Abstract
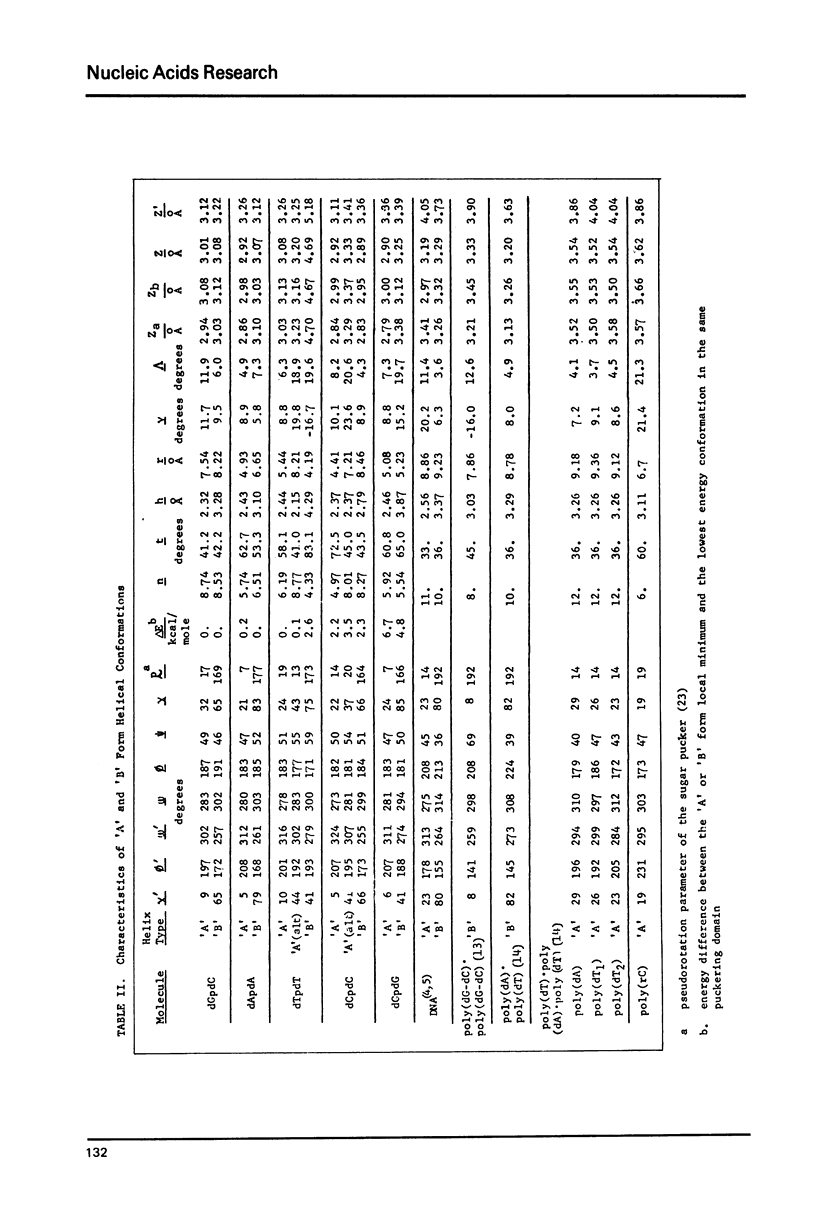
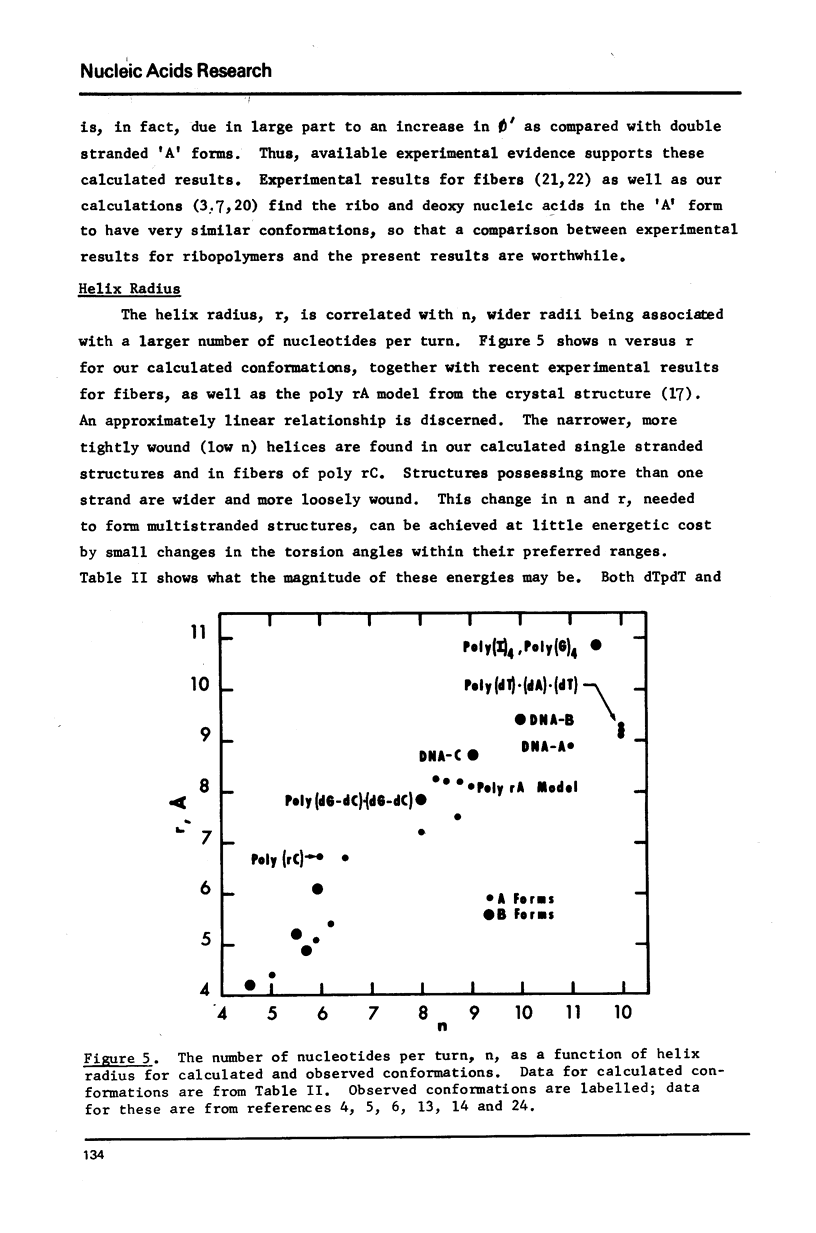
Low energy conformations with dihedral angles similar to those occurring in fibers of the 'A' and 'B' forms of DNAs have been calculated for the deoxydinucleoside phosphates dApdA, dCpdC, dTpdT, dGpdG and dGpdC (1-3). These conformers have been used as building blocks for generating larger single stranded polymers, whose helical parameters we have calculated. We find that single stranded 'A' and 'B' form helices tend to be narrower and more tightly wound than the duplexes obtained in fibers (4,5). This is consistent with experimental observations on single stranded fibers of poly (rC) (6). We also find that the different sequences have different helix geometries. In addition, it is observed that large variations in helix geometry for a given sequence are achievable at little energetic cost.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altona C., Sundaralingam M. Conformational analysis of the sugar ring in nucleosides and nucleotides. Improved method for the interpretation of proton magnetic resonance coupling constants. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Apr 4;95(7):2333–2344. doi: 10.1021/ja00788a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hukins D. W., Smith P. J., Watts L. Structural details of double-helix observed for DNAs containing alternating purine and pyrimidine sequences. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Leslie A. G. Structure of the single-stranded polyribonucleotide polycytidylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):735–748. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Optimised parameters for A-DNA and B-DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1504–1509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(72)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. The dimensions and shapes of the furanose rings in nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):453–465. doi: 10.1042/bj1300453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Structures for the polynucleotide complexes poly(dA) with poly (dT) and poly(dT) with poly(dA) with poly (dT). J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. The conformation of C-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):265–269. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahms J., Maurizot J. C., Pilet J. Interactions contributing to the stability of a polynucleotide helical chain role of the 2'-hydroxyl and of the phosphate groups. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 22;186(1):110–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyde S. B., Wartell R. M., Stellman S. D., Hingerty B., Langridge R. Classical potential energy calculations for ApA, CpC, GpG, and UpU. The influence of the bases on RNA subunit conformations. Biopolymers. 1975 Aug;14(8):1597–1613. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Tomita K. Conformational analysis of polynucleotides. I. The favorable left-handed helical model for the poly(8,2'-S-cycloadenylic acid) with high anti conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):1973–1984. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIZUSHIMA S. I., SHIMANOUCHI T. Possible polypeptide configurations of proteins from the viewpoint of internal rotation potential. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1961;23:1–27. doi: 10.1002/9780470122686.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Langridge R., Chamberlin M. J. The structure of a DNA-RNA hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1804–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. J., MacEwan A. W. Molecular and crystal structure of the polynucleotide complex: polyinosinic acid plus polydeoxycytidylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar 14;48(2):243–261. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson W. K. The spatial configuration of ordered polynucleotide chains. I. Helix formation and base stacking. Biopolymers. 1976 May;15(5):859–878. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICH A., DAVIES D. R., CRICK F. H., WATSON J. D. The molecular structure of polyadenylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1961 Feb;3:71–86. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saenger W., Riecke J., Suck D. A structural model for the polyadenylic acid single helix. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 25;93(4):529–534. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yathindra N., Sundaralingam M. Analysis of the possible helical structures of nucleic acids and polynucleotides. Application of (n-h) plots. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Mar;3(3):729–747. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


