.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding Sources
This work is supported by NIH grant R01GM085006 to A.S..
ABBREVIATIONS
- BMM
buffered minimal methanol
- BMD
buffered minimal dextrose
- BMDM
buffered minimal dextrose and methanol
- YPD
yeast extract peptone dextrose
- P. pastoris
Pichia Pastoris
- AOX1
alcohol oxidase 1
- HSQC
heteronuclear single quantum coherence
- X-gal
5-bromo-4-chloro-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside
- DTT
dithiothreitol
- EDTA
ethelenediaminetetraacidic acid
- AEBSF
4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride
- β-ME
2-mercaptoethanol
Footnotes
SUPPORTING INFORMATION AVAILABLE
Leakage Test. Immunofluorescence and differential interference (DI) contrast microscopy of P. pastoris overexpressing Ubiquitin grown on methanol with nitrogen starvation. Influence of nitrogen starvation on cellular distribution of Ubiquitin overexpressed in methanol. Immunofluorescence and differential interference contrast microscopy of P. pastoris overexpressing β-galactosidase. Dependence of cellular distribution of β-galactosidase on growth conditions. B-galactosidase is enzymatically actice when released from the protein storage bodies. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Creighton TE. Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties. 2. W. H. Freeman; New York: 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Inomata K, Ohno A, Tochio H, Isogai S, Tenno T, Nakase I, Takeuchi T, Futaki S, Ito Y, Hiroaki H, Shirakawa M. Nature. 2009;458:106–9. doi: 10.1038/nature07839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sakakibara D, Sasaki A, Ikeya T, Hamatsu J, Hanashima T, Mishima M, Yoshimasu M, Hayashi N, Mikawa T, Walchli M, Smith BO, Shirakawa M, Guntert P, Ito Y. Nature. 2009;458:102–5. doi: 10.1038/nature07814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Serber Z, Corsini L, Durst F, Dotsch V. Methods Enzymol. 2005;394:17–41. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)94002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Burz DS, Dutta K, Cowburn D, Shekhtman A. Nat Methods. 2006;3:91–3. doi: 10.1038/nmeth851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Maldonado A, Burz DS, Shekhman A. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. 2011;59:197–212. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2010.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fiaux J, Cakar ZP, Sonderegger M, Wuthrich K, Szyperski T, Sauer U. Eukaryot Cell. 2003;2:170–80. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.1.170-180.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sola A, Maaheimo H, Ylonen K, Ferrer P, Szyperski T. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:2462–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cregg JM, Cereghino JL, Shi J, Higgins DR. Mol Biotechnol. 2000;16:23–52. doi: 10.1385/MB:16:1:23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tschopp JF, Cregg JM. Biotechnology. 1991;18:305–22. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7506-9188-8.50020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Selenko P, Serber Z, Gadea B, Ruderman J, Wagner G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:11904–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604667103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sakai T, Tochio H, Tenno T, Ito Y, Kokubo T, Hiroaki H, Shirakawa M. J Biomol NMR. 2006;36:179–88. doi: 10.1007/s10858-006-9079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Selenko P, Wagner G. J Struct Biol. 2007;158:244–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2007.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ogino S, Kubo S, Umemoto R, Huang S, Nishida N, Shimada I. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:10834–5. doi: 10.1021/ja904407w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Narayanaswamy R, Levy M, Tsechansky M, Stovall GM, O’Connell JD, Mirrielees J, Ellington AD, Marcotte EM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:10147–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812771106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huang PH, Chiang HL. J Cell Biol. 1997;136:803–10. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sagot I, Pinson B, Salin B, Daignan-Fornier B. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:4645–55. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-04-0282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spivey HO, Merz JM. Bioessays. 1989;10:127–30. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.An S, Kumar R, Sheets ED, Benkovic SJ. Science. 2008;320:103–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1152241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang L, Maji SK, Sawaya MR, Eisenberg D, Riek R. PLoS Biol. 2008;6:e195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Winner B, Jappelli R, Maji SK, Desplats PA, Boyer L, Aigner S, Hetzer C, Loher T, Vilar M, Campioni S, Tzitzilonis C, Soragni A, Jessberger S, Mira H, Consiglio A, Pham E, Masliah E, Gage FH, Riek R. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:4194–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100976108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maji SK, Perrin MH, Sawaya MR, Jessberger S, Vadodaria K, Rissman RA, Singru PS, Nilsson KP, Simon R, Schubert D, Eisenberg D, Rivier J, Sawchenko P, Vale W, Riek R. Science. 2009;325:328–32. doi: 10.1126/science.1173155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xie J, Thapa R, Reverdatto S, Burz DS, Shekhtman A. J Med Chem. 2009;52:3516–22. doi: 10.1021/jm9000743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dinsdale EA, Edwards RA, Hall D, Angly F, Breitbart M, Brulc JM, Furlan M, Desnues C, Haynes M, Li L, McDaniel L, Moran MA, Nelson KE, Nilsson C, Olson R, Paul J, Brito BR, Ruan Y, Swan BK, Stevens R, Valentine DL, Thurber RV, Wegley L, White BA, Rohwer F. Nature. 2008;452:629–32. doi: 10.1038/nature06810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schwanhausser B, Busse D, Li N, Dittmar G, Schuchhardt J, Wolf J, Chen W, Selbach M. Nature. 2011;473:337–42. doi: 10.1038/nature10098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Murray WD, Duff SJ, Beveridge TJ. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990;56:2378–2383. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2378-2383.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang P, Zhang W, Zhou X, Bai P, Cregg JM, Zhang Y. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76:6108–18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00607-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM. Yeast. 2005;22:249–70. doi: 10.1002/yea.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sauer M, Branduardi P, Gasser B, Valli M, Maurer M, Porro D, Mattanovich D. Microb Cell Fact. 2004;3:17. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-3-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gancedo JM. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998;62:334–61. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.62.2.334-361.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Egli T, Kappeli O, Fiechter A. Arch Microbiology. 1982;131:1–7. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chang J, Ruiz V, Vancura A. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2008;457:1–9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-261-8_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Roman H. In: The Molecular and Cellular Biology of the Yeast Saccharomyces. Strathern JN, Jones EW, Broach JR, editors. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, New York: 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fields S, Song O. Nature. 1989;340:245–6. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sakai T, Tochio H, Inomata K, Sasaki Y, Tenno T, Tanaka T, Kokubo T, Hiroaki H, Shirakawa M. Anal Biochem. 2007;371:247–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cruzeiro-Silva C, Albernaz FP, Valente AP, Almeida FC. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006;44:497–502. doi: 10.1385/CBB:44:3:497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Valentine KG, Peterson RW, Saad JS, Summers MF, Xu X, Ames JB, Wand AJ. Structure. 2010;18:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pellecchia M, Bertini I, Cowburn D, Dalvit C, Giralt E, Jahnke W, James TL, Homans SW, Kessler H, Luchinat C, Meyer B, Oschkinat H, Peng J, Schwalbe H, Siegal G. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:738–45. doi: 10.1038/nrd2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lamy PP. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1982;30:S99–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1982.tb01364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Goodsell DS. The Machinery of Life. 2. Springer; New York: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Serber Z, Dotsch V. Biochemistry. 2001;40:14317–23. doi: 10.1021/bi011751w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Laemmli UK. Nature. 1970;227:680–5. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.