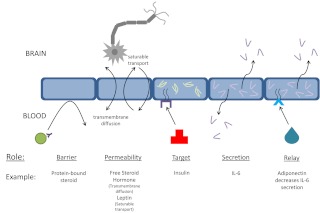
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms for translocation across the BBB of hormones and their messages between the brain and blood. The role of barrier prevents substances from crossing the BBB as exemplified by steroids that are protein bound. Permeability of the BBB is often by way of transmembrane diffusion as exemplified by unbound steroid hormone or by way of transporters as exemplified by leptin. The cells forming the BBB are themselves targets of circulating substances as exemplified by the many effects that insulin has on brain endotheial cell function. The cells that form the BBB are themselves endocrine-like in that they can secret substances into the blood or into the brain as exemplified by IL-6 secretion by brain endothelial cells. Relay is a special feature arising from the unique separation of brain endothelial cells into luminal and abluminal membranes and allows the BBB cell to receive an input on one membrane and to secrete from the other as exemplified here by adiponectin acting at the luminal membrane to alter secretion of IL-6 from the abluminal membrane. Extracellular pathways (data not shown) can be used by albumin and by very large and stable proteins (antibodies, erythropoietin) to gain access to the CNS.