Abstract
The transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 channel (TRPV3) is abundantly expressed in epidermal keratinocytes and plays important roles in sensory biology and skin health. Mg2+ deficiency causes skin disorders under certain pathological conditions such as type 2 diabetes mellitus. In this study, we investigated the effect of Mg2+ on TRPV3 in primary epidermal keratinocytes. Extracellular Mg2+ ([Mg2+]o) inhibited TRPV3-mediated membrane current and calcium influx. TRPV3 activation induced a calcium signaling pathway culminating in activation of the cAMP response element binding (CREB). TRPV3 inhibition by [Mg2+]o, the TRPV3 blocker ruthenium red or TRPV3 siRNA suppressed this response. In TRPV3-expressing Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, both extracellular and intracellular Mg2+ inhibited TRPV3 single-channel conductance but not open probability. Neutralization of an aspartic acid residue (D641) in the extracellular pore loop or two acidic residues (E679, E682) in the inner pore region significantly attenuated the inhibitory effect of extracellular or intracellular Mg2+ on TRPV3-mediated signaling, respectively. Our findings suggest that epidermal TRPV3 is tonically inhibited by both extracellular and intracellular Mg2+, which act on both sides of the channel pore loop. Mg2+ deficiency may promote the function of TRPV3 and contribute to the pathogenesis of skin diseases.
Keywords: transient receptor potential channel, TRPV3, magnesium, cAMP response element-binding, keratinocytes
Introduction
The transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 channel (TRPV3), a “thermoTRP”, belongs to a large family of Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channels with 6 transmembrane (TM) domains and a putative pore loop between TM5 and TM6 (Clapham, 2007). Like other TRP channels, TRPV3 is a polymodal cellular sensor that integrates several modalities including warm temperature, synthetic small molecules such as 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2APB), and natural compounds from plant such as camphor, carvacrol, and eugenol (Chung et al., 2004a; Hu et al., 2009; Hu et al., 2004; Moqrich et al., 2005; Vriens et al., 2009). The widespread expression of TRPV3 in neuronal and non-neuronal tissues suggests that TRPV3 may play important roles in many cellular and physiological functions (Peier et al., 2002; Smith et al., 2002; Xu et al., 2002; Yamada et al., 2010). In fact, activation of TRPV3 in arterial endothelial cells by the dietary agonist carvacrol elicits vasodilation of cerebral arteries in rats (Earley et al., 2010). In mammals, TRPV3 is expressed in dorsal root and trigeminal ganglia, spinal cord and brain (Facer et al., 2007; Kauer and Gibson, 2009; Smith et al., 2002; Xu et al., 2002), where it has been shown to play an important role in pain sensation and mediate psychoactive properties of incensole acetate (Bang et al., 2010; Huang et al., 2008; Moussaieff et al., 2008).
Recently, TRPV3 has come to the fore as a key regulator of physiological responses of skin. TRPV3 is required for normal skin development and function, as TRPV3 deficient mice have defects in hair morphogenesis and skin barrier function (Cheng et al., 2010). Paradoxically, a recent report revealed that active TRPV3 expressed in human outer root sheath (ORS) keratinocytes inhibits hair growth (Borbiro et al., 2011). Therefore, maintaining an appropriate balance of TRPV3 activity is essential to normal function of epidermal keratinocytes. Indeed, naturally occurring gain-of-function point mutations in TRPV3 (Gly573 to Ser or Cys) have been linked to autosomal-dominant hairless phenotypes and spontaneous dermatitis in DS-Nh mice likely due to their constitutive activities (Asakawa et al., 2006; Imura et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2008b; Yoshioka et al., 2009). Interestingly, these DS-Nh mice also develop severe scratching behavior, suggesting that epidermal TRPV3 may play a causative role in inflammation and pruritus (Steinhoff and Biro, 2009; Yoshioka et al., 2009), although much remains elusive regarding the molecular mechanism underlying these effects.
Mg2+ is the second most common divalent cation in the body and the most abundant intracellular divalent cation. Intracellular Mg2+ ([Mg2+]i) plays a pivotal role in structural, catalytic, and regulatory cellular functions. It serves as a cofactor of over 300 enzymes and regulates activity of many ion channels (Ahern et al., 2005; Bichet et al., 2003; Johnson and Ascher, 1990; Lee et al., 2005; Obukhov and Nowycky, 2005; Voets et al., 2003). Free [Mg2+]i undergoes dynamic changes due to the chelating effect of ATP and increases in ischemic neurons (Chinopoulos et al., 2007; Henrich and Buckler, 2008, 2009). Mg2+ deficiency, also known as hypomagnesemia, accompanies human pathological states including type 2 diabetes mellitus (Resnick et al., 1993; Sales and Pedrosa Lde, 2006; Tosiello, 1996). Mg2+ deficiency induces apoptosis in isolated hepatocytes (Martin et al., 2003) and increases incidence of stroke, hypertension, eclampsia, and atherosclerosis (Saris et al., 2000). Interestingly, magnesium deficiency has been widely used in rodents to experimentally model atopic dermatitis associated with a robust scratching behavior (Akamatsu et al., 2006; Biro et al., 2005; Neckermann et al., 2000). However, the mechanisms underlying the hypomagnesemia-mediated skin disorders are poorly understood.
Given the association of both TRPV3 and Mg2+ dysregulation with skin disorders, we hypothesized that TRPV3 may mediate some of the effects of magnesium deficiency in skin. In this study, we show that TRPV3 function is inhibited by both [Mg2+]i and extracellular Mg2+ ([Mg2+]o), which interacts with acidic residues on both sides of the channel pore loop region. The voltage-dependent inhibition contributes to the characteristic inward and outward rectification of TRPV3 current. The inhibitory effect of Mg2+ was also translated into inhibition of TRPV3-mediated cell signaling in primary mouse epidermal keratinocytes, a well established cell model to study the function of endogenous TRPV3 (Chung et al., 2004b), as evidenced by attenuation of TRPV3-mediated increase of cAMP response element binding (CREB) activity.
Results
[Mg2+]o suppresses TRPV3-mediated whole-cell currents in mouse keratinocytes
Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were performed to directly measure TRPV3-mediated current in mouse keratinocytes. To activate TRPV3 we used a TRPV3 agonist cocktail, a combination of 100 μM 2APB and 250 μM carvacrol, as previously described (Cheng et al., 2010). As expected, the TRPV3 agonist cocktail activated a nonselective cation current associated with both inward and outward rectification during a voltage ramp from -100 mV to +100 mV, characteristic of TRPV3 current in heterologous expression systems (Cheng et al., 2010; Chung et al., 2004a; Hu et al., 2004; Hu et al., 2006). No current was observed in keratinocytes from TRPV3-deficient mice, confirming the specificity of the agonist cocktail of TRPV3 in keratinocytes (Figure S1). Increasing [Mg2+]o to 10 mM decreased TRPV3-mediated whole-cell current. By contrast, reducing [Mg2+]o to 0 mM enhanced the current (Figure 1a). The effect of [Mg2+]o on inward current was more pronounced than the outward current. The rectification ratio (-I+100 mV/I-100 mV) was increased from 0.78 ± 0.03 to 1.39 ± 0.11 by 10 mM [Mg2+]o with 2 mM Mg2+ in the pipette solution (p<0.05, n=9) (Figure 1b & 1c). On the other hand, an increase of Mg2+ concentration from 2 to 10 mM in the pipette solution significantly diminished TRPV3-mediated outward current, evidenced by the reduced rectification ratio from 0.90 ± 0.02 to 0.69 ± 0.03 with 2 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution (p<0.05, n=9) (Figure 1c). These findings suggest that Mg2+ suppresses TRPV3 function in primary epidermal keratinocytes in a voltage-dependent manner on both sides of the cell membrane.
Figure 1. Inhibition of TRPV3-mediated current by [Mg2+]o in cultured mouse keratinocytes.
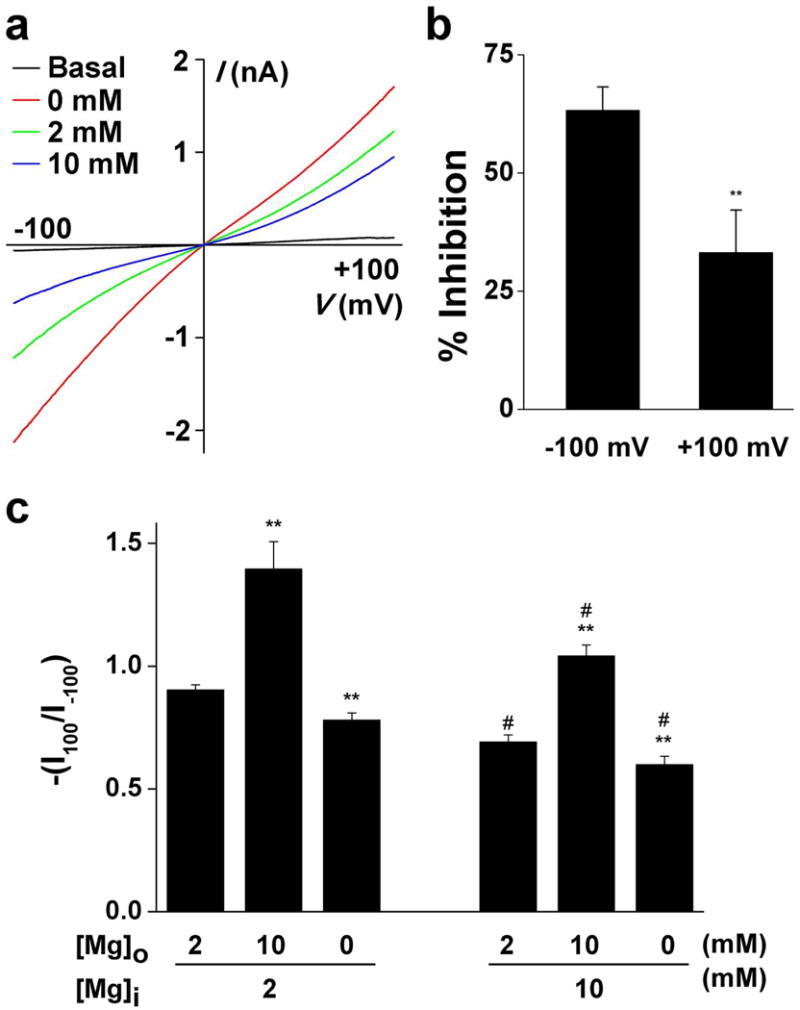
(a) Representative current traces in response to voltage ramp from -100 mV to +100 mV without (basal) and with the TRPV3 agonist cocktail in the absence (0 mM) and presence of 2 and 10 mM Mg2+. (b) Percentage of inhibition of TRPV3 agonist cocktail-activated current by 10 mM Mg2+ at holding potential of -100 mV and +100 mV obtained from the voltage ramp shown in (a). Please note the different inhibitory effects at -100 mV and +100 mV. (c) Rectification ratio [-(I100/I-100)] with different concentrations of Mg2+ in the intracellular and extracellular solutions. ** p<0.01 compared with 2 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution with 2 or 10 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution. ## p<0.01 compared with 2 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution with 0, 2, or 10 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution.
[Mg2+]o decreases TRPV3 single-channel conductance
Suppression of TRPV3-mediated current by [Mg2+]o could result from inhibition of TRPV3 single-channel conductance and/or open probability. We therefore used single-channel recordings on cultured mouse keratinocytes to elucidate the mechanism underlying [Mg2+]o inhibition of TRPV3. Surprisingly, no single-channel activities could be recorded with different configurations (cell attached, inside-out or outside-out) upon stimulation with the TRPV3 agonist cocktail that evoked TRPV3-dependent whole-cell currents (not shown). We then went on to use Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing recombinant TRPV3 to evaluate the impact of Mg2+ on TRPV3 single-channel properties based on the facts that it is feasible to record TRPV3 single-channel activities in heterologous expression systems(Chung et al., 2004a; Hu et al., 2006; Xu et al., 2002), and the voltage-dependent Mg2+ inhibition of recombinant TRPV3 expressed in CHO cells recapitulates that of native TRPV3 in mouse keratinocytes (Figure S2).
We first used outside-out single-channel recordings on CHO cells expressing TRPV3. To avoid TRPV3-mediated large macroscopic currents in outside-out membrane patches, we used a relatively low concentration of 2-APB (10 μM) to activate single TRPV3 channels (Hu et al., 2006). Increasing [Mg2+]o from 0 to 3 mM in the extracellular side did not affect 2-APB-evoked single-channel open probability (NPo) (0.21 ± 0.11 and 0.19 ± 0.12 in the presence and absence of 3 mM Mg2+, p>0.05, n=5) (Figure 2). However, single-channel conductance was decreased by 3 mM [Mg2+]o from 157.82 ± 11.25 pS to 57.64 ± 9.62 pS at negative membrane potentials (p<0.05, n=6). By contrast, [Mg2+]o did not significantly affect TRPV3 single-channel conductance at positive membrane potentials (90.35 ± 13.32 and 74.38 ± 11.79 in the absence and presence of 3 mM [Mg2+]o, p>0.05, n=6) (Figure 2). Therefore, [Mg2+]o suppresses TRPV3-mediated current preferably at negative holding potentials (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Effect of [Mg2+]o on the I-V relationship of TRPV3-mediated single-channel current.
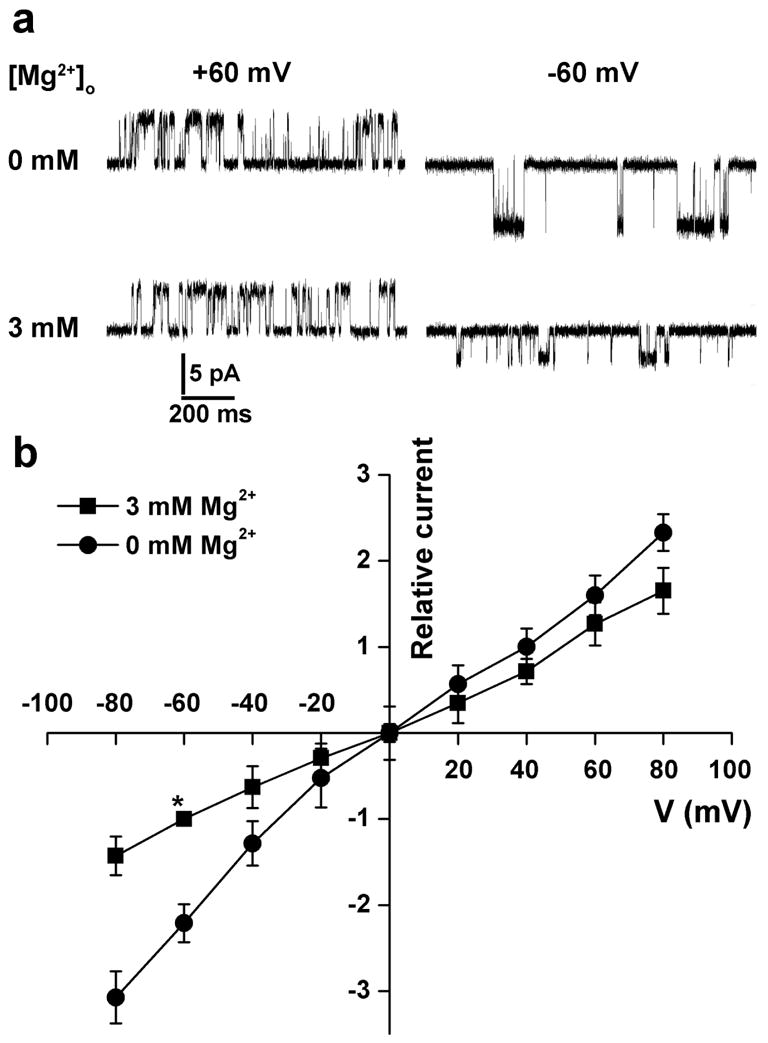
(a) Representative single-channel current traces activated by 10 μM 2APB at holding potentials of +60 and -60 mV in the absence and presence of 3 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution in CHO cells expressing mTRPV3. (b) I-V relationships of the TRPV3 single-channel current activated by 2APB in CHO cells expressing mTRPV3. Current amplitudes at different holding potentials are normalized to that at -60 mV in the presence of 3 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution (marked as asterisk).
[Mg2+]i modulates TRPV3 single-channel activity
[Mg2+]i fluctuates with metabolic states, especially during hypoxia when intracellular ATP concentration decreases (Wilson and Chin, 1991). We therefore investigated [Mg2+]i on TRPV3 activity. Increasing [Mg2+]i from 2 to 10 mM in the recording pipette significantly attenuated the TRPV3-mediated outward current in whole-cell patch-clamp recording on mouse keratinocytes (Figure 1c). We further probed the mechanism underlying the inhibitory effect of [Mg2+]i on TRPV3 using inside-out single-channel recordings. Increasing Mg2+ concentrations (0-3 mM) on the cytoplasmic side inhibited the outward unitary single-channel current amplitude in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 3a). [Mg2+]i mainly decreased the single-channel conductance of the outward current (165.34 ± 9.52 pS and 66.38 ± 7.84 pS in the absence and presence of 3 mM Mg2+, p<0.05, n=7) but barely affected the single-channel conductance of the inward current (67.47 ± 7.24 pS and 61.38 ± 6.35 pS in the absence and presence of 3 mM Mg2+, p>0.05, n=7) (Figure 3b). The single-channel NPo was not significantly affected by the change of [Mg2+]i (0.25 ± 0.13 and 0.23 ± 0.12 in the presence and absence of 3 mM Mg2+, p>0.05, n=5). The mean open time was not significantly affected by [Mg2+]i (1 mM) either (not shown, n=5). The results suggest that both [Mg2+]o and [Mg2+]i inhibit TRPV3 function by primarily decreasing TRPV3 single-channel conductance.
Figure 3. Effect of [Mg2+]i on the I-V relationship of TRPV3-mediated single-channel current.
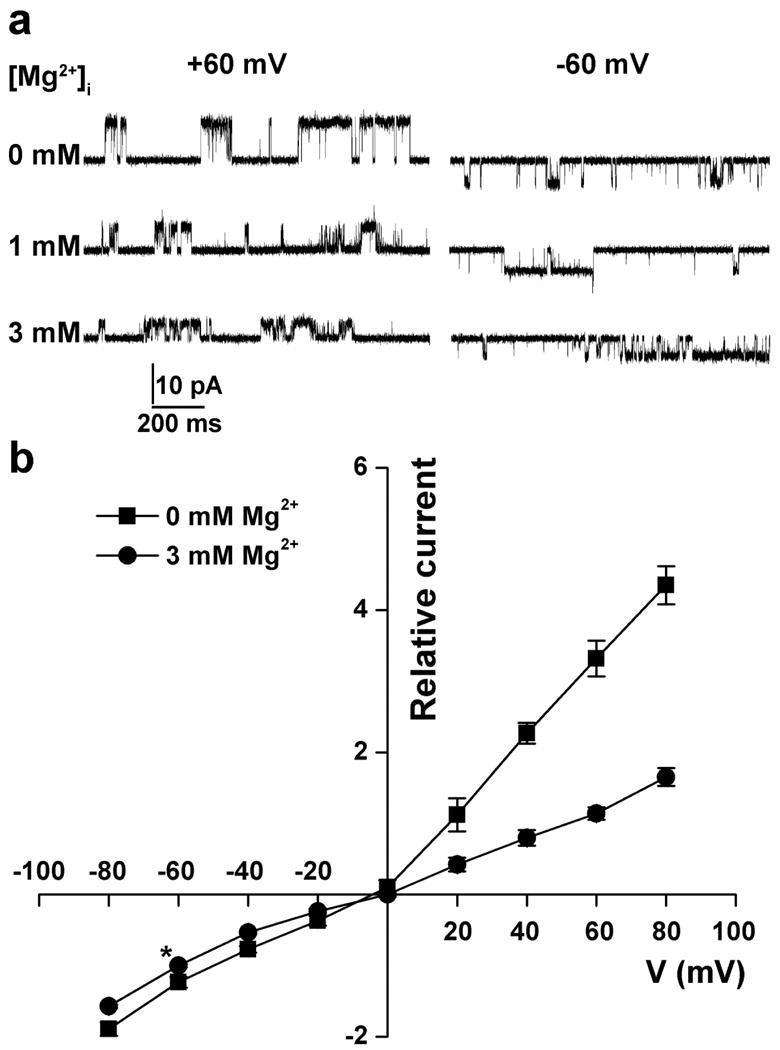
(a) Representative single-channel current traces activated by 10 μM 2APB at holding potentials of +60 and -60 mV in the absence and presence of 1 and 3 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution in CHO cells expressing mTRPV3. (b) I-V relationships of the TRPV3 single-channel current activated by 2APB in CHO cells expressing mTRPV3. Current amplitudes at different holding potentials are normalized to those at -60 mV in the presence of 3 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution (asterisk).
Inhibition of TRPV3 by Mg2+ involves distinct acidic amino acid residues on both sides of the channel pore loop
Previous studies have shown that the acidic residue D641 in the extracellular pore loop contributes to inhibition of TRPV3 by extracellular Ca2+ (Chung et al., 2005; Xiao et al., 2008a). We therefore hypothesized that D641 might be part of a common interaction site for divalent cations including Mg2+. To test this possibility, we examined the effect of increasing [Mg2+]o on a mutant TRPV3 (D641N) in which the negatively charged aspartic acid was replaced by neutral asparagine (N). The D641N mutation significantly decreased the inhibitory effect of 3 mM [Mg2+]o on the inward single-channel current amplitude from 54.77 ± 9.24% to 20.78 ± 8.93% (p<0.05, n=5) (Figure 4a). On the other hand, the inhibitory effect of [Mg2+]i on outward single-channel current amplitude was unaffected (60.37 ± 8.35% vs 61.41 ± 9.27% for wild-type and D641N, respectively, p> 0.05, n=6).
Figure 4. Amino acids required for Mg2+ inhibition of TRPV3.
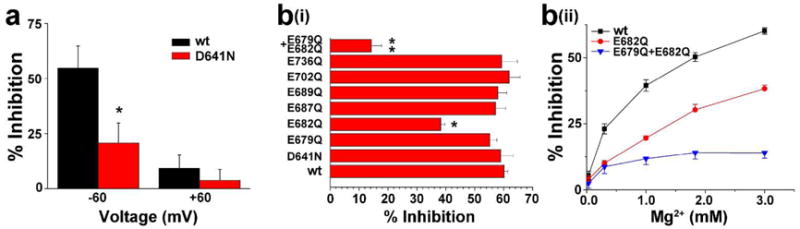
(a) Bar graph illustrating the inhibitory effect of 3 mM [Mg2+]o on TRPV3 mediated single-channel current amplitude with D641N mutation at holding potentials of -60 and −60 mV. (bi) Bar graph illustrating the inhibitory effects of 3 mM [Mg2+]i on wild-type and TRPV3 mutants with neutralizing mutaitons of acidic residues on the intracellular side near the channel pore. (bii) Graph illustrating the concentration-dependent inhibition of [Mg2+]i on the wild-type and TRPV3 mutants at concentrations ranging from 0 to 3 mM.
To examine if other negatively charged acidic residues in the intracellular side close to the inner pore region contribute to inhibition of [Mg2+]i on outward current, we further screened these residues by mutating each to glutamine (Gln or Q), which effectively neutralizes the charge. Out of the 6 glutamate residues, only neutralization of E682 significantly attenuated the inhibition of TRPV3 by [Mg2+]i (38.23 ± 1.39% vs 60.13 ± 1.21% in wild-type, p< 0.05, n=10) on outward current (Figure 4b). Since E679 and E682 are the closest negatively charged residues to the inner pore we mutated both of them into glutamine to examine if there exists a synergistic action between them. Remarkably, the inhibitory effect of [Mg2+]i was dramatically reduced on the TRPV3 (E679Q/E682Q) mutant to 14.2 ± 3.65% (p<0.01 compared with that on wild-type, n=8) (Figure 4b). The results suggest that Mg2+ affects TRPV3 activity by interacting with acidic residues on both sides of TRPV3 channel pore loop.
[Mg2+]o inhibits TRPV3-mediated [Ca2+]i increase in mouse keratinocytes
TRPV3 activation evokes calcium influx, which is involved in many cellular functions of keratinocytes (Ansari et al., 2008; Chung et al., 2004a, b; Peier et al., 2002; Savignac et al., 2011; Smith et al., 2002; Xu et al., 2002). To examine the effect of [Mg2+]o on TRPV3-mediated calcium influx we used ratiometric calcium imaging. The TRPV3 agonist cocktail evoked a rapid increase of intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) in Fura-2-loaded primary keratinocytes (Figure 5a). The agonist cocktail failed to increase [Ca2+]i when calcium-free extracellular buffer was used (not shown). This calcium response was also abolished in keratinocytes isolated from TRPV3 knockout mice ((Cheng et al., 2010) and Figure S1), which confirms that the agonist cocktail-evoked calcium influx is mediated exclusively by TRPV3. Interestingly, repetitive application of the TRPV3 agonist cocktail gradually caused desensitization of the [Ca2+]i response (Figure 5), similar to TRPV3-mediated responses evoked by monoterpenoids in a human keratinocyte-derived cell line (HaCaT cells) (Sherkheli et al., 2009). When 2 or 10 mM Mg2+ was added to the extracellular buffer, the calcium responses activated by the second and third applications of TRPV3 agonist cocktail were further suppressed by 24.89 ± 3.56% and 40.17 ± 4.25% (p<0.05, n=6), respectively (Figure 5b). The results suggest that [Mg2+]o tonically inhibits TRPV3 in epidermal keratinocytes to contribute to intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis.
Figure 5. Inhibition of TRPV3-mediated [Ca2+]i increase by [Mg2+]o in cultured mouse keratinocytes.
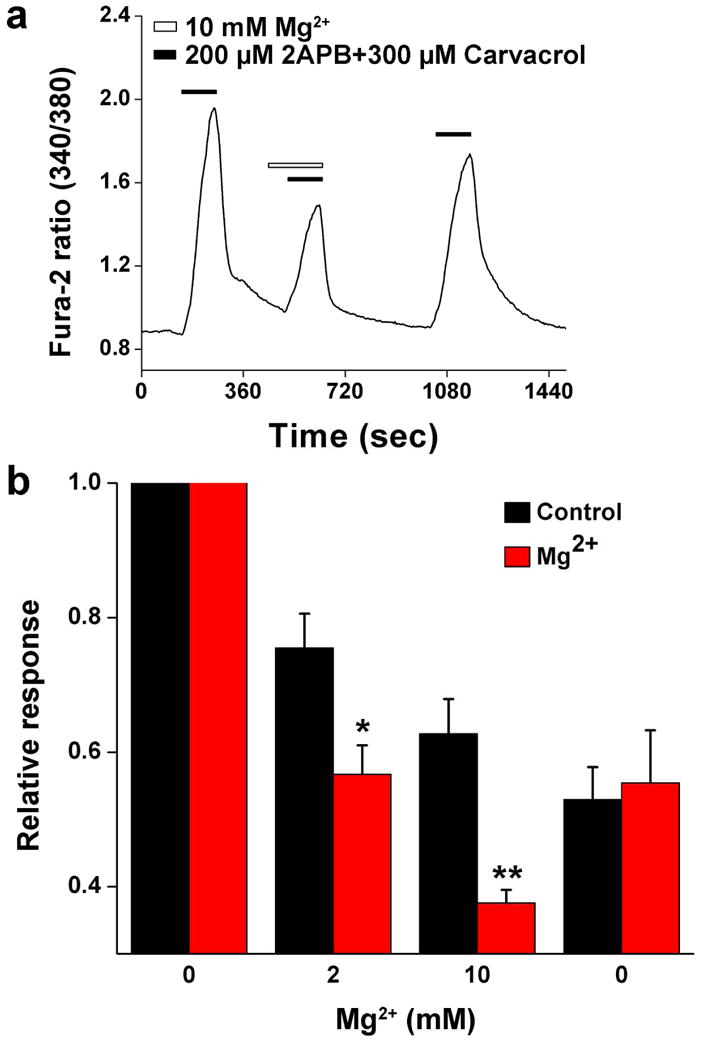
(a) Averaged response of 200 cells in time-lapse images from a representative coverslip illustrating the inhibitory effect of 10 mM Mg2+ on TRPV3 agonist cocktail-induced increase of [Ca2+]i. Horizontal bars indicate the time course of chemical applications. (b) Red bars are summarized data illustrating the responses to four consecutive applications of TRPV3 agonist cocktail in the absence (first and fourth response) and presence of 2 mM (second response) and 10 mM (third response) Mg2+. All responses are normalized to the first response. Black bars serve as non-treatment control showing the four consecutive responses without Mg2+ application in the control group.
[Mg2+]o attenuates TRPV3-mediated CREB signaling in mouse keratinocytes
Calcium/CREB signaling is critical for epidermal keratinocyte proliferation (Ansari et al., 2008; Rozenberg et al., 2009) and inflammatory pain mediated by TRPV1 in neurons (Nakanishi et al., 2010). To investigate whether TRPV3 activation is involved in the regulation of CREB activity, we prepared primary epidermal keratinocytes from transgenic mice that contain a genetically encoded CREB-depencent luciferase (CRE-luc) reporter gene (Song et al., 2010). We found that the TRPV3 agonist cocktail produced a 2.5 fold increase of CREB-dependent luciferase activity in the primary keratinocytes (Figure 6a). The effect of TRPV3 agonist cocktail was nearly completely abolished by a TRPV blocker ruthenium red or transfection of TRPV3-specific siRNA (Figure 6a). Scrambled siRNA control had no effect (Figure 6a). Moreover, increasing [Mg2+]o suppressed TRPV3-induced CREB luciferase activity in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 6b). These data present evidence that activation of TRPV3 enhances CREB activity in mouse keratinocytes and [Mg2+]o inhibits the TRPV3-mediated cell signaling.
Figure 6. Suppression of TRPV3-mediated increase of CREB transcriptional activity by Mg2+.
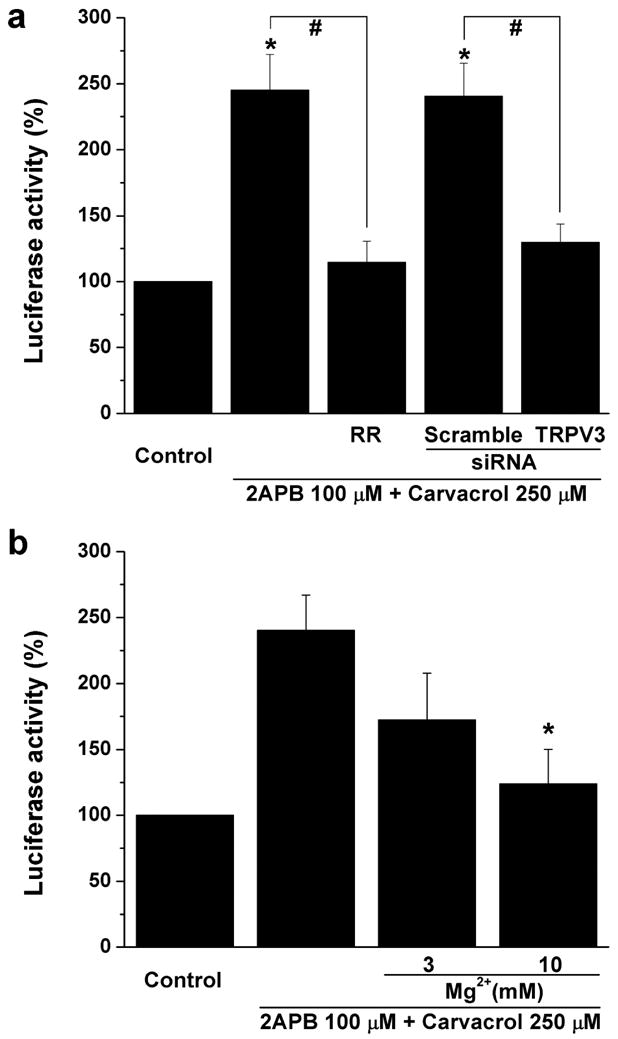
(a) The CRE-Luc activity in control groups is set to 100% for a and b, and treated groups are normalized to this value (mean ± s.e.m. from 15 animals). Summarized data showing TRPV3 agonist cocktail-induced CRE-Luc activity in the absence or presence of ruthenium red (RR) in transgenic mouse keratinocytes as well as transgenic mouse keratinocytes transfected with TRPV3 siRNA and control siRNA. * p<0.05 compared with control; # p < 0.05. (b) TRPV3 agonist cocktail-induced CRE-Luc activity in the absence or presence or different concentrations of Mg2+ in keratinocytes from transgenic mice. * p<0.05.
Discussion
Hypomagnesemia and intracellular Mg2+ deficiency are found in many pathological conditions associated with skin lesions and hypersensitivity, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus and neuropathic pain (Resnick et al., 1993; Sales and Pedrosa Lde, 2006; Tosiello, 1996; Xiao and Bennett, 1994). Hairless rats receiving Mg2+-deficient diet develop a long-lasting inflammatory dermatosis of unknown mechanism (Ponvert et al., 1984; Saurat et al., 1983). Interestingly, a gain-of-function TRPV3 mutation also causes “no hair” phenotype, dermatitis, and pruritus in rodents (Asakawa et al., 2006; Imura et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2008b; Yoshioka et al., 2009). As TRP channels are known to be regulated by pathophysiological concentrations of cations (Ahern et al., 2005; Lee et al., 2005; Obukhov and Nowycky, 2005; Voets et al., 2003), TRPV3 may mediate some of the Mg2+ deficiency-induced skin inflammation. This is also supported by the finding that TRPV3 function is directly enhanced by many inflammatory mediators (Hu et al., 2006).
Our findings show that increasing [Mg2+]o suppresses TRPV3-mediated intracellular calcium response, membrane current, and CREB activity in primary epidermal keratinocytes. Therefore, our data support a model in which TRPV3 function is activated under conditions of Mg2+ deficiency. Hyperactivated TRPV3 may, in turn, promote release of ATP, prostaglandins, nitric oxide and nerve growth factor from epidermal keratinocytes, which are known to sensitize nociceptors and initiate neurogenic inflammation and pain (Huang et al., 2008; Mandadi et al., 2009; Miyamoto et al., 2011).
At the single-channel level, extracellular Mg2+ inhibits TRPV3 mainly by reducing the single-channel conductance without significantly affecting the open probability. Moreover, we have identified an aspartic acid residue D641, neutralization of which significantly attenuated the inhibitory effect of [Mg2+]o on TRPV3, suggesting that this aspartic acid is required for [Mg2+]o action on TRPV3. By contrast, [Mg2+]o sensitizes and gates TRPV1 in the primary afferent neurons and initiates pain (Ahern et al., 2005). Although the mechanism underlying the difference between TRPV1 and TRPV3 remains unknown, it seems that the effects of [Mg2+]o on both channels are mediated by the negatively charged acidic residues in the extracellular pore loop (D641 for TRPV3 and E600/E648 for TRPV1). Interestingly, D641 is also involved in the interaction between extracellular Ca2+ and TRPV3 (Xiao et al., 2008a), and neutralization of this amino acid in TRPV3 severely attenuates the blocking effect of ruthenium red and extracellular calcium, similar to TRPV1 at the equivalent position D646 (Garcia-Martinez et al., 2000 and data not shown). Since ruthenium red is also an organic cation, this conserved acidic residue might be part of an extracellular cation sensor for both TRPV3 and TRPV1.
In addition to fluctuations of [Mg2+]o under some pathological conditions, [Mg2+]i also undergoes dynamic changes following changes of cellular metabolic state. Our results show that [Mg2+]i inhibited outward single-channel conductance more potently than the inward single-channel current without affecting the NPo. This result is consistent with whole-cell recording data showing that Mg2+ inhibited TRPV3 in a voltage-dependent manner, suggesting that Mg2+ likely interacts with TRPV3 in an area experiencing the transmembrane electric field.
Using site-directed mutagenesis we screened negatively charged acidic residues located in the inner pore loop and identified two glutamate residues between the sixth transmembrane domain and the TRP box, E679 and E682. Neutralization of these two residues nearly abolished the inhibitory effect of the [Mg2+]i. Interestingly, an increase of Mg2+ concentration in the intracellular and extracellular sides selectively depressed the outward and inward currents, respectively. Moreover, change of the ratio of intracellular and extracellular Mg2+ altered the rectification ratio of TRPV3 current, suggesting that Mg2+-induced voltage-dependent inhibition contributes to the characteristic rectification of TRPV3 current (Chung et al., 2005).
In summary, our study has revealed the molecular mechanism underlying the modulation of TRPV3 by both extracellular and intracellular Mg2+ in mouse epidermal keratinocytes. The data favor a pore blocking model in which Mg2+ interacts with negatively charged acidic residues on both sides of the channel pore loop. Enhanced TRPV3 function in hypomagnesemia resulting from the disinhibition by Mg2+ may be involved in the pathogenesis of magnesium deficiency-induced atopic dermatitis and pruritus, in which intracellular calcium signaling and CREB-dependent transcription are activated (Figure S2).
Materials and Methods
Mouse epidermal kerationcyte culture
Primary epidermal keratinocytes were prepared as described previously with minor modifications (Chung et al., 2004b; Miyamoto et al., 2011) with approval by The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Animal Welfare Committee. In brief, newborn mouse pups (P0–P2) were euthanized and soaked in 10% povidone-iodine, 70% ethanol, and PBS for 5 min respectively. The back skin was removed and placed in a Petri dish containing 2.5% dispase II (Life Technologies, NY) and incubated at 4°C overnight. Epidermis was then separated from subcutaneous tissues. Keratinocytes were dissected by gentle scraping and flushing with CnT-07 medium (CELLnTEC advanced cell systems, Switzerland). Harvested cells were plated on coverslips coated with collagen IV in serum-free, fully supplemented keratinocyte medium CnT-07. The culture medium was replaced every two days and cells were used 48 hrs later.
Luciferase activity measurement
Epidermal keratinocytes were cultured as described above from individual transgenic newborn pups containing a genomically encoded CREB-driven luciferase reporter transgene (CRE-Luc) (Song et al., 2010). Copy number was maintained as hemizygous by intercrossing CRE-luciferase transgenic males with wild-type albino C57Bl6/J-Tyrc females (The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor). Newborn pups were genotyped by PCR within the luciferase gene (forward: 5′-GCTGGGCGTTAATCAGAGAG; reverse: 5′-TTTTCCGTCATCGTCTTTCC). Confluent cells (>95%) were treated as described in the figure legends for 4 hrs and then lysed with Reporter Lysis Buffer containing (mM): 25 Glycyllglycine (GlyGly), 15 MgSO4, 4 EGTA, 1 DTT, and 1% Triton X-100. Lysates were mixed 1:1 with 2X luciferase assay buffer (mM): 25 GlyGly, 15 K2PO4, 2 ATP, 2 mM DTT and assayed immediately after injection of D-luciferin (0.1 mM in 25 mM GlyGly, 4 mM EGTA) using a BioTek Synergy II plate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski). Luciferase relative light units were normalized to total protein concentration determined using a BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Scientific, IL). Data are expressed as fold change above baseline.
Ratiometric measurement of intracellular free calcium
Primary keratinocytes were loaded with 4 μM Fura-2 AM (Life Technologies, NY) in culture medium at 37 °C for 60 min. Cells were then washed 3 times and incubated in Hank's buffered salt solution (HBSS) at room temperature for 30 min before use. Fluorescence at 340 nm and 380 nm excitation wavelengths was recorded on an inverted Nikon Ti-E microscope equipped with 340, 360 and 380 nm excitation filter wheels using NIS-Elements imaging software (Nikon Instruments Inc., NY). Fura-2 ratios (F340/F380) reflects changes in [Ca2+]i upon stimulation. Values were obtained from 100– 250 cells in time-lapse images from each coverslip.
Molecular biology, CHO cell culture and transfection
CHO cells were grown as a monolayer using passage numbers less than 30 and maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) (Life Technologies, NY), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Life Technologies, NY), 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin in a humidified incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO2. The cells were transiently transfected with cDNA for mouse TRPV3 (mTRPV3) in pIRES2-EGFP (Clontech Laboratories, Inc., Mountain View) using FuGENE 6 (Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis) with a ratio of 1.2:5. Following transfection, the cells were maintained in DMEM at 37 °C for 24 hrs before use. All mutants of mTRPV3 were made using the QuikChange II XL mutagenesis kit (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara) according to the manufacturer's directions. All mutations were confirmed by DNA sequencing.
Patch-clamp recording
Whole-cell and single-channel patch-clamp recordings were performed using an EPC 10 amplifier (HEKA Elektronik, Germany) at room temperature (22–24 °C) on the stage of an inverted phase-contrast microscope equipped with an appropriate filter set for green fluorescence protein visualization. Pipettes pulled from borosilicate glass (BF 150-86-10; Sutter Instrument Company, Novato) with a Sutter P-97 pipette puller had resistances of 2-4 and 8-10 MΩ for whole-cell and single-channel recordings, respectively, when filled with pipette solution containing 140 mM CsCl, 2 mM EGTA, and 10 mM HEPES with pH 7.3 and 315 mOsm/L in osmolarity. The extracellular solution for whole-cell recording contains 140 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 10 mM glucose, and 10 mM HEPES (the pH was adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH, and the osmolarity was adjusted to ∼340 mOsm/L with sucrose). A symmetrical solution with the same components as that in the pipette solution was used in single-channel recordings. Various concentrations of MgCl2 were included in the intracellular or extracellular solutions, as stated in the figure legends. The whole-cell membrane currents were recorded using voltage ramp from -100 to +100 mV during 500 ms at holding potential of 0 mV. Data were acquired using Patchmaster software (HEKA Elektronik, Germany). Currents were filtered at 2 kHz and digitized at 10 kHz. Data were analyzed and plotted using Clampfit 10 (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale). Single-channel events were identified on the basis of the half-amplitude threshold-crossing criteria. P(open) was determined from idealized traces as the ratio of the sum of all open durations to the total trace duration. Values are given as the means ± SEM; n represents the number of measurements.
Data analysis
All data are the means ± s.e.m. for n independent observations, and statistical analyses were performed using Student's t-test. p<0.05 is considered statistically significant.
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. Characterization of TRPV3 agonist cocktail-evoked intracellular calcium increase (a & b) and membrane current (c & d) in epidermal keratinocytes. The TRPV3 agonist cocktail evoked intracellular calcium responses and membrane current in primary keratinocytes from the wild type (a and c) but not TRPV3 deficient mice (b and d). Please note that black lines refer to baseline currents and red lines refer to currents evoked by the TRPV3 agonist cocktail in c and d.
Figure S2. Inhibition of TRPV3-mediated current by [Mg2+]o in TRPV3-expressing CHO cells. (a) Representative current traces in response to voltage ramp from -100 mV to +100 mV without (basal) and with the 100 Um 2APB in the absence (0 mM) and presence of 2 and 10 mM Mg2+. (b) Percentage of inhibition of 2APB-activated current by 10 mM Mg2+ at holding potential of -100 mV and +100 mV obtained from the voltage ramp shown in (a). Please note the difference between the inhibitory effect at -100 mV and +100 mV (n=8). (c) Rectification ratio [-(I100/I-100)] with different concentrations of Mg2+ in the intracellular and extracellular solutions. ** p<0.01 compared with 2 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution with 2 or 10 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution. ## p<0.01 compared with 2 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution with 0, 2, or 10 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution. n=8 for recordings with 2 mM Mg2+ and n=7 for recordings with 10 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solutions.
Figure S3. Schematic diagram illustrates the acidic amino acid residues required for Mg2+ inhibition of TRPV3 and TRPV3-mediated calcium influx promotes CREB-dependent activity.
Acknowledgments
We thank Hai-Tang Li for technical support and Dr. Feng Qin for help with single-channel analysis. We are grateful to our colleagues for comments and discussions. This project is partly supported by grants from the Texas Medical Center Digestive Diseases Center (to HH, 0008355) and Mission Connect/TIRR Foundation (to HH, 011-101), the University of Texas Health Science Center (to HH and RB), and the National Institutes of Health National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (R01 DK092590 to RB).
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahern GP, Brooks IM, Miyares RL, et al. Extracellular cations sensitize and gate capsaicin receptor TRPV1 modulating pain signaling. J Neurosci. 2005;25:5109–16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0237-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akamatsu H, Makiura M, Yamamoto N, et al. The effect of fexofenadine on pruritus in a mouse model (HR-ADf) of atopic dermatitis. J Int Med Res. 2006;34:495–504. doi: 10.1177/147323000603400506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari KM, Rundhaug JE, Fischer SM. Multiple signaling pathways are responsible for prostaglandin E2-induced murine keratinocyte proliferation. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6:1003–16. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa M, Yoshioka T, Matsutani T, et al. Association of a mutation in TRPV3 with defective hair growth in rodents. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:2664–72. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang S, Yoo S, Yang TJ, et al. Farnesyl pyrophosphate is a novel pain-producing molecule via specific activation of TRPV3. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2010;285:19362–71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.087742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D, Haass FA, Jan LY. Merging functional studies with structures of inward-rectifier K(+) channels. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:957–67. doi: 10.1038/nrn1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biro T, Ko MC, Bromm B, et al. How best to fight that nasty itch - from new insights into the neuroimmunological, neuroendocrine, and neurophysiological bases of pruritus to novel therapeutic approaches. Exp Dermatol. 2005;14:225–40. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-6705.2005.0321a.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borbiro I, Lisztes E, Toth BI, et al. Activation of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid-3 Inhibits Human Hair Growth. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:1605–14. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng X, Jin J, Hu L, et al. TRP channel regulates EGFR signaling in hair morphogenesis and skin barrier formation. Cell. 2010;141:331–43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinopoulos C, Connor JA, Shuttleworth CW. Emergence of a spermine-sensitive, non-inactivating conductance in mature hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons upon reduction of extracellular Ca2+: dependence on intracellular Mg2+ and ATP. Neurochem Int. 2007;50:148–58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2006.07.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung MK, Guler AD, Caterina MJ. Biphasic currents evoked by chemical or thermal activation of the heat-gated ion channel, TRPV3. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:15928–41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500596200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung MK, Lee H, Mizuno A, et al. 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate activates and sensitizes the heat-gated ion channel TRPV3. J Neurosci. 2004a;24:5177–82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0934-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung MK, Lee H, Mizuno A, et al. TRPV3 and TRPV4 mediate warmth-evoked currents in primary mouse keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 2004b;279:21569–75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401872200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham DE. SnapShot: mammalian TRP channels. Cell. 2007;129:220. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley S, Gonzales AL, Garcia ZI. A dietary agonist of transient receptor potential cation channel V3 elicits endothelium-dependent vasodilation. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;77:612–20. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.060715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facer P, Casula MA, Smith GD, et al. Differential expression of the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 and related novel receptors TRPV3, TRPV4 and TRPM8 in normal human tissues and changes in traumatic and diabetic neuropathy. BMC Neurol. 2007;7:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-7-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Martinez C, Morenilla-Palao C, Planells-Cases R, et al. Identification of an aspartic residue in the P-loop of the vanilloid receptor that modulates pore properties. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:32552–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002391200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich M, Buckler KJ. Effects of anoxia, aglycemia, and acidosis on cytosolic Mg2+, ATP, and pH in rat sensory neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;294:C280–94. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00345.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich M, Buckler KJ. Acid-evoked Ca2+ signalling in rat sensory neurones: effects of anoxia and aglycaemia. Pflugers Arch. 2009;459:159–81. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0715-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu H, Grandl J, Bandell M, et al. Two amino acid residues determine 2-APB sensitivity of the ion channels TRPV3 and TRPV4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:1626–31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812209106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu HZ, Gu Q, Wang C, et al. 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate is a common activator of TRPV1, TRPV2, and TRPV3. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:35741–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404164200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu HZ, Xiao R, Wang C, et al. Potentiation of TRPV3 channel function by unsaturated fatty acids. J Cell Physiol. 2006;208:201–12. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang SM, Lee H, Chung MK, et al. Overexpressed transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 ion channels in skin keratinocytes modulate pain sensitivity via prostaglandin E2. J Neurosci. 2008;28:13727–37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5741-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imura K, Yoshioka T, Hikita I, et al. Influence of TRPV3 mutation on hair growth cycle in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;363:479–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.08.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson JW, Ascher P. Voltage-dependent block by intracellular Mg2+ of N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated channels. Biophysical Journal. 1990;57:1085–90. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82626-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauer JA, Gibson HE. Hot flash: TRPV channels in the brain. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32:215–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Cha SK, Sun TJ, et al. PIP2 activates TRPV5 and releases its inhibition by intracellular Mg2+ J Gen Physiol. 2005;126:439–51. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200509314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandadi S, Sokabe T, Shibasaki K, et al. TRPV3 in keratinocytes transmits temperature information to sensory neurons via ATP. Pflugers Arch. 2009;458:1093–102. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0703-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H, Richert L, Berthelot A. Magnesium deficiency induces apoptosis in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Nutr. 2003;133:2505–11. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.8.2505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T, Petrus MJ, Dubin AE, et al. TRPV3 regulates nitric oxide synthase-independent nitric oxide synthesis in the skin. Nat Commun. 2011;2:369. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moqrich A, Hwang SW, Earley TJ, et al. Impaired thermosensation in mice lacking TRPV3, a heat and camphor sensor in the skin. Science. 2005;307:1468–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1108609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moussaieff A, Rimmerman N, Bregman T, et al. Incensole acetate, an incense component, elicits psychoactivity by activating TRPV3 channels in the brain. FASEB J. 2008;22:3024–34. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-101865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi M, Hata K, Nagayama T, et al. Acid activation of Trpv1 leads to an up-regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons via the CaMK-CREB cascade: a potential mechanism of inflammatory pain. Molecular biology of the cell. 2010;21:2568–77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-01-0049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckermann G, Bavandi A, Meingassner JG. Atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in hypomagnesaemic hairless rats are prevented and inhibited by systemic or topical SDZ ASM 981. Br J Dermatol. 2000;142:669–79. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov AG, Nowycky MC. A cytosolic residue mediates Mg2+ block and regulates inward current amplitude of a transient receptor potential channel. J Neurosci. 2005;25:1234–9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4451-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peier AM, Reeve AJ, Andersson DA, et al. A heat-sensitive TRP channel expressed in keratinocytes. Science. 2002;296:2046–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1073140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponvert C, Galoppin L, Burtin C, et al. Noninvolvement of histamine and prostaglandins in the dermatosis of magnesium-deficient hairless rats. Pharmacology. 1984;28:235–40. doi: 10.1159/000137968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick LM, Altura BT, Gupta RK, et al. Intracellular and extracellular magnesium depletion in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1993;36:767–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00401149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenberg J, Rishi V, Orosz A, et al. Inhibition of CREB function in mouse epidermis reduces papilloma formation. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:654–64. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sales CH, Pedrosa Lde F. Magnesium and diabetes mellitus: their relation. Clin Nutr. 2006;25:554–62. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2006.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris NE, Mervaala E, Karppanen H, et al. Magnesium. An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin Chim Acta. 2000;294:1–26. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(99)00258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saurat JH, Chavez P, Ponvert C, et al. Skin inflammation induced by hypomagnesaemia in the rat. Br J Dermatol 109 Suppl. 1983;25:106–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb11657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savignac M, Edir A, Simon M, et al. Darier disease : a disease model of impaired calcium homeostasis in the skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1111–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherkheli MA, Benecke H, Doerner JF, et al. Monoterpenoids induce agonist-specific desensitization of transient receptor potential vanilloid-3 (TRPV3) ion channels. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2009;12:116–28. doi: 10.18433/j37c7k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith GD, Gunthorpe MJ, Kelsell RE, et al. TRPV3 is a temperature-sensitive vanilloid receptor-like protein. Nature. 2002;418:186–90. doi: 10.1038/nature00894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Y, Altarejos J, Goodarzi MO, et al. CRTC3 links catecholamine signalling to energy balance. Nature. 2010;468:933–9. doi: 10.1038/nature09564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff M, Biro T. A TR(I)P to pruritus research: role of TRPV3 in inflammation and itch. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:531–5. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosiello L. Hypomagnesemia and diabetes mellitus. A review of clinical implications. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156:1143–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voets T, Janssens A, Prenen J, et al. Mg2+-dependent gating and strong inward rectification of the cation channel TRPV6. J Gen Physiol. 2003;121:245–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.20028752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriens J, Appendino G, Nilius B. Pharmacology of vanilloid transient receptor potential cation channels. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;75:1262–79. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.055624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson JE, Chin A. Chelation of divalent cations by ATP, studied by titration calorimetry. Anal Biochem. 1991;193:16–9. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90036-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao R, Tang J, Wang C, et al. Calcium plays a central role in the sensitization of TRPV3 channel to repetitive stimulations. J Biol Chem. 2008a;283:6162–74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706535200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao R, Tian J, Tang J, et al. The TRPV3 mutation associated with the hairless phenotype in rodents is constitutively active. Cell Calcium. 2008b;43:334–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao WH, Bennett GJ. Magnesium suppresses neuropathic pain responses in rats via a spinal site of action. Brain Res. 1994;666:168–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90768-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H, Ramsey IS, Kotecha SA, et al. TRPV3 is a calcium-permeable temperature-sensitive cation channel. Nature. 2002;418:181–6. doi: 10.1038/nature00882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T, Ueda T, Ugawa S, et al. Functional expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 (TRPV3) in corneal epithelial cells: involvement in thermosensation and wound healing. Exp Eye Res. 2010;90:121–9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka T, Imura K, Asakawa M, et al. Impact of the Gly573Ser substitution in TRPV3 on the development of allergic and pruritic dermatitis in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:714–22. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Characterization of TRPV3 agonist cocktail-evoked intracellular calcium increase (a & b) and membrane current (c & d) in epidermal keratinocytes. The TRPV3 agonist cocktail evoked intracellular calcium responses and membrane current in primary keratinocytes from the wild type (a and c) but not TRPV3 deficient mice (b and d). Please note that black lines refer to baseline currents and red lines refer to currents evoked by the TRPV3 agonist cocktail in c and d.
Figure S2. Inhibition of TRPV3-mediated current by [Mg2+]o in TRPV3-expressing CHO cells. (a) Representative current traces in response to voltage ramp from -100 mV to +100 mV without (basal) and with the 100 Um 2APB in the absence (0 mM) and presence of 2 and 10 mM Mg2+. (b) Percentage of inhibition of 2APB-activated current by 10 mM Mg2+ at holding potential of -100 mV and +100 mV obtained from the voltage ramp shown in (a). Please note the difference between the inhibitory effect at -100 mV and +100 mV (n=8). (c) Rectification ratio [-(I100/I-100)] with different concentrations of Mg2+ in the intracellular and extracellular solutions. ** p<0.01 compared with 2 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution with 2 or 10 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution. ## p<0.01 compared with 2 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solution with 0, 2, or 10 mM Mg2+ in the extracellular solution. n=8 for recordings with 2 mM Mg2+ and n=7 for recordings with 10 mM Mg2+ in the intracellular solutions.
Figure S3. Schematic diagram illustrates the acidic amino acid residues required for Mg2+ inhibition of TRPV3 and TRPV3-mediated calcium influx promotes CREB-dependent activity.


