Abstract
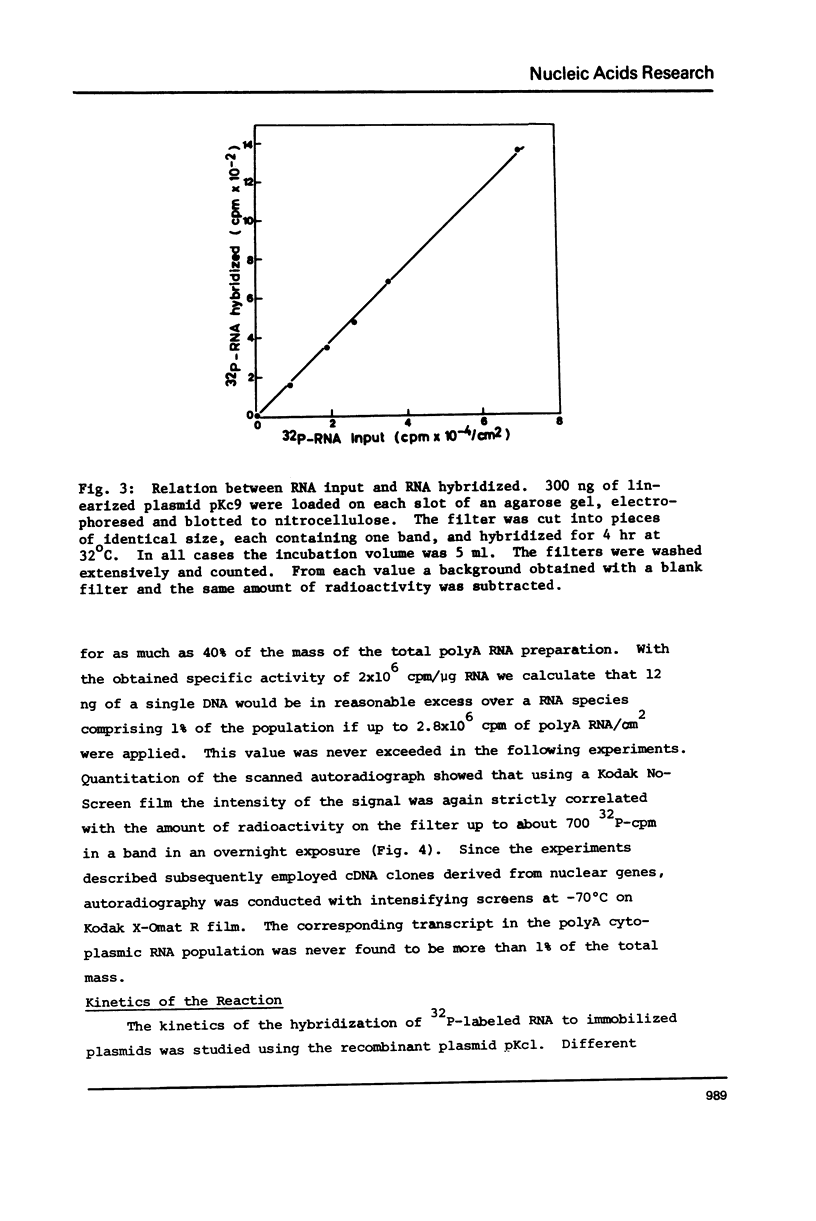
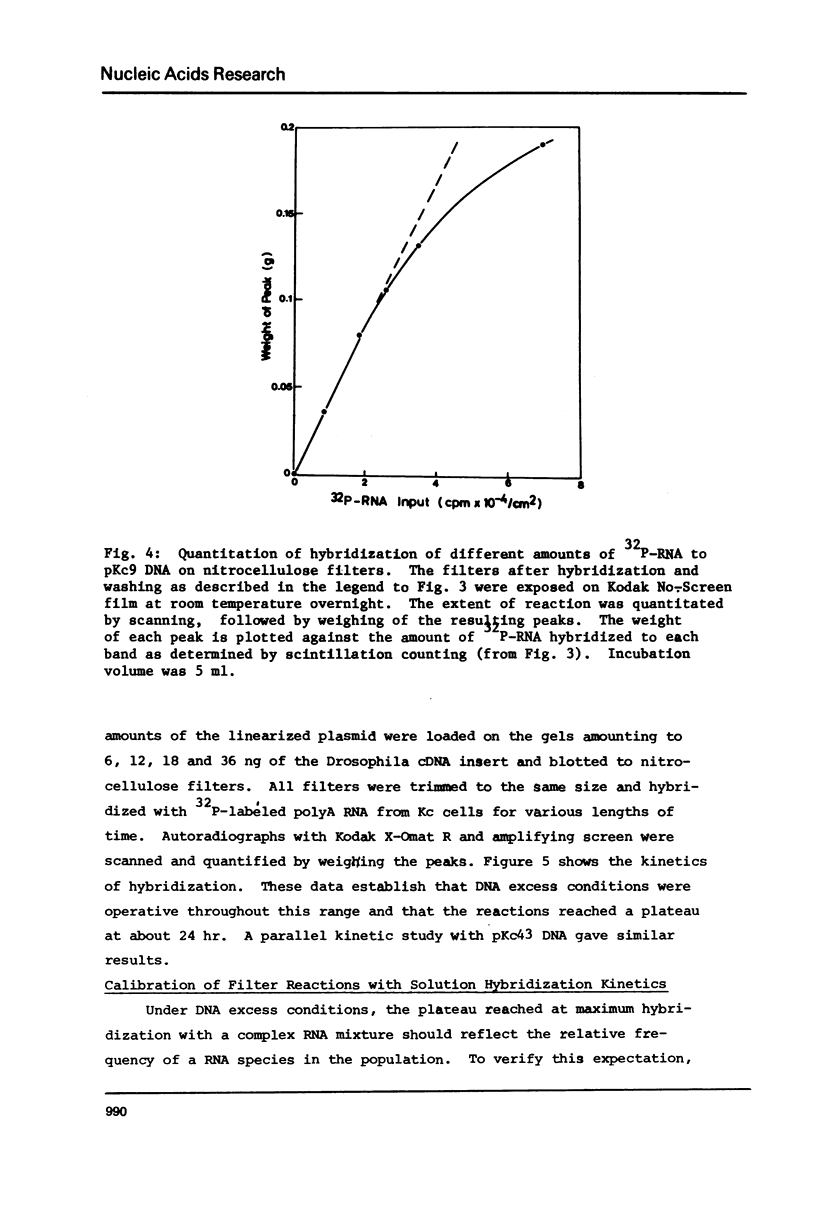
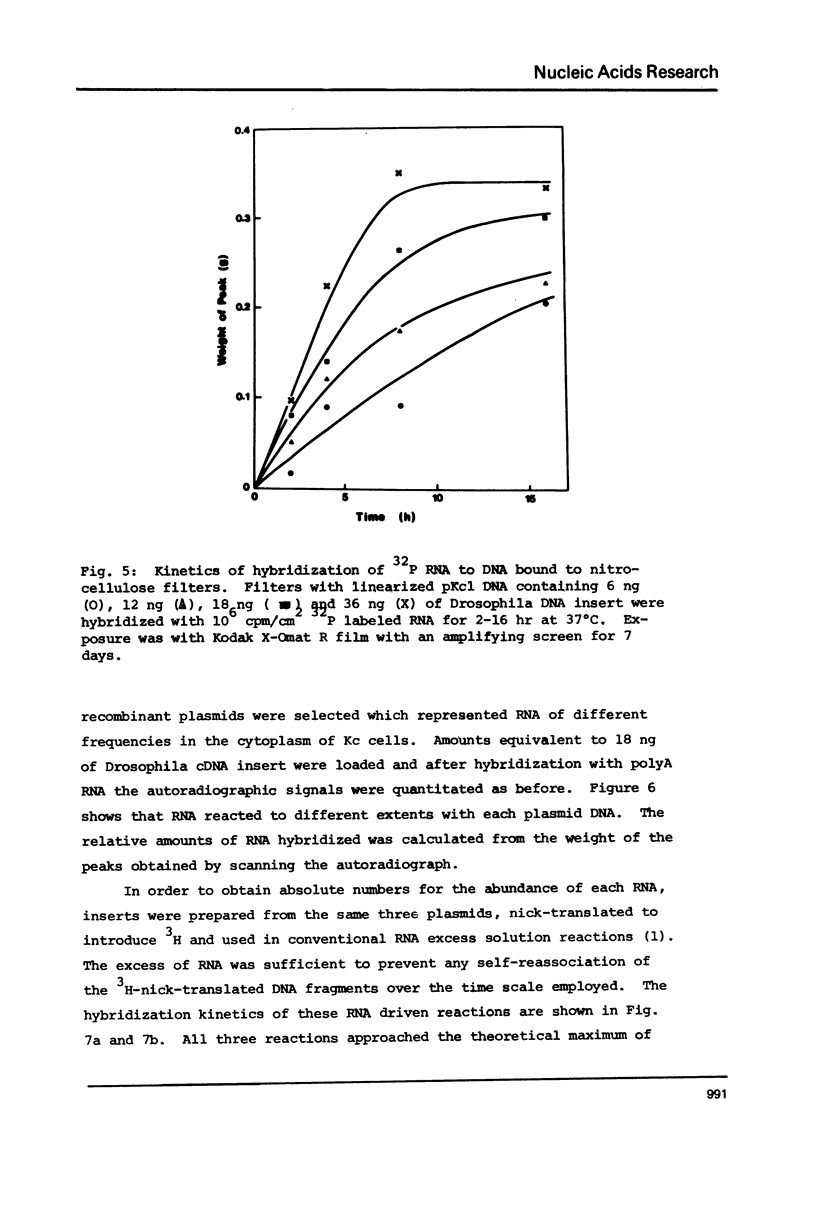
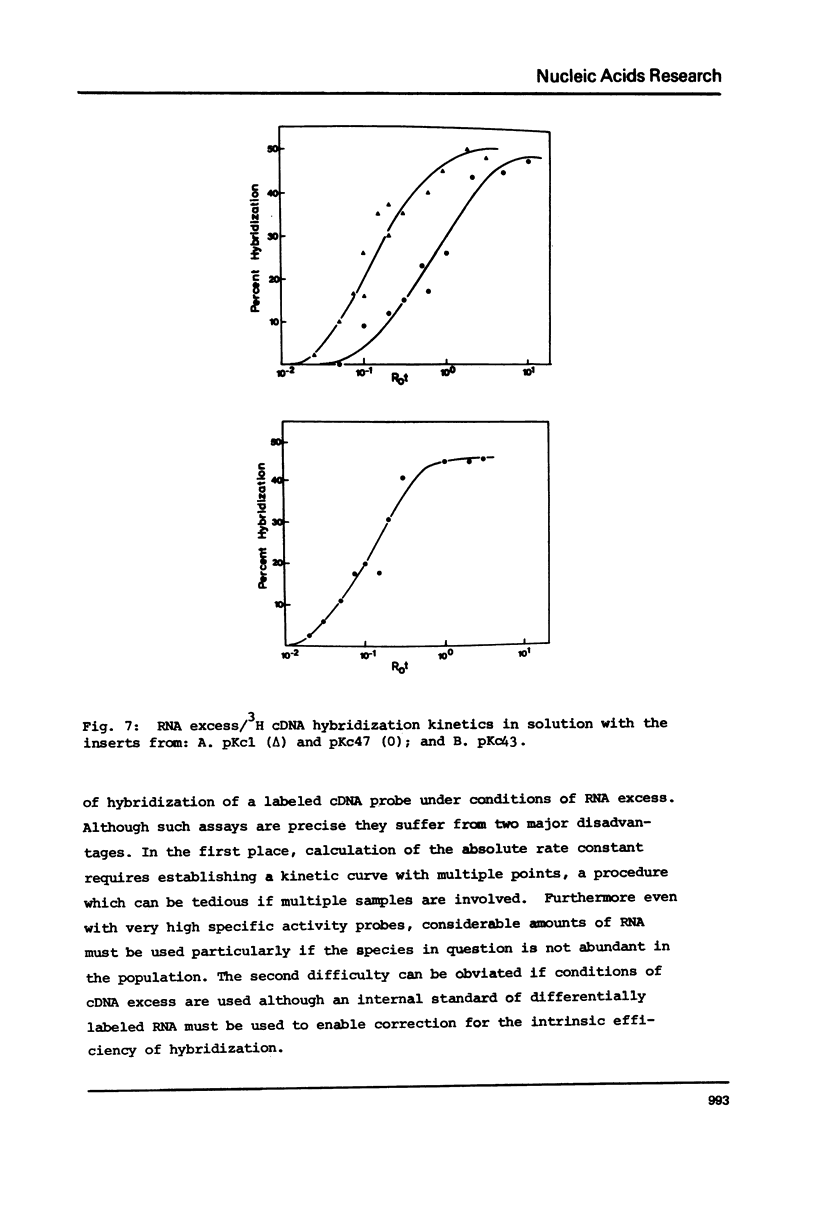
Many investigations require quantitation of one or more individual RNA species in complex populations. Existing methods are tedious when multiple samples are to be assayed. A method is presented which allows rapid and accurate quantitation of many species of RNA simultaneously. Recombinant plasmids containing cDNA inserts are electrophoresed in agarose and blotted to nitrocellulose. After hybridization with labeled RNA and autoradiography, bands are quantitated by scanning. The results were calibrated by solution hybridization. The approach has been validated through the use of plasmids containing inserts of Drosophila cDNA and RNA of cultured cells.
Full text
PDF




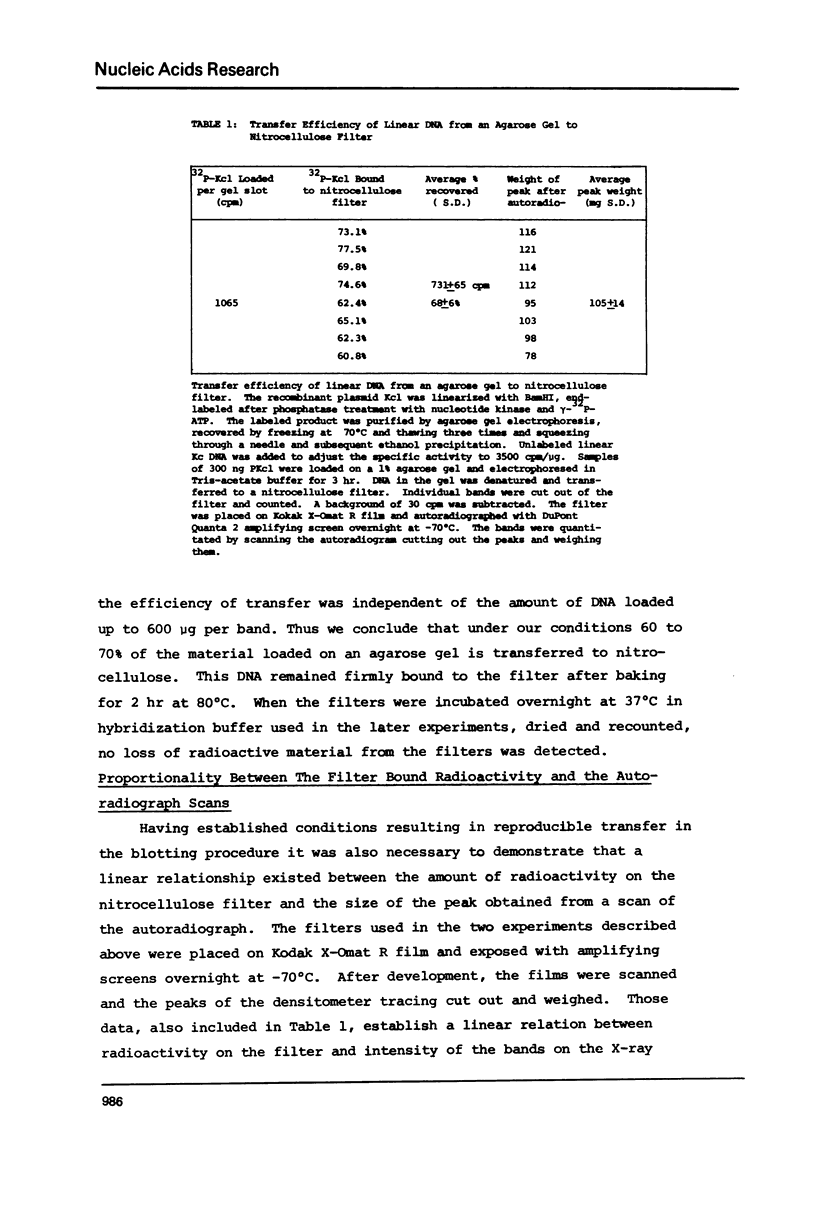
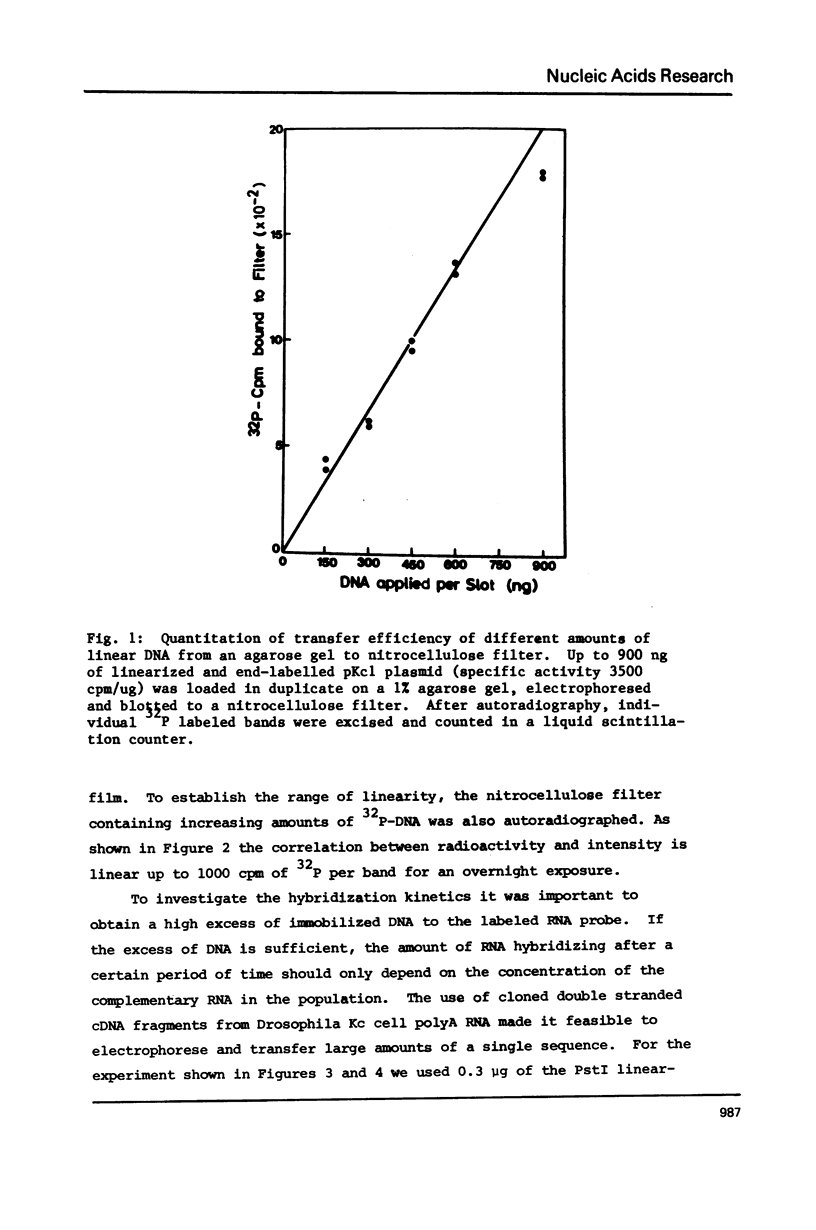
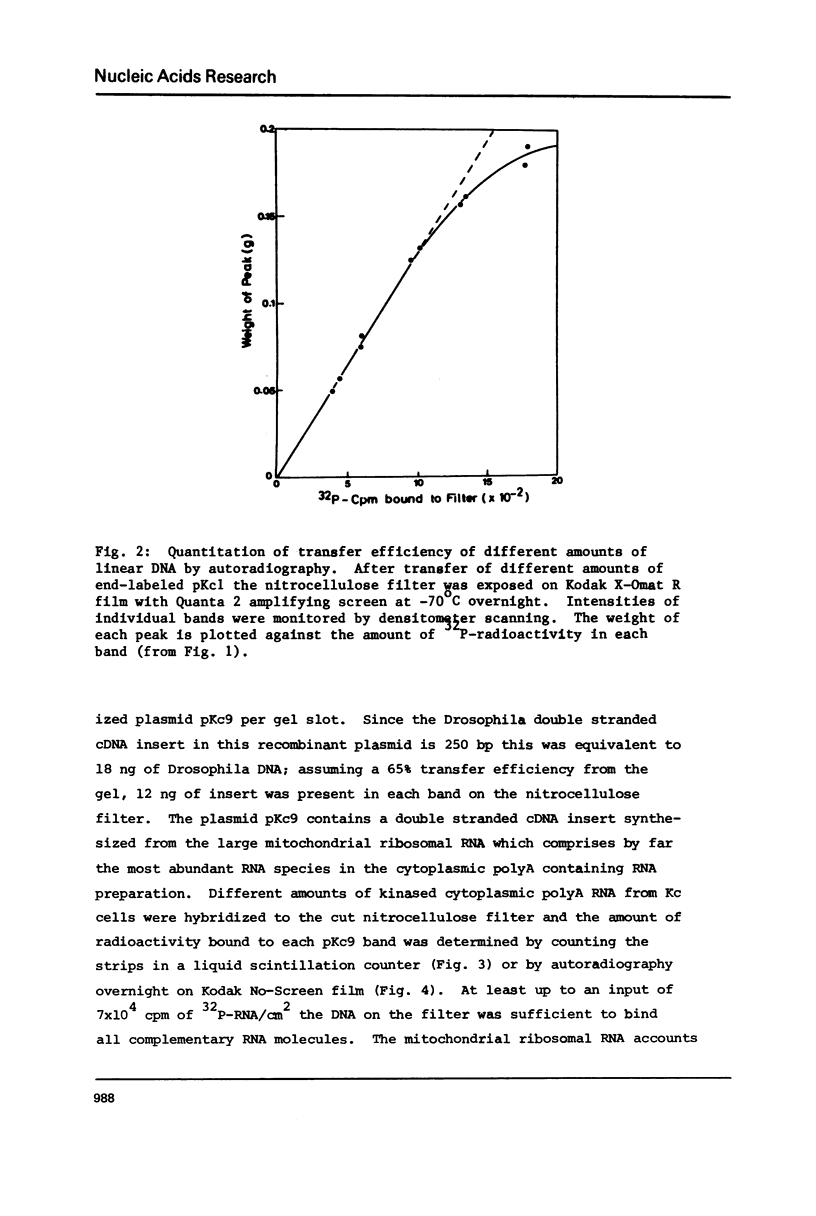

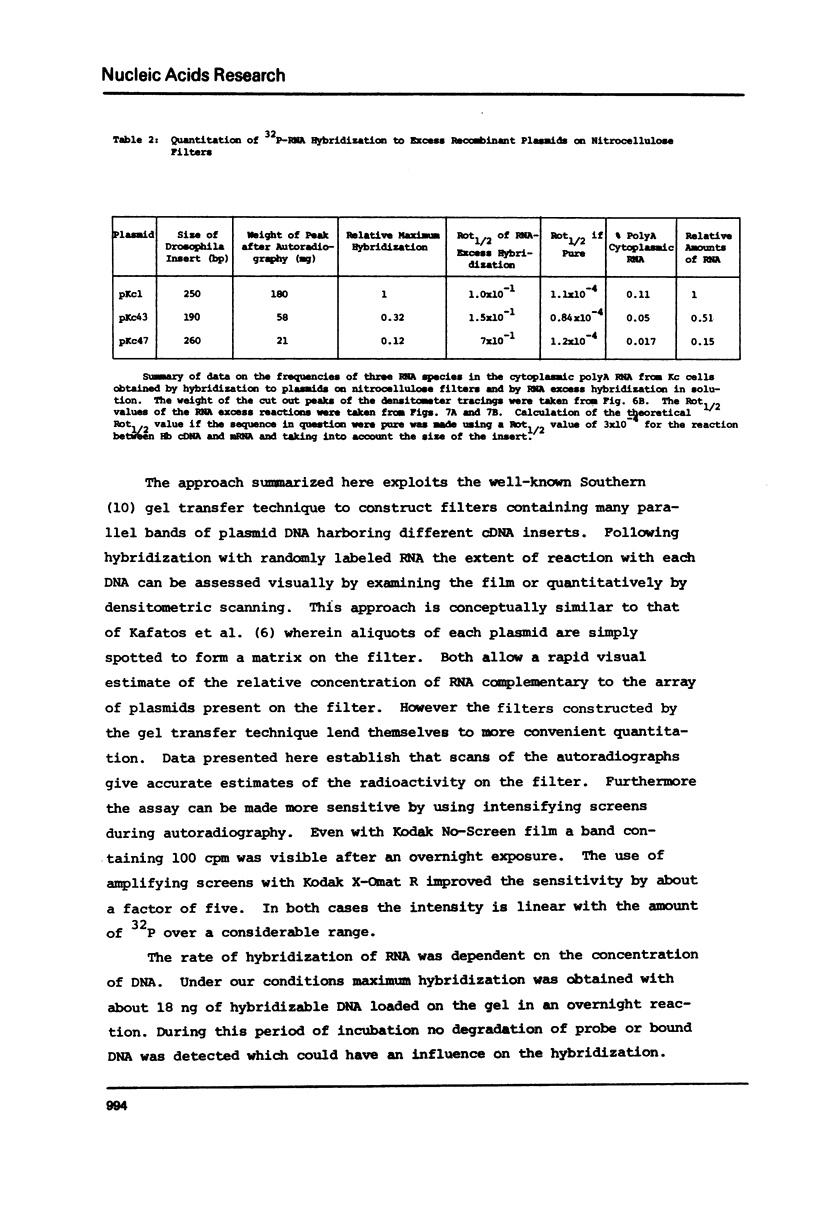


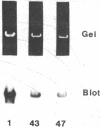
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastos R. N., Aviv H. Globin RNA precursor molecules: biosynthesis and process in erythroid cells. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):641–650. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J., Wadsworth S. C. Sequence organization of two recombinant plasmids containing genes for the major heat shock-induced protein of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):575–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freifelder D., Dewitt R. Thermal hydrolysis as a means of opening supercoiled circles of DNA. Gene. 1977 Jul;1(5-6):385–387. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi T., Diggelmann H., Scherrer K. Demonstration of globin messenger sequences in giant nuclear precursors of messenger RNA of avian erythroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1122–1126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. A., Garapin A. C., Jackson N., Fanshier L., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in cells producing rous sarcoma virus: detection and characterization. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):891–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.891-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels N. Dictyostelium 17S, 25S, and 5S rDNAs lie within a 38,000 base pair repeated unit. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Ikawa Y., Leder P. Globin messenger-RNA induction during erythroid differentiation of cultured leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3620–3623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. Isolation of galactose-inducible DNA sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by differential plaque filter hybridization. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Lloyd M. M. Changes in the abundance of polyadenylated RNA during slime mould development measured using cloned molecular hybridization probes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):19–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]