Abstract
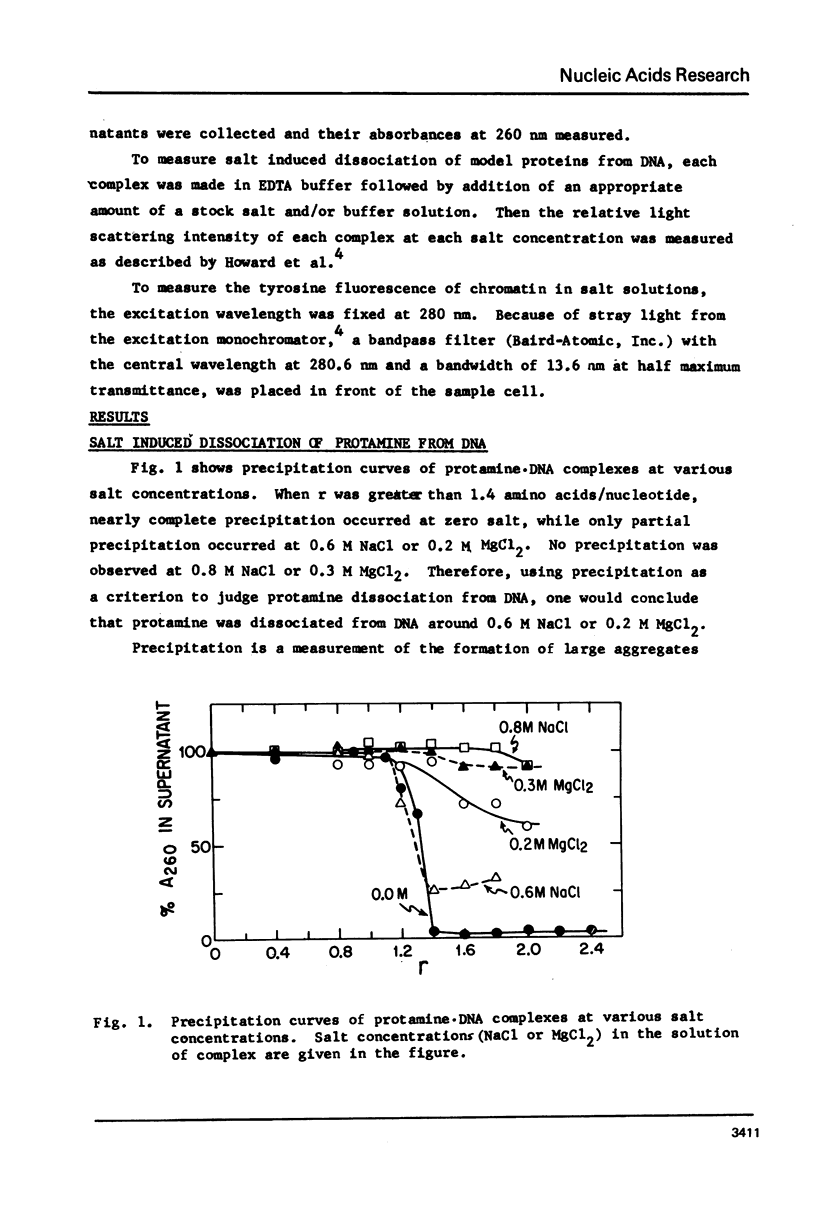
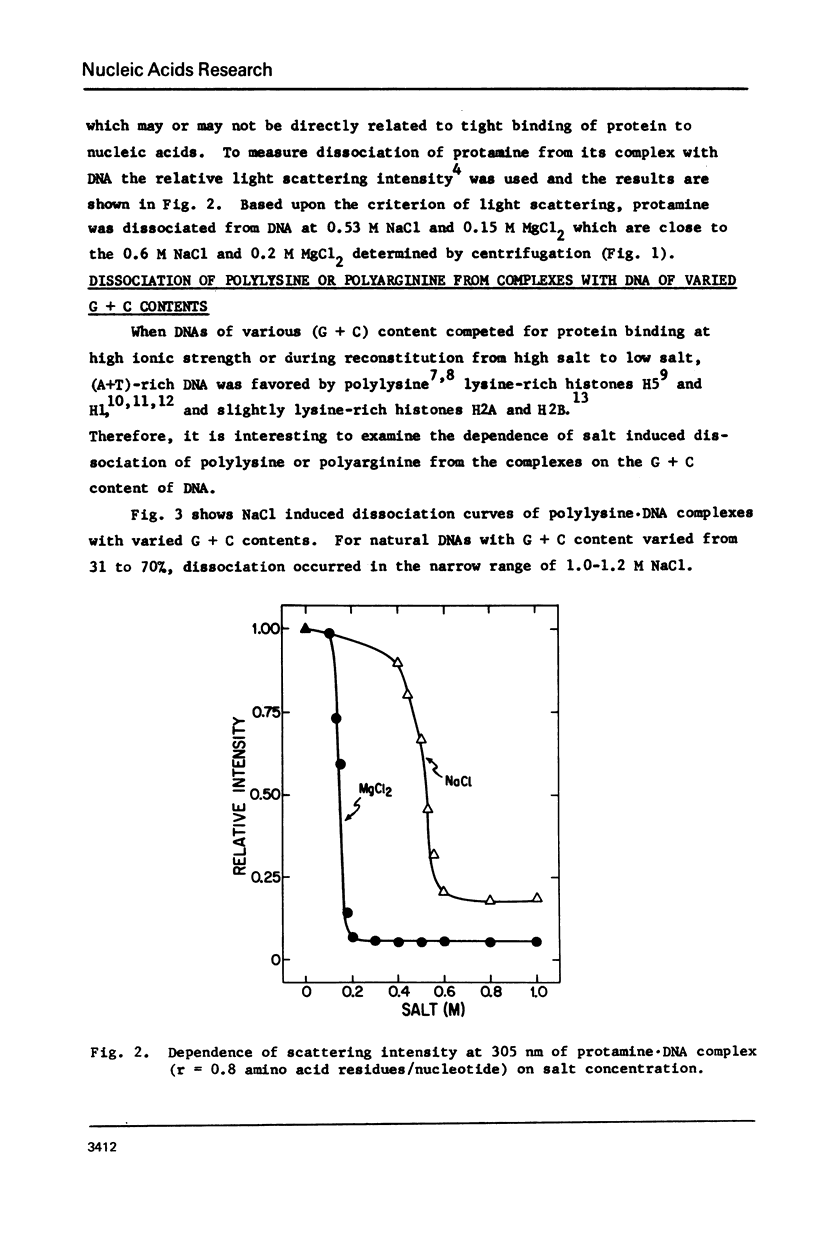
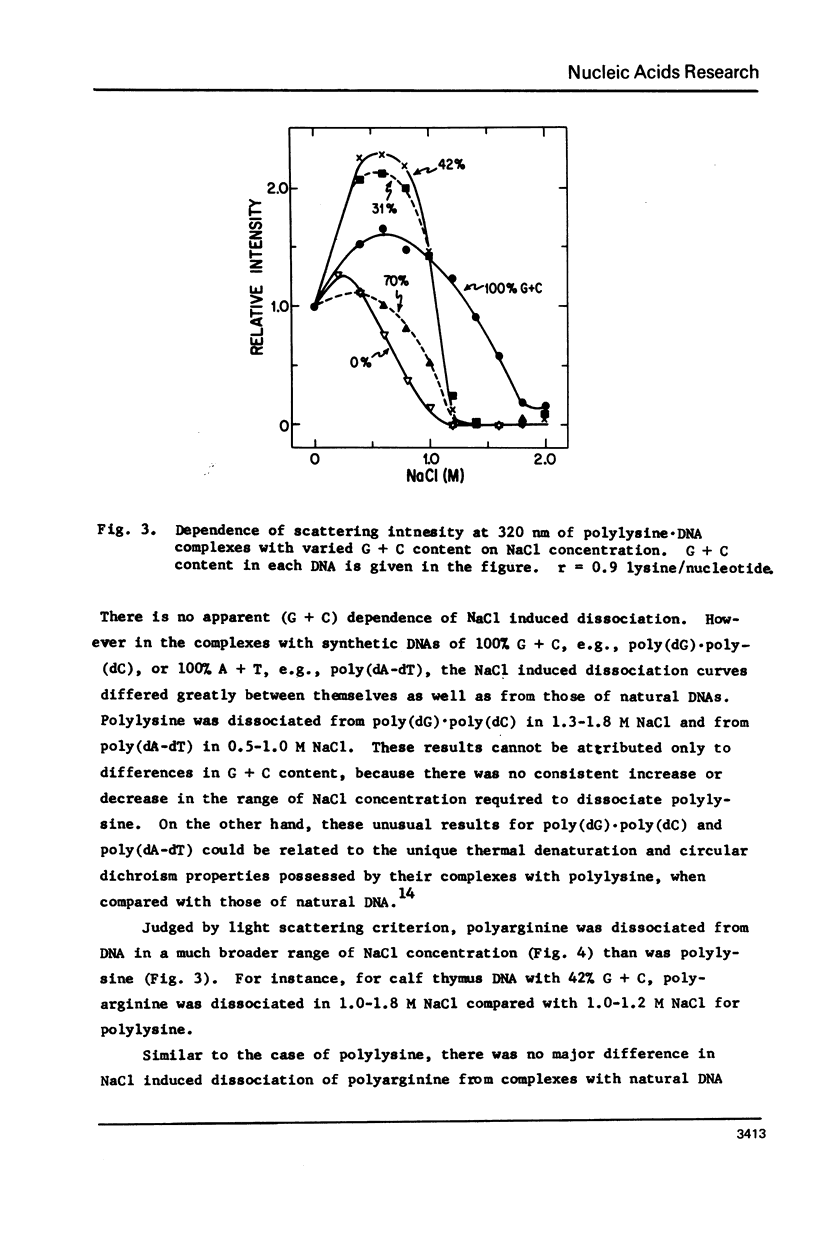
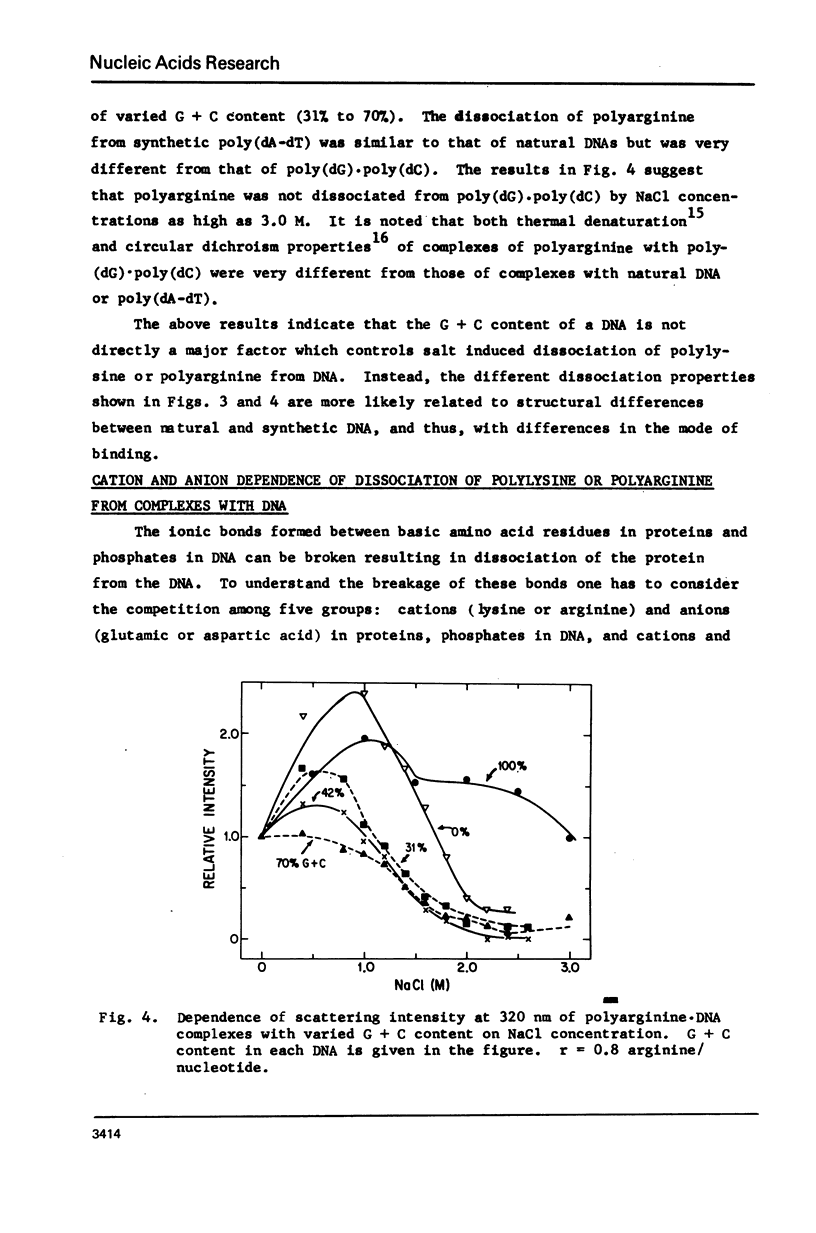
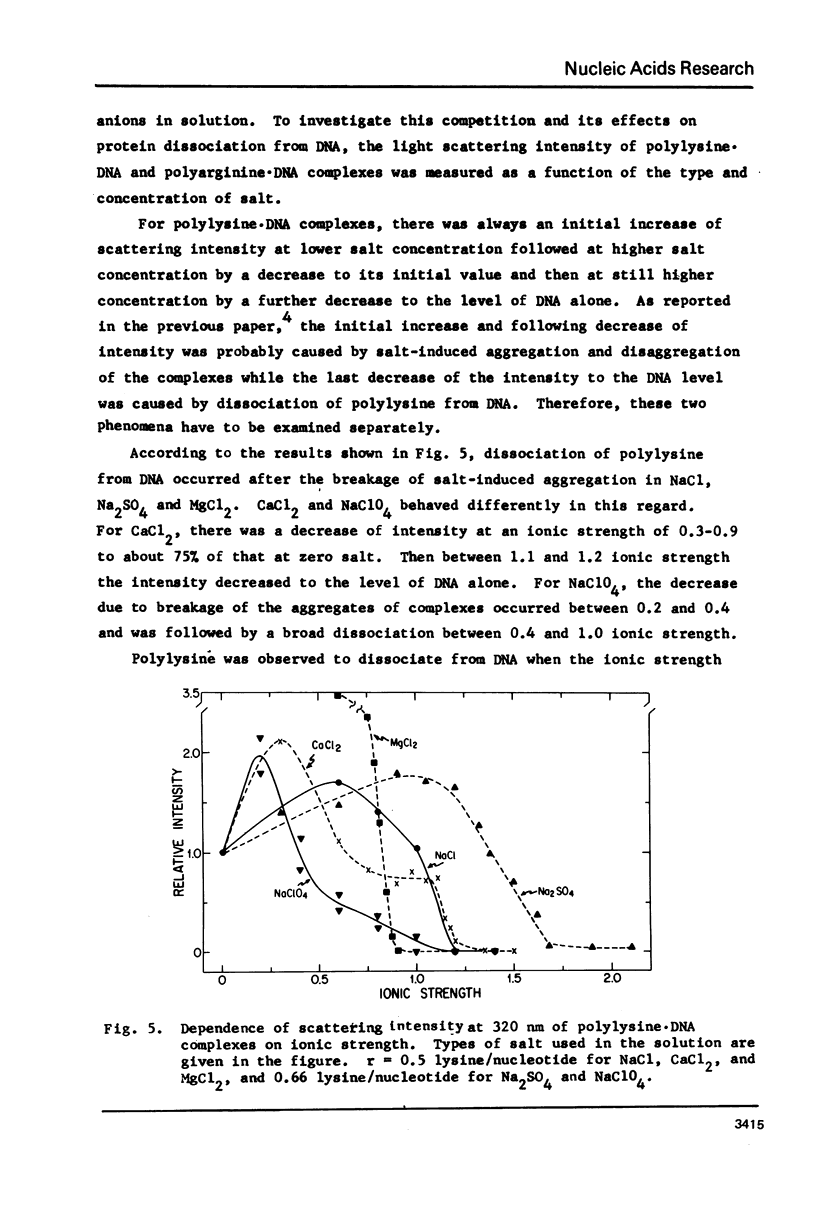
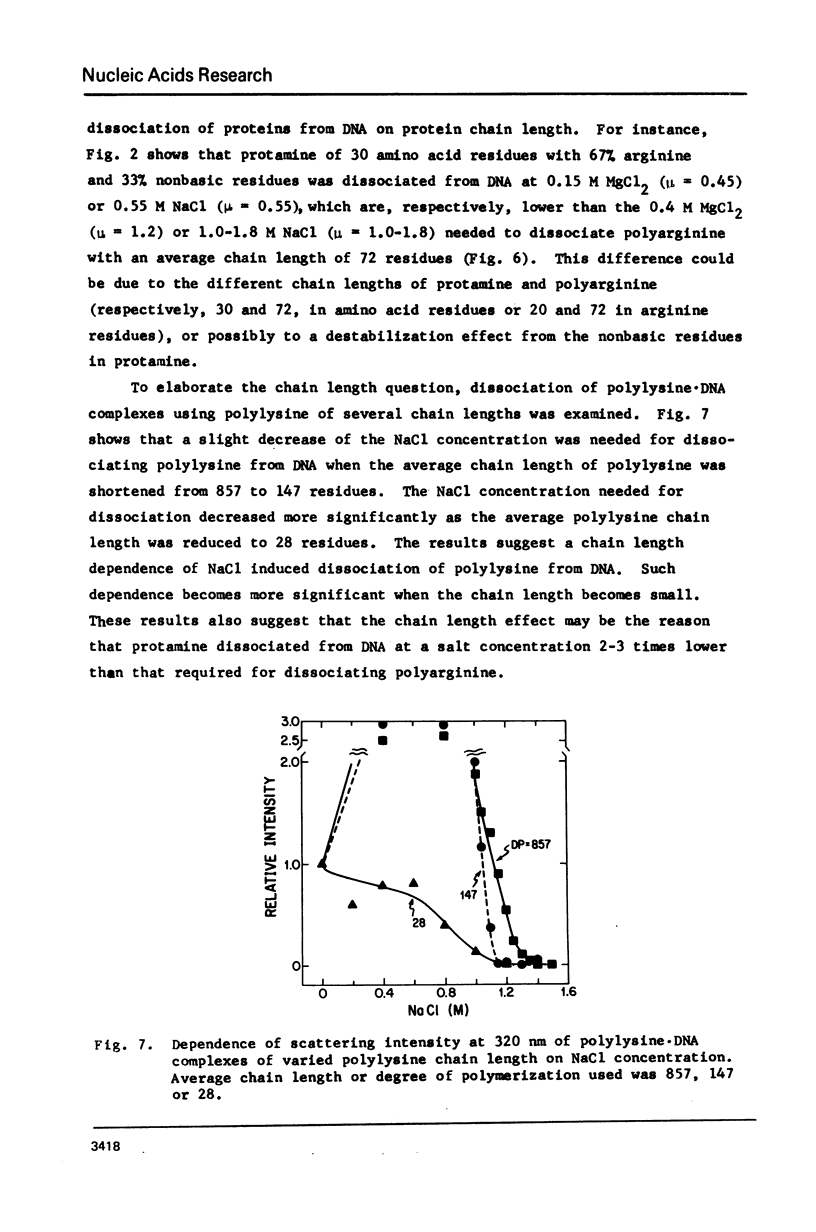
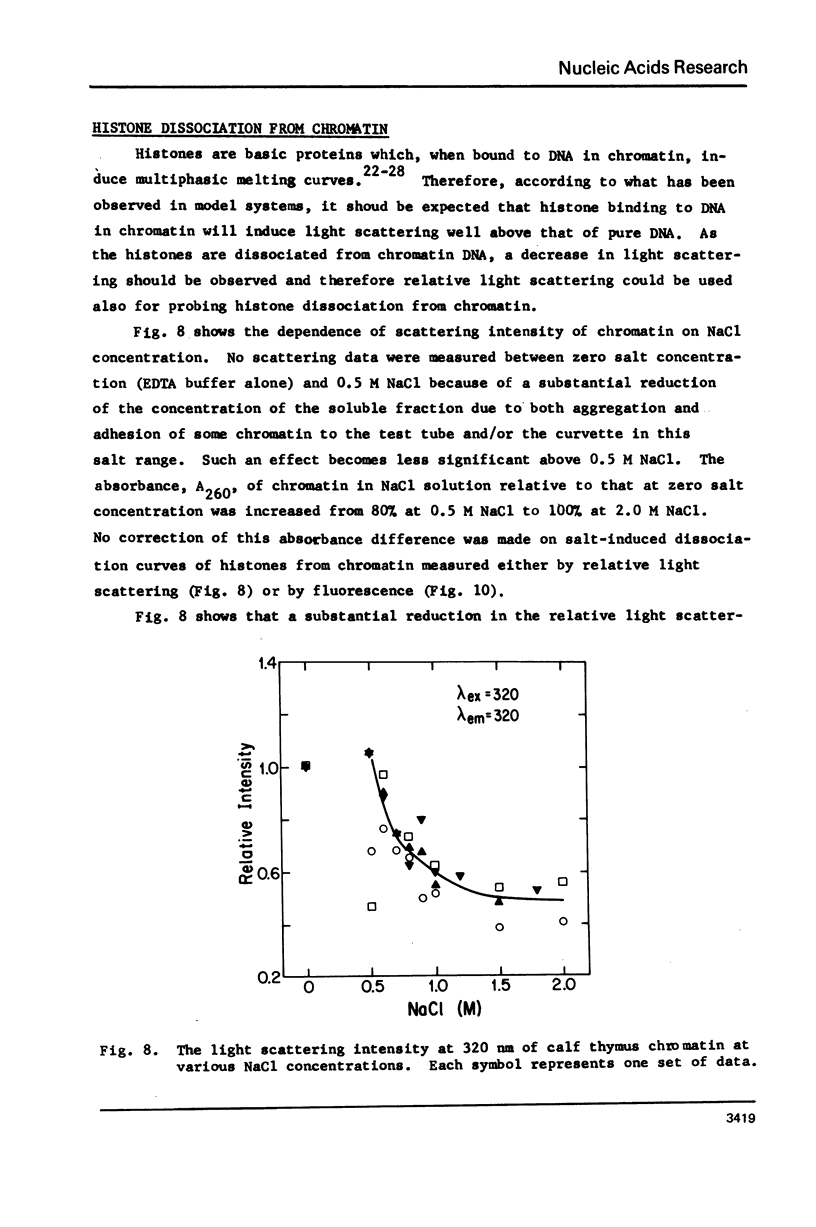
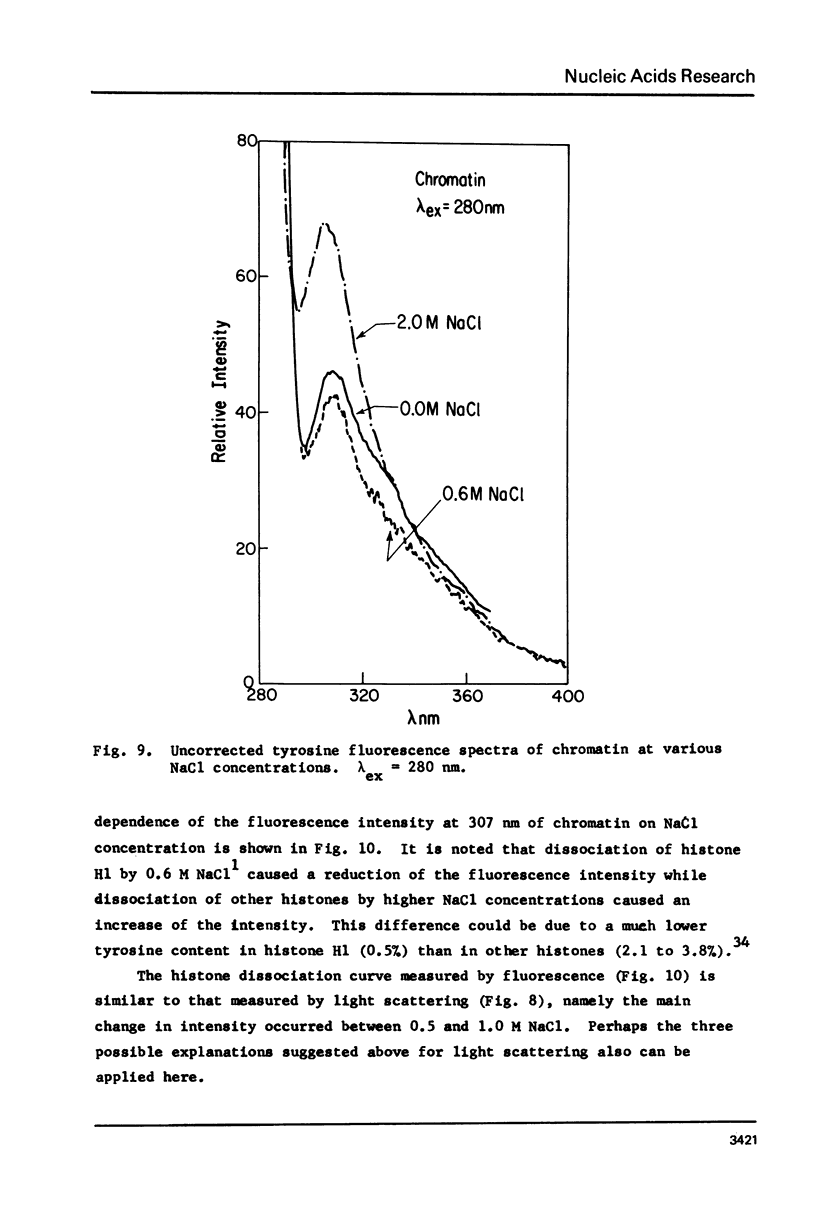
Salt induced dissociation of protamine, poly(L-lysine) and poly(L-arginine) from DNA was measured by relative light scattering at theta = 90 degrees and/or centrifugation. Dissociation of histones from DNA was studied using relative light scattering and intrinsic tyrosine fluorescence. Protamine was dissociated from DNA at 0.15 M MgCl2 (ionic strength mu = 0.45) or 0.53 M NaCl (mu = 0.53) based on light scattering data and at approximately 0.2 M MgCl2 (mu = 0.6) or 0.6 M NaCl based on centrifugation data. NaCl induced dissociation of poly(Lys) or poly(Arg) from natural DNAs measured by light scattering did not depend on the guanine plus cytosine content. To dissociate poly(Arg) from DNA higher ionic strength using NaCl, MgCl2, or CaCl2, similar ionic strength using NaClo4, and lower ionic strength using Na2SO4 was needed then to dissociated poly(Lys). Both the decrease in light scattering and the enhancement of tyrosine fluorescence of chromatin occurred between 0.5 and 1.5 M NaCl when histones were dissociated.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansevin A. T., Hnilica L. S., Spelsberg T. C., Kehm S. L. Structure studies on chromatin and nucleohistones. Thermal denaturation profiles recorded in the presence of urea. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 7;10(25):4793–4803. doi: 10.1021/bi00801a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boublík M., Bradbury E. M., Crane-Robinson C. An investigation of the conformational changes in histones F1 and F2a1 by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jul;14(3):486–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Yu S. S., Li H. J. Helix-coil transition and conformational studies of nucleoprotein: poly(L-arginine)- and poly(L-arginine87, L-ornithine13)-DNA complexes. I. Thermal denaturation. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3706–3712. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewars P. A., Sooter K. V. Ultracentrifuge tudies of histone fractions from calf thymus deoxyribonucleoprotein. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):227–235. doi: 10.1042/bj1140227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D., Bonner J. Selective dissociation of pea bud nucleohistone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):601–602. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanlon S., Johnson R. S., Wolf B., Chan A. Mixed conformations of deoxyribonucleic acid in chromatin: a preliminary report. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3263–3267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm R. P., Jr, Huang R. C. The role of histones in the conformation of DNA in chromatin as studied by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5275–5283. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwan J. C., Leffak I. M., Li H. J., Huang P. C., Mura C. Studies on interaction between histone V (f2c) and deoxyribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 8;14(7):1390–1396. doi: 10.1021/bi00678a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng M., Felsenfeld G. The preferential interactions of polylysine and polyarginine with specific base sequences in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1325–1332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J., Bonner J. Interaction of histone half-molecules with deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1461–1470. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J., Brand B., Rotter A. Thermal denaturation of calf thymus DNA: existence of a GC-richer fraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Feb;1(2):257–265. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J., Chang C., Weiskopf M. Helix-coil transition in nucleoprotein-chromatin structure. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1763–1772. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. J., Wickett R., Craig A. M., Isenberg I. Conformational changes in histone IV. Biopolymers. 1972 Feb;11(2):375–397. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360110206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marushige K., Bonner J. Template properties of liver chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):160–174. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlenbusch H. H., Olivera B. M., Tuan D., Davidson N. Selective dissociation of histones from calf thymus nucleoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):299–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins D. E., Olins A. L., Von Hippel P. H. Model nucleoprotein complexes: studies on the interaction of cationic homopolypeptides with DNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Mar 14;24(2):157–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins D. E., Olins A. L., Von Hippel P. H. On the structure and stability of DNA-protamine and DNA-polypeptide complexes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):265–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti R. A., Huang R. C. Characterization of sea urchin sperm chromatin and its basic proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1615–1625. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacow I., Cabasso L., Li H. J. Histone redistribution and conformational effect on chromatin induced by formaldehyde. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 19;15(21):4559–4565. doi: 10.1021/bi00666a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Day L. A. Transition from noncooperative to cooperative and selective binding of histone H1 to DNA. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3220–3228. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santella R. M., Li H. J. Studies on poly(L-lysine50, L-tyrosine50)-DNA interaction. Biopolymers. 1974;13(9):1909–1926. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligy V., Miyagi M. Studies of template activity of chromatin isolated from metabolically active and inactive cells. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Nov;58(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon M. J., Isenberg I. Conformational changes in histone GRK(f2a-1). Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4046–4049. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subirana J. A. Studies on the thermal denaturation of nucleohistones. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 5;74(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEALE F. W., WEBER G. Ultraviolet fluorescence of the aromatic amino acids. Biochem J. 1957 Mar;65(3):476–482. doi: 10.1042/bj0650476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. H., Ansevin A. T., Hnilica L. S. Association of tissue-specific histones with deoxyribonucleic acid. Thermal denaturation of native, partially dehistonized, and reconstituted chromatins. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 25;14(6):1257–1265. doi: 10.1021/bi00677a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiskopf M., Li H. J. Poly(L-lysine)-DNA interactions in NaCl solutions: B to C and B to psi transitions. Biopolymers. 1977 Mar;16(3):669–684. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickett R. R., Li H. J., Isenberg I. Salt effects on histone IV conformation. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):2952–2957. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. S., Epstein P., Li H. J. Helix-coil transition and conformational studies of nucleoprotein: poly(L-arginine)- and poly(L-arginine87, L-ornithine13)-DNA complexes. II. Circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3713–3717. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


