Abstract
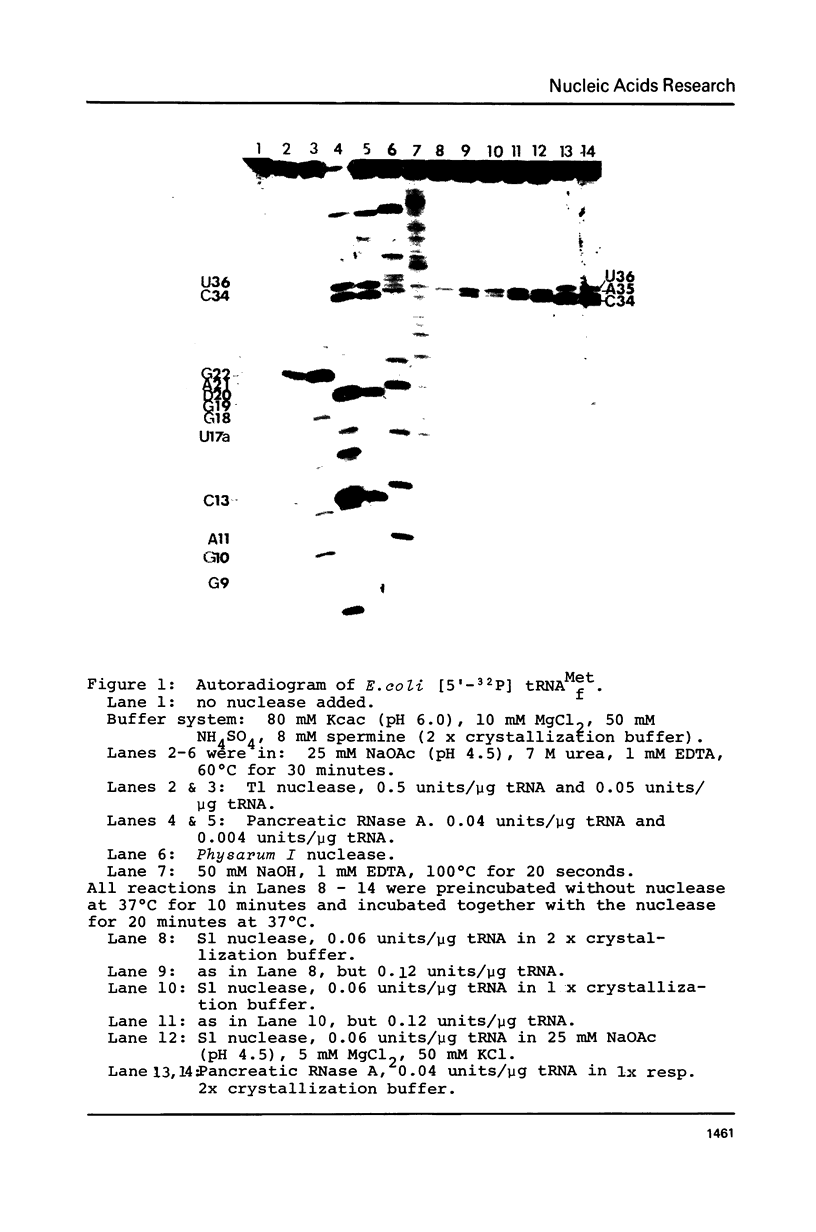
Initiator tRNAs have an anticodon loop conformation distinct from that of elongation tRNAs as detected by susceptibility to S1 nuclease. We now find the anticodon loop conformation of E. coli tRNAfMet to be stable under different salt conditions as detected by using S1 nuclease as a structural probe. In contrast, a conformational change is observed in the T- and D- loop of this tRNA in the absence of added Mg2+. This change can be suppressed by spermine. Even under those conditions effecting a change in T- and D- loop conformation, the anticodon loop does not change. This suggests that the conformational shift is controlled by Mg2+ and restricted to the D- and T- loop region only without affecting the anticodon domain. The use of S1 nuclease as a conformational probe requires the use of kinetic studies to determine the initial cleavage sites. Thus, the use of a strong inhibitor which immediately stops the action of this nuclease is necessary. ATP is shown to be such an inhibitor.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Marcker K. A. The nucleotide sequence of N-formyl-methionyl-transfer RNA. Partial digestion with pancreatic and T-1 ribonuclease and derivation of the total primary structure. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):256–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Rudland P. S., Clark B. F., Marcker K. A. A structural requirement for codon-anticodon interaction on the ribosome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:161–166. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Grüter F., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):r1–r19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckman J. E., Hecker L. I., Schwartzbach S. D., Barnett W. E., Baumstark B., RajBhandary U. L. Structure and function of initiator methionine tRNA from the mitochondria of Neurospora crassa. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schevitz R. W., Podjarny A. D., Krishnamachari N., Hughes J. J., Sigler P. B., Sussman J. L. Crystal structure of a eukaryotic initiator tRNA. Nature. 1979 Mar 8;278(5700):188–190. doi: 10.1038/278188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Woo N. H., Rich A. Initiator tRNAs have a unique anticodon loop conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3289–3293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N., Maxam A. M. Structure mapping of 5'-32P-labeled RNA with S1 nuclease. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4493–4499. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]