Abstract
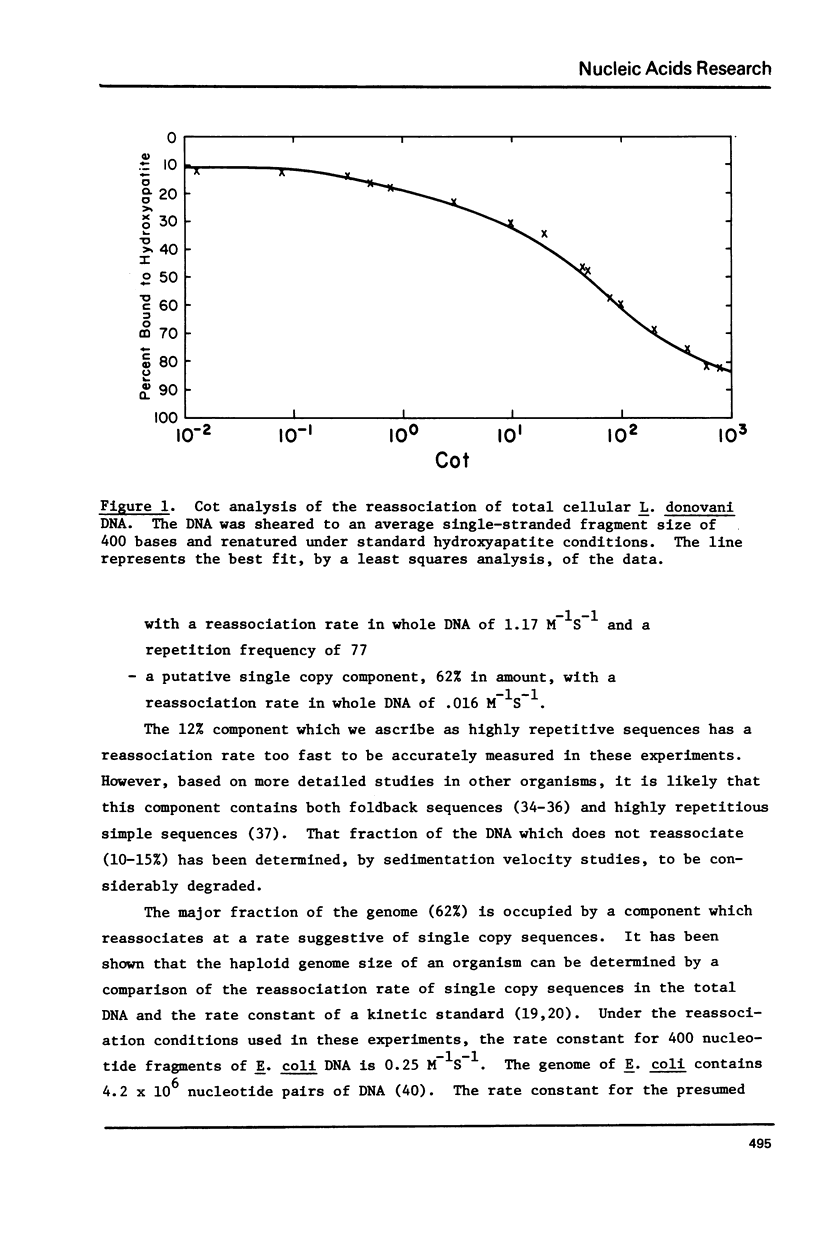
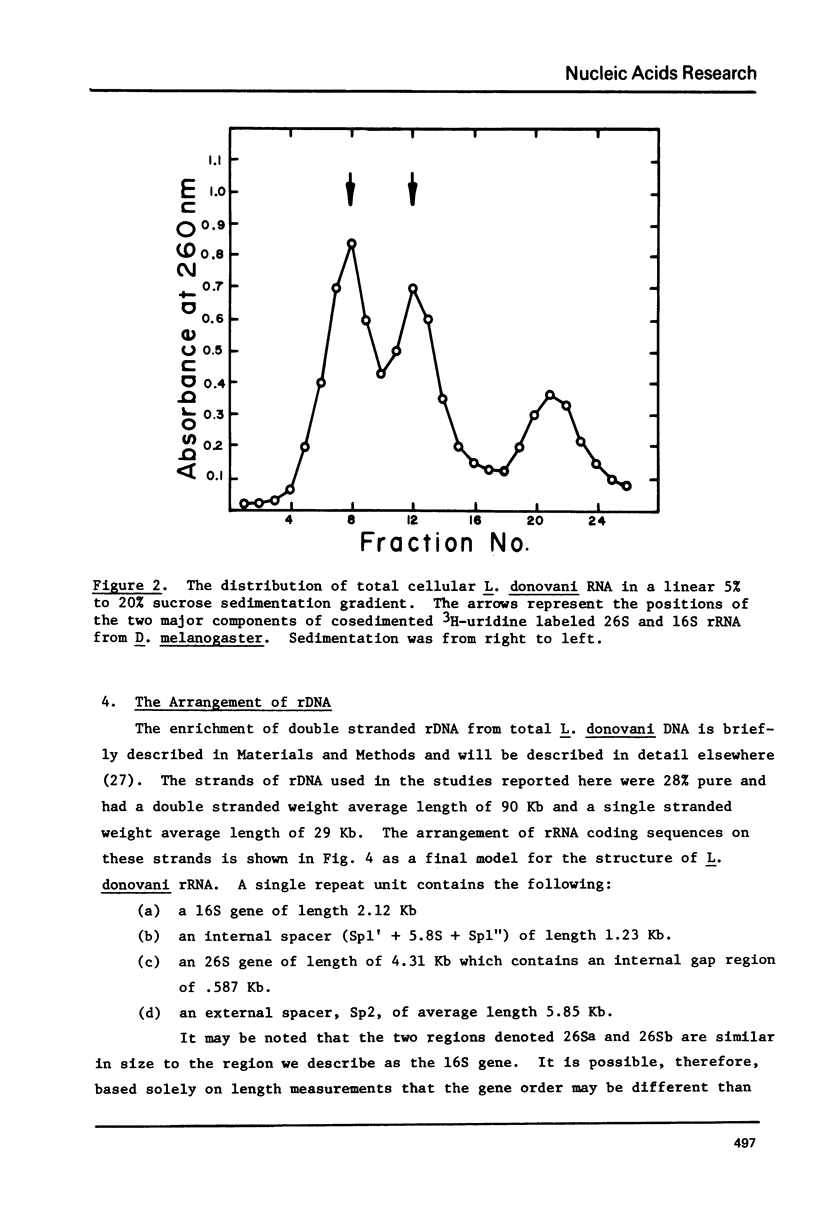
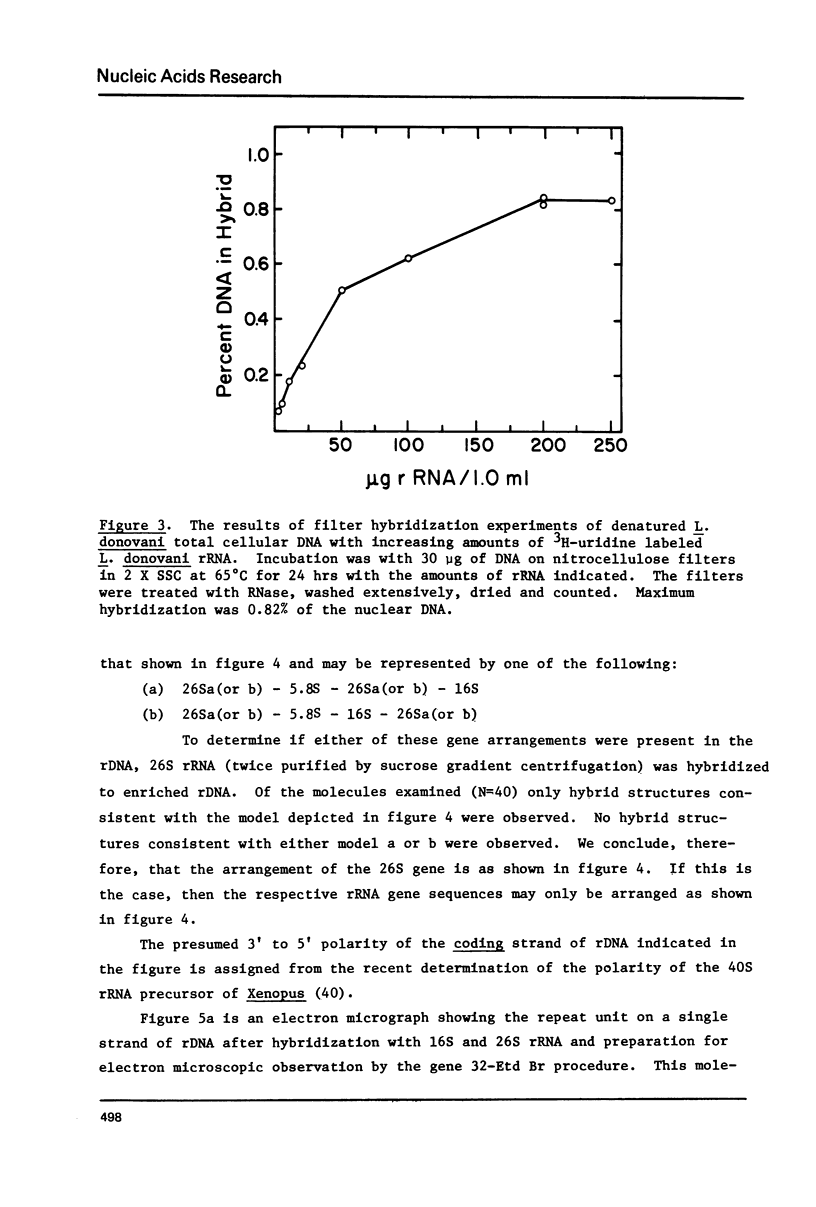
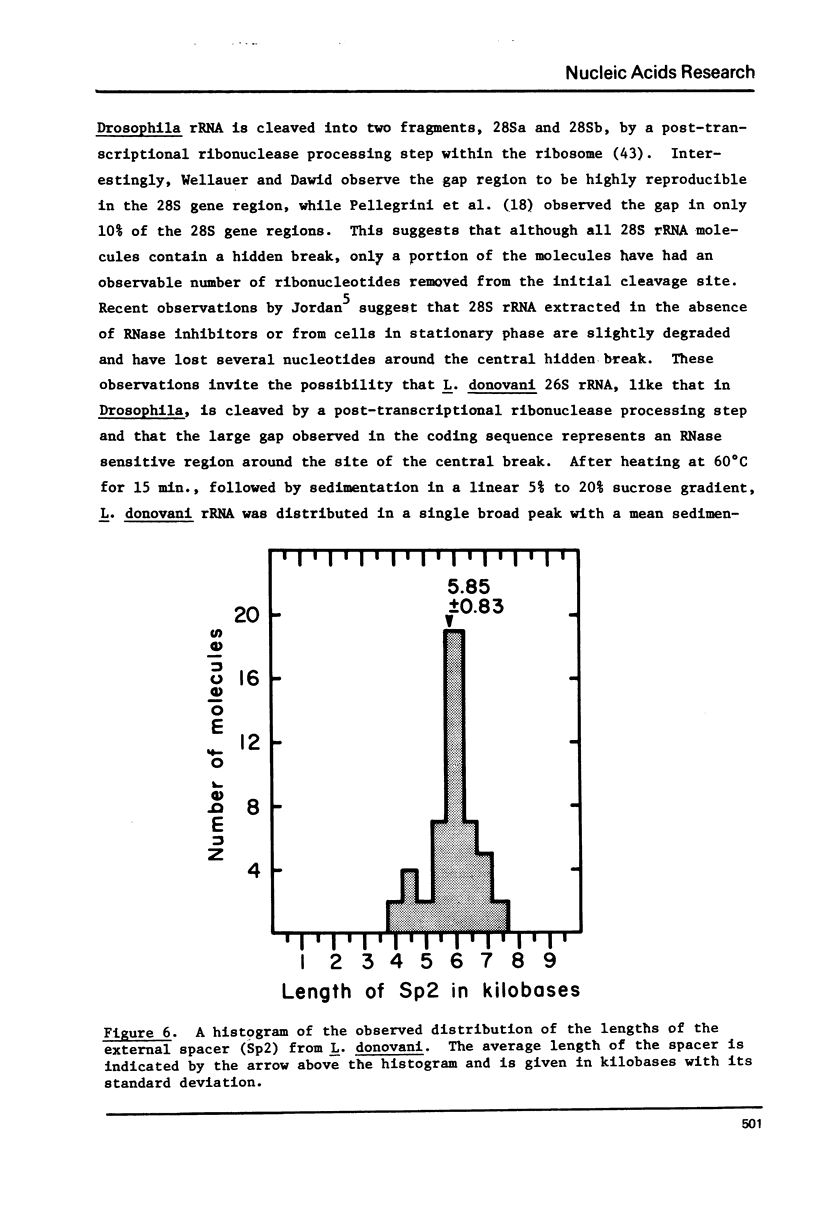
Kinetic and chemical analysis show that the haploid genome of Leishmania donovani has between 4.6 and 6.5 X 10(7) Kb pairs of DNA. Cot analysis shows that the genome contains 12% rapidly reassociating DNA, U3% middle repetitive DNA with an average reiteration frequency of 77 and 62% single copy DNA. Saturation hybridization experiments show that 0.82% of the nuclear DNA is occupied by rRNA coding sequences. The average repetition frequency of these sequences is determined to be 166. Sedimentation velocity studies indicate the two major rRNA species have sedimentation values of 26S and 16S, respectively. The arrangement of the rRNA genes and their spacer sequences on long strands of purified rDNA has been determined by the examination of the structure of rRNA:DNA hybrids prepared for electron microscopy by the gene 32-ethidium bromide technique. Long DNA strands are observed to contain several gene sets (16S + 26S). One repeat unit contains the following sequences in the order given: (a) A 16S gene of length 2.12 Kb, (b) An internal transcribed spacer (Spl) of length 1.23 Kb, which contains a short sequence that may code for a 5.8S rRNA, (C) 26S gene with a length of 4.31 Kb which contains an internal gap region of length 0.581 Ib, (d) An external spacer of average length 5.85 Kb.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnstiel M. L., Wallace H., Sirlin J. L., Fischberg M. Localization of the ribosomal DNA complements in the nucleolar organizer region of Xenopus laevis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Dec;23:431–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Weber C. S. Gene linkage by RNA-DNA hybridization. I. Unique DNA sequences homologous to 4 s RNA, 5 s RNA and ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):661–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Hearst J. E. An electron microscopic study of mouse foldback DNA. Cell. 1975 Aug;5(4):429–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn A. F., Newkirk M. J., Firtel R. A. Organization of the ribosomal RNA genes of Dictyostelium discoideum: mapping of the nontranscribed spacer regions. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Organization, transcription, and regulation in the animal genome. Q Rev Biol. 1973 Dec;48(4):565–613. doi: 10.1086/407817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Wellauer P. K. A reinvestigation of 5' leads to 3' polarity in 40S ribosomal RNA precursor of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Torres R. A., Pogo A. O. Factors affecting the estimation of nucleic acids in Euglena gracilis. Anal Biochem. 1965 Nov;13(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Bonner J. Characterization of the genome of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):339–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouts D. L., Manning J. E., Wolstenholme D. R. Physicochemical properties of kinetoplast DNA from Crithidia acanthocephali. Crithidia luciliae, and Trypanosoma lewisi. J Cell Biol. 1975 Nov;67(2PT1):378–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover D. M., Hogness D. S. A novel arrangement of the 18S and 28S sequences in a repeating unit of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover D. M., White R. L., Finnegan D. J., Hogness D. S. Characterization of six cloned DNAs from Drosophila melanogaster, including one that contains the genes for rRNA. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Warburton D., Atwood K. C. Location of ribosomal DNA in the human chromosome complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3394–3398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R. Demonstration of intact 26 S ribosomal RNA molecules in Drosophila cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):277–280. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrer K. M., Gall J. G. The macronuclear ribosomal DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis is a palindrome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):421–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D. Chromatid structure: relationship between DNA content and nucleotide sequence diversity. Chromosoma. 1971 Mar 16;32(4):378–406. doi: 10.1007/BF00285251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels N. Dictyostelium 17S, 25S, and 5S rDNAs lie within a 38,000 base pair repeated unit. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Hershey N. D., Broker T. R., Pellegrini M., Mitchell H. K., Davidson N. A new method of in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00333039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J., Pellegrini M., Davidson N. A method for gene enrichment based on the avidin-biotin interaction. Application to the Drosophila ribosomal RNA genes. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1364–1370. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molgaard H. V., Matthews H. R., Bradbury E. M. Organisation of genes for ribosomal RNA in Physarum polycephalum. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orosz J. M., Wetmur J. G. In vitro iodination of DNA. Maximizing iodination while minimizing degradation; use of buoyant density shifts for DNA-DNA hybrid isolation. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5467–5473. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardu M. L., Gerbi S. A., Eckhardt R. A., Gall J. G. Cytological localization of DNA complementary to ribosomal RNA in polytene chromosomes of Diptera. Chromosoma. 1970;29(3):268–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00325943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Hsu T. C. Locations of 18S and 28S ribosomal genes on the chromosomes of the Indian muntjac. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jan;64(1):251–254. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini M., Holmes D. S., Manning J. Application of the avidin-biotin method of gene enrichment to the isolation of long double-stranded DNA containing specific gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):2961–2973. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini M., Manning J., Davidson N. Sequence arrangement of the rDNA of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):213–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Higashinakagawa T., Miller O., Jr The 5' leads to 3' polarity of the Xenopus Ribosomal RNA precursor molecule. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Manning J. E., Davidson N. Inverted repeat sequences in the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speirs J., Birnstiel M. Arrangement of the 5-8 S RNA cistrons in the genome of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 5;87(2):237–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanowitz H., Wittner M., Sveda M., Soeiro R. Studies of ribosomal RNA of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Parasitol. 1975 Dec;61(6):1065–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Tewari K. K. Ribosomal-RNA genes in the chloroplast DNA of pea leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 15;361(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. The molecular basis for length heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):461–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA and DNA. I. Processing of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA and structure of single-stranded ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):379–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):193–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Reeder R. H., Dawid I. B., Brown D. D. Arrangement of length heterogeneity in repeating units of amplified and chromosomal ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 25;105(4):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. L., Hogness D. S. R loop mapping of the 18S and 28S sequences in the long and short repeating units of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. A., Thomas C. A., Jr Palindromes in chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 25;84(1):115–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N. Use of gene 32 protein staining of single-strand polynucleotides for gene mapping by electron microscopy: application to the phi80d3ilvsu+7 system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4506–4510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




