Abstract
During palatogenesis, the palatal mesenchyme undergoes increased cell proliferation resulting in palatal growth, elevation and fusion of the two palatal shelves. Interestingly, the palatal mesenchyme expresses all three TGFβ isoforms (1, 2 and 3) throughout these steps of palatogenesis. However, the role of TGFβ in promoting proliferation of palatal mesenchymal cells has never been explored. The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of TGFβ on human embryonic palatal mesenchymal (HEPM) cell proliferation. Our results showed that all isoforms of TGFβ, especially TGFβ3, increased HEPM cell proliferation by up-regulating the expression of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases as well as c-Myc oncogene. TGFβ activated both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways to induce c-Myc gene expression. Furthermore, TBE1 is the only functional Smad binding element (SBE) in the c-Myc promoter and Smad4, activated by TGFβ, binds to the TBE1 to induce c-Myc gene activity. We conclude that HEPM proliferation is manifested by the induction of c-Myc in response to TGFβ signaling, which is essential for complete palatal confluency. Our data highlights the potential role of TGFβ as a therapeutic molecule to correct cleft palate by promoting growth.
Keywords: TGFβ, human embryonic palatal mesenchyme, proliferation, c-Myc
INTRODUCTION
In mammals, the secondary palate forms by the growth and fusion of the two palatal shelves as a result of mesenchymal cell proliferation. These shelves, which arise as bilateral outgrowths from the maxillary processes [Burdett et al., 1988], fuse at approximately 14.0 dpc, varying slightly from species to species. Within the next 48 to 72 hours, a continuous palate forms [Chai and Maxson, 2006]. Elevation and fusion of the palatal shelves during embryonic development can result in incomplete palate development and failure of the palatal shelves to grow after elevation is the most common type of cleft palate defect documented in animal studies [Chai and Maxson, 2006]. Overwhelming evidence in mice suggests that at about 13.0~14.0 dpc, the palatal shelves are elevated, and on 14.0~14.5 dpc, the palatal shelves grow toward each other in anticipation of fusion [Fitzpatrick et al., 1990], also known as “adhesion”. At this stage, the palatal mesenchyme undergoes increased cell proliferation to achieve optimum growth and fusion. However, what regulates mesenchymal cell proliferation during palatal growth is not known. Interestingly, transforming growth factor (TGF) β, a potent regulator of cellular function and behavior, including cell proliferation, has been shown to be expressed in the palatal mesenchyme during palatal growth and elevation. Therefore, TGFβ may play a role in the proliferation of palatal mesenchyme and palatal growth.
The TGFβ superfamily includes a large number of cytokines, such as: Activins, Inhibins, Bone Morphogenic Proteins (BMPs) and others. In mammals, TGFβ exists in three isoforms: TGFβ1, TGFβ2 and TGFβ3, encoded by three different genes [Khalil, 1999]. Among the diverse repertoire of cytokines that mediate palatogenesis, TGFβ is expressed throughout all stages of palate development, particularly in the highly proliferative palatal shelves [Pelton et al., 1990b]. During mouse palate development, TGFβ1 and TGFβ3 are expressed in the medial edge epithelium (MEE), whereas TGFβ2 is expressed in the mesenchyme beneath the MEE [Fitzpatrick et al., 1990; Pelton et al., 1990a]. TGFβ receptor II (TrII) is expressed in both the MEE and the cranial neural crest (CNC)-derived palatal mesenchyme [Cui et al., 1998]. Notably, ablation of TrII in the palatal mesenchyme compromises cell proliferation and causes complete cleft palate [Ito et al., 2003].
TGFβ functions in a variety of cellular processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, migration/invasion, matrix synthesis and the immune response [Bierie and Moses, 2006; Massague and Wotton, 2000; Shi and Massague, 2003]. TGFβ initiates these processes by binding to cell surface receptors which possess intrinsic serine/threonine kinase activity, designated TGFβ receptor types 1, 2 and 3. Binding of the ligand to these receptors then activates Smad-dependent or Smad-independent pathways, such as the PIK3 and MAPK signaling pathways [Bakin et al., 2000; Moustakas and Heldin, 2005]. Additionally, the Erk, Jnk, p38MAPK and Erk5 pathways operate in parallel [Rubinfeld and Seger, 2005].
Previously, Shuler, Ferguson and others [Carette and Ferguson, 1992; Cui et al., 2003; Kaartinen et al., 1997; Martinez-Alvarez et al., 2000; Nawshad, 2008; Proetzel et al., 1995; Shuler et al., 1992] have shown that TGFβ3 causes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cell death and cell cycle arrest in the palatal epithelial cells. TGFβ3 knockouts are always born with cleft palate. But the role of TGFβ in the growth of the palatal mesenchyme has yet to be fully explored. In this study, using human embryonic palatal mesenchymal (HEPM) cells, we investigate the role of TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 in mesenchymal cell proliferation. Because the proliferative effect of TGFβ is associated with progression of the palatal mesenchymal cell cycle, these studies were designed to test the hypothesis that TGFβ signaling induces HEPM cell proliferation by activating transcription factors that induce cell cycle progression during palatogenesis. While all isoforms of TGFβ are known to be expressed in the palatal mesenchymal compartment, we demonstrated that TGFβ3 is the most effective isoform in inducing cell proliferation. TGFβ3 also has a more pronounced effect in activating cyclins and CDKs than the other isoforms. We additionally demonstrate that TGFβ1, -2 and- 3 activate both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways, recruiting Smad4 to the TBE1 Smad binding element (SBE) of the c-Myc promoter, thereby promoting HEPM cell proliferation. Based on our results, we conclude that while TGFβ1 and 2 might have other distinct cellular functions, including stimulation of low level mesenchymal cell proliferation, TGFβ3 induces the highest level of mesenchymal cell proliferation and palatal shelf growth.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines and treatments
We obtained HEPM cells from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). The cells were cultured at 37°C in an incubator with 5% CO2. The culture medium consisted of DMEM (Invitrogen, CA) supplemented with 10% and/or 0.5% (v:v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% (v:v) penicillin streptoMycin glutamine. The medium was changed every 2 days, and the cells were split (1:4) every week. To mimic the in vivo condition, where TGFβ isoforms are abundantly available, 80% confluent HEPM cells in culture were treated with different isoforms of recombinant TGFβ proteins, TGFβ1, TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 (all 10ng/ml) (R&D Systems, CA) in DMEM with 0.5% FBS and 1% penicillin streptoMycin glutamine for 30 minutes (min), 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 36 and 48 hours (h). HEPM cells were synchronized at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle by serum starvation for 24/48 h with 0.5% FBS. HEPM cells were also transiently transfected with a full length human c-Myc cDNA, pcDNA3.3 c-Myc (Addgene, MA) and small hairpin RNA (shRNA) c-Myc, pRetrosuper-sh-cMyc (Addgene, MA) for 24 h in the presence of TGFβ treatments. To inhibit the Smad-dependent pathway, shRNA Smad4, pRetrosuper-shSmad4 (Addgene, MA) was used which specifically targets the coding region of human Smad4. The pcDNA3.3 c-Myc, pRetrosuper-sh-cMyc and pRetrosuper-shSmad4 were transfected into the HEPM cells by gently adding solution containing 10μl of Lipofectamine 2000 in 300μl of Opti-MEM medium for 24 h, as described previously [Medici and Nawshad, 2010]. The Smad-independent pathways were blocked using commercially available small synthetic chemical inhibitors, such as SB202190 (20μM), an inhibitor of ERK1/2 (Sigma-Aldrich, MO); U0126 (20μM), an inhibitor of MEK1/2 (Cell Signaling, MA); and LY294002 (20μM), an inhibitor of PI3 Kinase (Cell Signaling, MA) for 60 min. Following all inhibitions (pRetrosuper-shSmad4 and chemical inhibitors) TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 (10ng/mL) were added in the presence of these molecules for another 24 h prior to mRNA extraction. All antibodies and inhibitors were used at the concentration and time point recommended by the respective manufacturer/provider as well as confirmed by us previously [Ahmed et al., 2007; Iordanskaia and Nawshad, 2011; Nawshad and Hay, 2003; Nawshad et al., 2007]
Palate dissection
Palates from 13.5 mouse embryos TGFβ3 wild type (+/+) and homozygous (-/-) embryos were dissected from pregnant TGFβ3 heterozygous (+/-) (obtained from Prof. Tom Doetschman, University of Arizona), following breeding with male TGFβ3 heterozygotes (+/-) to generate TGFβ3 homozygous (-/-), as described previously [Nawshad et al., 2004]. 13.5 dpc palates were fixed in Bouin’s fixative overnight and embedded in paraffin for 8μm sections.
BrdU incorporation
13.5 dpc pregnant TGFβ3 heteozygous (+/-) transgenic mice (mated with male heterozygous; +/-) were administered vehicle (saline), or BrdU (200mg/Kg of body weight; Sigma-Aldrich,MO) by intra-peritoneal injection. Two hours after BrdU administration, mice were euthanized; the head of the embryos were excised and fixed with Bouin’s fixative for 5 h followed by embedding in paraffin. 8μm coronal sections were used for immunohistochemistry as described previously [Nawshad et al., 2004]. Briefly, sections were incubated at 37°C with 3% H2O2 for 10 min, followed by denaturation of DNA in 2N HCl for 30 min and enzymatic pretreatment with Trypsin for 30 min. Sections were blocked for 1 h with 5% goat serum followed by incubation with mouse anti-BrdU antibody (1:1000) (Sigma-Aldrich, MO) overnight at 4°C. The sections were incubated with biotinylated anti-IgG secondary antibody (1:50; Anti-Ig HRP Detection Kit, BD Pharmingen, CA) for 30 min at room temperature (RT) followed by streptavidin-HRP incubation for another 30 min at RT and a brief wash with DAB chromogen substrate solution. The primary antibody was omitted in the negative control. Genotyping was undertaken to confirm the TGFβ3 wildtype, heterozygous and homozygous pups.
EdU incorporation and flow cytometry assay
To assess cell proliferation status, EdU expression profile for an actively-proliferating cell population was evaluated HEPM cells were seeded into 6 well plates at a density of 2.5 × 104 cells/well in DMEM containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin streptoMycin glutamine. After 24 h serum starvation, the cells were treated with recombinant TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 (10ng/mL) and full length human c-Myc cDNA for 24 h in 0.5% FBS. 30uM of 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) was added per well and incubated for 1 h. Cells were then harvested and the EdU incorporation was determined using the Click-iT EDU flow cytometry assay kit (Invitrogen, CA). The same kit was used for cell cycle distribution with DNA content assessed by Propidium Iodide (PI) stain. Using BD Biosciences FACSArray, a significant proportion of cells were found to occupy distinct cell cycle phases including G0/G1, S, and G2/M within the selected boxed region. Larger boxed region identifies all proliferating cells as determined by their levels of DNA synthesis as assessed by PI within the G0/G, S and G2/M phases of the cycle. The smaller inset box includes the cells that are incorporated with EdU or S phase cells. Here, we only show the cells that are EdU positive cells in the S phase
Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry and Immunobloting
Both HEPM cells and embryonic palates from 13.5 dpc were used for immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting techniques as described previously [Ahmed et al., 2007; Iordanskaia and Nawshad, 2010; Nawshad and Hay, 2003; Nawshad et al., 2007]. For EdU incorporation, HEPM cells were seeded onto sterile cover glass for 24 h. After serum starvation for 24 h, the cells were treated with recombinant TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 (10ng/mL) for 24 h. After treatment, EdU was added to the medium at a 40μM final concentration and incubated for another 3 h. The slides were fixed for 15 min with 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized for 20 min with 1 ml 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS. Click-iT reaction cocktail, containing Alexa Fluor 488 labeled EdU, was prepared according to the protocol (Invitrogen,CA) and the cells were incubated with the Click-iT reaction cocktail reagents for 30 min. EdU treated HEPM cells were also incubated with PCNA primary antibody (Cell Signaling, MA.1:1000) for 2 h at RT, followed by incubation with rhodamine conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h at RT, mounted and stained with DAPI (4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole), sealed and fluorescence was observed with a fluorescence microscope (Zeiss, Germany).
For protein expression of HEPM cells, the cells were serum starved for 48 h, followed by treatment with TGFβ 1, 2, 3 (10ng/mL) in 0.5% FBS DMEM for 24 h and/or 30 min, and total protein was extracted. For nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, we used the nuclear extraction kit from Chemicon Nuclear Extraction Kit (Millipore, MA) as performed previously [Ahmed et al., 2007; Iordanskaia and Nawshad, 2011]. The concentration of the nuclear, cytoplasmic and total proteins was obtained with the using NanoDrop 2000c spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL). 25μg of protein extract was electrophoresed on a 10% denaturing gel and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The membranes were blocked with gelatin, washed with PBS-Tween, and incubated with the following primary antibodies: c-Myc (Invitrogen, CA 1:1000), PCNA (1:200), cyclin A (1:50), cyclin B1 (1:200), cyclin D1 (1:100), cyclin D2 (1:200), cyclin D3 (1:100), cyclin E2 (1:200), CDK1 (1:200), CDK2 (1:100), CDK4 (1:200), ERK1/2, phosphor (p) ERK1/2 (1:500), pMEK1/2 (1:1000), pSmad2 (1:200), Smad2 (1:100), Smad3 (1:50), pSmad3 (1:50) Smad4 (1:100), β-actin (1:200) AKT (1:100), MEK1/2 (1:500), pAKT (1:100), pp38MAPK (1:100), p38MAPK (1:200) (all from Cell Signaling, MA). The secondary antibodies were anti-mouse and anti-rabbit (Cell Signaling, MA; 1:5000). The bands were visualized by using an odyssey scanner (Li-Cor, NE). Intensity of the band was measured using the Carestream Molecular Imaging Software version 5.3.1 (Rochester, NY). To perform a t-test analysis of mean intensity measurements, a ROI analysis was done from the data to Microsoft Excel software from the exported “.txt” files. Data points for all samples are paired by spatial arrangement on gel and compared pairwise to minimize the impact of subtle background artifacts on image analysis.
HEPM cells were used for immunofluorescence protein expression. The primary antibodies included: pSmad2 (1:100) and Smad4 (1:00) (Cells Signaling, MA).
For protein expression on palates, 8μm sections of 13.5 dpc palates from TGFβ3 wild type (+/+) and homozygous (-/-) embryos were used for immunohistochemistry (Cyclin D, 1:100; Cell Signaling, MA) and immunofluorescence (c-Myc, 1:50; Invitrogen, CA, PCNA, 1:500; Cell signaling, MA, Cleaved Caspase 3 (1:400; Cell signaling, MA) E-Cadherin (1:200, Santa Cruz, CA) following techniques as described previously [Ahmed et al., 2007; Nawshad and Hay, 2003; Nawshad et al., 2007]. Secondary antibodies used for immunofluorescence are: Alexa Fluor® 568 Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (1:500) (Invitrogen, CA); Goat anti-Mouse IgG, Rhodamine conjugate (1:100) (Millipore, MA), Alexa Fluor® 488 Rabbit Anti-Goat IgG (H+L) (1:500) (Invitrogen, CA) and Alexa Fluor® 488 Goat Anti-Mouse IgG, IgM (H+L) (1:500) (Invitrogen, CA). A biotinylated anti-IgG secondary antibody was used for immunohistochemistry (Anti-Ig HRP Detection Kit, BD Pharmingen, CA).
TUNEL Assay
To clarify the spatial distribution of DNA fragmentation during palate development, we performed TUNEL which employs TdT to add dUTP to the fragmented DNA ends. We used DeadEnd Fluorometric TUNEL System (Promega,WI Cat # G3250) according to manufacturer’s manual. Briefly, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were rehydrated through xylene and ethanol gradients; antigen retrieval was achieved using Proteinase K, and tissues were incubated with fluorescein conjugated-12-dUTP at 37°C for 1 hour. Fluorescein-12-dUTP-labeled fragmented DNA was visualized by fluorescence microscopy.
qRT-PCR
As described previously, [LaGamba et al., 2005], HEPM cells were serum starved for 24 h, followed by treatment with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/ml) for 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 36 and 48 h. RNA was harvested using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA integrity was assessed using formaldehyde gels in 1×TAE buffer, and RNA purity and concentration were determined by the 260/280 ratio on a Nanodrop 2000C (Thermoscientific, MA). The sequences of primers for c-Myc and GAPDH were obtained from the Invitrogen online PCR primer design site, and were synthesized at the Molecular Biology Core Facility, UNMC.
| MYC | (forward) 5’-ACCAGAGAAACCTAACAGTGC-3’ |
| (reverse) 5’-CTCTTTCATTTCGGCCAGTTC-3’ | |
| GAPDH | (forward) 5’-ACATCGCTCAGACACCATG-3’ |
| (reverse) 5’-TGTAGTTGAGGTCAATGAAGGG-3’ |
Gene expression was determined by normalization with the control gene, GAPDH. Each RT-PCR experiment was performed in triplicate.
Transfection and luciferase assay
The TGFβ-mediated effect on c-Myc promoter activity was measured through firefly luciferase assays in HEPM cells transiently transfected with a pBV-Luc plasmid harboring the human c-Myc promoter (2500bp; pBV-Luc-Myc-WT plasmid) or derivative plasmids containing mutations in the TBE1 (pBV-Luc-TBE1mut) or TBE2 (pBV-Luc-TBE2mut) or both sites (pBV-Luc-TBE1/2mut). Additionally, we used c-Myc promoter region deletion constructs: pBV-Luc-DEL1 (WT, with intact TBE1, TBE2 and TIE sites), pBV-Luc-DEL3 (without TBE1, but with intact TBE2 and TIE), pBV-Luc-DEL4 (without TBE1 and TBE2 but with intact TIE). The details of the luciferase protocol have been reported previously [Ahmed et al., 2007; Iordanskaia and Nawshad, 2011]. Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent (Invitrogen, CA) was used following the manufacturer’s protocol. Transfection of HEPM cells with pBV-Luc vector without a c-Myc promoter region (empty vector) was performed as a negative control. Human recombinant TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/ml) was added to the transfected cells. After 24h of TGFβ treatment, luciferase activity was detected using the Sirius luminometer (Berthold Detection Systems, NC). The results are reported as the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay
Equal quantities (4×107cells) of the control (0.5% FBS), TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/ml) stimulated HEPM cells in 80%-90% monolayers were fixed with 1% formaldehyde for 10 min at RT for chromatin cross-linking. The reaction was stopped by adding glycine to a final concentration of 0.125M and the cells were immediately washed twice with ice-cold PBS and harvested by scraping cells in ice-cold 1×PBS+PMSF. The Simple ChIP™ Enzymatic Chromatin IP kit (Magnetic beads) (Cell Signaling, MA) was used according to the method successfully used by us previously [Iordanskaia and Nawshad, 2011]. Briefly, cross-linked chromatin was isolated from the lysates by sonication 3 times for 6 seconds each, using the Microson XL 2000 sonicator. Immune precipitation of the cross-linked chromatin with rabbit anti-Smad4 antibody (Cell Signaling, MA) was subsequently performed. For the negative control, rabbit IgG (Cell Signaling, MA) and for the positive control, Histone H3 antibody were used. The 100 μl chromatin samples in binding buffer from the Chromatin IP kit (Cell Signaling, MA), containing 15μg chromatin DNA were incubated overnight with antibodies at 4°C. The subsequent binding with magnetic beads, immunocomplex washing and DNA extraction were carried out following the manufacturer’s protocol. Purified DNA was analyzed by PCR with primers specific for Smad4-binding elements in the c-Myc promoter. The following primers were used:
| Human c-Myc (TBE1): | |
| (forward) | 5’-TCTCCACTTGCCCCTTTTAG-3’ |
| (reverse) | 5’-CGGAGTTCCCAATTTCTCAG-3’ |
| Human c-Myc (TBE2): | |
| (forward) | 5’-GCGCCCATTATTACCCTTCTT-3’ |
| (reverse) | 5’-GAAAGGGCCGCGCTTT-3’ |
| Human c-Myc (TIE): | |
| (forward) | 5’-CTTTATAATGCGAGGGTCTGGACG-3’ |
| (reverse) | 5’-GCTATGGGCAAAGTTTCGTGGATG-3’ |
Resulting DNA fragments were detected by electrophoresis in 1.5% agarose gel. To quantitatively analyze Smad4 binding with the three potential Smad binding sites in the c-Myc promoter following TGFβ1, TGFβ2 or TGFβ3 treatment, real-time PCR analysis of the DNA, purified from the immunocomplexes with the anti-Smad4 antibody, was performed. DNA samples were subjected to quantitation by real-time PCR using RealMasterMix Sybr Rox (5Prime, Hamburg, Germany). Reactions were performed in a 20μl volume according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The mean ±SD obtained from three independent experiments were compared.
Statistical Analysis
Data from at least three replicates for each parameter were evaluated and analyzed for significance by SPSS 14.0. The treatment groups included TGFβ1, TGFβ2, and TGFβ3, and the control groups were 10% FBS (+ve control) and/or 0.5% FBS (-ve control). The observation times were collapsed due to the convenience of the study, and one-way ANOVA was conducted. The significance level was set as 0.05. A p-value of ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. The one-way ANOVA indicated that the values differ significantly across the treatment groups. Bonferroni post-hoc comparisons of the 4+ treatment groups indicated that the two control groups, positive control and negative control significantly differ from each other (p ≤ 0001). All three TGFβ treatment groups also differed significantly from the positive and negative control groups, (p ≤ 0001). The comparison of each treatment group showed that there were no significant differences between the TGFβ1 and TGFβ2 treatment groups, p = 0.056. However, they both differed significantly from the TGβ3 treatment group (p ≤ 0005).
RESULTS
Localization of cell proliferation and apoptotic proteins in developing palates
During embryonic development, the palatal shelves are in the process of growth throughout all phases of palate development, starting at 11dpc when the rudimentary palatal shelf emerges by descending on both sides of the embryonic tongue. Immunuhistochemical analysis of coronal sections of 13.5 dpc palates was undertaken to localize BrdU incorporation 3 h after TGFβ (+/-) maternal exposure (Fig. 1). Genotyping confirmed the TGFβ3 wildtype, heterozygous and homozygous pups. BrdU was incorporated into the DNA of a large number of palatal mesenchymal cells and palatal epithelium, as observed by the dark DAB stain (Fig. 1A) in the TGFβ3 WT (+/+) palates when compared to the TGFβ3 homozygous (-/-) mice (Fig. 1). In accordance with the BrdU results, the cell proliferation proteins, c-Myc (Fig. 1B by immunofluorescence), PCNA (Fig. 1C by immunofluorescence) and cyclin-D (Fig. 1D by immunohistochemistry) were also expressed in increased intensity and number of cells in the palatal mesenchyme of the WT palate, compared to homozygous palates, suggesting a functional role of these cell proliferation proteins in palatal shelf growth. Moreover, the apoptotic proteins such as cleaved-Caspase 3 did not show staining in the palatal mesenchyme except for few periderm cells, covering the medial edge epithelial cells in both wildtype and homozygous palates (Fig. 1E by immunofluorescence). TUNEL staining was also negative in both wildtype and homozygous palates (Fig. 1F). All Immunofluorescence experiments underwent nuclear staining with DAPI (blue) and epithelial marker, E-cadherin with Alexa Fluor® 488, as secondary antibody. The scale bar represents 20μm. Interestingly, as observed in Fig. 1B, many WT palates at 13.5 dpc were already in very close proximity, whereas most of the (+/-) and (-/-) palates showed delayed growth and remained separated at the same time point, suggesting that loss of TGFβ may delay palatal growth.
Fig. 1. Assessment of embryonic palatal mesenchymal proliferation and apoptosis.
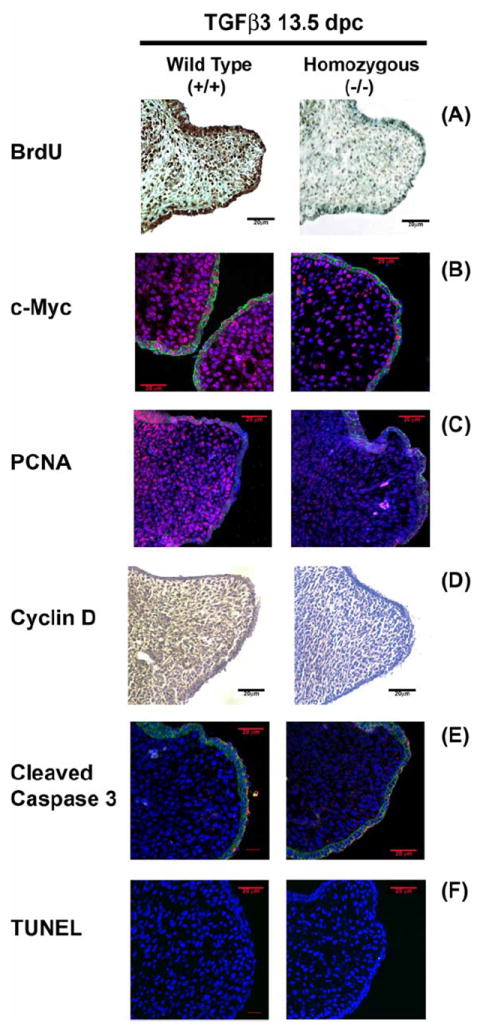
(A) Intraperitoneal injection of BrdU was measured in the coronal sections of 13.5 dpc Wild Type, WT (+/+) and TGFβ3 homozygous (-/-) mice palates by staining with mouse anti-BrdU antibody. All mesenchymal cells undergoing DNA synthesis, incorporated BrdU and were identified by the dark brown DAB substrate stain. A significantly higher number of palatal mesenchymal cells showed increased BrdU stain in WT compared to homozygous (-/-) mice. Immunofluorescence expression of cell proliferation protein markers, c-Myc (B; Rhodamine) and PCNA (C; Rhodamine) were increased for both the proteins throughout the nucleus of palatal mesenchymal cells in vivo at 13.5 dpc, compared to homozygous palates. (D) Immunohistochemistry staining of cyclin D protein expression in palates showed higher expression of dark brown HPA-DAB substrate in the palatal mesenchyme in the WT than the homozygous palates; (E) No expression of cleaved caspase 3 was detected by secondary antibody Alexa Fluor® 568 at 13.5 dpc of WT mice throughout the palatal mesenchyme except for few periderm cells overlying the medial edge epithelia for both WT and homozygous palates. (F) The palatal mesenchyme was negative for any TUNEL positive staining for both WT and homozugous palates. All Immunofluorescence experiments underwent nuclear staining with DAPI (blue) and epithelial marker, E-cadherin with Alexa Fluor® 488, as secondary antibody. The scale bar represents 20μm.
TGFβ1, TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 stimulate DNA synthesis in HEPM cells
Following 24 h synchronization by serum starvation, the HEPM cells were treated with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10 ng/ml) +/- full length c-Myc cDNA and +/- pRetrosuper-sh-cMyc for an additional 24 h with 0.5% and/or 10% FBS to assess the effect of the TGFβ isoforms on DNA synthesis. EdU incorporation in the HEPM cells is shown in Fig.2A. Uptake of EdU, indicative of new DNA synthesis and cell proliferation, was increased by all isoforms of TGFβ when compared with the negative control (0.5% FBS treatment only) (Fig. 2A & B). The percentages of EdU incorporation were 5.18%, 11.75% and 15.97%, with TGFβ1, TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 treatment, respectively. These values were significantly higher than the negative control, treated with 0.5% FBS (1.20%) and lower than the positive control treated with 10% FBS (21.80%). Interestingly, HEPM cells treated with full length c-Myc cDNA alone (with 0.5% FBS) for 24 h also showed increased EdU incorporation (13.55%) and increased EdU incorporation by 10% FBS can be significantly reduced (1.73%) by inhibiting c-Myc with sh-cMyc implying its unilateral (sans TGFβ) role in HEPM proliferation. These results suggest that all three isoforms of TGFβ promote DNA synthesis in HEPM cells. However, TGFβ3 had the greatest effect on cellular DNA synthesis in HEPM cells compared to TGFβ1 and 2.
Fig. 2. The Effect of TGFβ on DNA synthesis in HEPM cells.
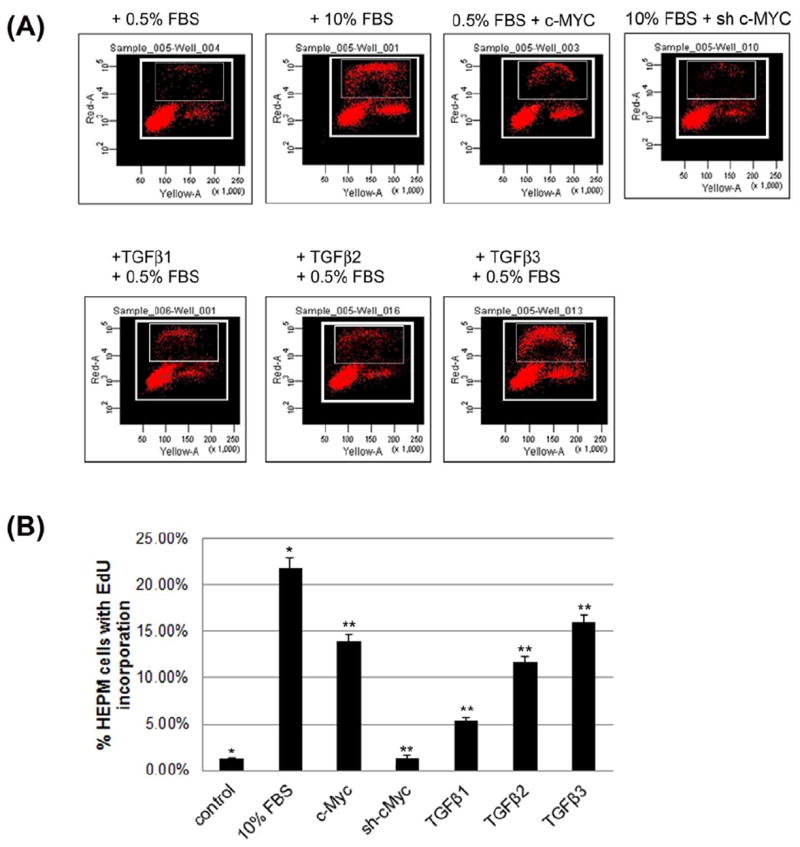
(A) To investigate the effect of TGFβ on DNA synthesis in HEPM cells, serum starved synchronized HEPM cells were treated with 10ng/ml of TGFβ1, 2 and 3 as well as transiently transfected with a full length human c-Myc cDNA, (pcDNA3.3 c-Myc) and and small hairpin RNA (shRNA) c-Myc, pRetrosuper-sh-cMyc (Addgene, MA) for 24 h followed by addition of 30μM 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine (EdU). TGFβ1, 2, 3 and c-Myc treatment stimulated cell cycle progression, measured by EdU incorporation as DNA synthesis progresses, compared to negative control (0.5% FBS). 10% FBS was used as a positive control to show stimulation of DNA synthesis. TGFβ3 had the greatest effect on EdU incorporation compared to TGFβ1 and 2. (B) The percentage of cells incorporated with EdU was measured and values were presented as means ±SD from at least three measurements. Using BD Biosciences FACSArray, a significant proportion of cells were found to occupy distinct cell cycle phases including G0/G1, S, and G2/M within the selected boxed region. Larger boxed region identifies all proliferating cells as determined by their levels of DNA synthesis as assessed by PI within the G0/G, S and G2/M phases of the cycle. The smaller inset box includes the cells that are incorporated with EdU or S phase cells. Here, we only show the cells that are EdU positive cells in the S phase. A p-value of ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. The one-way ANOVA indicated that the values differ significantly across the treatment groups. All three TGFβ treatment groups and c-Myc also differed significantly from the positive (10% FBS) and negative (0.5% FBS) control groups, (p ≤ 001, as indicated by **, while between the controls, the different was also significant p≤0001, as indicated by *).
TGFβ promotes cell cycle progression and cell cycle protein expression
Synchronized HEPM cells, serum starved for 24 hours, were treated with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10 ng/ml) +/- full length c-Myc cDNA and +/- pRetrosuper-sh-cMyc for an additional 24 h with 0.5% and/or 10% FBS to demonstrate the effect of TGFβ on cell cycle distribution, as measured by DNA content with propidium iodide (PI). TGFβ treatment enhanced HEPM cell cycle progression, as shown by the reduction in the number of cells remaining in G0/G1 and the subsequent increase in the number of cells in S and G2/M compared with the negative control (0.5% FBS) (Fig. 3A). The percentage of HEPM cells in the negative control (0.5% FBS) was 91.67% in G0/G1, 2.13% in S and 4.92% in G2/M. The HEPM cells in the positive control (10% FBS) were at 57.77% in G0/G1, 7.17% in S and 33.21% in G2/M. A significant (p ≤ 0.05) increase in the number of cells was seen in S phase and G2/M while the number of cells in G0/G1 was reduced in TGFβ treated cells as compared to the negative control cells. HEPM cells treated with TGFβ1 resulted in approximately 86.07% of the cells in the G0/G1 phase, 4.67% in S and 7.33% in the G2/M phases (Fig. 3B). TGFβ2 treatment resulted in approximately 76.47% of the cells in the G0/G1 phase and 9.9% in S and 10.67% in the G2/M phases (Fig 3B). When compared with all three isoforms of TGFβ, TGFβ3 treatment induced the highest progression through the cell cycle with 66.19% of the cells in the G0/G1 phase, 8.51% in S and 23.93% in the G2/M phases. Treatment with full length c-Myc cDNA alone (with 0.5% FBS) for 24 h also stimulated cell cycle progression (76.21% of the cells were in the G0/G1 phase, 9.51% in S and 12.09% in the G2/M phases). The progressive cell cycle by 10% FBS can be stalled (82.22% in G0/G1, 5.13% in S and 12.45% in G2/M) by inhibiting c-Myc with sh-cMyc.
Fig 3. Induction of cell cycle progression by TGFβ.
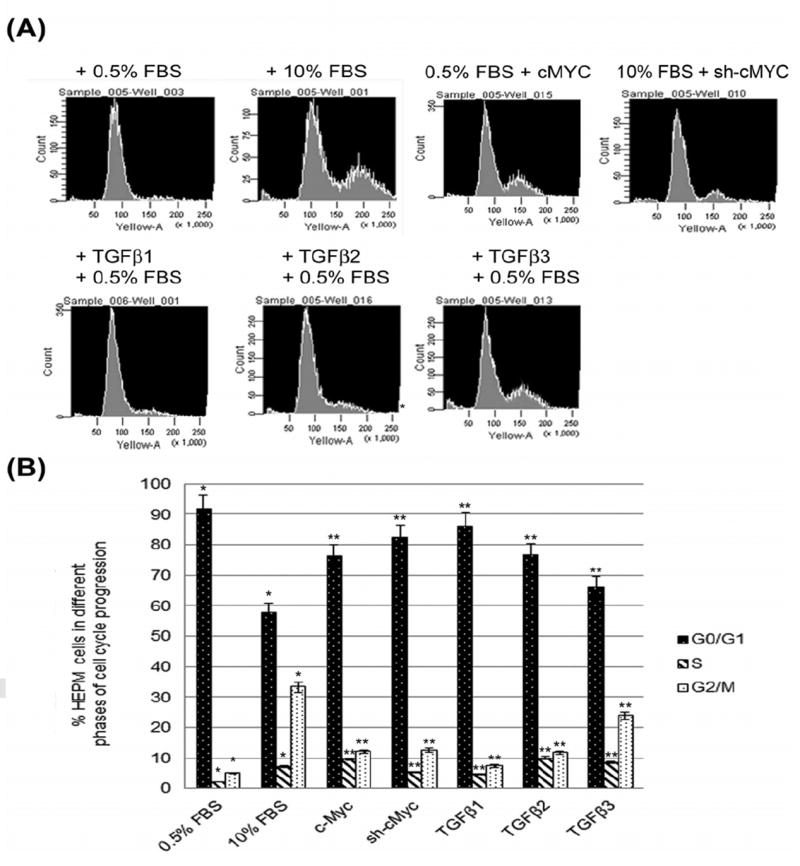
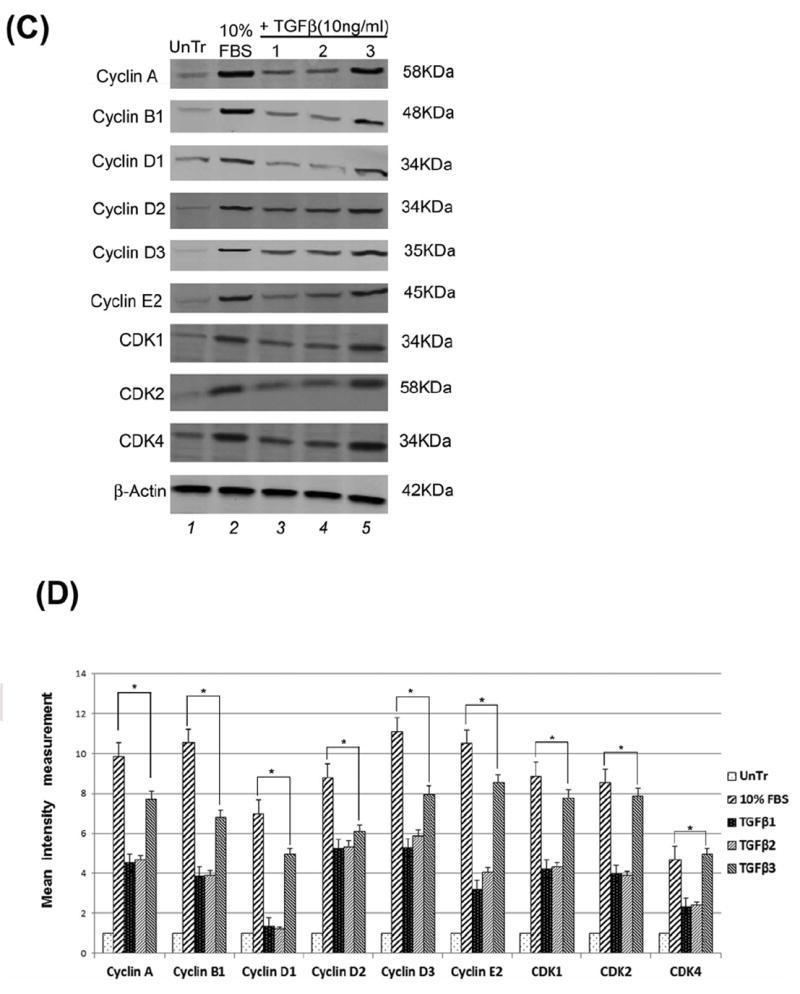
(A) DNA content and cell cycle distribution of HEPM cells treated with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/mL) and transiently transfected with a full length human c-Myc cDNA, (pcDNA3.3 c-Myc) and small hairpin RNA (shRNA) c-Myc, pRetrosuper-sh-cMyc (Addgene, MA) for 24 h, was assessed by PI staining, as described in Materials and Methods. All isoforms of TGFβ and full length c-Myc cDNA treatment enhanced HEPM cell cycle progression, as shown by the reduction in the number of G0/G1 phase cells, with a subsequent increase in the number of cells in S and G2/M compared with the negative control (0.5% FBS). (B) The percentage of HEPM cells in each phase of the cell cycle. TGFβ3 treatment induced the most progression through the cell cycle and treatment with full length c-Myc cDNA alone also stimulated cell cycle progression. A p-value of ≤ 0.05 was considered significant. The one-way ANOVA indicated that the values differ significantly across the treatment groups. All three TGFβ treatment groups and c-Myc cDNA/sh treatments of cell cycle stages differed significantly from the positive control (10% FBS) and negative control (0.5%) groups, (p ≤ 0001, as indicated by *) (C) Western blot analysis of the expression of cell cycle related proteins (Cyclins and CDKs) in HEPM cells in response to TGFβ. TGFβ1, 2 and 3 induced higher expression of the cell-cycle regulatory proteins: cyclin A, cyclin B1, cyclin D1, cyclin D2, cyclin D3, cyclin E2, CDK1, CDK2 and CDK4 when compared with negative control (0.5% FBS). TGFβ3 treatment generated the maximum stimulatory effect on cell cycle proteins compared to TGFβ1 and 2. (D) Results from the blots and the intensity of the bands were measured using the Carestream Molecular Imaging Software version 5.3.1 (Rochester, NY). To perform a t-test analysis of mean intensity measurements, a ROI analysis was done from the data to Microsoft Excel software. Data points for all samples are paired by spatial arrangement on gel and compared pairwise to minimize the impact of subtle background artifacts on image analysis. All three TGFβ treatment groups and c-Myc also differed significantly from the positive (10% FBS) and negative (0.5% FBS) control groups, (p ≤ 001, as indicated by **, while between the controls, the different was also significant p≤ 0001, as indicated by *).
These results suggest that TGFβ as well as exogenous c-Myc treatment by itself can induce progression of successive cell cycles in HEPM cells. Similar to our other findings, TGFβ3 had the greatest effect on cell cycle progression compared to the other isoforms. This suggests that TGFβ3 is more important for proliferation of HEPM cells. Moreover, TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 (10ng/ml) treatment increased the protein expression level of the cell cycle related proteins, cyclins (A, B1, D1, D2, D3 and E2) and CDKs (1, 2 and 4) compared to untreated control cells (0.5% FBS without TGFβ). Among all three isoforms of TGFβ, TGFβ3 stimulated higher expression of the cyclins and CDKs compared to TGFβ1 and 2 (Fig. 3C). Results from the blots and the intensity of the bands were measured using the Carestream Molecular Imaging Software version 5.3.1 (Rochester, NY). To perform a t-test analysis of mean intensity measurements, a ROI analysis was done from the data to Microsoft Excel software. Data points for all samples are paired by spatial arrangement on gel and compared pairwise to minimize the impact of subtle background artifacts on image analysis (Fig, 3D).
TGFβ isoforms activate both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent signaling pathways in HEPM cells
When compared to untreated control cells, phospho (p) Smad2 expression was significantly upregulated both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm of HEPM cells after treatment with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/mL). TGFβ treatment (30 min) resulted in the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Smad2 in HEPM cells when compared to untreated (0.5% FBS) cells, which showed no nuclear expression of pSmad2 and very limited pSmad2 in the cytoplasm. TGFβ3 treatment induced the highest level of pSmad2 expression compared to the other TGFβ isoforms (Fig. 4A). Smad2 showed limited expression in both cytoplasm and the nucleus with no difference in its expression in TGFβ treated and untreated cells. While Smad4 was strongly expressed in both cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts following all isoforms of TGFβ treatments, however, Smad3 showed very limited cytoplasmic and no nuclear expression in both treated and untreated cells. Unlike, pSmad2, pSmad3 did not show any expression (data not shown). Similarly, immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that TGFβ3 treatment for 30 min compared to control, resulted in the nuclear translocation of pSmad2 (Fig. 4Bii and Fig. 4Bi, respectively) and Smad4 (Fig. 4Biv and Fig. 4Biii, respectively), which is a clear indication of an active and functional Smad pathway. These results indicate that TGFβ activates the Smad-dependent signaling pathway in HEPM cells, with TGFβ3 producing the most pronounced effect.
Fig 4. Pathways used by TGFβ during HEPM cell proliferation.
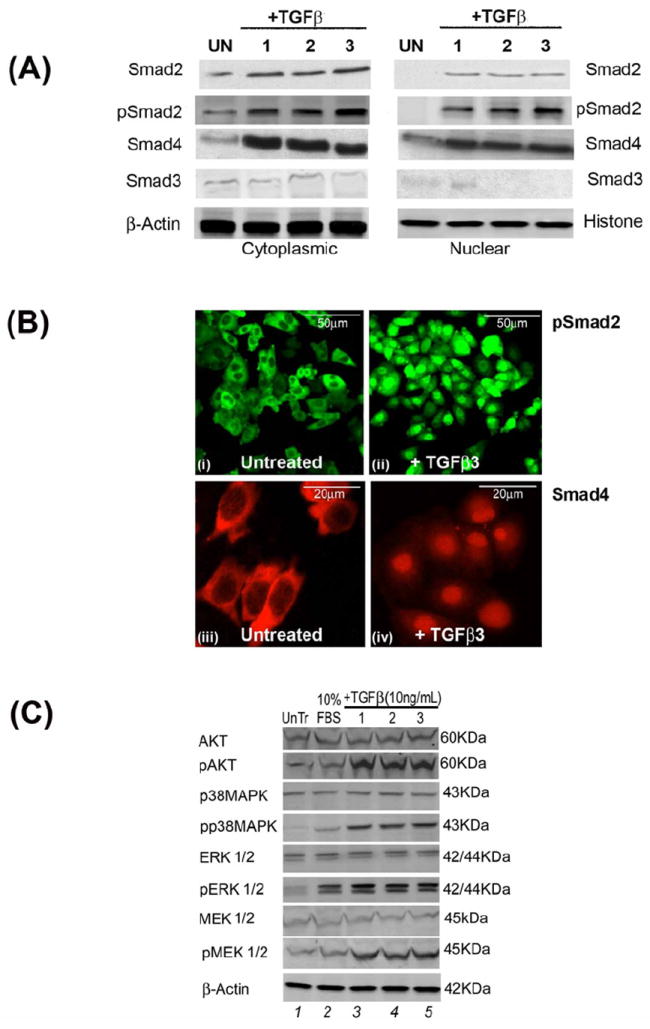
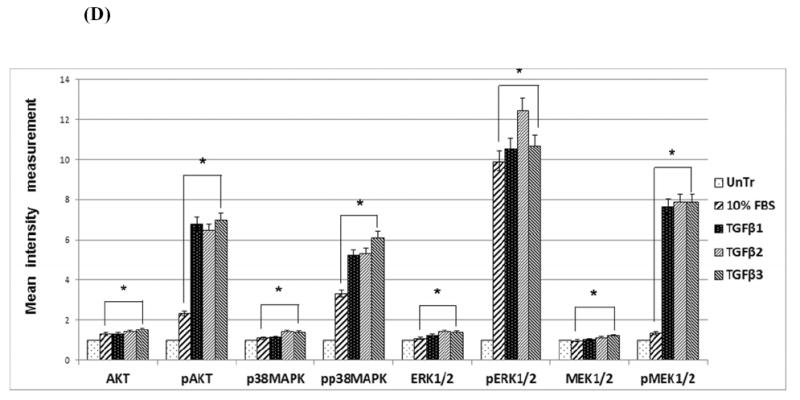
(A) To evaluate the pathways TGFβ uses to induce cell cycle progression, protein expression by Western blot analysis of phospho-Smad2, phospho-Smad3, Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4 were undertaken in both cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts. TGFβ1, 2 and 3 treatment (30 min) of HEPM cells showed an increase in phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of pSmad2 and Smad4. Smad2 was expressed in the cytoplasm but the expression was indifferent with TGFβ treatments, however, its nuclear expression was very low. Smad3 had very limited expression in the cytoplasm but no expression in the nucleus. And pSmad3 did not show any expression in any compartment of the cell in either treated or untreated cells (data not shown). Untreated control cells (0.5% FBS) showed no nuclear expression of pSmad2. TGFβ3 treatment resulted in the highest level of nuclear pSmad2 expression compared to TGFβ1 and 2. (B) Immunofluorescence expression of pSmad2 (fluorescence, green) and Smad4 (rhodamine, red) in untreated control (i and iii) (0.5% FBS) and TGFβ3 treated cells (ii and iv) showed that pSmad2 (i and ii) and Smad4 (iii and iv) translocated into the nucleus within 30 min of treatment. (C) Activation of Smad- independent pathways by TGFβ in HEPM cells. HEPM cells were treated with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 for 30 minutes and the expression levels of MAPK proteins were assessed by western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. TGFβ treatment resulted in increased expression and phosphorylation of AKT, p38MAPK, ERK and MEK which are associated with Smad-independent signaling, compared to untreated (0.5%) control HEPM cells, with TGFβ3 showing the greatest induction. (D) Results from the blots and the intensity of the bands were measured using the Carestream Molecular Imaging Software version 5.3.1 (Rochester, NY). To perform a t-test analysis of mean intensity measurements, a ROI analysis was done from the data to Microsoft Excel software. Data points for all samples are paired by spatial arrangement on gel and compared pairwise to minimize the impact of subtle background artifacts on image analysis. All three TGFβ treatment groups differed significantly from the positive control (10% FBS) groups, (p ≤ 0001, as indicated by *)
Western blot analysis of total and phosphorylated proteins was performed to determine the effects of TGFβ on Smad-independent pathways. The results (Fig. 4C) showed increased phosphorylation levels of AKT, p38MAPK, ERK1/2 and MEK1/2 by TGFβ1, 2, and 3 (10ng/mL) treatments compared to the control treatment, indicating that Smad-independent pathways were also activated by the TGFβ isoforms. 10% FBS treatment, which previously enhanced cell cycle progression and cell proliferation (as shown in Fig 2 and 3) did not phosphorylate these selected proteins, suggesting that activation of Smad-independent pathways is strictly regulated by TGFβ. The current results support the notion that TGFβ stimulates both Smad-dependent and -independent pathways, including the AKT, MAPK and ERK signaling pathways, in HEPM cells. Results from the blots and the intensity of the bands were measured using the Carestream Molecular Imaging Software version 5.3.1 (Rochester, NY)(Fig, 4D).
TGFβ3 promotes EdU uptake and cell cycle protein expression
Treatment of HEPM cells with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/mL) for 24 h, resulted in higher expression of PCNA and EdU, markers of cell proliferation. As shown in Fig. 5A, PCNA was detected with red (Rhodamine), while EdU was identified with green (Fluorescence) and DAPI staining is shown in blue in the nucleus of HEPM cells. Compared with the negative control (0.5% FBS), the number of cells taking up EdU was significantly higher upon treatment with TGFβ1, TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 (Fig. 5A). Furthermore, the cells which acquired EdU were also PCNA positive (Fig 5A). Similar to previous results, the number of EdU and PCNA co-expressing HEPM cells was highest when treated with TGFβ3, compared to TGFβ1 and 2. Western blot analysis of HEPM cells treated with TGFβ 1, 2, 3 (10ng/ml) for 24 h indicated an increase in the levels of two common cell proliferation proteins, PCNA and c-Myc, compared to the negative control (0.5% FBS), while TGFβ3 treatment stimulated higher levels of PCNA and c-Myc expression compared to the other isoforms of TGFβ (Fig. 5B). Results from the blots and the intensity of the bands were measured using the Carestream Molecular Imaging Software version 5.3.1 (Rochester, NY) (Fig, 5C).
Fig 5. TGFβ enhances HEPM cell proliferation.
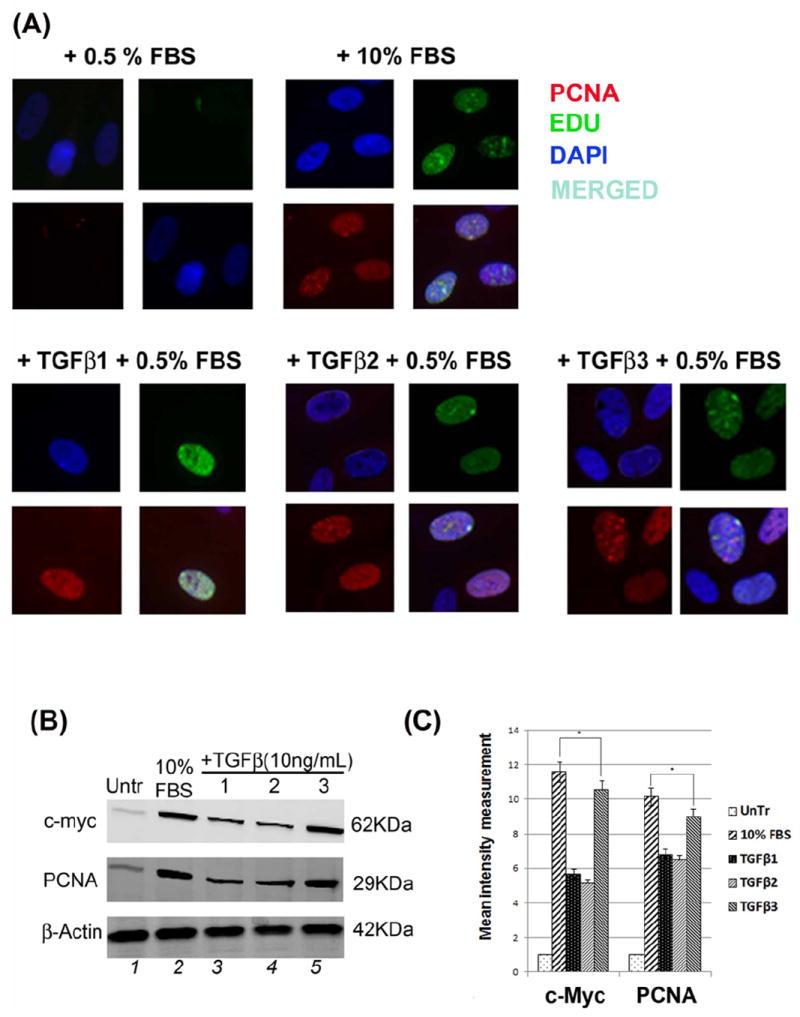
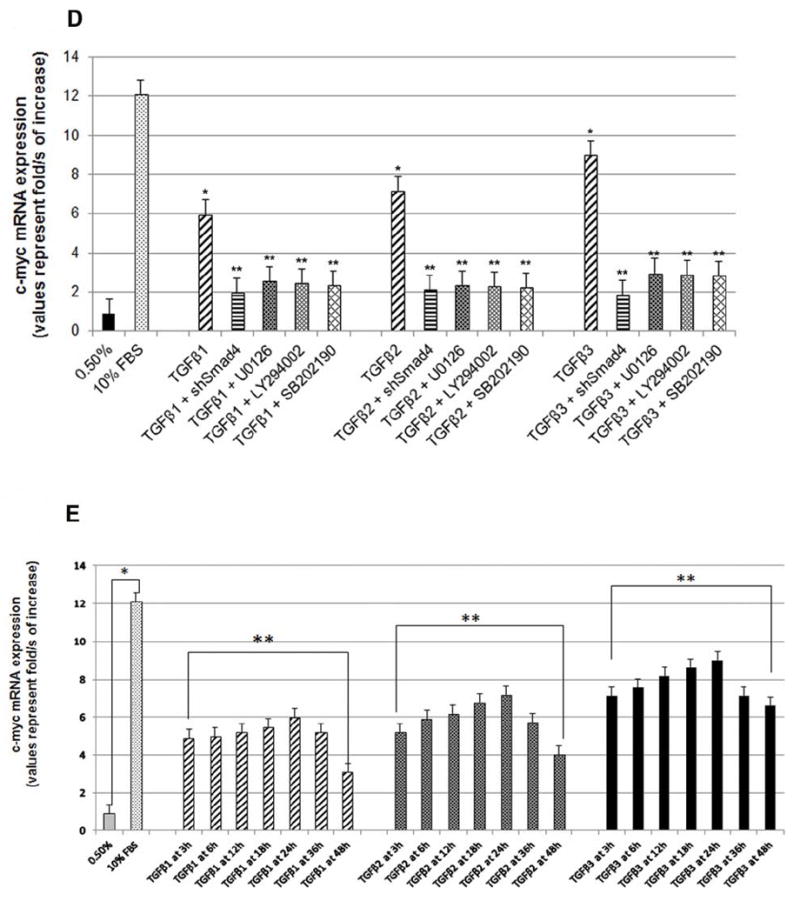
(A) HEPM cell proliferation was assessed by EdU and nuclear localization of PCNA as detected by immunofluorescence. 24 h treatment with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 increased the number and the intensity of PCNA (rhodamine, red) and EdU (fluorescence, green) expressing HEPM cells compared to negative control (0.5% FBS). Once merged with DAPI (blue), HEPM cells treated with TGFβ3 showed increased numbers of cells with colocalization of PCNA and EdU in the nucleus when compared to negative control as well as other isoforms of TGFβ. (B) The effect of TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 on the levels of PCNA and c-Myc proteins. Western blot analysis showed an increase in the levels of PCNA and c-Myc proteins in TGFβ treated (24 h) HEPM cells when compared with negative control (0.5% FBS), TGFβ3 having the highest protein expression compared to TGFβ1 and 2 (C) Results from the blots and the intensity of the bands were measured using the Carestream Molecular Imaging Software version 5.3.1 (Rochester, NY). To perform a t-test analysis of mean intensity measurements, a ROI analysis was done from the data to Microsoft Excel software. Data points for all samples are paired by spatial arrangement on gel and compared pairwise to minimize the impact of subtle background artifacts on image analysis. All three TGFβ treatment groups differed significantly from the positive control (10% FBS) groups, (p ≤ 0001, as indicated by *). (D) Regulation of c-Myc mRNA by TGFβ. c-Myc mRNA expression was determined by real-time PCR in TGFβ1, 2 and 3 treated (24h) HEPM cells. TGFβ treated cells had higher c-Myc mRNA expression levels compared to the negative control (0.5% FBS). The change in mRNA levels was determined by comparison to control (0.5% FBS) and plotted as fold change/s (mean ± s.d.; n=3; *P<0.005 compared with controls; **P <0.05 compared with TGFβ treatments with different inhibitors). When compared to control (x0.9), TGFβ1 (x6.63), TGFβ2 (x7.97), and TGFβ3 (x10.01) had higher c-Myc mRNA levels. To establish the pathways TGFβ uses to induce c-Myc mRNA, Smad-dependent pathways were blocked by shRNASmad4 (pRetrosuper-shSmad4) for 24 h and Smad-independent pathways were blocked using commercially available small synthetic chemical inhibitors for 60 minutes: SB202190 (20μM), an inhibitor of ERK1/2; U0126 (20μM), an inhibitor of MEK1/2; and LY294002 (20μM), an inhibitor of PI3 Kinase. Following all inhibitions (pRetrosuper-shSmad4 and chemical inhibitors) TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 (10ng/mL) were added in the presence of these molecules for another 24 h to sustain the effect of inhibition throughout the TGFβ induction phase, after which mRNA was extracted. TGFβ stimulated c-Myc mRNA expression fell more than 50% of its value (compared to uninhibited TGFβ1, 2 and 3 values) when both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways were inhibited. (E) Regulation of c-Myc mRNA by TGFβ in time dependent fashion. c-Myc mRNA expression was determined by real-time PCR in TGFβ1, 2 and 3 treated (3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 36 and 48 h) HEPM cells. TGFβ treated cells had higher c-Myc mRNA expression levels compared to the negative control (0.5% FBS). The change in mRNA levels was determined by comparison to control (0.5% FBS) and plotted as fold change/s (mean ± s.d.; n=3; *P<0.005 compared with controls; **P <0.05 compared with TGFβ treatments. When compared to control (x0.9), TGFβ1 (x6.63), TGFβ2 (x7.97), and TGFβ3 (x10.01) had higher c-Myc mRNA levels and the trend shows that the c-Myc mRNA expression remain stable and reach a peak at 24 h after which the expression decreases by 48 h.
In order to assess the pathways that TGFβ utilizes to activate c-Myc protein expression, HEPM cells were treated with exogenous TGFβ (10ng/mL) and mRNA was collected at 24 h. The Smad pathway was blocked by treating the HEPM cells with shSmad4 for 24 h, and the Smad-independent pathways were blocked using small synthetic chemical inhibitors (LY294002 for PI3 Kinase, SB202190 for ERK1/2 and U0126 for MEK1/2) for 60 min in order to delineate the precise signaling molecules required for TGFβ induced c-Myc expression. In this experiment, we demonstrated that c-Myc mRNA is significantly increased in response to all TGFβ isoforms when compared to the negative control (0.5% FBS treatment). However, TGFβ3 induced the highest level of c-Myc mRNA when compared to TGFβ1 and 2. Moreover, c-Myc expression was inhibited when the Smad-dependent pathway was blocked with shSmad4. We also observed that the TGFβ induced mRNA expression of c-Myc was repressed when the Smad-independent pathways were blocked. The data support the hypothesis that TGFβ uses both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways to induce c-Myc mRNA levels, as inhibition of these pathways significantly reduce c-Myc mRNA expression (Fig.5D). To confirm the overall c-Myc mRNA expression in time dependent fashion, our results show that c-Myc mRNA levels remain gradually increases from 3h reaching the peak at 24 h after which the mRNA levels deceases by 48 h, following TGFβ 1, 2 or 3 treatments (Fig 5E). Gene expression was determined by normalization with the control gene GAPDH. These results indicate that c-Myc is a possible downstream TGFβ-inducible gene associated with HEPM cell proliferation.
c-Myc promoter activity and Smad binding elements
From earlier studies [Frederick et al., 2004; Lim and Hoffmann, 2006; Singh et al., 2010], it has been shown that c-Myc has several potential Smad Binding Elements (SBEs), namely TBE1, TBE2 and TIE. A schematic diagram of the 2.5kb c-Myc promoter showing the three potential SBEs is shown in Figure 6A.
Fig. 6. TGFβ induces c-Myc gene activity by stimulating Smad promoter binding.
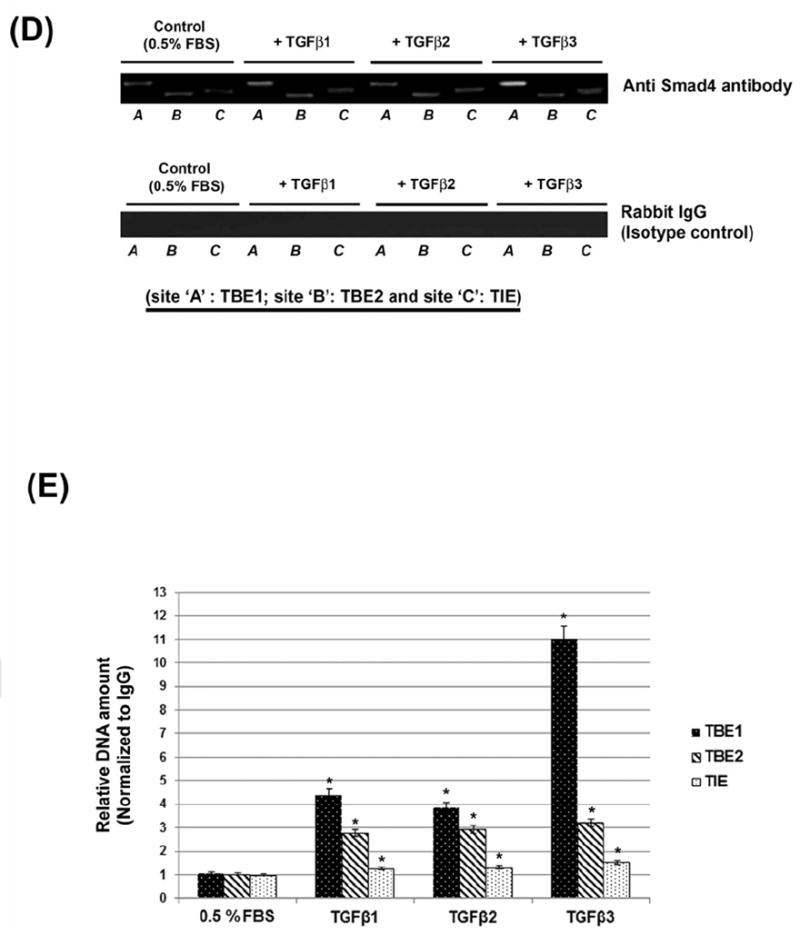
(A) Schematic diagram of the human c-Myc promoter, ~2.5 kb, based on previous studies [Frederick et al., 2004; Lim and Hoffmann, 2006; Singh et al., 2010] showing potential Smad Binding Elements (SBE) to TBE1, TBE2 and TIE. These are predicted SBE and nucleotide positions are shown under the respective box diagram. (B) HEPM cells were transiently transfected with the c-Myc promoter: pBV-Luc-DEL1 (WT, with intact TBE1, TBE2 and TIE sites) and deletion constructs: pBV-Luc-DEL3 (without TBE1, but with intact TBE2 and TIE) and pBV-Luc-DEL4 (without TBE1 and TBE2 but with intact TIE). After transfection, the cells were incubated with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/ml) for 24 h. TGFβ1, 2 and 3 increase c-Myc promoter activity by ~16, ~17 and ~23 fold, respectively, in HEPM cells. The TGFβ effect is Smad-dependent, since the plasmids containing deletions of the TBE1 site did not increase luciferase activity. Luciferase data shows that c-Myc gene activity is significantly repressed when the TBE1 region +/- TBE2 are absent. (C) HEPM cells were transiently transfected with the human c-Myc promoter (2500bp; pBV-Luc-Myc-WT plasmid) harboring all presumed SBEs or derivative plasmids containing mutations in the SBEs, namely TBE1 (pBV-Luc-TBE1mut) or TBE2 (pBV-Luc-TBE2mut) or both sites (pBV-Luc-TBE1/2mut). Following TGFβ1, 2 and 3 treatment for 24 h, a substantial decrease in c-Myc luciferase levels was observed (80% or more) with TBE1 and TBE1/TBE2 mutation. Mutation of TBE2 demonstrated no significant decrease (4% or less). Background luciferase activity (empty vector) was subtracted from all data. Error bars indicate standard deviation of three independent preparations. (D) Chromatin was isolated from TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/ml) or 0.5% FBS treated HEPM cells, immunoprecipitated with anti-Smad4 antibody (overnight) and analyzed by RT PCR with primers recognizing TBE1, TBE2 and TIE Smad binding elements in the c-Myc promoter. All TGFβ isoforms increase binding of Smad4 with TBE1 (but not to TIE and significantly less to TBE2) with TGFβ3 showing the most significant effect (p ≤ 0.005 as indicated by *). Primers recognizing TBE1 binding elements display higher efficiency than primers specific for TBE2 and TIE. (E) The PCR products were also analyzed by quantitative real-time. Serial dilutions of pGL3-cMyc wild type plasmid were used as quantitative standards. The results are shown as a mean ± SD obtained from three independent chromatin preparations (p ≤ 0.005 as indicated by *), For Input control for quantitative real-time PCR of immunoprecipitated chromatin, chromatin was isolated as described in D and analyzed by quantitative PCR with primers recognizing TBE1, TBE2 and TIE Smad4 binding elements in c-Myc promoter with DNA standards described in D. Primers recognizing Smad4 binding elements on TBE2 display higher efficiency than primers specific for other SBE, however statistically significant differences between TGFβ1, 2 and 3-treated or untreated samples. (p ≤ 0.005 as indicated by *), Error bars show the standard deviation of three independent chromatin preparations.
The effect of TGFβ1, 2 and 3 on c-Myc promoter activity was explored by transfecting HEPM cells with the pBV-Luc plasmid containing the human c-Myc promoter (2500bp; pBV-Luc-DEL1-WT, with intact TBE1, TBE2 and TIE sites) or c-Myc promoter region deletion constructs: pBV-Luc-DEL3 (without TBE1, but with intact TBE2 and TIE), and pBV-Luc-DEL4 (without TBE1 and TBE2 but with intact TIE). Additionally, we used derivative plasmids containing mutations in the TBE1 (pBV-Luc-TBE1mut) or TBE2 (pBV-Luc-TBE2mut) or both sites (pBV-Luc-TBE1/2mut). The transfected cells were treated with TGFβ1, 2 and 3 (10ng/ml) for 24h, and luciferase assays demonstrated increased transactivation of the c-Myc promoter in response to all isoforms of TGFβ (Fig. 6B; pBV-Luc-DEL1-WT). Treatment with 10ng/ml of TGFβ1 resulted in an approximate 15-fold increase of luciferase activity in cells transfected by pBV-Luc-DEL1-WT compared with an empty vector (control), whereas c-Myc gene activity increased by approximately 18 and 25 fold in response to TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 respectively, attesting that TGFβ3 is more potent in activating the c-Myc promoter compared to TGFβ1 and 2. However, deletions in the SBE in the c-Myc promoter, pBV-Luc-DEL3 and pBV-Luc-DEL4, dramatically reduced the TGFβ transactivation effect (Fig. 6B), with no differences observed in c-Myc activation between TBE1 and TBE1/2 (both with an intact TIE region). When the TBE1 region was mutated either by itself (pBV-Luc-TBE1mut) or with TBE2 (pBV-Luc-TBE1/2mut), c-Myc gene activity was reduced significantly (Fig. 6C). However, the mutation on TBE2 (pBV-Luc-TBE2mut) had no effect on c-Myc gene activity. These data suggest that only TBE1 is important for TGFβ induced c-Myc gene activity in the HEPM cells, since mutation in this (TBE1) region drastically reduced the effect of TGFβ on c-Myc promoter activity.
Since the SBEs are functional and important in the activation of the c-Myc promoter, as shown in Figure 6A, we wanted to identify if these SBEs harbor Smad proteins on the c-Myc promoter. We performed the chromatin immunoprecipitation assay to determine if Smad4 was bound to the SBEs (TBE1, TBE2 and TIE). The agarose gel RT-PCR analysis of the chromatin immunoprecipitated with anti-Smad4 antibody from TGFβ1, 2 and 3 treated or untreated cells displayed that TBE1 site is strongly bound to Smad4 protein, when compared to other potential bindings sites (TBE2 and TIE) (Fig. 6D, upper panel). However, amongst the TGFβ isoforms, it is TGFβ3 that showed highest binding to the TBE1. The specificity of the bindings was confirmed by the positive (Histone H3, data not shown) and negative (Rabbit Ig G) controls (Fig. 6D, lower panel). The real-time PCR (RT-PCR) analysis of the chromatin immunoprecipitated with the anti-Smad4 antibody from TGFβ1, 2 and 3 treated cells displayed selective binding of Smad4 protein to only the TBE1 site (Fig. 6E). Compared to immunoprecipitated chromatin from the same cells (input control IgG), these results were statistically significant. The specificity of the binding was confirmed by the positive (Histone H3, and negative (Rabbit Ig G) controls (Fig. 6D). We found that when compared to TGFβ1 and 2, TGFβ3 significantly increased binding of Smad4 to the TBE1 in the c-Myc promoter. The differences in response to TGFβ isoforms are significant as there are no statistically significant differences between treated and control samples in non-IP chromatin. This data, combined with the observation that mutation of TBE1 decreased luciferase expression by the greatest fold (Fig. 6C), suggests that TBE1 is the most important region in the c-Myc promoter for Smad4 mediated transactivation induced by TGFβ signaling.
DISCUSSION
Non-syndromic (without other associated abnormalities) cleft lip and/or palate (NS-CLP) is a common congenital anomaly affecting approximately 1:700 births worldwide [Jugessur and Murray, 2005]. A variety of factors, including environmental, teratological and genetic abnormalities, have been implicated in the development of NS-CLP. In mice, the TGFβ family has been shown to be essential for normal palatogenesis, implying that the absence of TGFβ isoforms might contribute to the development of cleft palate. The role of the three isoforms of TGFβ in palatogenesis were studied earlier using mutant mice models [Cui et al., 2003; Fitzpatrick et al., 1990; Gehris et al., 1991; Gehris et al., 1994; Pelton et al., 1990a; Pelton et al., 1990b]. Results demonstrate that TGFβ1 knockout mice have abnormal hair follicle, bone, teeth and Langerhans cells in the skin [Borkowski et al., 1996; Foitzik et al., 2000; Geiser et al., 1998], and 20% of the TGFβ2 (-/-) mutant mice exhibit a complete anterior-posterior cleft palate resulting from a failure of secondary palate fusion [Dunker and Krieglstein, 2000]. In TGFβ3 (-/-) mutants, however, the palatal shelves develop normally but fail to fuse, due to a lack of midline seam disintegration, resulting in complete penetrance of the cleft palate phenotype [Proetzel et al., 1995]; [Kaartinen et al., 1995]. Furthermore, mutations in TGFβ3 have been associated with cleft palate in humans, underscoring the crucial function of TGFβ signaling in regulating palatogenesis [Lidral et al., 1998]. Decreased palatal mesenchyme cell proliferation resulted in compromised palatal shelf extension and failure of palatal fusion in TrII fl/fl mutant mice [Ito et al., 2003], suggesting a critical function of TGFβ signaling in regulating palatogenesis.
In humans with cleft birth defects, failure of palatal fusion after proper palatal adhesion only represents a small percentage of the cleft palate cases, while failure of palatal shelf extension is associated with the majority of the cleft palate cases. Moreover, all isoforms (1, 2 and 3) of the TGFβ ligand are expressed to various degrees throughout all phases of palate development. [Cui et al., 1998; Fitzpatrick et al., 1990; Gehris et al., 1991; Gehris et al., 1994; Pelton et al., 1990a; Pelton et al., 1990b]. The temporal and spatial distribution of TGFβ1, 2 and 3 RNAs, together with the knowledge of in vitro TGFβ biological activities, suggests an important role for TGFβ in palatal development. Since the majority of the cells in embryonic palatal shelves are mesenchymal, it is important to explore the proliferation and cell cycle status of these cells to understand the etiology of palatal shelf growth during palatogenesis. First, we established that the palatal shelves grow with increased cellular mesenchymal proliferation as detected by BrdU expression in the embryonic palates at 13.5 dpc in TGFβ3 WT (+/+; Fig. 1A), and homozygous (-/-; Fig. 1A) mice. This was associated with increased expression of well-established cell proliferation proteins, c-Myc (Fig. 1B), PCNA (Fig. 1C), Cyclin D (Fig. 1D) at 13.5 dpc. Similarly, both apoptotic markers such as cleaved caspase 3 (Fig. 1E) and TUNEL (Fig. 1F) were negative in the palatal mesenchyme. Our results clearly indicate an increase in palatal mesenchymal cell proliferation (assessed by number of BrdU positive cells) in the TGFβ3 WT (+/+) palates at 13.5 dpc compared to homozygous palates (-/-), supporting the notion that mice with compromised TGFβ3 have less mesenchymal cell proliferation and palatal growth. The WT palates continued to express higher levels of these cell proliferation proteins. In this study, we further our investigation to explore if the proliferation of mesenchyme (as shown in Fig. 1), is regulated by TGFβ 1, 2 and 3, since they are expressed to various degrees in the mesenchyme as reported earlier [Cui et al., 1998; Fitzpatrick et al., 1990; Gehris et al., 1991; Gehris et al., 1994; Pelton et al., 1990a; Pelton et al., 1990b].
[Linask et al., 1991] investigated the effect of TGFβ1 on mesenchymal cell proliferation by using human embryonic palate mesenchymal (HEPM) and murine embryonic palate mesenchymal (MEPM) cells. Their results revealed that TGFβ1 stimulated proliferation of HEPM cells. However, in MEPM cells, TGFβ1 inhibited cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Interestingly, contrary to TGFβ1, TGFβ3 was found to be critical for proper proliferation of the CNC-derived palatal mesenchyme [Lidral et al., 1998]. These contradictory results can be resolved by using improved reagents and newer technologies, and by inclusion of all TGFβ isoforms.
In order to investigate the roles of the three isoforms of TGFβ in cell proliferation, we used the EdU incorporation assay to assess the ability of TGFβ to promote DNA synthesis in HEPM cells (Figs. 2A and B). We demonstrated that while all isoforms of TGFβ stimulated the cell cycle to a certain degree, TGFβ3 had the greatest effect on cell cycle progression. In accord with increased DNA synthesis (Fig. 2A and B), a significantly higher percentage of HEPM cells progressed from the G1/S phase to the G2/M phase of the cell cycle in response to TGFβ treatment, as shown by flow cytometry (Fig. 3A). Results from Figs. 2 and 3, attest that TGFβ is capable of inducing DNA synthesis as well as progression through subsequent phases of the cell cycle, with TGFβ3 having the most pronounced effect.
c-Myc is a well-established oncogene whose role in cell proliferation has been demonstrated in various systems [Feng et al., 2002; Oster et al., 2002; Pelengaris and Khan, 2003; Yagi et al., 2002]. While we show that all isoforms of TGFβ are capable of inducing cell cycle progression, we also demonstrate that HEPM cell proliferation can be achieved by increasing c-Myc expression with a full length human c-Myc cDNA by itself as well as blocked by inhibiting c-Myc with sh-cMyc (Fig. 2A and 3A). The TGFβ independent increase in cell cycle progression by c-Myc alone supports the hypothesis that TGFβ may induce cell cycle progression through stimulation of the downstream oncogene, c-Myc (Fig. 4B, C and D).
The nuclear migration of PCNA is an indication of cell proliferation during the late G1 and S phases of the cell cycle [Tsurimoto, 1998]. Our immunofluorescence study demonstrated that PCNA is highly expressed in the TGFβ treated cells which are undergoing DNA synthesis, as shown by the co-expression of EdU and PCNA in the cell nucleus (Fig 5A). Once again, TGFβ3 treatment resulted in a higher number of cells coexpressing EdU and PCNA when compared to TGFβ1 and 2. Similar results were shown by immunoblotting (Fig. 5B, C), where the expression of PCNA and c-Myc in HEPM cells treated with TGFβ3 is higher than TGFβ1 and 2. This data supports the notion that while all isoforms of TGFβ can promote palatal mesenchymal cell proliferation, it is TGFβ3, rather than TGFβ1 or 2, which has the robust effect on HEPM cell proliferation. Furthermore, TGFβ3-induced proliferation may be mediated by the c-Myc oncogene, as described below.
Promotion of cell proliferation can occur from a progression of cell-cycle at a specific stage resulting from an increase in the levels and activities of various proteins that influence cell-cycle progression (i.e. cyclin D and E for G1/S phase, cyclin A for S phase, cyclin A and B for G2/M phase) [Iordanskaia and Nawshad, 2011; Sherr, 2000; Vigneron et al., 2006; Yam et al., 2002]. Our flow cytometry data demonstrated that HEPM cells undergo cell cycle progression upon treatment with TGFβ 1, 2 and 3 (Fig. 3A and B), with TGFβ3 having the most pronounced effect on HEPM cell cycle progression. Furthermore, TGFβ1, 2 and 3 can also promote the expression of proteins that regulate cell cycle checkpoints (Fig 3C). Similar to previous results, TGFβ3 induced cell cycle protein expression more than TGFβ1 and 2. Progression through the first phase of cell cycle, G1, requires cyclin D/CDK4 or 6 and cyclin E/CDK2 activity. The levels of cyclin E/ CDK2 are highest during the G1/S transition and decline on entry into S-phase [Sherr, 2000]. Our immunoblot analysis demonstrated that cyclin D, CDK4, cyclin E and CDK2 were significantly upregulated after TGFβ treatment compared to control (Fig, 3C). These results support the flow cytometry data (Fig. 3A), that shows following TGFβ treatment, HEPM cells progress from G0/G1 to S phase. Cyclin A/CDK2 activity is essential in S-phase not only to enhance the activity of DNA polymerase [Bashir et al., 2000], but also to limit the number of DNA replications to one per cycle [Yam et al., 2002]. In this study (Fig. 3C), expression of cyclin A and CDK2 proteins are also increased as HEPM cells undergo TGFβ induced S phase progression (Fig. 3A). The activity of cyclin A/CDK1 and cyclin B/CDK1 are important in G2/M phases [Yam et al., 2002], and our results demonstrate that Cyclin A, Cyclin B and CDK1 protein levels are upregulated (Fig 3C) to promote G2/M phase progression, as shown in Fig. 3A. In brief, our results demonstrate that TGFβ has an effect on HEPM cell cycle that is in accordance to chronological progression through different phases of cell cycle.
It is well established that TGFβ can signal using either Smad-dependent or Smad-independent pathways, or both [Hornberg et al., 2005; Khalil, 1999; Massague and Wotton, 2000; Moses and Serra, 1996]. Therefore, we assumed that TGFβ might activate these pathways during HEPM cell proliferation. Our data reveal that TGFβ stimulates Smad2 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of both Smad2 and Smad4 during HEPM cell proliferation (Fig 4A and B). Smad 3, on the contrary, is not activated by TGFβ, as it is expressed in a very low amount in both treated and untreated cells in the cytoplasm and showed no expression in the nucleus. pSmad3 was not detected in either chamber of the HEPM cells in TGFβ treated or untreated conditions. Since these events are indicators of active and functional Smad dependent TGFβ signaling [Abdollah et al., 1997], therefore, we conclude that Smad2/Smad4 are functional regulator of Smad pathway. TGFβ is also known to signal by activating pathways independent of the Smads [Bodart, 2010], such as the MAP kinase kinase kinase cascade (MAPKKK, MEKK, MAPK). Activation of ERK and p38 MAPK pathways are known to be induced by TGFβ in different cell types [Axmann et al., 1998; Frey and Mulder, 1997; Hartsough and Mulder, 1995; Mucsi et al., 1996]. And TGFβ integrates these signals to modulate many aspects of cellular functions such as cell cycle, survival, differentiation and cell migration [Axmann et al., 1998; Goldberg et al., 2002; Hartsough and Mulder, 1995; Hornberg et al., 2005; Mulder, 2000; Rubinfeld and Seger, 2005; Wang et al., 2002; Yue and Mulder, 2000]. The role of the MAPK/ERK cascade in spindle formation and the G2/M transition has been confirmed in somatic cells [Horne and Guadagno, 2003; Roberts, 2002; Roberts et al., 2006].
In the present study, we have demonstrated that in HEPM cells, TGFβ activates the MAP kinases, ERK and p38MAPK. Similarly, our results show that TGFβ induces HEPM cell proliferation through the MAPK/ERK pathway, resulting in ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Additionally, AKT, p38MAPK and MEK1/2 were also phosphorylated within 30 minutes after stimulation with the TGFβ isoforms. Once again, TGFβ3 induced higher phosphorylation compared to TGFβ1 or 2. These results indicate that Smad-independent signaling pathways are involved in TGFβ stimulated HEPM cell proliferation (Fig 4 C and D). Additionally, when these pathways were blocked by inhibiting Smad4 and/or PI3Kinase, ERK1/2 and MEK1/2, the downstream TGFβ effector, c-Myc, failed to effectively induce cell proliferation (Fig. 5D). These combined results indicate that TGFβ signals via both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in HEPM cells, resulting in stimulation of c-Myc.
The c-Myc proto-oncogene encodes a multifunctional transcription factor that plays a critical role in a broad range of cellular processes, including the regulation of cell cycle progression, cell growth, differentiation, transformation and apoptosis [Eisenman, 2001; Oster et al., 2002] For example, the c-Myc/Max heterodimeric complex has been shown to promote cell proliferation by activating cyclins (cyclin D1, cyclin D2, cyclin E1, cyclin A2) and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK4) that are required for cell-cycle progression [Pelengaris and Khan, 2003]. TGFβ is known to regulate the fate of multipotential progenitor cells instructively, by regulating the expression or function of tissue-specific transcription factors [Moses and Serra, 1996]. For example, Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) upregulates the expression of c-Myc and affects cell proliferation by stimulating DNA synthesis in embryonic hamster palate mesenchymal cells (HPMC) [Izadnegahdar et al., 1999]. Our data demonstrate that c-Myc expression was significantly upregulated in response to TGFβ signaling in HEPM cells (Fig. 5B, C). Moreover, we demonstrate that induction of c-Myc mRNA expression occurs upon activation of Smad4, PI3K, MEK1/2 and ERK1/2 (Fig. 4A, B, C & D). These results confirm that c-Myc is a downstream effector of both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent TGFβ pathways and that TGFβ stimulated HEPM cell proliferation and cell cycle progression is dependent on the availability of c-Myc (Fig. 2A and 3A) induced by TGFβ (Fig. 5B).
Studies showed that multiple factors, including Smads, bind to different DNA elements of the c-Myc promoter to mediate TGFβ-induced gene expression [Frederick et al., 2004; Lim and Hoffmann, 2006; Singh et al., 2010]. These studies have found three probable SBEs, located in the region between -359 and -329 bp and between -95 and 46bps of the c-Myc promoter. Based on these findings, we predicted that Smad-dependent transcriptional regulation is mediated by these SBEs, which might suggest that c-Myc is a direct down-stream TGFβ target.
Our experiments into gene activity using luciferase assays in HEPM cells transfected with the human c-Myc promoter contained in the pBV-Luc-Myc-WT plasmid, demonstrated that TGFβ3 stimulated c-Myc gene activity to the greatest extent, compared to TGFβ1 and 2 (Fig. 6B and C). The three probable SBEs (TBE1, TBE2 and TIE) have variable roles in c-Myc gene activity, since deletion or mutation of these sites (Fig. 6 B and C) significantly affected c-Myc gene activity in TGFβ1, 2 and 3 treated HEPM cells. Deletion of TBE1 had the most pronounced effect on c-Myc gene activity, as deletion of both TBE1 and TBE2 had the same effect as deletion of TBE1 alone. (Fig. 6B). Moreover, we demonstrated that c-Myc gene activity is significantly lower when the TBE1 site is mutated compared to mutation of the TBE2 site (Fig. 6C). Our data also indicates that TGFβ mediates its effect on c-Myc via binding of Smad to the promoter region. Analysis of Smad binding with the SBEs in the c-Myc promoter showed that Smad4 binds to the TBE1 element (Fig. 6D and E), particularly when cells are activated with TGFβ1, 2 and 3. While TGFβ1 and TGFβ2 increased binding of Smad4 protein with the TBE1 site of c-Myc promoter, the effect of TGFβ3 was significantly greater (Fig. 6D and E), as shown by higher levels of immunoprecipiated DNA, indicating that activated Smad4, in response to TGFβ, binds to the TBE1 site (Fig. 6D and E). These results correlate with TGFβ3’s more pronounced effect on c-Myc gene activity, and mRNA and protein expression (Figs. 6B, C and Figs.1E, 5B, C).
In conclusion, our results support the hypothesis that the three isoforms of TGFβ (1, 2 and 3) in the palate are involved in palatal shelf growth by activating cell proliferation in HEPM cells. Moreover, these studies have confirmed that TGFβ uses both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways during the induction of the HEPM cell cycle. Among the three isoforms of TGFβ, TGFβ3 has the greatest effect on HEPM cell proliferation and expression of cell-cycle regulatory proteins by inducing c-Myc. It is not evident which isoform is the primary functional protein in vivo, but some research groups suggested a functional connection between TGFβ1 and TGFβ3 during development based on a shared mechanism of activation [Mu et al., 2008; Yang and Kaartinen, 2007]. Since the expression of TGFβ1, 2 and 3 are variable in different phases of palate development, it is likely that the induction of mesenchyme proliferation in vivo is facilitated by all isoforms of TGFβ in order to facilitate a higher degree of palatal growth. Palatal mesenchymal growth is a highly conserved, fundamental process that governs morphogenesis in development. Palatal shelf growth does not cease when two opposite shelves meet in the midline to form a seam. As the face continues to grow, the newly unified single palatal shelf continues to grow as well. Therefore, it is likely that TGFβ isoforms continue to play diverse roles throughout development, continuously switching from one isoform to another, as well as from one morphological function to another, such as palatal cell death or EMT. The key to understanding mesenchymal cell proliferation lies not only in the instructions that the HEPM cells possess, but also within the local microenvironment. In this study, for the first time, we suggest that induction of the cell cycle is a key phase that takes place during palatal growth, and induction of c-Myc expression by TGFβ is a key event in palatal growth. Without TGFβ dependent c-Myc induction, palatal growth and further stages of palatogenesis cannot proceed. We further conclude that while all isoforms of TGFβ have distinct functions in palatal cells, mesenchyme and epithelium, it is TGFβ3 that has the most pronounced effect on mesenchymal cell proliferation during palatogenesis.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Aimin Peng and Jason Glanzer for their valuable suggestions and technique advice. This research is supported by NIDCR, NIH grant (R01DE017986) to Dr. Ali Nawshad.
List of abbreviations and acronyms
- TGFβ
Transforming Growth Factor β
- HEPM
Human Embryonic Palatal Mesenchyme
- EdU
5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine
- PCNA
Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen
- CDK
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase
- MAPK
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
- Erk
Extracellular-regulated kinase
Footnotes
This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as an “Accepted Article,” doi: 10.1002/jcb.24184
References
- Abdollah S, Macias-Silva M, Tsukazaki T, Hayashi H, Attisano L, Wrana JL. TbetaRI phosphorylation of Smad2 on Ser465 and Ser467 is required for Smad2-Smad4 complex formation and signaling. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:27678–85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.44.27678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S, Liu CC, Nawshad A. Mechanisms of palatal epithelial seam disintegration by transforming growth factor (TGF) beta3. Dev Biol. 2007;309:193–207. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.06.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axmann A, Seidel D, Reimann T, Hempel U, Wenzel KW. Transforming growth factor-beta1-induced activation of the Raf-MEK-MAPK signaling pathway in rat lung fibroblasts via a PKC-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;249:456–60. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses HL, Arteaga CL. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36803–10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005912200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashir T, Horlein R, Rommelaere J, Willwand K. Cyclin A activates the DNA polymerase delta -dependent elongation machinery in vitro: A parvovirus DNA replication model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:5522–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.090485297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierie B, Moses HL. Tumour microenvironment: TGFbeta: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:506–20. doi: 10.1038/nrc1926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodart JF. Extracellular-regulated kinase-mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade: unsolved issues. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109:850–7. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski TA, Letterio JJ, Farr AG, Udey MC. A role for endogenous transforming growth factor beta 1 in Langerhans cell biology: the skin of transforming growth factor beta 1 null mice is devoid of epidermal Langerhans cells. J Exp Med. 1996;184:2417–22. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.6.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdett DN, Waterfield JD, Shah RM. Vertical development of the secondary palate in hamster embryos following exposure to 6-mercaptopurine. Teratology. 1988;37:591–7. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420370608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carette MJ, Ferguson MW. The fate of medial edge epithelial cells during palatal fusion in vitro: an analysis by DiI labelling and confocal microscopy. Development. 1992;114:379–88. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai Y, Maxson RE., Jr Recent advances in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev Dyn. 2006;235:2353–75. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui XM, Chai Y, Chen J, Yamamoto T, Ito Y, Bringas P, Shuler CF. TGF-beta3-dependent SMAD2 phosphorylation and inhibition of MEE proliferation during palatal fusion. Dev Dyn. 2003;227:387–94. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui XM, Warburton D, Zhao J, Crowe DL, Shuler CF. Immunohistochemical localization of TGF-beta type II receptor and TGF-beta3 during palatogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Int J Dev Biol. 1998;42:817–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker N, Krieglstein K. Targeted mutations of transforming growth factor-beta genes reveal important roles in mouse development and adult homeostasis. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267:6982–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman RN. Deconstructing myc. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2023–30. doi: 10.1101/gad928101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng XH, Liang YY, Liang M, Zhai W, Lin X. Direct interaction of c-Myc with Smad2 and Smad3 to inhibit TGF-beta-mediated induction of the CDK inhibitor p15(Ink4B) Mol Cell. 2002;9:133–43. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick DR, Denhez F, Kondaiah P, Akhurst RJ. Differential expression of TGF beta isoforms in murine palatogenesis. Development. 1990;109:585–95. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foitzik K, Lindner G, Mueller-Roever S, Maurer M, Botchkareva N, Botchkarev V, Handjiski B, Metz M, Hibino T, Soma T, Dotto GP, Paus R. Control of murine hair follicle regression (catagen) by TGF-beta1 in vivo. FASEB J. 2000;14:752–60. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.14.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick JP, Liberati NT, Waddell DS, Shi Y, Wang XF. Transforming growth factor beta-mediated transcriptional repression of c-myc is dependent on direct binding of Smad3 to a novel repressive Smad binding element. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:2546–59. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.6.2546-2559.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey RS, Mulder KM. TGFbeta regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 1997;117:41–50. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(97)00211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehris AL, D’Angelo M, Greene RM. Immunodetection of the transforming growth factors beta 1 and beta 2 in the developing murine palate. Int J Dev Biol. 1991;35:17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehris AL, Pisano MM, Nugent P, Greene RM. Regulation of TGF beta 3 gene expression in embryonic palatal tissue. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1994;30A:671–9. doi: 10.1007/BF02631270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser AG, Zeng QQ, Sato M, Helvering LM, Hirano T, Turner CH. Decreased bone mass and bone elasticity in mice lacking the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene. Bone. 1998;23:87–93. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(98)00078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg PL, MacNaughton DE, Clements RT, Minnear FL, Vincent PA. p38 MAPK activation by TGF-beta1 increases MLC phosphorylation and endothelial monolayer permeability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;282:L146–54. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2002.282.1.L146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartsough MT, Mulder KM. Transforming growth factor beta activation of p44mapk in proliferating cultures of epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7117–24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornberg JJ, Binder B, Bruggeman FJ, Schoeberl B, Heinrich R, Westerhoff HV. Control of MAPK signalling: from complexity to what really matters. Oncogene. 2005;24:5533–42. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne MM, Guadagno TM. A requirement for MAP kinase in the assembly and maintenance of the mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol. 2003;161:1021–8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200304144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordanskaia T, Nawshad A. Mechanisms of transforming growth factor b induced cell cycle arrest in palate development. J Cell Physiol. 2010 doi: 10.1002/jcp.22477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordanskaia T, Nawshad A. Mechanisms of transforming growth factor beta induced cell cycle arrest in palate development. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226:1415–24. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y, Yeo JY, Chytil A, Han J, Bringas P, Jr, Nakajima A, Shuler CF, Moses HL, Chai Y. Conditional inactivation of Tgfbr2 in cranial neural crest causes cleft palate and calvaria defects. Development. 2003;130:5269–80. doi: 10.1242/dev.00708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izadnegahdar MF, Rathanaswami P, Shah RM. Effects of EGF and TGFbeta1 on c-myc gene expression and DNA synthesis in embryonic hamster palate mesenchymal cells. Anat Rec. 1999;254:453–64. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(19990401)254:4<453::AID-AR1>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jugessur A, Murray JC. Orofacial clefting: recent insights into a complex trait. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:270–8. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaartinen V, Cui XM, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J, Shuler CF. Transforming growth factor-beta3 regulates transdifferentiation of medial edge epithelium during palatal fusion and associated degradation of the basement membrane. Dev Dyn. 1997;209:255–60. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199707)209:3<255::AID-AJA1>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaartinen V, Voncken JW, Shuler C, Warburton D, Bu D, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J. Abnormal lung development and cleft palate in mice lacking TGF-beta 3 indicates defects of epithelial-mesenchymal interaction. Nat Genet. 1995;11:415–21. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil N. TGF-beta: from latent to active. Microbes Infect. 1999;1:1255–63. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(99)00259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGamba D, Nawshad A, Hay ED. Microarray analysis of gene expression during epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Dev Dyn. 2005;234:132–42. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidral AC, Romitti PA, Basart AM, Doetschman T, Leysens NJ, Daack-Hirsch S, Semina EV, Johnson LR, Machida J, Burds A, Parnell TJ, Rubenstein JL, Murray JC. Association of MSX1 and TGFB3 with nonsyndromic clefting in humans. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63:557–68. doi: 10.1086/301956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim SK, Hoffmann FM. Smad4 cooperates with lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1/T cell-specific factor to increase c-myc expression in the absence of TGF-beta signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:18580–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604773103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linask KK, D’Angelo M, Gehris AL, Greene RM. Transforming growth factor-beta receptor profiles of human and murine embryonic palate mesenchymal cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991;192:1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90149-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Alvarez C, Tudela C, Perez-Miguelsanz J, O’Kane S, Puerta J, Ferguson MW. Medial edge epithelial cell fate during palatal fusion. Dev Biol. 2000;220:343–57. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J, Wotton D. Transcriptional control by the TGF-beta/Smad signaling system. Embo J. 2000;19:1745–54. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.8.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medici D, Nawshad A. Type I collagen promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through ILK-dependent activation of NF-kappaB and LEF-1. Matrix Biol. 2010;29:161–5. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2009.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses HL, Serra R. Regulation of differentiation by TGF-beta. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996;6:581–6. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moustakas A, Heldin CH. Non-Smad TGF-{beta} signals. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:3573–84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mu Z, Yang Z, Yu D, Zhao Z, Munger JS. TGFbeta1 and TGFbeta3 are partially redundant effectors in brain vascular morphogenesis. Mech Dev. 2008;125:508–16. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucsi I, Skorecki KL, Goldberg HJ. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and the small GTP-binding protein, Rac, contribute to the effects of transforming growth factor-beta1 on gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:16567–72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.28.16567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder KM. Role of Ras and Mapks in TGFbeta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000;11:23–35. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(99)00026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawshad A. Palatal seam disintegration: to die or not to die? that is no longer the question. Dev Dyn. 2008;237:2643–56. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawshad A, Hay ED. TGF{beta}3 signaling activates transcription of the LEF1 gene to induce epithelial mesenchymal transformation during mouse palate development. J Cell Biol. 2003;163:1291–1301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200306024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawshad A, LaGamba D, Olsen BR, Hay ED. Laser capture microdissection (LCM) for analysis of gene expression in specific tissues during embryonic epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Dev Dyn. 2004;230:529–34. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawshad A, Medici D, Liu CC, Hay ED. TGFbeta3 inhibits E-cadherin gene expression in palate medial-edge epithelial cells through a Smad2-Smad4-LEF1 transcription complex. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:1646–53. doi: 10.1242/jcs.003129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster SK, Ho CS, Soucie EL, Penn LZ. The myc oncogene: MarvelouslY Complex. Adv Cancer Res. 2002;84:81–154. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(02)84004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelengaris S, Khan M. The many faces of c-MYC. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003;416:129–36. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(03)00294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelton RW, Dickinson ME, Moses HL, Hogan BL. In situ hybridization analysis of TGF beta 3 RNA expression during mouse development: comparative studies with TGF beta 1 and beta 2. Development. 1990a;110:609–20. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelton RW, Hogan BL, Miller DA, Moses HL. Differential expression of genes encoding TGFs beta 1, beta 2, and beta 3 during murine palate formation. Dev Biol. 1990b;141:456–60. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proetzel G, Pawlowski SA, Wiles MV, Yin M, Boivin GP, Howles PN, Ding J, Ferguson MW, Doetschman T. Transforming growth factor-beta 3 is required for secondary palate fusion. Nat Genet. 1995;11:409–14. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts AB. The ever-increasing complexity of TGF-beta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:3–5. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(01)00027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts EC, Hammond K, Traish AM, Resing KA, Ahn NG. Identification of G2/M targets for the MAP kinase pathway by functional proteomics. Proteomics. 2006;6:4541–53. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200600365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinfeld H, Seger R. The ERK cascade: a prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol. 2005;31:151–74. doi: 10.1385/MB:31:2:151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr CJ. Cell cycle control and cancer. Harvey Lect. 2000;96:73–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuler CF, Halpern DE, Guo Y, Sank AC. Medial edge epithelium fate traced by cell lineage analysis during epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in vivo. Dev Biol. 1992;154:318–30. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90071-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G, Singh SK, Konig A, Reutlinger K, Nye MD, Adhikary T, Eilers M, Gress TM, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Ellenrieder V. Sequential activation of NFAT and c-Myc transcription factors mediates the TGF-beta switch from a suppressor to a promoter of cancer cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:27241–50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.100438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T. PCNA, a multifunctional ring on DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1443:23–39. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(98)00204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigneron A, Cherier J, Barre B, Gamelin E, Coqueret O. The Cell Cycle Inhibitor p21waf1 Binds to the myc and cdc25A Promoters upon DNA Damage and Induces Transcriptional Repression. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:34742–34750. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602492200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Ma R, Flavell RA, Choi ME. Requirement of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 (MKK3) for activation of p38alpha and p38delta MAPK isoforms by TGF-beta 1 in murine mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:47257–62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208573200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K, Furuhashi M, Aoki H, Goto D, Kuwano H, Sugamura K, Miyazono K, Kato M. c-myc is a downstream target of the Smad pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:854–61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104170200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam CH, Fung TK, Poon RY. Cyclin A in cell cycle control and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002;59:1317–26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8510-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang LT, Kaartinen V. Tgfb1 expressed in the Tgfb3 locus partially rescues the cleft palate phenotype of Tgfb3 null mutants. Dev Biol. 2007;312:384–95. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.09.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue J, Mulder KM. Requirement of Ras/MAPK pathway activation by transforming growth factor beta for transforming growth factor beta 1 production in a Smad-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:30765–73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000039200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


