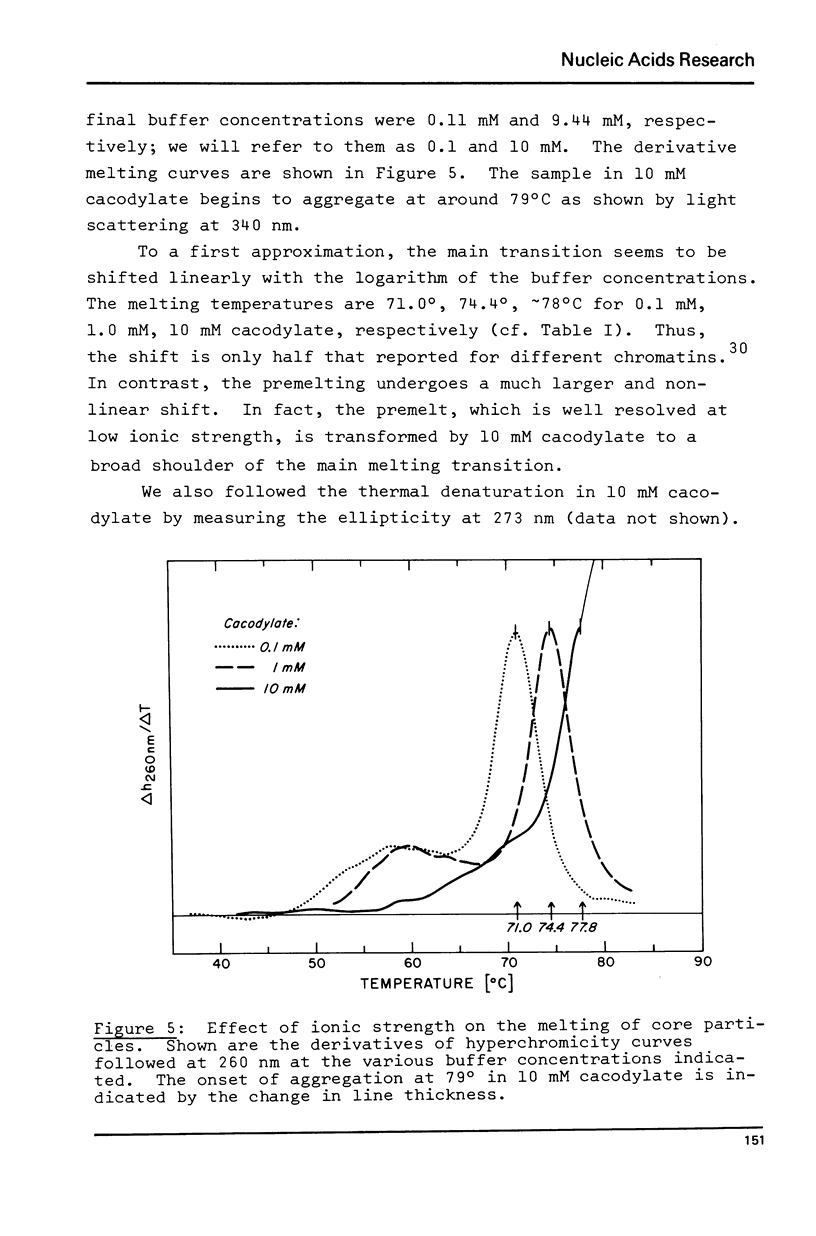
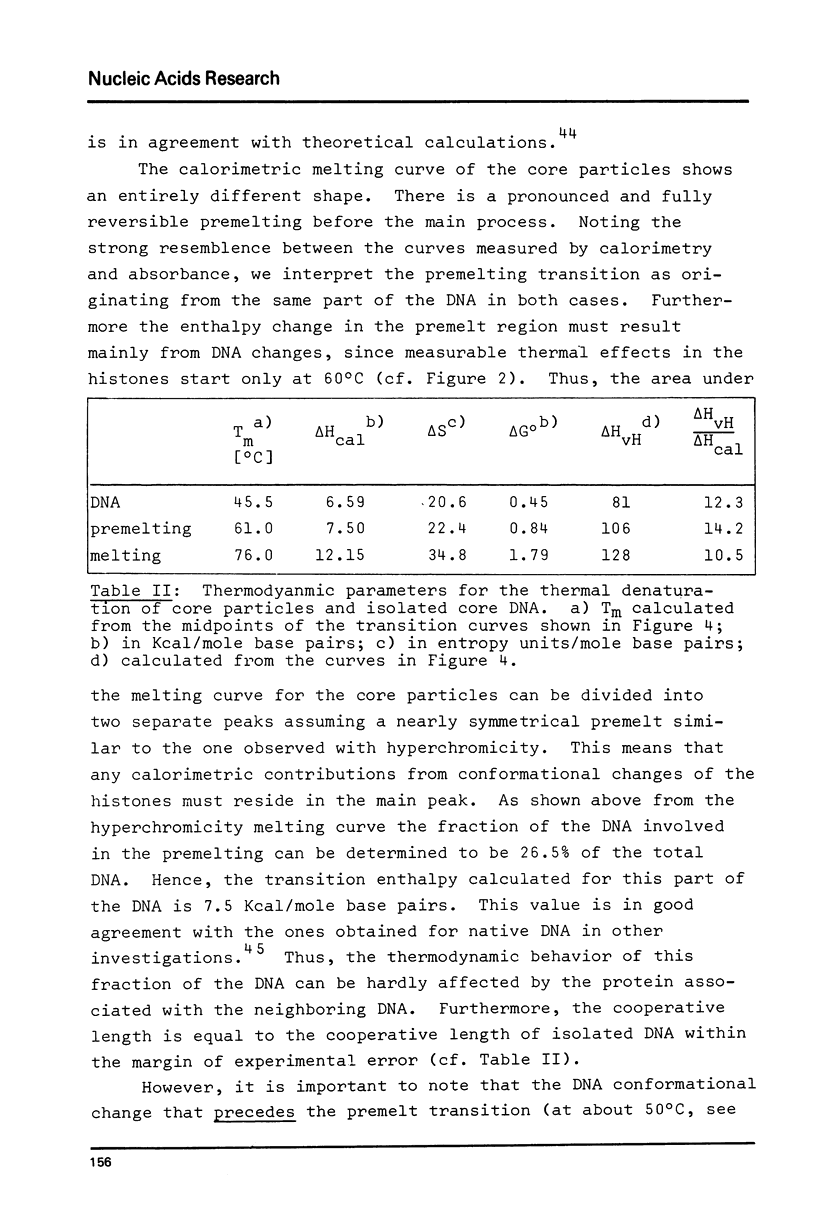
Abstract
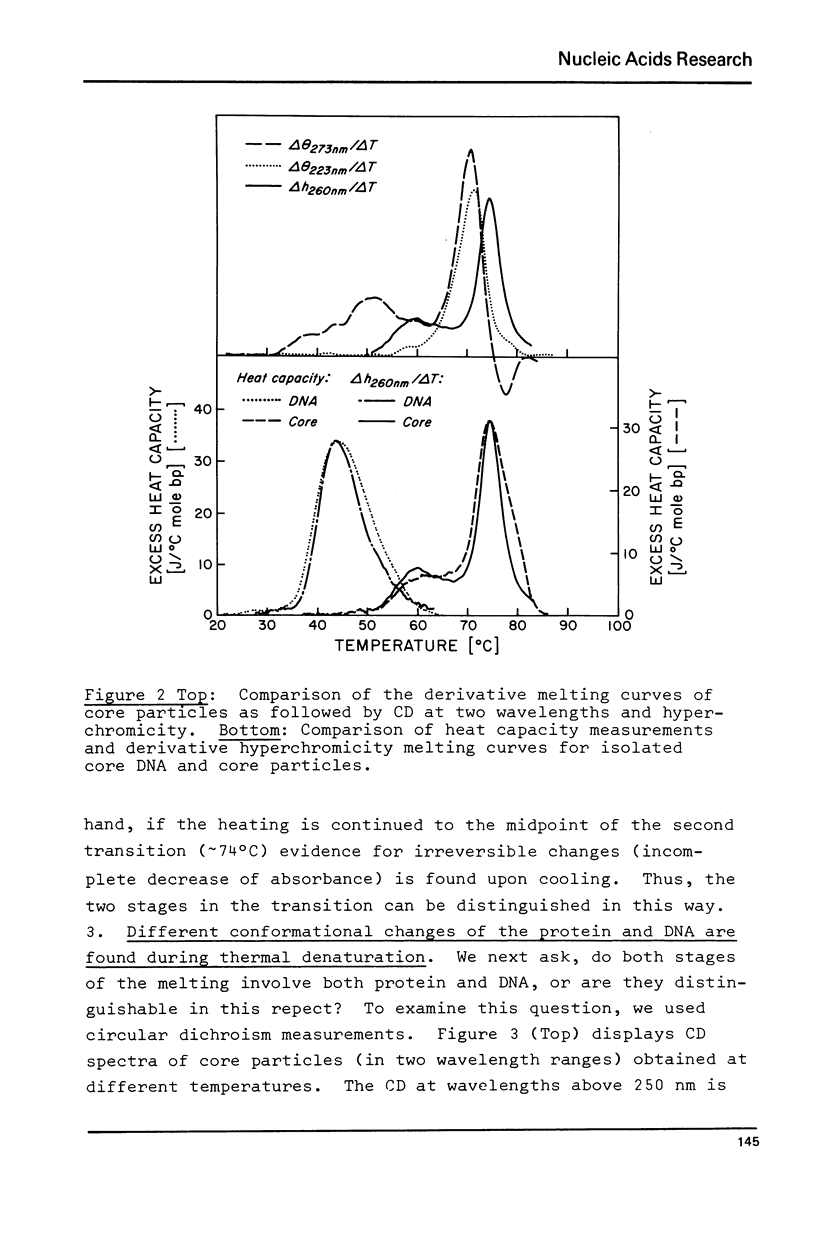
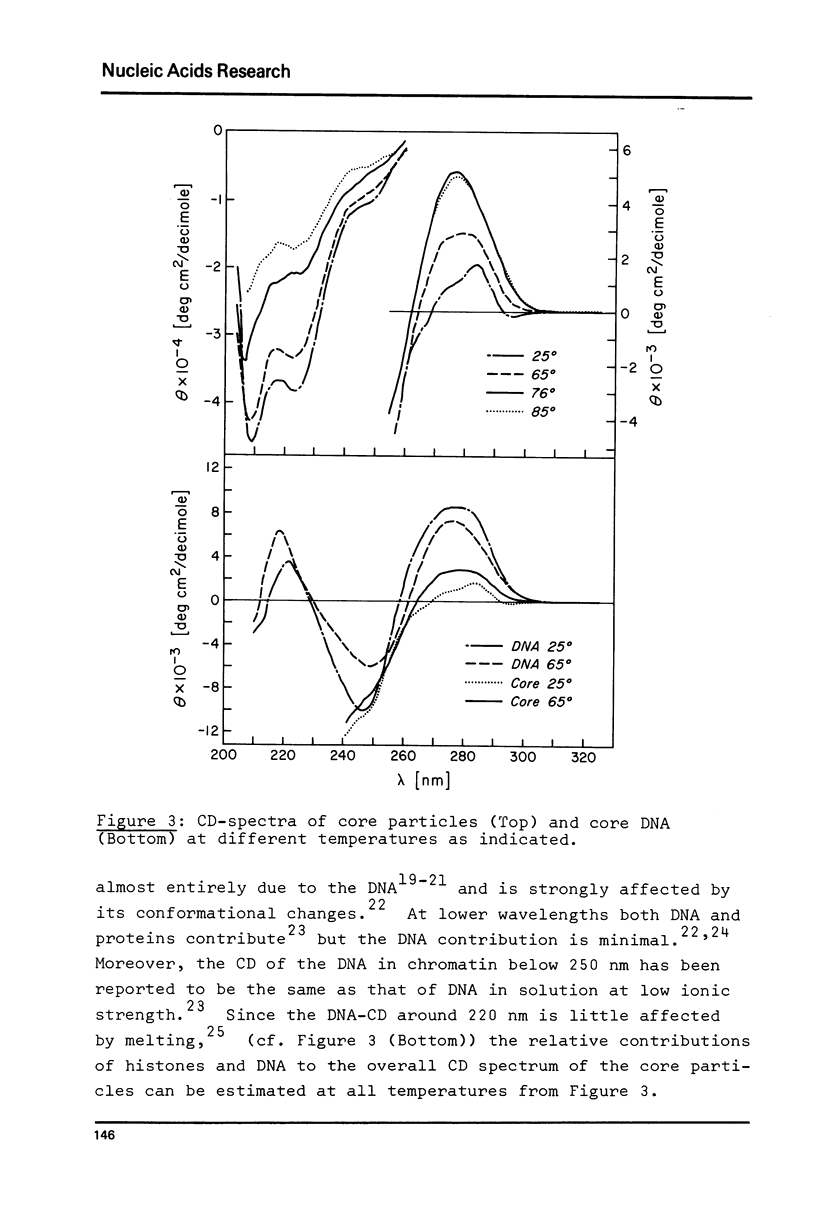
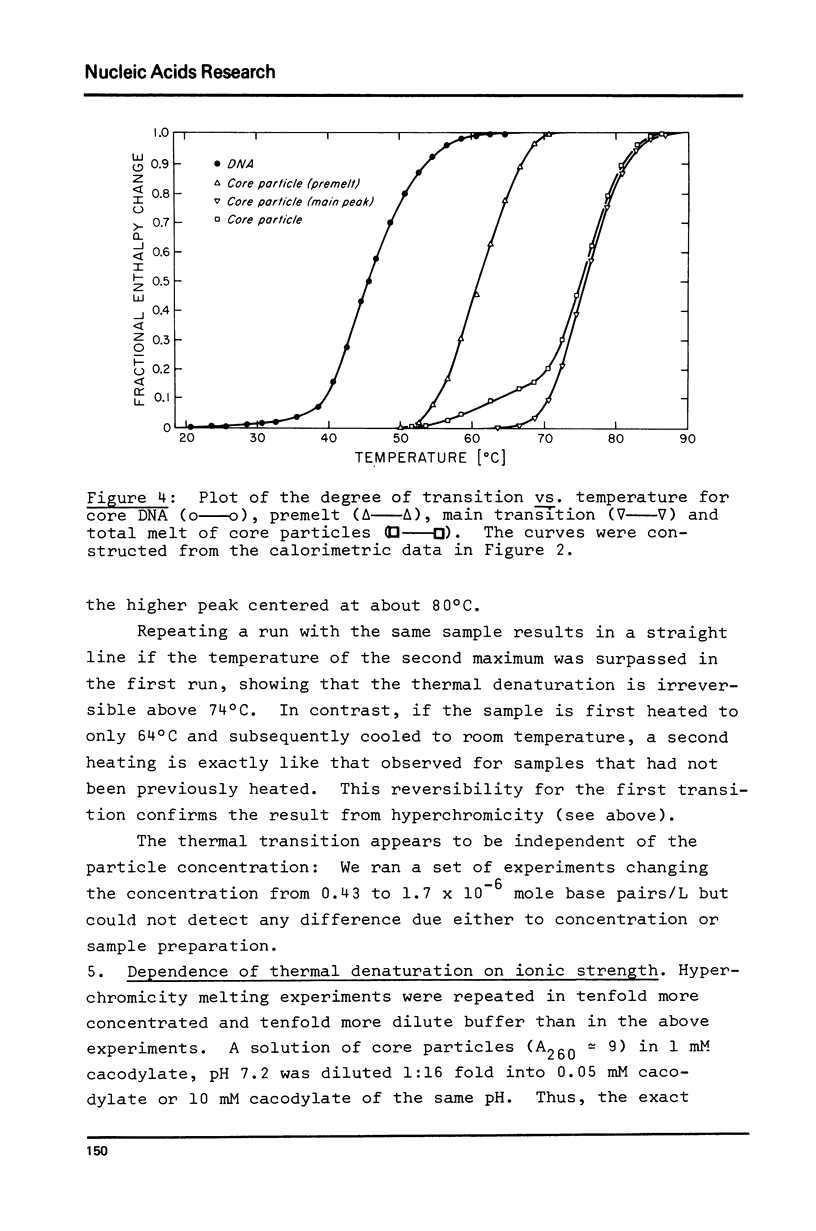
Thermal denaturation of very homogeneous preparations of core particles from chicken erythrocyte chromatin is studied by several techniques. The change in absorbance, which is very closely paralleled by changes in heat capacity, which is very closely paralleled by changes in heat capacity, is a biphasic process with inflexions at 60 degrees C and 74 degrees C. In contrast, isolated DNA of the same length denatures in a single transition around 44 degrees C. Monitoring the circular dichroism of the cores during thermal denaturation reveals biphasic changes in the secondary structure of the DNA, preceding the base unstacking by 10 degrees C in the first and 3 degrees C in the second phase. However, measurable alterations in the secondary structure of the histones are confined to the second phase with a melting temperature at 71 degrees C. Increase in the ionic strength of the buffer from 1 mM to 10 mM leads to almost monophasic melting curves as measured by absorbance and CD, while not causing any measurable conformational changes at room temperature. The melting of core particles is interpreted as a denaturation of about 40 base pairs in the first phase, followed by a massive breakdown of the native structure of a tight histone-DNA complex, which frees the remaining 100 base pairs for unstacking.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Isenberg I. On the analysis of circular dichroic spectra of proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):629–634. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Rattle H. W. Simple computer-aided approach for the analyses of the nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectra of histones. Fractions F1, Fsa1, F2B, cleaved halves of F2B and F2B-DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May 23;27(2):270–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Sturtevant J. M., Tinoco I., Jr Calorimetric and spectroscopic investigation of the helix-to-coil transition of a ribo-oligonucleotide: rA7U7. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):549–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasman G. D., Schaffhausen B., Goldsmith L., Adler A. Conformational changes associated with f-1 histone-deoxyribonucleic acid complexes. Circular dichroism studies. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 7;9(14):2814–2822. doi: 10.1021/bi00816a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Bagi G., Berg B., Bonner J. Sequence composition of the template-active fraction of rat liver chromatin. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2472–2483. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N., Fasman G. D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4108–4116. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanlon S., Johnson R. S., Chan A. Relationship between protein and DNA structure in calf thymus chromatin. II. Conformational aspects. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):3972–3981. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm R. P., Jr, Huang R. C. The conformation of proteins in chromatin. A circular dichroism study below 250 nm. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 17;14(12):2766–2774. doi: 10.1021/bi00683a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klump H. Calorimetric studies of the interaction between DNA and poly-L-lysine. Biophys Chem. 1976 Sep;5(3):363–367. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacic R. T., van Holde K. E. Sedimentation of homogeneous double-strand DNA molecules. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1490–1498. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Axel R. Analysis of DNA of isolated chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D., Wilkinson L. E., Foe V. E., Chooi W. Y. Analysis of chromatin-associated fiber arrays. Chromosoma. 1976 Oct 28;58(2):169–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00701357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. J., Chan D. C., Piette L. H. Conformational state of DNA in chromatin subunits. Circular dichroism, melting, and ethidium bromide binding analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):2879–2893. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J., Chang C., Evagelinou Z., Weiskopf M. Circular dichroism of histone-bound regions in chromatin. Biopolymers. 1975 Jan;14(1):211–226. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J. Thermal denaturation of nucleohistones--effects of formaldehyde reaction. Biopolymers. 1972;11(4):835–847. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360110408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Howarth O. W., Clark V. W., Pardon J. F., Richards B. M. An investigation of the conformational and self-aggregational processes of histones using 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4590–4600. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel R., Fasman G. D. Chromatin and nucleosome structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):1839–1855. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty K. S., Jr, Vollmer R. T., McCarty K. S. Improved computer program data for the resolution and fractionation of macromolecules by isokinetic sucrose density gradient sedimentation. Anal Biochem. 1974 Sep;61(1):165–183. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D. Theoretical calculations of the helix-coil transition of DNA in the presence of large, cooperatively binding ligands. Biopolymers. 1976 Jul;15(7):1345–1375. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Cary P. D., Abercrombie B. D., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. A pH-dependent interaction between histones H2A and H2B involving secondary and tertiary folding. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):337–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. Physical studies on the H3/H4 histone tetramer. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2261–2267. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver A. L., Wartell R. M., Ratliff R. L. Helix coil transitions of d(A)n-d(T)n, d(A-T)n-d(A-T)n, and d(A-A-T)n-d(A-T-T)n; evaluation of parameters governing DNA stability. Biopolymers. 1977 May;16(5):1115–1137. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permogorov V. I., Debabov V. G., Sladkova I. A., Rebentish B. A. Structure of DNA and histones in the nucleohistone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):556–558. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeck G. R. Histone-DNA interactions in erythrocyte chromatin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):117–122. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Van Holde K. E. The effect of trypsin on nuclease-resistant chromatin fragments. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. R., Herman T. M., Kovacic R. T., Beaudreau G. S., Van Holde K. E. Analysis of subunit organization in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Prescott B., Olins D. E. Secondary structure of histones and DNA in chromatin. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):385–388. doi: 10.1126/science.560060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien Kuo M., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Saunders G. F. Presence of messenger specifying sequences in the DNA of chromatin subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1572–1575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usatyi A. F., Shlyakhtenko L. S. Temperature dependence of CD spectra of DNA from various sources. Biopolymers. 1973;12(1):45–51. doi: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Localization of the sites along nucleosome DNA which interact with NH2-terminal histone regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6516–6520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Preparation and physical characterization of a homogeneous population of monomeric nucleosomes from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2255–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm F. X., de Murcia G. M., Champagne M. H., Daune M. P. Conformational changes of histones and DNA during the thermal denaturation of nucleoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):431–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. E., Lurquin P. F., Seligy V. L. Circular dichroism of avian-erythrocyte chromatin and ethidium bromide bound to chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):426–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock C. L., Frado L. L. Thermal denaturation of subchromosomal particles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):403–410. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80342-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



