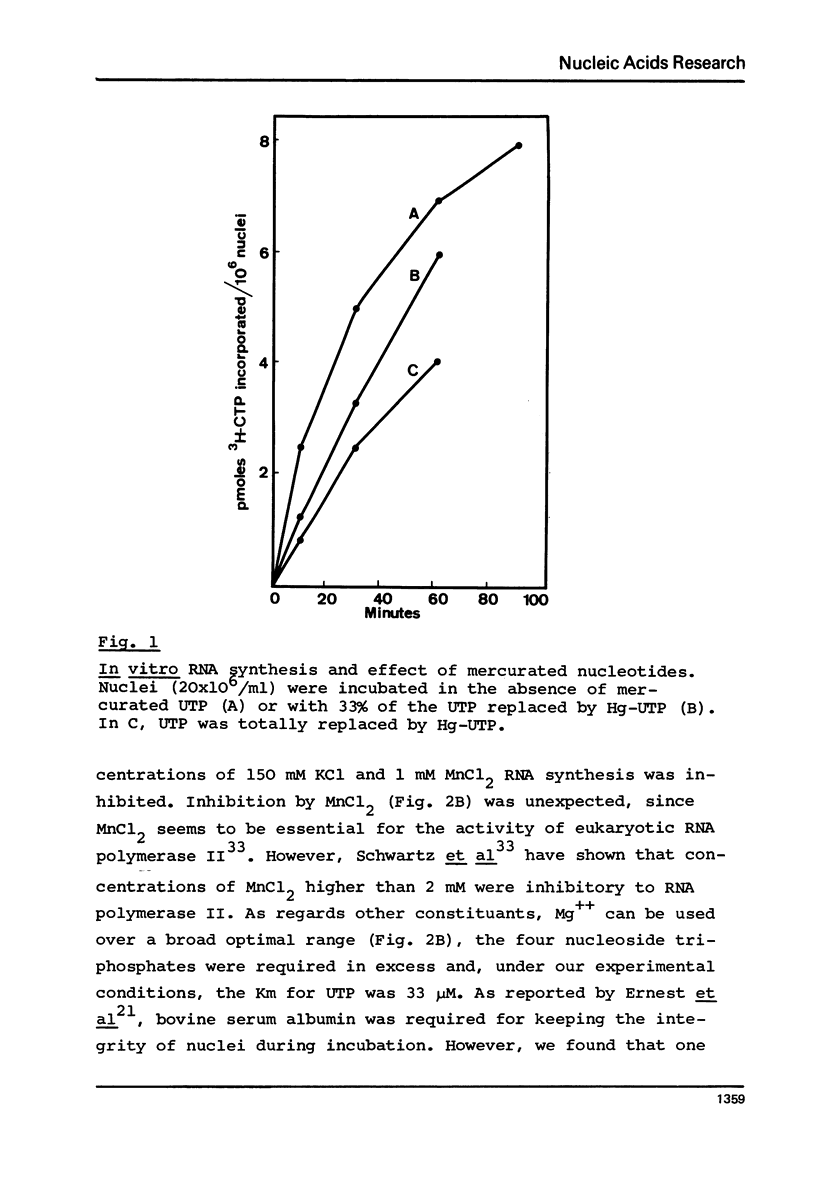
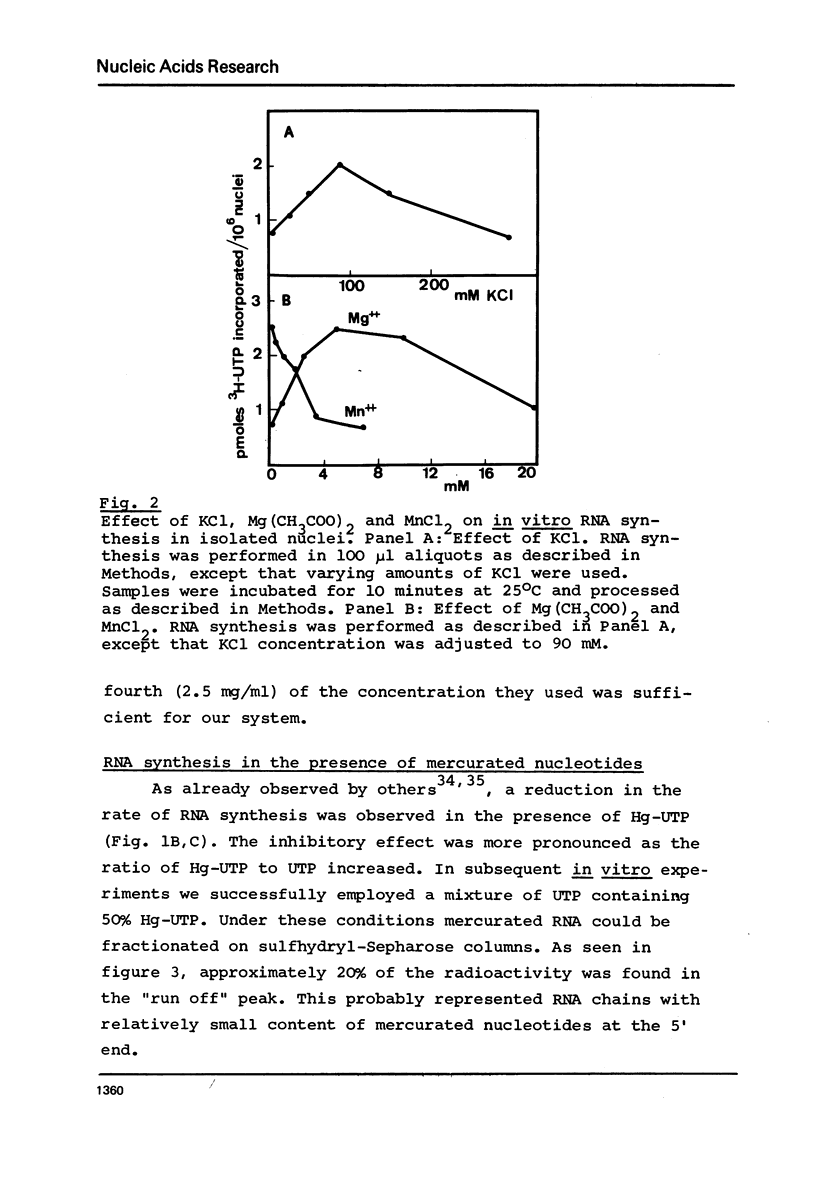
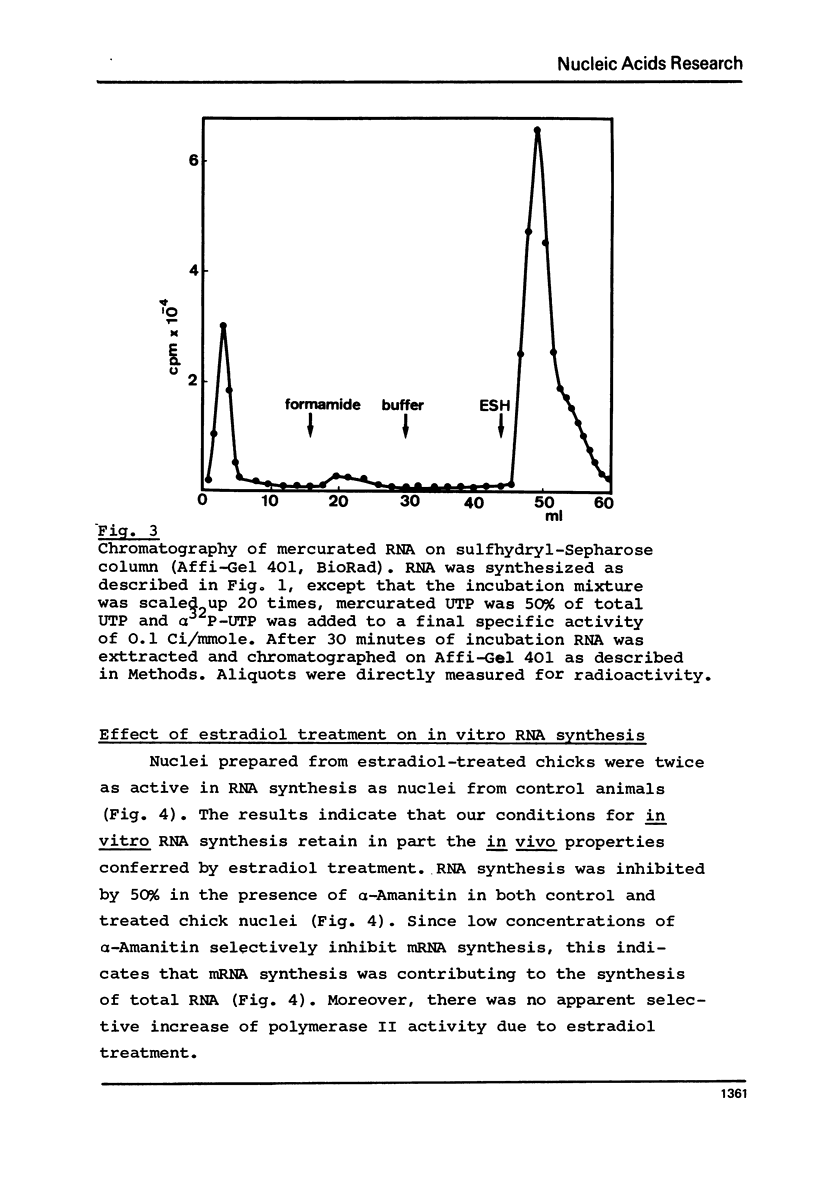
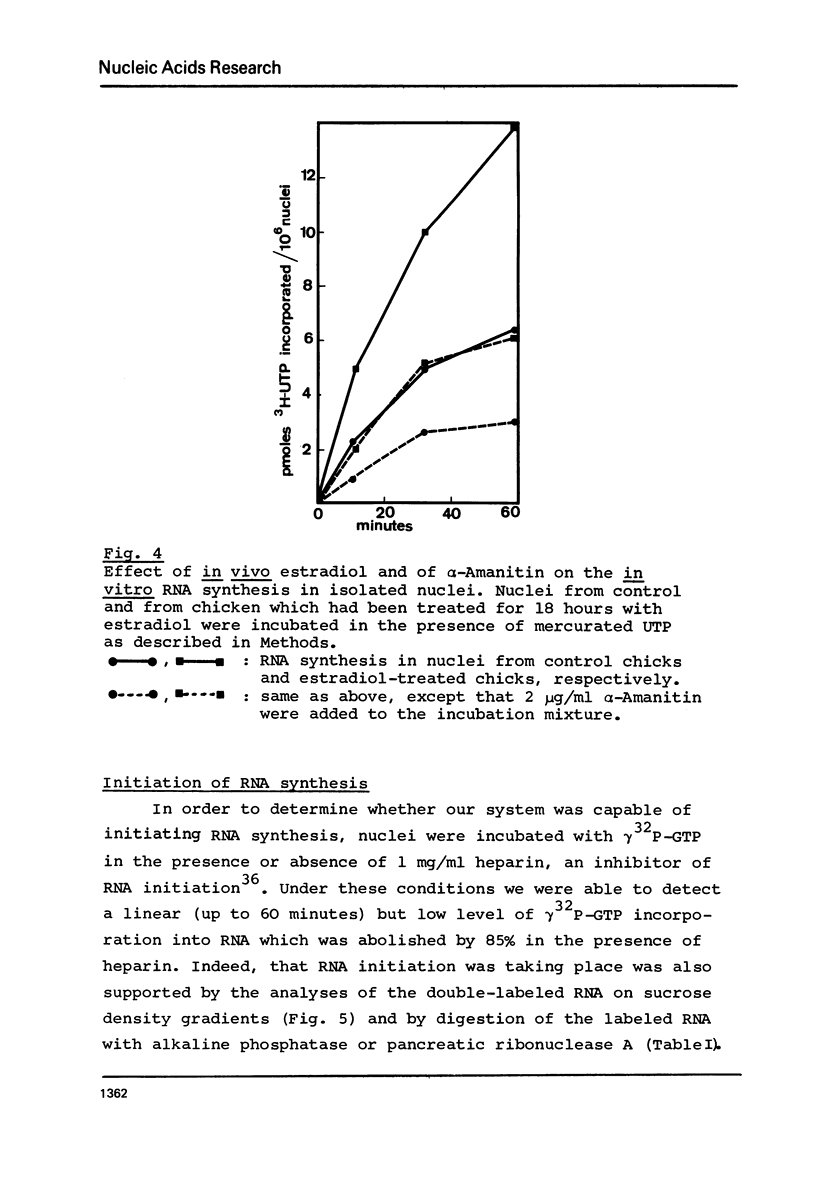
Abstract
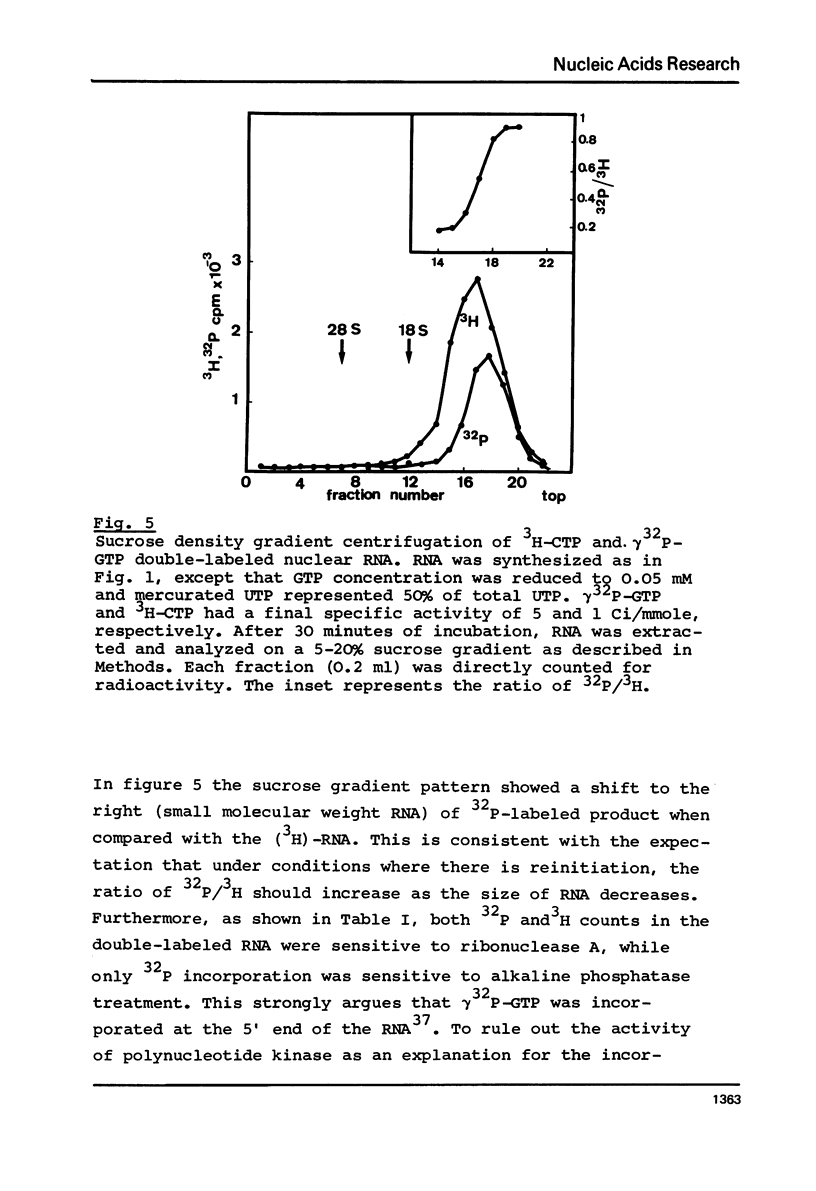
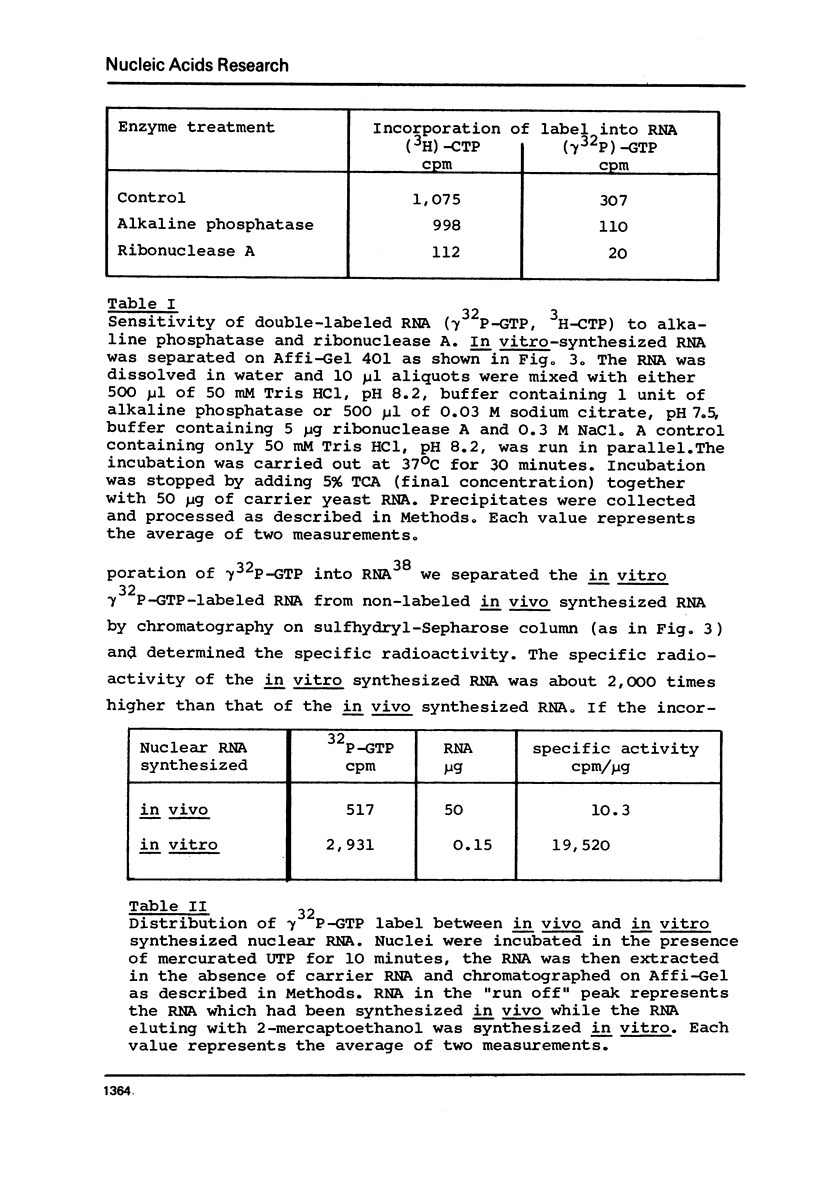
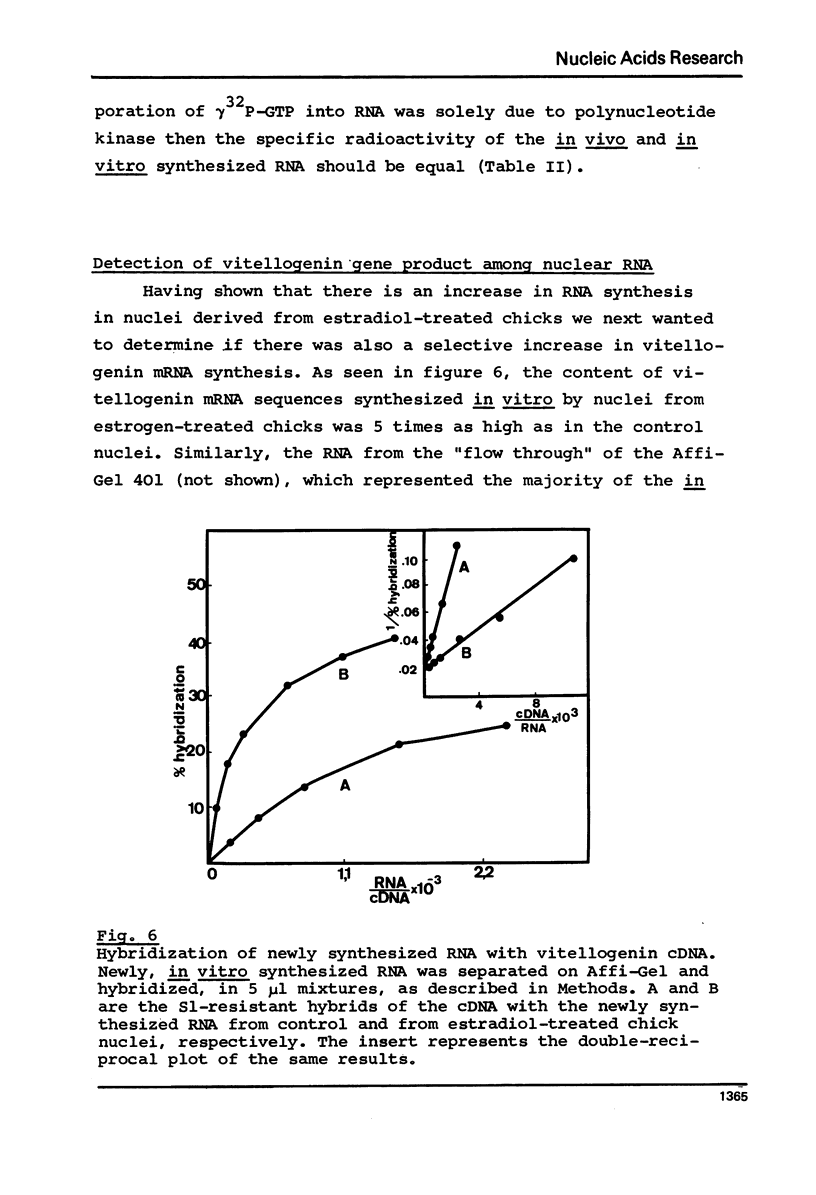
Optimal conditions for prolonged in vitro synthesis of RNA in isolated chicken liver nuclei have been described. It is shown by incorporation of gamma32P-GTP into RNA, analysis of the product on sucrose density gradient, and digestion with alkaline phosphatase and ribonuclease A that there is reinitiation of RNA synthesis. Polynucleotide kinase activity has been ruled out as explanation for the incorporation of gamma32P-GTP. alpha-Amanitin inhibits RNA synthesis by about 50%. Nuclei prepared from estradiol-treated chicks have twice the RNA synthesis activity as the controls. RNA is synthesized in the presence of Hg-UTP and the mercurated product separated by affinity chromatography on sulfhydryl-Sepharose column under stringent conditions. Vitellogenin mRNA sequences are measured by hybridization with DNA complementary to vitellogenin mRNA. Estradiol treatment leads to a 10-fold increase in vitellogenin mRNA sequences.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bast R. E., Garfield S. A., Gehrke L., Ilan J. Coordination of ribosome content and polysome formation during estradiol stimulation of vitellogenin synthesis in immature male chick livers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3133–3137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebee T. J., Butterworth P. H. The use of mercurated nucleoside triphosphate as a probe in transcription studies in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Gjerset R. A., Levy B., McCarthy B. J. Fidelity of chromatin transcription in vitro. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4356–4363. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Lazzarini R. A., Kalbacher B. An improved method for thin-layer chromatography of nucleotide mixtures containing 32P-labelled orthophosphate. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 11;40(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96624-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Transcription of high-molecular-weight RNA from hen-oviduct chromatin by bacterial and endogenous form-B RNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., Ward D. C. Mercurated polynucleotides: new probes for hybridization and selective polymer fractionation. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2458–2469. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Udell D. S., Burns A. T., Gordon J. I., Goldberger R. F. Kinetics of avian vitellogenin messenger RNA induction. Comparison between primary and secondary response to estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7913–7915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks-Ventling C., Bieri-Bonniot F. Stimulation of RNA polymerase I and II activities by 17 beta -estradiol receptor on chick liver chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Feb;4(2):381–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernest M. J., Schutz G., Feigelson P. RNA synthesis in isolated hen oviduct nuclei. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):824–829. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPEL L. A., HARKNESS D. R., HILMOE R. J. A study of the substrate specificity and other properties of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:841–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Keller R., Dierks-Ventling C. Deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid synthesis during phosvitin induction by 17beta-estradiol in immature chicks. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5262–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Pehling G., Baca O. G. Rate of synthesis of beta L-lipovitellin in the liver of immature chicks treated with 17beta estradiol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 17;62(4):957–965. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90416-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Pehling G. Immunochemical isolation and characterization of vitellogenin mRNA from liver of estradiol-treated chicks. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):339–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Pehling G. Organization of vitellogenin polysomes, size of the mRNA and polyadenylate fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Pehling G., Panyim S., Ohno T. An improved method for isolation of active vitellogenin messenger RNA from chicken liver. Use of diethylpyrocarbonate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 16;517(2):338–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. A., Garapin A. C., Jackson N., Fanshier L., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in cells producing rous sarcoma virus: detection and characterization. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):891–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.891-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. C., Rose K. M., Jacob S. T. Evidence for the nuclear origin of RNA polymerases identified in the cytosol: release of enzymes from the nuclei isolated in isotonic sucrose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90968-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Murphy E. C., Jr, Huang R. C. Transcription of ribonucleic acid in isolated mouse myeloma nuclei. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3440–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullinix K. P., Wetekam W., Deeley R. G., Gordon J. I., Meyers M., Kent K. A., Goldberger R. F. Induction of vitellogenin synthesis by estrogen in avian liver: relationship between level of vitellogenin mRNA and vitellogenin synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Swerdlow P. S. Globin RNA synthesis in vitro by isolated erythroleukemic cell nuclei: direct evidence for increased transcription during erythroid differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2475–2479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Palmiter R. D., Schimke R. T. Identification and isolation of ovalbumin-synthesizing polysomes. I. Specific binding of 125 I-anti-ovalbumin to polysomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2316–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Carey N. H. Rapid inactivation of ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid after acute withdrawal of estrogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2357–2361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskam W. G., Tichelaar W., Schirm J., Gruber M., Ab G. Estradiol-induced synthesis of vitellogenin. I. The isolation of large polysomes from estrogenized rooster liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 2;435(1):82–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Wahli W., Weber R. Quantitation of vitellogenin messenger RNA in the liver of male Xenopus toads during primary and secondary stimulation by estrogen. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5889–5897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. J., Tsai M-J, Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. V. Changes in the number of RNA polymerase binding and initiation sites in chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5175–5182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer K. P. Mercurated nucleotides: assessment of a new tool to study RNA synthesis and processing in isolated nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3109–3122. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekeris C. E., Schmid W. Action of alpha-Amanitin in vivo and in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80405-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Baker H. J. Purification and characterization of Xenopus laevis vitellogenin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5244–5250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Baker B. Differential subnuclear distribution of polyadenylate-rich ribonuclei acid during induction of egg-yolk protein synthesis in male Xenopus liver by oestradiol-17 beta. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):345–355. doi: 10.1042/bj1500345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Hamilton M. J., Shields D. Effects of alpha-amanitin in vivo on RNA polymerase and nuclear RNA synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 9;238(84):161–164. doi: 10.1038/newbio238161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. The expression of the vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle H. C., Tsai M. J., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2396–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Harris S. E., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Effects of estrogen on gene expression in chick oviduct. The role of chromatin proteins in regulating transcription of the ovalbumin gene. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4713–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Harris S. E., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Effects of estrogen on gene expression in chick oviduct. The role of chromatin proteins in regulating transcription of the ovalbumin gene. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4713–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., Schwartz R., Kalimi M., Clark J. H., O'Malley B. W. Effects of estrogen on gene expression in chick oviduct: nuclear receptor levels and initiation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Seifart K. H. Transcription of specific genes in isolated nuclei from HeLa cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):353–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W. Estrogen induces lipophosphoprotein in serum of male Xenopus laevis. Science. 1968 Apr 5;160(3823):91–92. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3823.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckler C., Gschwendt M. The effect of estradiol on the activity of the nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases from chicken liver. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winicov I. RNA phosphorylation: a polynucleotide kinase function in mouse L cell nuclei. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4233–4237. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Seifart K. H. Synthesis of ribosomal 5S RNA by isolated nuclei from HeLa cells in vitro. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3201–3209. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



