Abstract
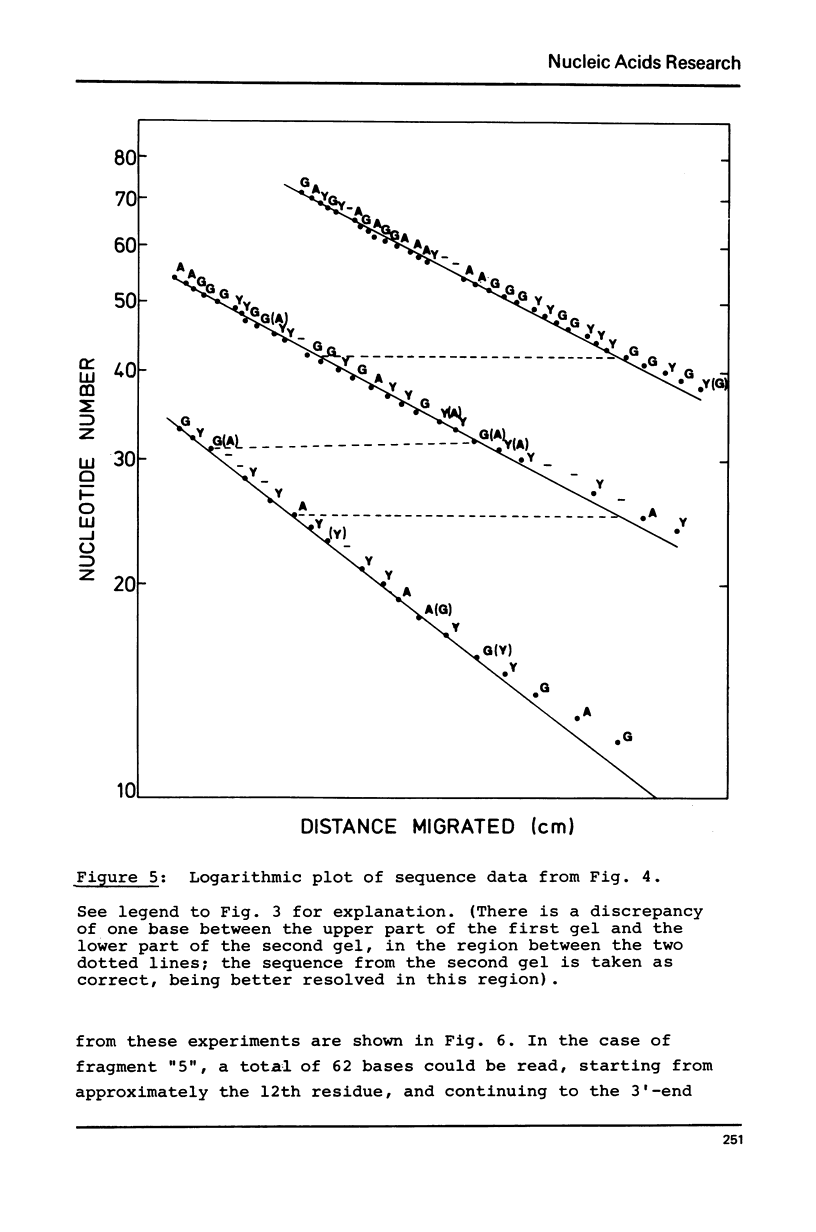
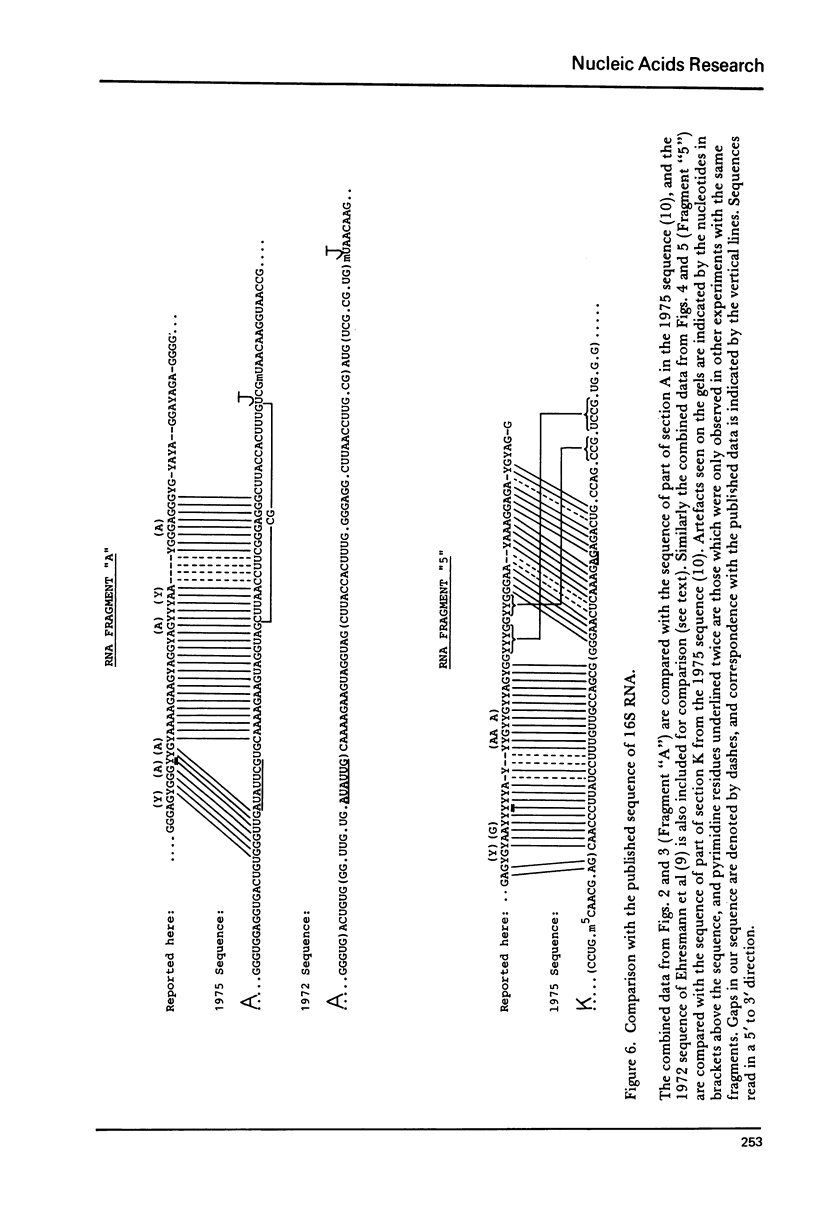
A gel sequencing method has been applied to two 5' end-labelled fragments of the 16S ribosomal RNA from E. coli. The procedure involves partial enzymatic hydrolysis by ribonucleases T1, U2 or A, in order to generate series of end-labelled subfragments terminating in guanine, adenine, or pyrimidine residues, respectively. The two fragments concerned were approximately 75 and 90 nucleotides in length, and both arose from the 3' region of the 16S RNA. The sequences deduced are compared with the published sequence of 16S RNA, and contribute information to the final ordering of the ribonuclease T1 oligonucleotides in the latter, as well as revealing some probable errors.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun R., Behrens K. A ribonuclease from Physarum. Biochemical properties and synthesis in the mitotic cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 19;195(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90605-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Cartwright E. M. Rapid gel sequencing of RNA by primed synthesis with reverse transcriptase. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):93–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Fiers W. A method for the isolation of cytidylate series from ribonuclease T1-oligonucleotides. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Fellner P., Ebel J. P. The determination of the primary structure of the 16S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. 2. Nucleotide sequences of products from partial enzymatic hydrolysis. Biochimie. 1972;54(7):901–967. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Fellner P., Ebel J. P. The determination of the primary structure of the 16S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. III. Further studies. Biochimie. 1975;57(6-7):711–748. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Randerath K. Use of specific endonuclease cleavage in RNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1957–1978. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J., Brimacombe R. A series of specific ribonucleoprotein fragments from the 30-S subparticle of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):542–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. C. Phosphorylation of nucleic acid by an enzyme from T4 bacteriophage-infected Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):158–165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Ross A., Brimacombe R. Characterisation of RNA fragments obtained by mild nuclease digestion of 30-S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Yuki A., Brimacombe R. Studies on the environment of protein S7 within the 30-S subunit Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):77–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Bonen L., Schaup H. W., Lewis B. J., Zablen L., Woese C. The use of ribonuclease U2 in RNA sequence determination. Some corrections in the catalog of oligomers produced by ribonuclease T1 digestion of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol. 1974 Feb 28;3(1):63–77. doi: 10.1007/BF01795977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki A., Brimacombe R. Nucleotide sequences of Escherichia coli 16-S RNA associated with ribosomal proteins S7, S9, S10, S14 and S19. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):23–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]