Abstract
The nucleotide sequence of a secondary attachment site for bacteriophage lambda was determined in a region near the rrnB gene at 88 min on the E. coli chromosome. The sequence has a 8 base pair interrupted homology GCT TTTTA to the common core of the primary attachment site (attB) and the corresponding phage sequence (attP). The site of crossover during integration lies probably between nucleotides -3 and +1. The flanking regions have no obvious homology to the arms of either attP or attB.
Full text
PDF

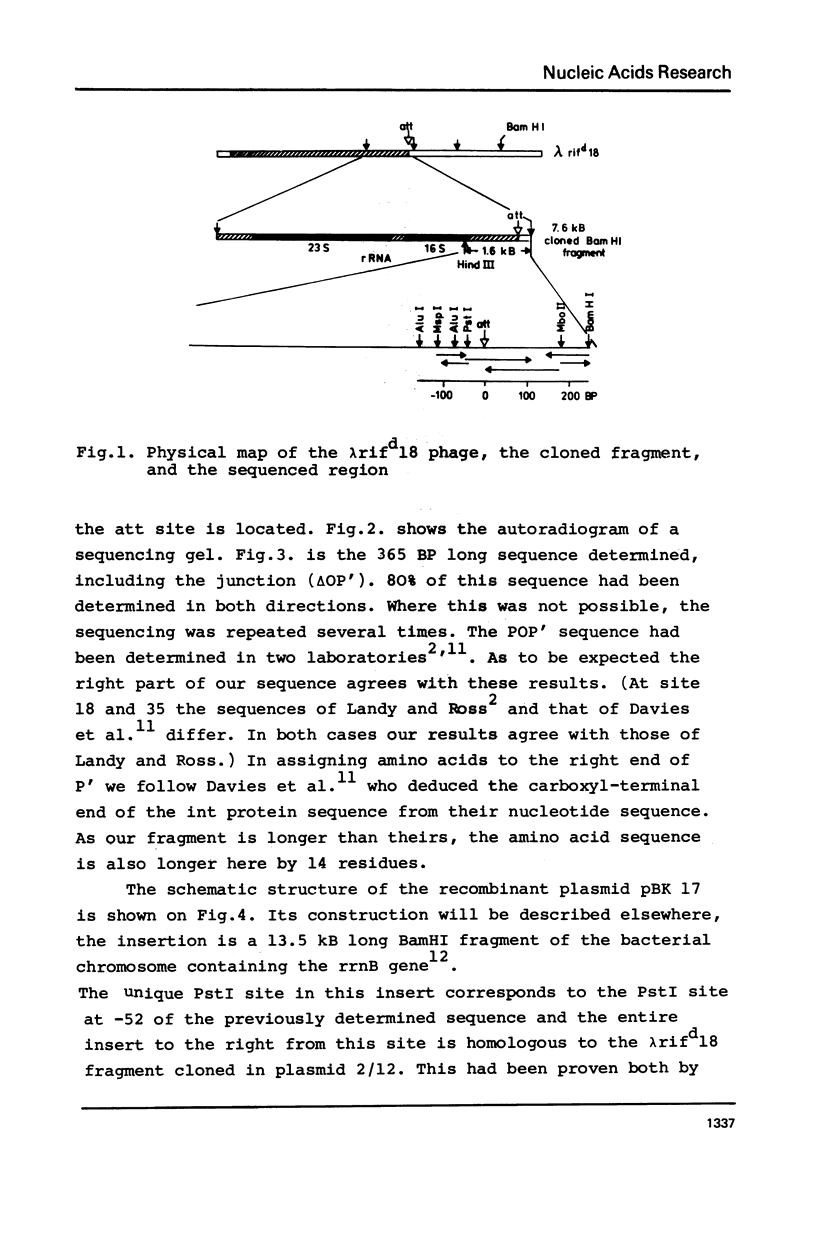

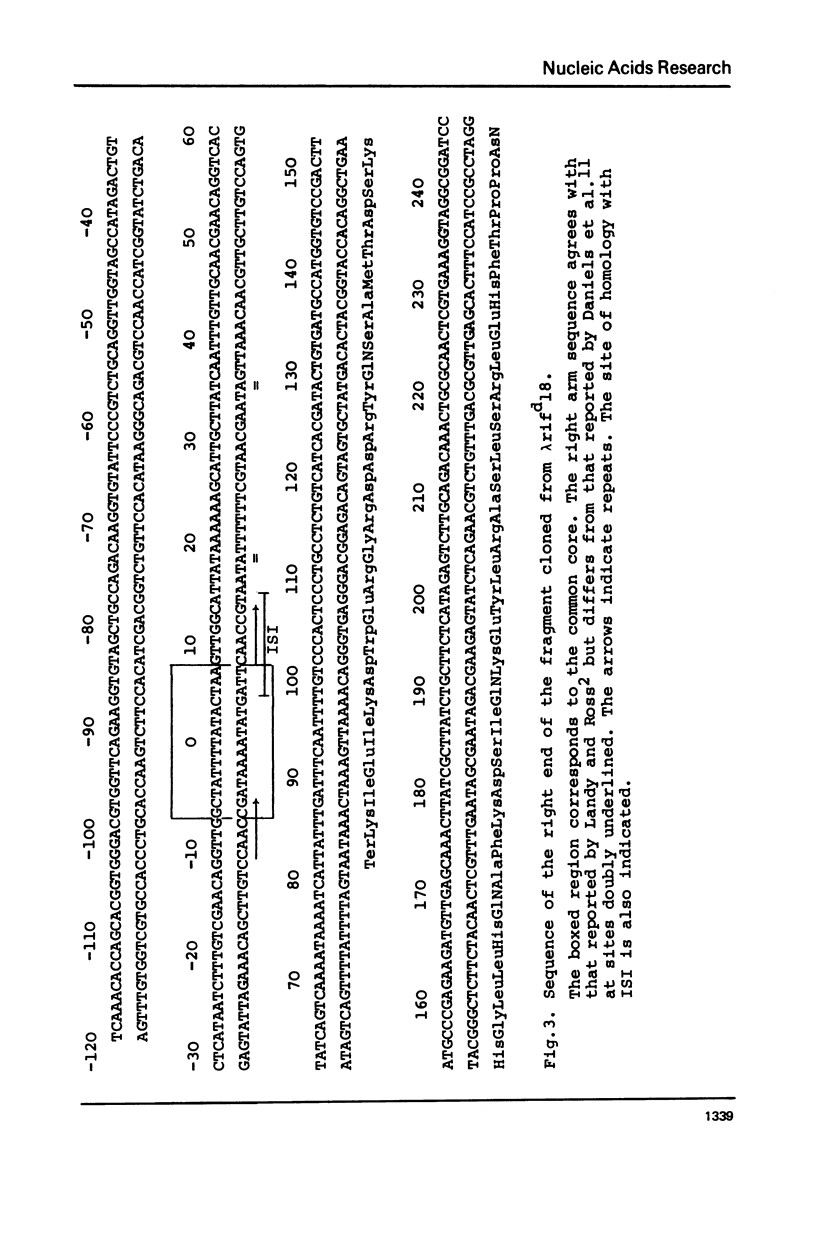


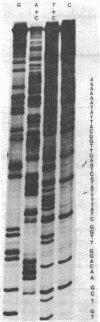
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidwell K., Landy A. Structural features of lambda site-specific recombination at a secondary att site in galT. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros I., Kiss A., Venetianer P. Physical map of the seven ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(5):1817–1830. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.5.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Platt T. A secondary attachment site for bacteriophage lambda in trpC of E. coli. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Schreier P. H., Buchel D. E. Nucleotide sequence of the attachment site of coliphage lambda. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):757–760. doi: 10.1038/270757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum J. B., Konrad E. B. Isolation of a specialized lambda transducing bacteriophage carrying the beta subunit gene for Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):517–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.517-526.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A., Sain B., Kiss I., Boros I., Udvardy A., Venetianer P. Cloning of an E. coli ribosomal RNA gene and its promoter region from lambdarifd18. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):137–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., van de Sande J. H., Loewen P. C., Khorana H. G., Raae A. J., Lillehaug J. R., Kleppe K. Physical characterization and simultaneous purification of bacteriophage T4 induced polynucleotide kinase, polynucleotide ligase, and deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5045–5050. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction and modification enzymes and their recognition sequences. Gene. 1978 Nov;4(3):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Prophage lambda at unusual chromosomal locations. I. Location of the secondary attachment sites and the properties of the lysogens. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):483–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. J., Mizuuchi K., Gottesman M. M. New att mutants of phage lambda. Virology. 1976 Jul 1;72(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]