Abstract
Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) is the most common form of porphyria across the world. Unlike other forms of porphyria, which are inborn errors of metabolism, PCT is usually an acquired liver disease caused by exogenous factors, chief among which are excess alcohol intake, iron overload, chronic hepatitis C, estrogen therapy, and cigarette smoking. The pathogenesis of PCT is complex and varied, but hereditary or acquired factors that lead to hepatic iron loading and increased oxidative stress are of central importance. Iron loading is usually only mild or moderate in degree (less than that associated with full-blown hemochromatosis) and is usually acquired and/or due to mutations in HFE. Among acquired factors are excessive alcohol intake and chronic hepatitis C infection, which, like mutations in HFE, decrease hepcidin production by hepatocytes. The decrease in hepcidin leads to increased iron absorption from the gut. In the liver, iron-loading and increased oxidative stress leads to the formation of non-porphyrin inhibitor(s) of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase and to oxidation of porphyrinogens to porphyrins. The treatment of choice of active PCT is iron reduction by phlebotomy and maintenance of a mildly iron-reduced state without anemia. Low-dose anti-malarials (cinchona alkaloids) are also useful as additional therapy or as alternative therapy for active PCT in those without hemochromatosis or chronic hepatitis C. In this review, we provide an update of PCT with special emphasis upon the important role often played by the hepatitis C virus.
Keywords: chloroquine, chronic hepatitis C, hepatitis C virus, hereditary hemochromatosis, iron, porphyria cutanea tarda, oxidative stress, reactive oxygen species, therapeutic phlebotomy, uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
Overview of Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)
Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) is the most common type of porphyria worldwide with an estimated prevalence in various countries ranging from 1:5,000 to 1:70,000 (1-4). PCT is known by many other names, including symptomatic porphyria, idiosyncratic porphyria, chemical porphyria, or acquired hepatic porphyria (5). PCT typically presents as a chronic, gradually progressive cutaneous disorder, with vesicles, milia, and bullae on the backs of the hands and forearms. Clinical features rarely develop unless there is at least 75% decrease in activity of hepatic uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (UROD) (6-8). UROD is the fifth enzyme in the heme biosynthetic pathway. UROD deficiency is usually acquired (75-80% of cases), but 20-25% of subjects with familial PCT have a genetic predisposition with partial (~50%) deficiency in UROD activity. Those with genetic predisposition need fewer other factors to decrease the activity further down to the threshold of ~75% in order for symptomatic disease to occur.
Nature of Metabolic Defect and Pathogenesis of PCT
PCT is a heterogeneous disease and has been classified into three subtypes [Table1]. Type I, accounting for 75-80%, is acquired PCT, in which deficiency of UROD is limited to hepatocytes. Type II, accounting for 20-25%, is hereditary, in which there is partial deficiency [~50%] of UROD in all tissues. Type III is a very rare form in which there exists an apparently genetic predisposition that leads to decreased UROD activity limited to hepatocytes (9-11). It is thought that the genetic abnormality in type III PCT is in a still unidentified gene other than UROD. There is only one UROD gene in humans; it is located on chromosome 1P34, is around 10 kb in length, and consists of 10 exons (12).
Table 1.
Classification of Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
| Type | Percent of Cases | Nature of Defect |
|---|---|---|
| I | 75-80 | Acquired defect leading to decreased activity of hepatic UROD [<25% normal activity] |
| II | 20-25 | Hereditary partial defect in UROD activity [~50% of normal] in all tissues. Other factors also required to produce clinical features |
| III | <1 | Very rare. Apparently inherited defect in an as yet unknown gene that leads to a secondary critical decrease in hepatic UROD activity. |
UROD is uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
Several lines of evidence support the concept that, in PCT, there occurs in the liver the formation of an inhibitor of UROD, which is derived from uroporphyrinogen or hydroxymethylbilane, the tetrapyrrole precursor of uroporphyrinogen. Formation of the inhibitor, which more likely than not is an oxidation product, is increased by iron, a well-known oxidant, by activity of cytochrome P-4501A2, by alcohol excess, and by estrogen therapy [Fig. 1]. Based on mass spectroscopic evidence obtained from studies in a murine model of PCT, it has been claimed that uroporphomethene is the inhibitor (13). However, others have cast doubt upon the interpretation of the mass spectroscopic evidence (14). Thus, the precise structure and nature of the UROD inhibitor remains unresolved.
Figure 1. Pathogenesis of Porphyria Cutanea Tarda.
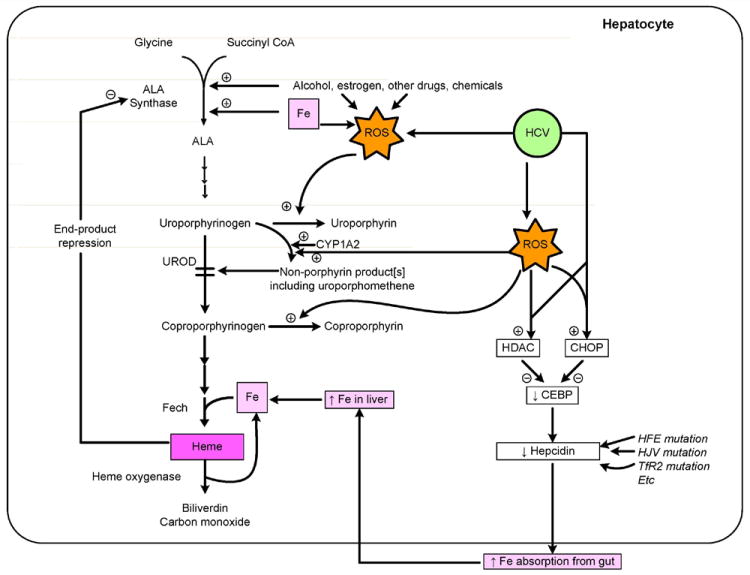
The figure shows a summary of the normal pathway of heme biosynthesis, with emphasis on uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase [UROD] and its inhibition by an oxidation product thought to be derived from uroporphyrinogen. Formation of the inhibitor is thought also to require the action of CYP1A2. Several sites of action of iron are shown, including synergistic induction of ALA synthase 1, increases in oxidative stress (reactive oxygen species [ROS], and induction of heme oxygenase 1. Alcohol and estrogens also increase ROS and induce ALA Synthase 1. HCV infection increases ROS and decreases hepcidin production. The latter decrease is due to up-regulation of histone deacetylase [HDAC] and C/CBP homology protein [CHOP], which result in decreased binding of C/EBP to the hepcidin gene promoter region and thus decreased hepcidin production. Mutations in the HFE gene, [or more rarely, HJV, and/or TfR2 genes] also lead to decreased hepcidin production. The decrease in hepcidin leads to increased absorption of iron from the small intestine, leading to further hepatic iron overload and to amplification of the metabolic disarray.
UROD catalyzes the step-wise decarboxylation of uroporphyrinogen to the corresponding coproporphyrinogen. Uroporphyrins [which contain 8-carboxylate groups] and heptacarboxylated porphyrins accumulate in various organs as a consequence of impaired UROD activity and increased oxidative stress (2). Porphyrins with many carboxylate residues are water soluble, while those with few [e.g., protoporphyrin with 2 carboxylate (-COOH) residues] are insoluble in water. Thus, those with higher numbers of −COOH residues, such as uro- and heptacarboxyl-porphyrins are excreted primarily in the urine; those with intermediate numbers of −COOH groups [e.g., coproporphyrins, with 4-COOH] are excreted in both urine and stool; whereas, protoporphyrin is secreted only into the bile and excreted only in the stool. Within cells, different water solubilities influence where various porphyrins accumulate. Due to their hydrophilic nature, uro –and heptacarboxyl- porphyrins accumulate in the cytosol and lysosomes and are not associated with or dissolved in membranes to any appreciable extent. The ability of porphyrins to absorb light of 400-410 nm (the Soret band) (1, 15-17) is the key factor in producing the photocutaneous lesions observed on sun-exposed areas in affected individuals. The delocalized Pi-electrons of aromatic porphyrins readily absorb energy of violet light and enter a higher energy state. This excited state then transfers its excess energy to molecular oxygen which in turn raises electrons of oxygen to a higher energy state [“singlet oxygen”] (18). The reactive oxygen species give rise to the phototoxic damage characteristic of PCT (18), as well as further catalyzing the oxidation of porphyrinogens to porphyrins (8) [Fig 1].
Major Clinical, Laboratory, Histopathological Features, and Risk Factors of PCT
PCT clinically presents with blisters, vesicles, and/or milia days to weeks after sun exposure (5, 8, 19) in areas likely to be exposed to the sun and to minor trauma, such as the dorsa of the hands and forearms. These lesions typically first arise and are worse in the summer and often take weeks or months to resolve. Chronic skin damage may result in scarring, changes in cutaneous pigmentation at the sites of blisters and milia [Fig 2]. Other skin manifestations may include a purplish heliotrope suffusion of periorbital areas (2), hypertrichosis, usually involving the lateral aspects of the face, chloracne, sclerodermatous changes, dystrophic calcification with ulceration, alopecia, and onycholysis (8).
Figure 2. Typical Cutaneous Manifestations of PCT.
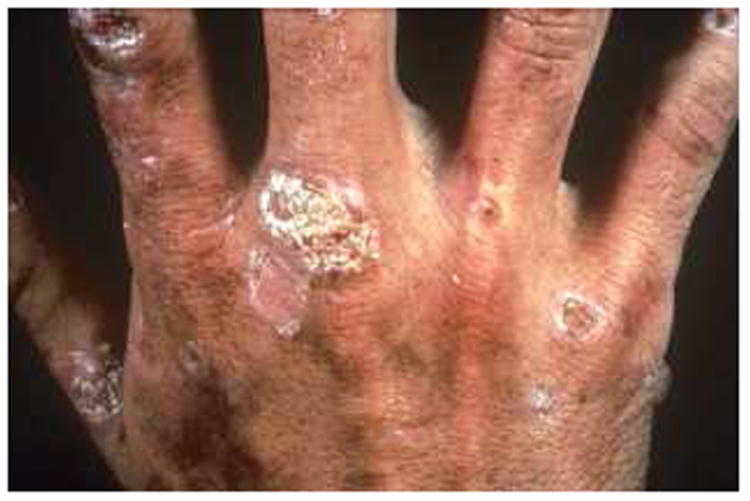
Cutaneous lesions with bullae, vesicles, and erosions on the dorsum of the hand.
Due to marked excretions of porphyrins in the urine, patients with PCT may have urine that appears pink, red, or brown, especially after exposure of the urine to air and light (2, 8). Because the free porphyrins do not contain iron, urine tests for heme, hemoglobin, or myoglobin are all negative. Thus, despite the pink-red color of urine, routine urinalysis and blood counts are normal in most patients. Persons with active PCT are usually found to have mildly elevated serum aminotransferases and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (5). The nonspecific findings of routine laboratory tests make it clear that special studies are needed to diagnose PCT. A useful initial test is direct fluorometric assay of plasma. In patients with symptomatic PCT, plasma porphyrins are elevated with maximal excitation and emission wavelengths at ~400 nm and ~620 nm, respectively. When this fluorometric pattern is observed, tests for levels of porphyrins and porphyrin precursors in urine, and porphyrins in feces are used to confirm the diagnosis. If PCT is present, elevated levels of uro- and heptacarboxyl-porphyrins are found in the urine along with elevated fecal isocoproporphyrin, and plasma 8- and 7- carboxylporphyrins, with little or no elevation of erythrocyte porphyrin levels (9). Urinary levels of delta-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) are normal or slightly increased [less than 2 times the upper limit of normal], and levels of urinary porphobilinogen (PBG) are normal. The latter help to distinguish PCT from the acute or inducible hepatic porphyrias [hereditary coproporphyria, variegate porphyria], which may be present with cutaneous features indistinguishable from those of PCT. In addition, in variegate porphyria, the peak emission wavelength of plasma fluorescence is 626-628 nm, finding of considerable diagnostic value.
In active PCT, vesiculo-bullous lesions “festoon” the dermal papillae whereby these dermal projections rise irregularly into the cavities of subepidermal fluid collections. There is also deposition of periodic acid-Schiff positive, diastase-resistant glycoproteins, various immunoglobulins and complement around both the dermo-epithelial junction and blood vessels. These lesions are not unique to PCT and are found in other porphyrias of the bullous type. Similarly, liver histopathology is mostly non-specific and includes red fluorescence of unfixed hepatic tissue (which is seen in various types of porphyria), necrosis, inflammation, varying siderosis and steatosis (8, 20, 21) [Fig 3]. Hemosiderosis is usually mild to moderate but may be severe when accompanied by mutations that underlie hemochromatosis. Indeed, PCT shows a clear dose-response relationship in individuals carrying either C282Y or H63D gene mutations. In a meta-analysis done by Ellervik and colleagues, C282Y homozygotes were demonstrated to have the highest risk for PCT while H63D heterozygozity with wild type conferred the lowest risk (22). Other features include needle-shaped hydrophilic cytoplasmic inclusions thought to be mainly composed of uro-and/or heptacarboxyl porphyrin crystals. These crystals have been localized to the areas of cytoplasm that contain ferritin granules further suggesting the role of iron in oxidation of porphyrinogens and subsequent crystallization of porphyrins (8).
Figure 3. Hepatic Histopathology in PCT.
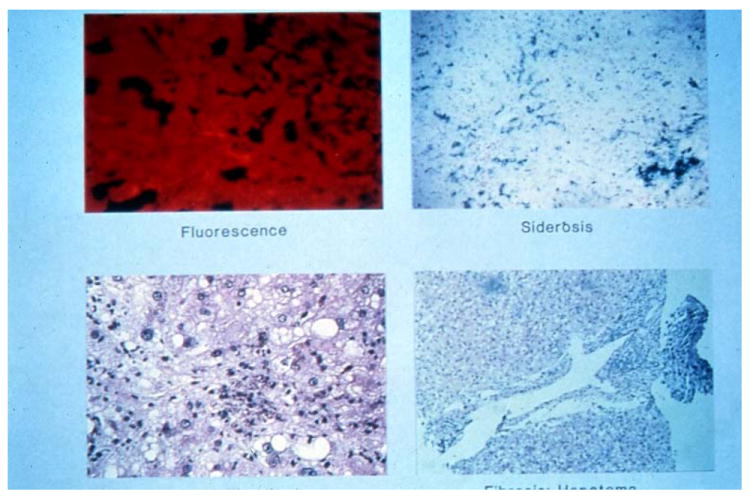
Fresh unfixed liver fluoresces a bright pin) [upper left, (unstained, 1X] due to excess porphyrins. Typically, there is some degree of iron loading [upper right, (Prussian Blue stain, 10X)] and fatty change and inflammation [lower left, (H&E stain, 20X)]. The latter are often due to alcohol and/or chronic hepatitis C. Sometimes, cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma develop [lower right, (H&E stain 10X)]. Photomicrographs kindly provided by JR Bloomer.
Iron enhances uroporphyrin overproduction in several ways [Fig 1]. First, iron increases reactive oxygen species (ROS), which increase the rate at which uroporphyrinogen and heptacarboxylporphyrinogen are oxidized into their respective porphyrins (8). Second, it decreases the activity of UROD by increasing formation of an inhibitor, probably derived from hydroxymethylbilane and/or uroporphyrinogen. Third, iron increases intracellular ALA levels providing more substrate for uroporphyrinogen and subsequent uroporphyrin synthesis.
Despite the importance of hepatic siderosis in PCT, iron by itself is insufficient to cause uroporphyrin overproduction in the absence of other predisposing factors (8, 15, 23-25). Other known risk factors for PCT include UROD mutations (7), alcohol, smoking (25, 26), hepatotoxic aromatic hydrocarbons (e.g., hexachlorobenzene, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, and others), certain genetic variations in the genes for cytochrome P4501A2, and glutathione-S-transferase GSTM1 (27), hepatic tumors (benign, malignant, or metastatic) (15), dialysis, sarcoidosis, estrogens, and chronic infection with the hepatitis C or human immunodeficiency virus.
Overview of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC)
HCV is a hepatotropic member of the flaviviridae family and is known to infect an estimated 170-200 million people worldwide (8, 28, 29). HCV has six known major genotypes (1-6) which may be further divided into 50 subtypes (1a, 1b, etc.). Certain genotypes are more prevalent at different parts of the globe. Genotype 1 is predominant in the USA, accounting for 70% of infections. Furthermore, 55% of these are subtype 1a while 40% are 1b; the remaining small proportion is due to subtype 1a/1b co-infection. Most of the remaining 30% of infected individuals in the USA are due to HCV of genotypes 2 or 3, while genotypes 4-6 account for a small proportion (29). In contrast, 80% of HCV infections in Europe are due to subtype 1b. Other global variations include the predominance of genotype 2a in Japan, Taiwan, and China; genotype 3 in Scotland and other parts of the UK (30); genotype 4 in the Middle East and Northern and Central Africa; genotype 5 in South Africa; and genotype 6 in South East Asia (29).
The virus is transmitted mainly by the parenteral route and to a lesser extent by vertical and sexual transmission. Acute HCV infection may begin insidiously or present abruptly. It has a limited course that usually lasts one or two months. Acute infection is rarely detected because the majority of patients are asymptomatic. Indeed, only 10-20% of patients develop jaundice, with a greater proportion presenting with non-specific symptoms (e.g., anorexia, fatigue, nausea, tiredness). Of those acutely infected by HCV, 60-85% develop chronic infection and approximately 70% of these develop chronic liver disease, 10-20% of which progress to cirrhosis (31). Indeed, CHC has become the single most common indication for orthotopic liver transplantation in the western world. Thus, cirrhosis due to CHC accounts for 40-50% of patients listed for transplant (32).
While the majority of patients with CHC have elevated serum aminotransferases, about a third of those infected have persistently normal levels despite a high viral load and continued hepatic injury. Patients with chronic infection frequently complain of fatigue. Other non-specific symptoms such as myalgias, arthralgias, paresthesias, pruritus, and sicca syndrome are also frequent complaints.
Epidemiology/Association of PCT with HCV
In most studies, there is a strong association between HCV infection and PCT [Table 2] (20, 33-35). Furthermore, it has been observed that HCV-infected individuals develop PCT at an earlier age than do uninfected persons with PCT (24, 25). Although the presence of any single risk factor is likely not sufficient to cause PCT, HCV is thought to be a strong trigger for the development of deranged porphyrin metabolism in those with other known predisposition (1, 3, 16, 20, 35, 36). O’Reilly et al. reported only minimal elevations of urinary porphyrins in 59 subjects infected with HCV but with few or no concomitant susceptibilities. Subjects found to have mildly elevated porphyrins were on a variety of medications that may have influenced porphyrin metabolism, and none had overt PCT (36). Nomura et al. confirmed these results and also found HCV and HIV co-infection to be significantly associated with elevated serum porphyrins (3). In addition, Jalil et al. analyzed records of 143 patients with well documented PCT. They found that most subjects with clinically manifest PCT had three or more known susceptibility factors (17) [Table 2].
Table 2.
Prevalence of susceptibility factors in published series of patients with PCT from different geographic areas
| 1st author (publication year) | Cases | HCV | ETOH | Smoking | HIV | Estrogen* | HFE= |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n) | Percent with risk factor | ||||||
| North America | |||||||
| Jalil et al(17) (2010) | 143 | 69 | 88 | 81 | 13 | 66 | 51 |
| Egger et al.(86) (2002) | 39 | 74 | 79 | 86 | 25 | 73 | 65 |
| Bulaj et al.(87) (2000) | 108 | 59 | 46 | - | - | 63 | 63 |
| Bonkovsky(26) et al. (1998) | 70 | 56 | 90 | - | - | 47 | 73 |
| Europe | |||||||
| Sweden, Rossmann et al.(88) (2005) | 84 | 19 | 25 | - | - | 55 | 24 |
| Hungary, Nagy et al.(89) (2004) | 50 | 44 | 66 | - | - | 60 | 50 |
| Germany, Tannapfel et al.(90) (2001) | 190 | 15 | - | - | - | - | 69 |
| Bulgaria, Ivanova et al.(91) (1999) | 48 | - | - | - | - | - | 23 |
| France, Lamoril et al.(92) (1998) | 124 | 21 | 73 | - | - | 37 | - |
| UK, Roberts et al.(93) (1997) | 41 | - | - | - | - | - | 37 |
| Scotland, Hussain et al.(16) (1996) | 12 | 92 | 33 | - | 8 | - | - |
| Spain, Herrero et al.(94) (1993) | 100 | 79 | 71 | - | - | - | - |
| Italy, Fargion et al.(95) (1992) | 74 | 76 | 38 | - | - | - | 53 |
| Australia | 27 | 26 | - | - | - | - | 44 |
| Stuart et al.(96) (1998) | |||||||
| South America | |||||||
| Argentina, Mendez et al.(97) (2005) | 1000 | 35 | 42 | - | 6 | 29 | 53 |
| Brazil, Martinelli et al.(98) (2000) | 23 | 65 | 74 | - | - | - | 44 |
Abbreviations: ETOH, alcohol excess; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HFE, the gene mutated in classical HLA-linked hereditary hemochromatosis; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus;
Use among women (note that estrogen therapy of men for prostate cancer is also a recognized risk factor)
C282Y and H63D mutations
Adapted from Ref 17. Used with permission of the authors and publisher.
Factors that Underlie the Association of HCV and PCT
Although CHC is among factors known to increase risk of PCT, it is not clear if the virus, per se, plays a role in the development and pathogenesis of PCT, or whether this association is mainly due to iron overload and/or increased oxidative stress, which often occur in the context of CHC. It has been known for many years that 1) most patients with PCT have some degree of iron overload; 2) iron removal ameliorates porphyrin overproduction and clinical features; and 3) administration of iron produces relapse of PCT (26). Serum iron indices and iron content of the liver are often elevated in patients with CHC (20, 37). The precise molecular mechanisms by which iron may influence HCV-induced liver disease are not fully understood. Among several proposed mechanisms are iron-induced immunologic modifications and iron effects on signal transduction and HCV proliferation (38). Elevated hepatic iron and increased serum iron indices also have been associated with PCT [Table 2] (39), and iron is known to exert several actions that increase oxidation of porphyrinogens and lead to inhibition of UROD [Fig 1]. Therefore, iron can be considered as a common factor for the development and progression of both CHC- and PCT- induced liver diseases. Based on these facts, it can be anticipated that patients with iron overload like those with hereditary hemochromatosis (HH) have a higher risk for the development and progression of both CHC- and PCT- induced liver diseases. Indeed, significantly increased frequencies of both C282Y and H63D mutations of HFE in PCT patients have been reported from studies in Northern Europe and the USA (26, 40, 41). The preponderance of the evidence suggests that patients with CHC who are heterozygous for H63D or C282Y mutations are at a higher risk of severe hepatocellular injury and fibrosis (42). Therefore, even in patients harboring HFE mutations that cause milder defects in iron homeostasis, it is possible that the presence of HFE mutations leads to the inactivation of UROD through interaction with other factors like HCV infection, which change iron homeostasis in the liver.
Transgenic mice expressing an HCV polyprotein and fed a high-iron diet were found to have not only higher degrees of hepatic steatosis, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial injury, but also a higher risk of development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), compared to mice fed a normal diet (43). Using human hepatoma cells, expressing an HCV subgenomic replicon, Fillebeen et al. (44) showed that HCV replication altered the expression of several genes related to iron metabolism. Alteration of these genes, in turn, can contribute to development of PCT in the context of HCV infection.
Recently, Nishina et al. have shown that HCV increases reactive oxygen species (ROS), which leads to increase hepatic expression of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) (45) via an increase in histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity (46). CHOP is a nuclear protein that inhibits C/EBPα via the binding of their carboxy terminal domains. Thus, the CHOP-C/EBPα heterodimer renders the C/EBPα monomer unavailable to bind its DNA enhancer elements that lead to hepcidin production.
Hepcidin, a 25-amino acid cysteine-rich peptide, is the key regulator of iron absorption and metabolism in humans, which induces internalization and degradation of ferroportin, and this in turn leads to the reduction of iron exported from cells. Therefore, over-expression of hepcidin in mice and humans leads to iron deficiency, whereas its deficiency leads to iron overload. In HCV-infected individuals (as with FL-N/35 transgenic mice with the full length HCV polyprotein (45)), compared to controls, hepcidin expression levels are low relative to the iron content of hepatocytes (47, 48). Interestingly, in a recent study, Ajioka et al. showed that hepatic hepcidin expression in patients with PCT was significantly reduced, regardless of HFE genotype, when compared with patients with HH but without PCT with comparable iron overload (49). Therefore, they suggested that the hepatic siderosis associated with PCT likely results from dysregulated hepcidin. Taken together, it appears that HCV leads to down-regulation of hepcidin, and this can lead to iron overload, which in turn facilitates development of PCT by inhibiting UROD activity [Figure 1].
In addition to CHC, there are also reports that show concurrence of other viral infection like HBV, HIV, and HHV6 with PCT (26, 50). These associations suggest that viral infection, per se, may play a role in reducing the activity of (UROD). Additional studies investigating alteration of UROD activity in HCV infected cell lines may help to unravel the mechanism of this association.
As mentioned above, besides HCV infection and HFE mutations, several environmental factors have been shown to precipitate overt clinical PCT, including alcohol abuse, tobacco use, and use of oral estrogens [Table 2] (17). Alcohol may cause liver damage, ranging from reversible steatosis to alcoholic cirrhosis. Alcohol also exacerbates the hepatopathy of CHC. Alcohol, estrogens, iron, and CHC all produce increased oxidative stress in liver cells. Besides, it is also anticipated that there might be common molecular pathways for triggering both PCT, and its predisposing factors. In mice, cytochrome P4501A2 (Cyp1A2) plays a major role in the development of uroporphyria. Unlike mice with normal Cyp1A2, knockout mice deficient in Cyp1A2 do not develop uroporphyria following exposure to halogenated polyaromatic hydrocarbons (51). As mentioned above, in a recent study, it was found that genetic variations in human CYP1A2(*1F) and GST(M1) alleles are associated with susceptibility to PCT (27). GSTM1 is particularly important in the deactivation of reactive intermediates of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Management of PCT
As in other types of cutaneous porphyria, avoidance of sun exposure and/or strong light of 400-410 nm wavelength (Soret band) is the most effective way to prevent the cutaneous manifestations of PCT. Avoidance of sun exposure involves the use of protective clothing (Solumbrex®) and opaque sunscreens that contain zinc or titanium oxide. In addition, preventing or controlling various predisposing factors [Table 2] should be a routine part of management.
Definitive therapy aimed at the pathogenic mechanism of PCT includes iron reduction, and anti-malarials that remove porphyrins from the liver and other tissues. Among these, phlebotomy is the treatment of choice and has generally been shown to be cheap, safe, and effective. Although moderate hepatic iron overload is common in PCT, presence of hepatic siderosis in PCT is not a prerequisite for successful treatment with venesection (52, 53). It is recommended that a unit (450-500 mL) of blood be removed either once a week or every other week (54) until the serum ferritin is <25 ng/mL (13, 55-58). Clinical remission is usually evident after removal of 2-4 L of blood (59). Indeed, with the regimen recommended dose, cutaneous manifestations gradually improve with resolution of bullae in 2-3 months, improvement of cutaneous fragility in 6-9 months, and complete biochemical remission in 13 months (59, 60). Care should be taken to prevent pre-phlebotomy hemoglobin from falling below 11 g/dL. Pre-existent anemia, severe serum protein deficiency, e.g., due to cirrhosis and bleeding disorders, are unusual relative contraindications to phlebotomy.
Diets somewhat restricted in iron, liver, and red meats (the latter are rich in heme) are also recommended because with iron reduction there is a compensatory increase of iron absorption from the GI tract. This compensatory mechanism is attributed to the reduction of serum hepcidin post-iron reduction. Reduced hepcidin in turn, increases ferroportin expression and function, which ultimately results in enhanced intestinal iron absorption (61, 62). Heme iron is particularly well absorbed, so that a modest restriction of heme intake is good general dietary advice, except for those with iron deficiency.
If phlebotomy is contraindicated, low-dose chloroquine (125 mg every other day) is usually the next best choice. Indeed, although relapse of PCT following chloroquine treatment occurs earlier than after iron reduction, it has been found to be cheap and effective, and to achieve remission at a similar rate as venesection (60). Chloroquine binds 8 and 7–carboxylate porphyrins, which accumulate in lysosomes, and forms water-soluble complexes with them that lead to tissue mobilization and increased urinary excretion (25, 59). After initiation of chloroquine treatment, initial elevations of serum aminotransferases and porphyrins sometimes occur. These elevations are generally mild and usually normalize within two months (59, 60). At least 3 months of treatment, however, are needed before clinical remission is seen. Similar to phlebotomy-monotherapy, complete biochemical remission usually is not achieved until at least 1 year of chloroquine treatment (59). Another anti-malarial agent, hydroxychloroquine (200 mg twice weekly), has also been shown to be an effective treatment for PCT; however, it is less preferred because remission is shorter than with chloroquine (60). In severe cases, or when the most rapid therapeutic response is sought, phlebotomy and anti-malarials may be used together and may result in faster remission than does either treatment alone (although this has not been shown in prospective randomized trials).
The reason for recommending low-dose chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine therapy in PCT is that, if full usual doses are used for initial therapy, a symptomatic acute hepatitis, with fever, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, and marked increases in serum aminotransferase levels often ensue, due to a too rapid removal of accumulated porphyrins from hepatic stores with hepatocyte necrosis.
Iron chelation with deferoxamine has also been described as an alternative treatment for PCT in those who are intolerant of therapeutic phlebotomy (25, 62). Subcutaneous infusions of deferoxamine (40-50 mg/kg BW) 5 nights a week for 8-10 hours in 16 patients were able to normalize urinary porphyrin excretion. Once normalized, infusions were reduced to 5-10 days per month or every other month (25). Although not as convenient or cheap as therapeutic phlebotomy, deferoxamine is able to remove the toxic highly reactive, loosely-bound iron implicated in the pathogenesis of PCT. Furthermore, it may reduce the compensatory increase of intestinal iron absorption often seen in remission induced by the greater degree of iron reduction achieved by phlebotomies. Oral iron chelators [deferasirox, deferiprone] are also available in some countries. They, too, may be effective and relatively safe for therapy of PCT, especially in those with elevated serum ferritins and increased total body iron stores. However, to the best of our knowledge, prospective randomized controlled trials of their use in PCT have not been performed.
Patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing dialysis, who typically are anemic at baseline, may benefit from iron mobilization via a combination of erythropoietin and smaller volume phlebotomies. Dialyzers with ultra-permeable membranes and plasmapheresis may also be employed. Renal transplantation has been curative in refractory cases of PCT associated with chronic renal failure (62).
Treatment of CHC in the Context of PCT
The principles of treatment described above can also generally be used for PCT in the setting of chronic hepatitis C (CHC). Although chloroquine effectively reduces uroporphyrin levels, it does not address the loosely-bound hepatic iron thought to be of importance in PCT pathogenesis. Due to the fact that patients with homozygous C282Y mutations of HFE (a risk factor for PCT) also failed to respond to chloroquine treatment, most investigators prefer phlebotomy in patients with both HFE gene mutations and CHC (63). While treatment of PCT alone with iron chelators is possible, such therapy is far more expensive and involved and phlebotomy is preferred. Furthermore, there is paucity of data regarding use of iron-chelators in those with CHC and PCT (25).
It has been reported that interferon alpha (IFN) therapy improved the levels of serum aminotransferases and urinary porphyrins and resolved skin lesions along with decreasing HCV RNA levels in patients with concurrent CHC and PCT (64, 65). On the other hand, there are also a few reports of de novo occurrence of PCT during IFN plus ribavirin therapy for CHC (23).
In one small study reported only in abstract form, Rossini et al (66) randomized 20 patients with both PCT and CHC into two cohorts. Group 1 received phlebotomy prior to dual therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin while group 2 received dual therapy without pretreatment venesection. The investigators measured levels of HCV RNA in serum before and after iron depletion in group 1 and found no significant difference, in keeping with earlier results of others (67, 68). No comparisons between the viral levels of the two groups were reported in the abstract. Mainly based on the results in their group 1, the investigators concluded that iron depletion did not seem to improve the rate of response to anti-HCV treatment in these patients. In addition to providing little data on group 2 (especially in comparison to group 1), the study was small in size and thus, lacks statistical power. Furthermore, while group 1 subjects were all infected with HCV of genotype 1b, there were two patients with genotype 2a in group 2. It is well-known that genotype 2 HCV is more responsive to interferon-based therapy. Thus the two rather small groups were not comparable, rendering interpretation of results problematical.
Treatment of PCT by iron reduction is successful even in patients with CHC. Because iron overload is found in most cases of PCT (8, 13, 21), and iron is a recognized factor that influence severity and course of chronic viral hepatitis (6, 61), reduction of iron stores by venesection can lead to improvement of both conditions. Furthermore, the fact that patients with CHC and PCT respond poorly to interferon (IFN) (69) and that phlebotomy enhances sustained virological response (SVR) of patients who received IFN monotherapy (70), suggest that venesection preceding combination anti-viral therapy may be ideal. Therefore, it is usually wise to treat the PCT with therapeutic phlebotomies first and then deal with the treatment for CHC with peg-IFN and ribavirin or, now, with triple therapy [peg-IFN+ribavirin+HCV protease inhibitor, either boceprevir or telaprevir]. Iron reduction prior to combination anti-viral therapy not only helps to reduce possible deleterious effects of iron on UROD, and hence improves symptoms of PCT, but also facilitates decreasing of HCV RNA levels, and impedes the synergistic effect of iron and HCV in the progression of liver disease. It is not yet known whether the newer triple [or, in future] quadruple –drug regimens for CHC will prove effective also as therapy for PCT with CHC. These issues will require future study.
Venesection prior to ribavirin (RBV)-based therapy may prove challenging because of the frequent development of hemolytic anemia associated with RBV therapy. Thus optimal timing of when to stop phlebotomy prior to initiating RBV-based regimen is unknown (25). Due to paucity of data, some authors suggest that the hemoglobin levels be between 12-14 g/dL prior to starting RBV-based therapy after appropriate phlebotomy (25).
Treatment of HCV-Infected Patients without PCT with Phlebotomy
Iron reduction may improve the severity of CHC and increase the likelihood of response of CHC to antiviral therapy. Prior to the advent of combination therapy with pegylated IFN and ribavirin, multiple clinical trials demonstrated improved clinical response in CHC patients treated with phlebotomy and IFN monotherapy compared to IFN monotherapy alone (71). Desai et al. (70) conducted a meta-analysis of these randomized controlled trials and reported highly significant improvements in virological response rates (P<0.001) from phlebotomy and IFN therapy compared to IFN alone.
Some investigators have reported that phlebotomy with dual therapy (ribavirin and interferon) does not improve viral response (66, 72, 73). However, in a recent prospective, randomized controlled trial on the effect of phlebotomy in well-matched subjects with CHC undergoing combination therapy with pegIFN and ribavirin, six of 10 (60%) of subjects who underwent phlebotomies vs only two of 8 (25%) of subjects who did not undergo phlebotomies achieved an SVR (74).
Distante and colleagues (75) treated a total of 256 patients with CHC from 30 different hospitals with dual therapy for 6 months and found that, prior to treatment, non-responders (n=127) compared to sustained responders (n=129) had significantly higher median serum ferritin (SF) values (130μg/L vs. 75μg/L, P=0.001). In this study, sustained responders were defined as having negative HCV RNA at six months after the end of 26 weeks of dual therapy. The study showed the following results: a. only 10% of patients with SF ≥ 500μg/L responded to dual therapy; b. patients with transferrin saturation ≥ 50% had lower sustained response rates; and c. there was an inverse correlation between SF values and sustained response rate by multivariate analysis.
Although SF was not found to be a reliable predictor of hepatic siderosis by some investigators (12), raised SF clearly is a predictor of non-response in patients with CHC (75). Regardless of whether SF is a marker of hepatic siderosis or not, lowering SF via phlebotomy may be an alternative or adjunctive method of increasing SVR even in those without PCT. In an attempt to clarify the effects of dual therapy on iron status, Ferrara et al conducted a prospective observational study in previously untreated subjects with CHC (76). They found that, although SF prior to treatment had good specificity in predicting stainable iron in the liver (89%), its sensitivity in detecting iron overload was low (25%). Furthermore, they found that SVR is more likely to occur in subjects with lower baseline SF, who experienced a greater rise in SF levels during treatment than did those who did not achieve SVR. More specifically, they found an inverse correlation between serum iron, transferrin saturation, and SF with the degree of hemolysis up until week 4 of treatment. Indeed, they noted that a 2.5 fold increase in SF at week 12 was associated with increased SVR rates. Their results suggest that SF levels after 4 weeks of dual therapy are more reflective of other phenomena than siderosis due to ribavirin-induced hemolysis alone. Perhaps, a greater rise in SF during antiviral therapy is a marker of greater biological responsiveness to therapy, similar to other changes in laboratory variables, previously shown to be associated with responsiveness to therapy (77). Thus, although limited in sensitivity, SF at baseline provides a cheap and effective method to estimate siderosis if phlebotomy is planned prior to treatment, as well as prediction of likelihood of response to therapy.
A retrospective study by Rulyak et al (73), concluded that pre-treatment hepatic iron concentration (HIC) is not a predictor of response to combination IFN and RBV therapy. Similarly, although Pianko et al. (72) confirmed the possible beneficial effects of lower HIC in IFN monotherapy, they found the mean HIC in both sustained responders and non-responders to RBV based dual therapy was not significantly different. As pointed out by Desai and colleagues (13), however, the mean HICs for subjects described in these studies were only 523μg/g and <700 μg/g dry weight, respectively. The fact that previous studies showed that HIC of at least 1,100 μg/g separates responders from non-responders to IFN-based therapy may account for these discordant results.
In the previously discussed study by Ferrara and colleagues, the presence of iron in the mesenchymal cells (Kupffer cells and endothelial cells of the portal tract) and not the total iron score (TIS) correlated with SVR. This finding agrees well with the analysis done by Bonkovsky et al. three years earlier when they reported that stainable iron in endothelial cells or in portal triads predicted a lower likelihood of SVR in those who underwent dual therapy (61, 78). The distribution of iron among cell types in the liver is thus likely to be more important than HIC. However, in absence of selective iron-removal techniques, pre-treatment phlebotomy is the least expensive and most effective method to decrease HIC and iron in mesenchymal cells. In subjects with chronic hepatitis C and PCT [and most other conditions associated with iron loading] therapeutic phlebotomies will mobilize iron from storage sites throughout the body. Furthermore, when combined with an iron deficient diet, the concern posed by Ferrara and colleagues in regards to how the down-regulation of hepcidin may affect the targeted iron pool can be reasonably addressed. Of course, larger, adequately-powered prospective studies are needed to confirm these tentative conclusions.
It is nonetheless clear that higher baseline levels of SF and/or hepatic iron concentrations have been associated with more severe and advanced CHC and with decreased likelihood of responding to interferon (61, 67) or even dual therapy (76). These observations understandably led to studies on effects of iron reduction in CHC without concomitant PCT. Iron reduction by therapeutic phlebotomy did not lead to any significant change in HCV RNA levels in sera, but it did lead to improvements in serum ALT levels (79), to improvements in hepatic histopathology (68) and to decreases in histological progression and risk of development of HCC (80). Indeed, iron reduction and low iron diets continue to be used, especially in Japan and China, as safe and inexpensive therapy for CHC among those who have not responded to, or have not tolerated, IFN-based anti-viral therapy (81) [H Hayashi, L-Y Zheng, personal communication]. Iron reduction is also used by some clinicians in the USA and Europe, (82) for similar indications [H Bonkovsky, unpublished; T Desai, S Shedlofsky, personal communication] although we acknowledge that this approach is not used in most centers. In several small studies, iron reduction before and during IFN therapy has been shown to improve CVR, EOTR, and SVR, and a meta-analysis established significant benefit of such therapy (70).
Recently, investigators from Japan and Italy concluded that patients with CHC are more sensitive to iron hepatotoxicity than patients with HH and recommended venesection to reduce activity of liver disease in both conditions (83). Others in Japan concluded that iron reduction by venesection was superior to dietary iron redirection in CHC (81).
Furthermore, other benefits of phlebotomy in CHC patients without PCT include known improvement of serum aminotransferase levels (8, 37, 70, 84), improvement of fibrosis (70), and decreased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (25, 70). In light of the above data, it is not unreasonable to recommend pretreatment phlebotomy in CHC patients without PCT, who have not responded to or have been intolerant of or unable to afford anti-viral double or triple therapy, especially if they are found to have hepatic iron concentrations >1,100 μg/g dry liver or >1+ stainable iron (85), and if siderosis is primarily mesenchymal. However, additional larger prospective clinical trials are needed in order to better assess whether there is a role for iron reduction in management of some patients with chronic hepatitis C. Furthermore, with the several new stat-C small molecule drugs with potent activity against the HCV virus now under development, perhaps, in the not-too-distant future, rates of cure and tolerability of therapy will both improve further, and the numbers of subjects for whom iron reduction may be considered will decrease. Nevertheless, especially in less developed countries or in those without the means to afford expensive new multiple drug regimens, the inexpensive and safe measures of iron reduction and low iron diets may retain a useful place in the therapeutic armamentarium.
Summary and Conclusions
An important etiological association between CHC and PCT is well-established. Both CHC and PCT are also associated with hepatic iron overload and with increased oxidative stress. Other factors associated with PCT, such as excess alcohol and estrogen therapy, also increase oxidative stress in hepatocytes [Fig 1]. The importance of iron is further emphasized by the fact that iron reduction regularly and reliably leads to amelioration of PCT, whether associated with CHC or not. In addition, studies, especially from the Far East, indicate that iron reduction that is sustained for several years leads to improvement of the histopathological severity of CHC, to reduced risk of histopathological progression, and to reduced risk of development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Thus, we recommend iron reduction as initial therapy of PCT and of CHC with PCT. In addition, iron reduction and maintenance of an iron-reduced state are reasonable therapeutic alternatives for those who do not respond to, who do not tolerate, or cannot afford, dual or triple anti-viral therapy of CHC.
Table 3.
Recommended Management of Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
| Management/Treatment | Monitoring | |
|---|---|---|
| All cutaneous porphyrias |
|
Clinical |
| PCT |
|
Urinary or plasma porphyrins may be followed every 2-3 months. Porphyrin levels typically become normal as the target ferritin is approached. |
Adapted from Ref 99(99). Used by permission of the authors and publisher.
Acknowledgments
Supported by a grant (DK R01 38825) and contracts (U01 DK065201, U01 DK065176) from NIH (NIDDK) and by funds provided by the American Porphyria Foundation and the Carolinas HealthCare Foundation. We thank Melanie McDermid and Kay Snider for assistance with typing and preparation of the manuscript.
Statement of Conflicts of Interest: During the past three years, Dr. Bonkovsky has served as an advisor to and has received research support from Clinuvel, Inc and Novartis, Inc. He has been an adviser to Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gmbh, and Lundbeck A/S. He has received research support from Vertex, Inc. Dr. Bonkovsky is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of the American Porphyria Foundation and is Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board of the Iron Disorders Institute. He is a member of the Board of Directors of the Iron Disorders Institute. Dr. Bonkovsky is site PI at Carolinas Medical Center for the US Porphyria Consortium, a part of the Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network, supported by the NIH office of Rare Diseases and the NIDDK.
References
- 1.Chan OT, Tsai N, Wong RL, Izumi AK. The additive effects of hepatitis C infection and end-stage renal disease in porphyria cutanea tarda. Cutis. 2006;78(6):397–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Frank J, Poblete-Gutierrez P. Porphyria cutanea tarda--when skin meets liver. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24(5):735–45. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2010.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lim HW. Role of viral infection in porphyria cutanea tarda. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1997;13(3):75–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.1997.tb00116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sams H, Kiripolsky MG, Bhat L, Stricklin GP. Porphyria cutanea tarda, hepatitis C, alcoholism, and hemochromatosis: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2004;73(3):188–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chemmanur AT, Bonkovsky HL. Hepatic porphyrias: diagnosis and management. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8(4):807–38. viii. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Alla V, Bonkovsky HL. Iron in nonhemochromatotic liver disorders. Semin Liver Dis. 2005;25(4):461–72. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-923317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Badenas C, To-Figueras J, Phillips JD, Warby CA, Munoz C, Herrero C. Identification and characterization of novel uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase gene mutations in a large series of porphyria cutanea tarda patients and relatives. Clin Genet. 2009;75(4):346–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2009.01153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bonkovsky HL, Lambrecht RW. Hemochromatosis, iron overload, and porphyria cutanea tarda. In: Barton JC, Edwards CQ, editors. Hemochromatosis-Genetics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. 2. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2000. pp. 453–67. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Desnick RJ, Astrin KH. The porphyrias. In: Fauci A, Braunwald E, Kasper D, editors. Harrison’s: Principles of Internal Medicine. 17. New York: McGraw Hill; 2008. pp. 2434–44. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Foran SE, Abel G. Guide to porphyrias A historical and clinical perspective. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003;119(Suppl):S86–93. doi: 10.1309/8TGG-7CX1-4XCM-6N4L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pietrangelo A. The porphyrias: pathophysiology. Intern Emerg Med. 2010;5(Suppl 1):S65–71. doi: 10.1007/s11739-010-0452-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Desnick RJ, Bishop DF, Sassa S, Anderson KE. Disorders of heme biosynthesis: X-linked sideroblastic anemia and the porphyrias. In: Scriver C, editor. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8. New York: McGraw Hill; 2001. pp. 2991–3062. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Phillips JD, Bergonia HA, Reilly CA, Franklin MR, Kushner JP. A porphomethene inhibitor of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase causes porphyria cutanea tarda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(12):5079–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700547104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Danton M, Lim CK. Porphomethene inhibitor of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase: analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr. 2007;21(7):661–3. doi: 10.1002/bmc.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.English JC, 3rd, Peake MF, Becker LE. Hepatitis C and porphyria cutanea tarda. Cutis. 1996;57(6):404–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hussain I, Hepburn NC, Jones A, O’Rourke K, Hayes PC. The association of hepatitis C viral infection with porphyria cutanea tarda in the Lothian region of Scotland. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1996;21(4):283–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1996.tb00095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jalil S, Grady JJ, Lee C, Anderson KE. Associations among behavior-related susceptibility factors in porphyria cutanea tarda. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8(3):297–302. 02 e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.11.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sarkany RP. Making sense of the porphyrias. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008;24(2):102–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2008.00336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mahmoud BH, Hexsel CL, Hamzavi IH, Lim HW. Effects of visible light on the skin. Photochem Photobiol. 2008;84(2):450–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2007.00286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Anderson KE. The Porphyrias. In: Boyer T, Wright T, Manns M, editors. Zakim and Boyer’s Hepatology: A textbook of liver disease. 5. Philadelphia: Saunders-Elsevier; 2006. pp. 1391–420. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chiaverini C, Halimi G, Ouzan D, Halfon P, Ortonne JP, Lacour JP. Porphyria cutanea tarda, C282Y, H63D and S65C HFE gene mutations and hepatitis C infection: a study from southern France. Dermatology. 2003;206(3):212–6. doi: 10.1159/000068895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ellervik C, Birgens H, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG. Hemochromatosis genotypes and risk of 31 disease endpoints: meta-analyses including 66,000 cases and 226,000 controls. Hepatology. 2007;46(4):1071–80. doi: 10.1002/hep.21885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Azim J, McCurdy H, Moseley RH. Porphyria cutanea tarda as a complication of therapy for chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(38):5913–5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.5913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cribier B, Chiaverini C, Dali-Youcef N, et al. Porphyria cutanea tarda, hepatitis C, uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase and mutations of HFE gene. A case-control study. Dermatology. 2009;218(1):15–21. doi: 10.1159/000173696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dienhart P, Sterling R. Management of hepatitis C virus in patients with porphyria cutanea tarda. Current Hepatitis Reports. 2005;4(3):104–11. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bonkovsky HL, Poh-Fitzpatrick M, Pimstone N, et al. Porphyria cutanea tarda, hepatitis C, and HFE gene mutations in North America. Hepatology. 1998;27(6):1661–9. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wickliffe JK, Abdel-Rahman SZ, Lee C, et al. CYP1A2*1F and GSTM1 alleles are associated with susceptibility to porphyria cutanea tarda. Mol Med. 2011;17(3-4):241–7. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Scribner A, Houck D, Huang Z, Mosier S, Peel M, Scorneaux B. Synthesis and biological evaluation of [D-lysine]8cyclosporin A analogs as potential anti-HCV agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010;20(22):6542–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.09.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wright TL, Manns M. Hepatitis C. In: Boyer T, Wright TL, Manns M, editors. Zakim and Boyer’s Hepatology: A textbook of liver disease. 5. Philadelphia: Saunders-Elsevier; 2006. pp. 665–86. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bostan N, Mahmood T. An overview about hepatitis C: a devastating virus. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2010;36(2):91–133. doi: 10.3109/10408410903357455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ashfaq UA, Javed T, Rehman S, Nawaz Z, Riazuddin S. An overview of HCV molecular biology, replication and immune responses. Virol J. 2011;8:161. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Berenguer M, Lopez-Labrador FX, Wright TL. Hepatitis C and liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2001;35(5):666–78. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chuang TY, Brashear R, Lewis C. Porphyria cutanea tarda and hepatitis C virus: a case-control study and meta-analysis of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41(1):31–6. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(99)70402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dabrowska E, Jablonska-Kaszewska I, Bielawski KP, Falkiewicz B. Influence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection on porphyrin and iron metabolism in porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) patients. Med Sci Monit. 2001;7(Suppl 1):190–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gisbert JP, Garcia-Buey L, Pajares JM, Moreno-Otero R. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in porphyria cutanea tarda: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2003;39(4):620–7. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.O’Reilly FM, Darby C, Fogarty J, et al. Porphyrin metabolism in hepatitis C infection. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 1996;12(1):31–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.1996.tb00241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kawamura Y, Akuta N, Sezaki H, et al. Determinants of serum ALT normalization after phlebotomy in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40(9):901–6. doi: 10.1007/s00535-005-1636-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Narang T, Sendi H, Scobey M, Bonkovsky H. Iron and Hepatitis C. Current Hepatitis Reports. 2010;9(3):169–77. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lambrecht RW, Thapar M, Bonkovsky HL. Genetic aspects of porphyria cutanea tarda. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27(1):99–108. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-960173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Roberts AG, Whatley SD, Morgan RR, Worwood M, Elder GH. Increased frequency of the haemochromatosis Cys282Tyr mutation in sporadic porphyria cutanea tarda. Lancet. 1997;349(9048):321–3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)09436-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Santos M, Clevers HC, Marx JJ. Mutations of the hereditary hemochromatosis candidate gene HLA-H in porphyria cutanea tarda. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(18):1327–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199705013361817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Price L, Kowdley KV. The role of iron in the pathophysiology and treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Can J Gastroenterol. 2009;23(12):822–8. doi: 10.1155/2009/290383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Furutani T, Hino K, Okuda M, et al. Hepatic iron overload induces hepatocellular carcinoma in transgenic mice expressing the hepatitis C virus polyprotein. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(7):2087–98. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fillebeen C, Muckenthaler M, Andriopoulos B, et al. Expression of the subgenomic hepatitis C virus replicon alters iron homeostasis in Huh7 cells. J Hepatol. 2007;47(1):12–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nishina S, Hino K, Korenaga M, et al. Hepatitis C virus-induced reactive oxygen species raise hepatic iron level in mice by reducing hepcidin transcription. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(1):226–38. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Miura K, Taura K, Kodama Y, Schnabl B, Brenner DA. Hepatitis C virus-induced oxidative stress suppresses hepcidin expression through increased histone deacetylase activity. Hepatology. 2008;48(5):1420–9. doi: 10.1002/hep.22486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fujita N, Sugimoto R, Takeo M, et al. Hepcidin expression in the liver: relatively low level in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Mol Med. 2007;13(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.2119/2006-00057.Fujita. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Girelli D, Pasino M, Goodnough JB, et al. Reduced serum hepcidin levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2009;51(5):845–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.06.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ajioka RS, Phillips JD, Weiss RB, et al. Down-regulation of hepcidin in porphyria cutanea tarda. Blood. 2008;112(12):4723–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-138222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Weber T, Theurich S, Christopeit M, Klapperstueck T, Behre G. Human herpesvirus-6 as an inducer of porphyria cutanea tarda: implications from a case. Transpl Infect Dis. 2010;12(5):432–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3062.2010.00511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sinclair PR, Gorman N, Walton HS, et al. CYP1A2 is essential in murine uroporphyria caused by hexachlorobenzene and iron. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2000;162(1):60–7. doi: 10.1006/taap.1999.8832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dereure O, Jumez N, Bessis D, Gallix B, Guillot B. Measurement of liver iron content by magnetic resonance imaging in 20 patients with overt porphyria cutanea tarda before phlebotomy therapy: a prospective study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88(4):341–5. doi: 10.2340/00015555-0472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Linde Y, Harper P, Floderus Y, Ros AM. The prevalence of hepatitis C in patients with porphyria cutanea tarda in Stockholm, Sweden. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005;85(2):164–6. doi: 10.1080/00015550410023518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gil-Mosquera M, Vano-Galvan S, Gomez-Guerra R, Jaen P. Lesions on the hands, high aminotransferase levels. Cleve Clin J Med. 2010;77(1):34–6. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.77a.08104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Di Padova C, Marchesi L, Cainelli T, et al. Effects of phlebotomy on urinary porphyrin pattern and liver histology in patients with porphyria cutanea tarda. Am J Med Sci. 1983;285(1):2–12. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198301000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Moran MJ, Fontanellas A, Brudieux E, et al. Hepatic uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase activity in porphyria cutanea tarda patients: the influence of virus C infection. Hepatology. 1998;27(2):584–9. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ratnaike S, Blake D, Campbell D, Cowen P, Varigos G. Plasma ferritin levels as a guide to the treatment of porphyria cutanea tarda by venesection. Australas J Dermatol. 1988;29(1):3–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.1988.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rocchi E, Gibertini P, Cassanelli M, Pietrangelo A, Borghi A, Ventura E. Serum ferritin in the assessment of liver iron overload and iron removal therapy in porphyria cutanea tarda. J Lab Clin Med. 1986;107(1):36–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kostler E, Wollina U. Therapy of porphyria cutanea tarda. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005;6(3):377–83. doi: 10.1517/14656566.6.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sarkany RP. The management of porphyria cutanea tarda. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26(3):225–32. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2230.2001.00825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bonkovsky HL, Naishadham D, Lambrecht RW, et al. Roles of iron and HFE mutations on severity and response to therapy during retreatment of advanced chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2006;131(5):1440–51. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Harper P, Wahlin S. Treatment options in acute porphyria, porphyria cutanea tarda, and erythropoietic protoporphyria. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2007;10(6):444–55. doi: 10.1007/s11938-007-0044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Stolzel U, Kostler E, Koszka C, et al. Low prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in porphyria cutanea tarda in Germany. Hepatology. 1995;21(6):1500–3. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840210604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Okano J, Horie Y, Kawasaki H, Kondo M. Interferon treatment of porphyria cutanea tarda associated with chronic hepatitis type C. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997;44(14):525–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Takikawa H, Yamazaki R, Shoji S, Miyake K, Yamanaka M. Normalization of urinary porphyrin level and disappearance of skin lesions after successful interferon therapy in a case of chronic hepatitis C complicated with porphyria cutanea tarda. J Hepatol. 1995;22(2):249–50. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Rossini A, Contessi G, Bozzetti F. Efficacy of iron depletion and antiviral therapy in patients with porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) chronic infection. Hepatology. 2004;40(4):320A. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bonkovsky HL, Banner BF, Rothman AL. Iron and chronic viral hepatitis. Hepatology. 1997;25(3):759–68. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Di Bisceglie AM, Bonkovsky HL, Chopra S, et al. Iron reduction as an adjuvant to interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C who have previously not responded to interferon: a multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology. 2000;32(1):135–8. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.8700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Fernandez I, Castellano G, de Salamanca RE, et al. Porphyria cutanea tarda as a predictor of poor response to interferon alfa therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(3):314–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Desai TK, Jamil LH, Balasubramaniam M, Koff R, Bonkovsky HL. Phlebotomy improves therapeutic response to interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a meta-analysis of six prospective randomized controlled trials. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(3):815–22. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9945-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Scobey M, Bonkovsky HL. Iron: a putative reason for gender-based differences in chronic liver disease. In: Simizu I, editor. Female Hepatology: Impact of Female Sex against Progression of Liver Disease. Kerala, India: Research Signpost Publishing; 2009. pp. 97–128. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Pianko S, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, et al. Hepatic iron concentration does not influence response to therapy with interferon plus ribavirin in chronic HCV infection. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002;22(4):483–9. doi: 10.1089/10799900252952271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Rulyak SJ, Eng SC, Patel K, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Kowdley KV. Relationships between hepatic iron content and virologic response in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with interferon and ribavirin. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100(2):332–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gentile I, Viola C, Paesano L, et al. Iron depletion before HCV antiviral therapy: a pilot, randomized, controlled trial. J Clin Apher. 2009;24(5):190–6. doi: 10.1002/jca.20210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Distante S, Bjoro K, Hellum KB, et al. Raised serum ferritin predicts non-response to interferon and ribavirin treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Liver. 2002;22(3):269–75. doi: 10.1046/j.0106-9543.2002.01672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ferrara F, Ventura P, Vegetti A, et al. Serum ferritin as a predictor of treatment outcome in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(3):605–16. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2008.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lindsay KL, Morishima C, Wright EC, et al. Blunted cytopenias and weight loss: new correlates of virologic null response to re-treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6(2):234–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2007.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Lambrecht RW, Sterling RK, Naishadham D, et al. Iron levels in hepatocytes and portal tract cells predict progression and outcomes of patients with advanced chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(5):1490–500. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Hayashi H, Takikawa T, Nishimura N, Yano M, Isomura T, Sakamoto N. Improvement of serum aminotransferase levels after phlebotomy in patients with chronic active hepatitis C and excess hepatic iron. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89(7):986–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kato J, Miyanishi K, Kobune M, et al. Long-term phlebotomy with low-iron diet therapy lowers risk of development of hepatocellular carcinoma from chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42(10):830–6. doi: 10.1007/s00535-007-2095-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sumida Y, Kanemasa K, Fukumoto K, Yoshida N, Sakai K. Effects of dietary iron reduction versus phlebotomy in patients with chronic hepatitis C: results from a randomized, controlled trial on 40 Japanese patients. Intern Med. 2007;46(10):637–42. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.46.6085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Sartori M, Andorno S, Rossini A, et al. A case-control histological study on the effects of phlebotomy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23(12):1178. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328349923c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Hayashi H, Piperno A, Tomosugi N, et al. Patients with chronic hepatitis C may be more sensitive to iron hepatotoxicity than patients with HFE-hemochromatosis. Intern Med. 2010;49(22):2371–7. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.49.4088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Alsatie M, Kwo P. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C in patients who have failed to respond to IFN or IFN and ribavirin combination therapy. Current Hepatitis Reports. 2003;2(1):32–39. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Scheuer P, Lefkowitch J. Liver biopsy interpretation. Philadelphia: Saunders Co.; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Egger NG, Goeger DE, Payne DA, Miskovsky EP, Weinman SA, Anderson KE. Porphyria cutanea tarda: multiplicity of risk factors including HFE mutations, hepatitis C, and inherited uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase deficiency. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47(2):419–26. doi: 10.1023/a:1013746828074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Bulaj ZJ, Phillips JD, Ajioka RS, et al. Hemochromatosis genes and other factors contributing to the pathogenesis of porphyria cutanea tarda. Blood. 2000;95(5):1565–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Rossmann-Ringdahl I, Olsson R. Porphyria cutanea tarda in a Swedish population: risk factors and complications. Acta Derm Venereol. 2005;85(4):337–41. doi: 10.1080/00015550510033688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Nagy Z, Koszo F, Par A, et al. Hemochromatosis (HFE) gene mutations and hepatitis C virus infection as risk factors for porphyria cutanea tarda in Hungarian patients. Liver Int. 2004;24(1):16–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.00884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Tannapfel A, Stolzel U, Kostler E, et al. C282Y and H63D mutation of the hemochromatosis gene in German porphyria cutanea tarda patients. Virchows Arch. 2001;439(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/s004280100401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ivanova A, von Ahsen N, Adjarov D, Krastev Z, Oellerich M, Wieland E. C282Y and H63D mutations in the HFE gene are not associated with porphyria cutanea tarda in Bulgaria. Hepatology. 1999;30(6):1531–2. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lamoril J, Andant C, Bogard C, et al. Epidemiology of hepatitis C and G in sporadic and familial porphyria cutanea tarda. Hepatology. 1998;27(3):848–52. doi: 10.1002/hep.510270329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Roberts AG, Whatley SD, Nicklin S, et al. The frequency of hemochromatosis-associated alleles is increased in British patients with sporadic porphyria cutanea tarda. Hepatology. 1997;25(1):159–61. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Herrero C, Vicente A, Bruguera M, et al. Is hepatitis C virus infection a trigger of porphyria cutanea tarda? Lancet. 1993;341(8848):788–9. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90562-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Fargion S, Piperno A, Cappellini MD, et al. Hepatitis C virus and porphyria cutanea tarda: evidence of a strong association. Hepatology. 1992;16(6):1322–6. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Stuart KA, Busfield F, Jazwinska EC, et al. The C282Y mutation in the haemochromatosis gene (HFE) and hepatitis C virus infection are independent cofactors for porphyria cutanea tarda in Australian patients. J Hepatol. 1998;28(3):404–9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Mendez M, Rossetti MV, Del CBAM, Parera VE. The role of inherited and acquired factors in the development of porphyria cutanea tarda in the Argentinean population. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;52(3 Pt 1):417–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2004.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Martinelli AL, Zago MA, Roselino AM, et al. Porphyria cutanea tarda in Brazilian patients: association with hemochromatosis C282Y mutation and hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(12):3516–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Caballes FR, Bonkovsky HL. Cutaneous porphyrias. In: Bacon BR, Spechler S, Forsmark C, editors. Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Wilmington, DE: Decision Support in Medicine, LLC; 2011. in press. [Google Scholar]


