Abstract
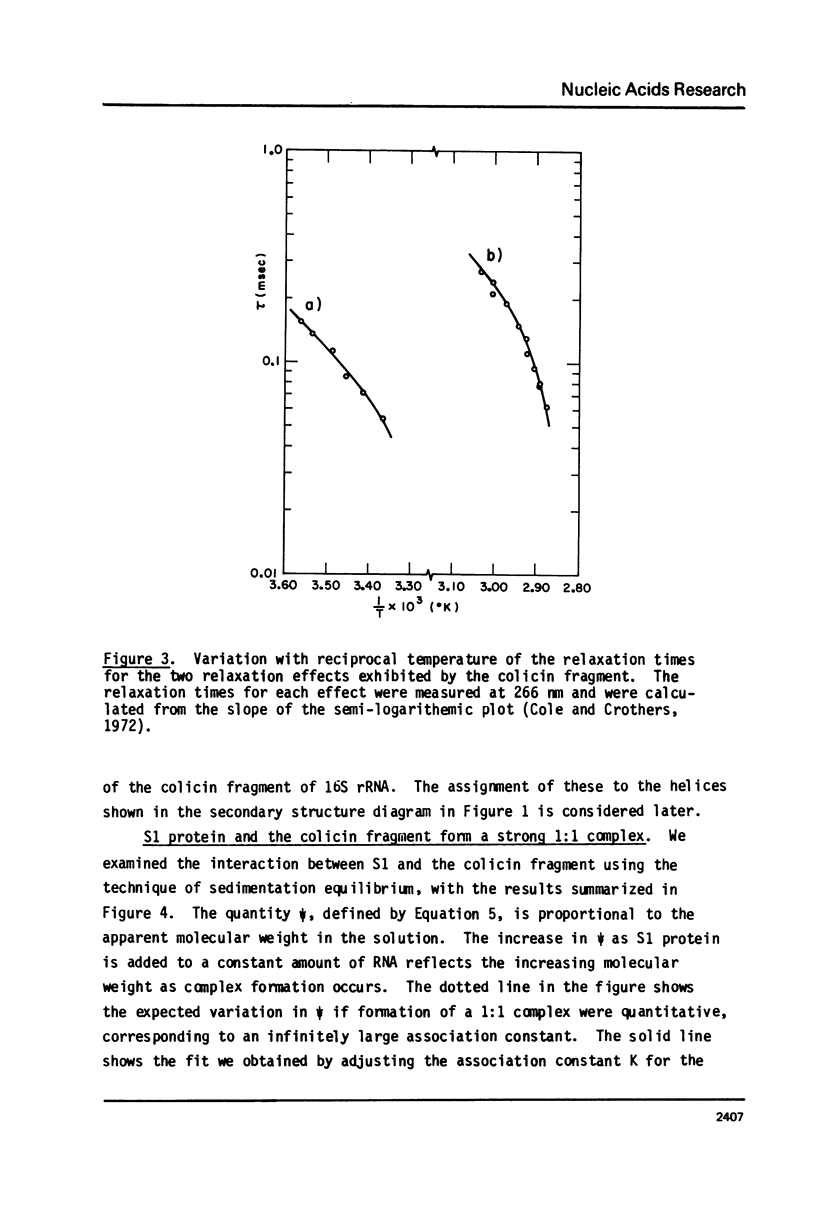
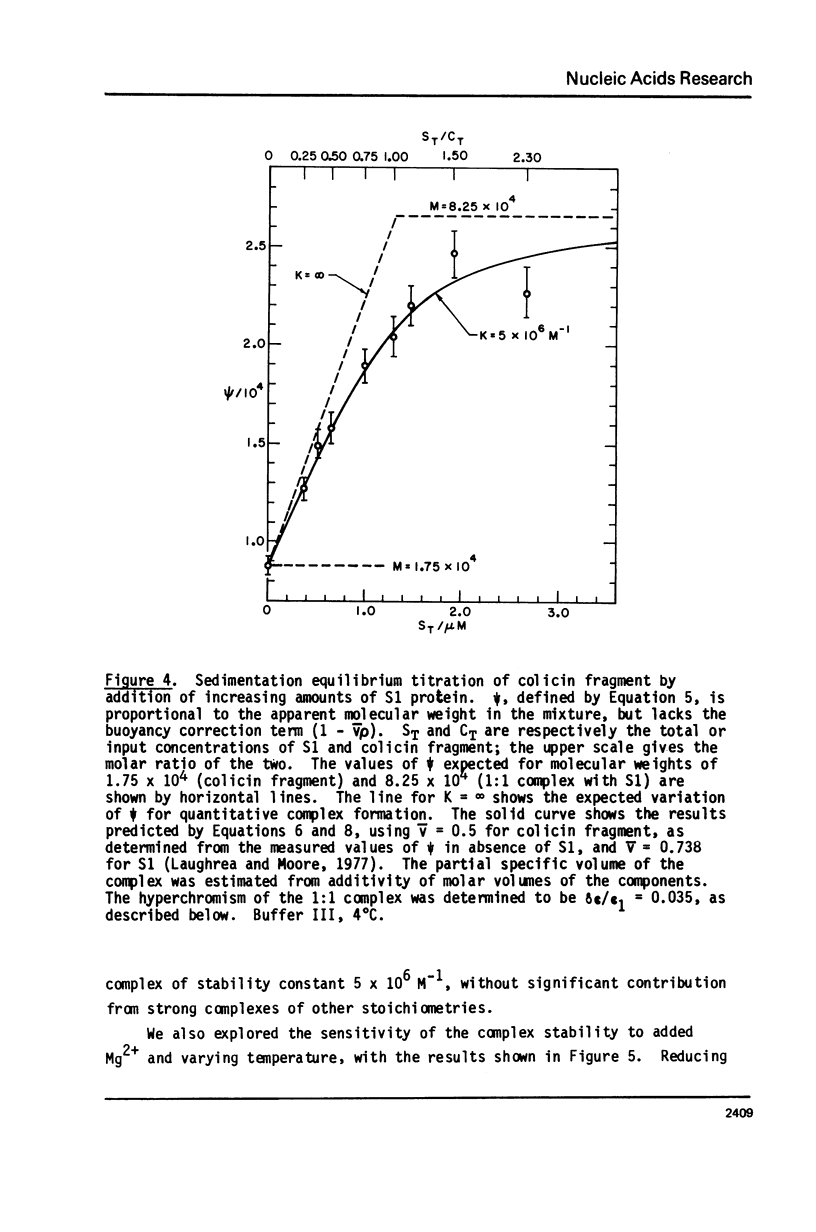
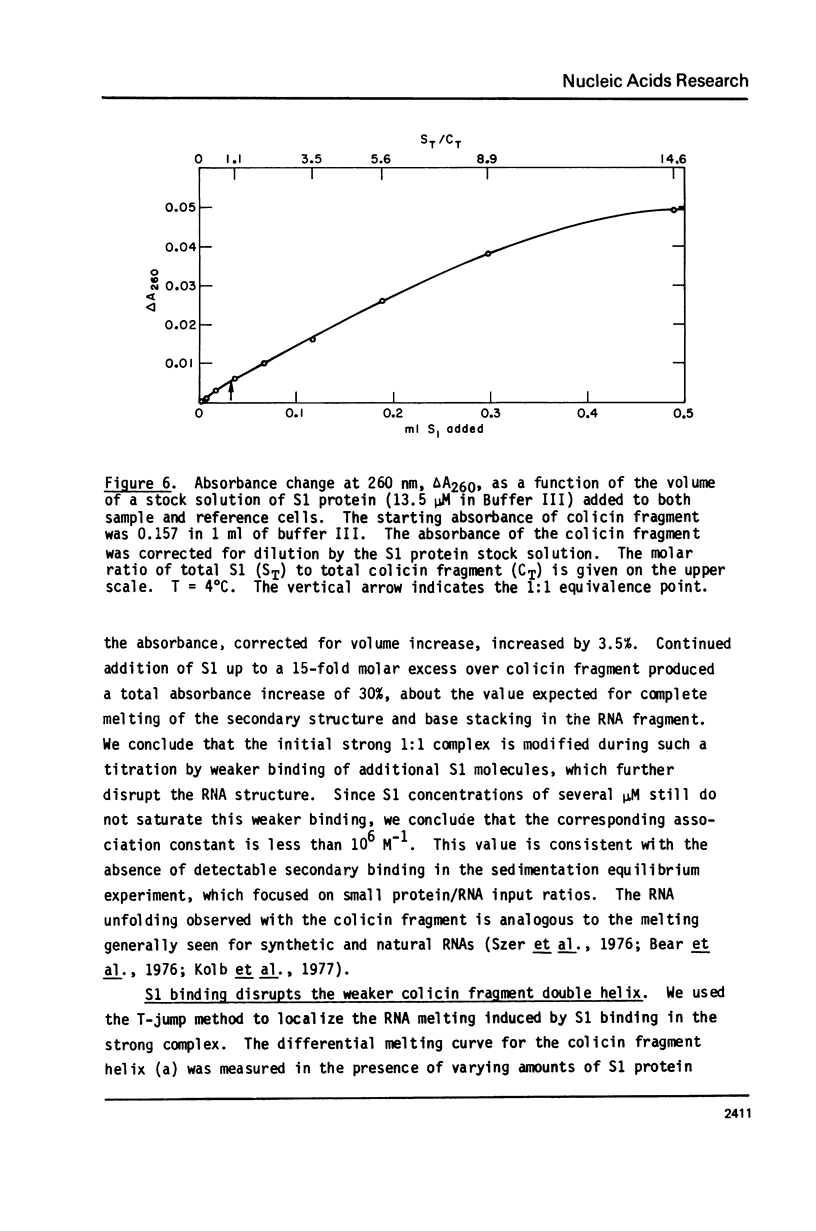
We report studies of the secondary structure and S1 ribosomal protein binding properties of the colicin fragment, containing 49 residues from the 3' terminus of E. coli 16S rRNA. Temperature jump relaxation kinetic measurements reveal two helices in the structure. One of these, melting at 81 degrees C in 5 mM Mg2+, is associated with the 9-base pair hairpin helix predicted by the nucleotide sequence. The other melting transition, at 21 degrees C in 5 mM Mg2+, is assigned to a 4-base pair helix which constrains the pyrimidine tract of the colicin fragment into a bulge loop. S1 protein forms a strong 1:1 complex with the colicin fragment, with an association constant of 5 x 10(6) M-1 in 5 mM Mg2+. More protein molecules are bound, but with weaker affinity, when the S1 concentration is increased. S1 binding causes melting of the colicin fragment secondary structure, as inferred from the observed absorbance increase. The S1 binding site on the colicin fragment has been localized in the region of the bulge loop, since the melting transition corresponding to the 4-base pair helix is lost in the complex. We discuss current models for the role of S1 protein in polypeptide chain initiation in light of these and previous results.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. S., Bretscher M. S., Clark B. F., Marcker K. A. A GTP requirement for binding initiator tRNA to ribosomes. Nature. 1967 Jul 29;215(5100):490–492. doi: 10.1038/215490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baan R. A., Hilbers C. W., Van Charldorp R., Van Leerdam E., Van Knippenberg P. H., Bosch L. High-resolution proton magnetic resonance study of the secondary structure of the 3'-terminal 49-nucleotide fragment of 16S rRNA from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1028–1031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear D. G., Ng R., Van Derveer D., Johnson N. P., Thomas G., Schleich T., Noller H. F. Alteration of polynucleotide secondary structure by ribosomal protein S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1824–1828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G. Isolation of bacterial and phage proteins by homopolymer RNA-cellulose chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. E., Crothers D. M. Conformational changes of transfer ribonucleic acid. Relaxation kinetics of the early melting transition of methionine transfer ribonucleic acid (Escherichia coli). Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4368–4374. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Cole P. E., Hilbers C. W., Shulman R. G. The molecular mechanism of thermal unfolding of Escherichia coli formylmethionine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 25;87(1):63–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90560-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Kurland C. G., Stöffler G. 30S ribosomal proteins associated with the 3'-terminus of 16S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E., Dahlberg J. E. Binding of ribosomal protein S1 of Escherichia coli to the 3' end of 16S rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2940–2944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E. Two forms of the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7673–7678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delisi C., Crothers D. M. Prediction of RNA secondary structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2682–2685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. E., Pratt C. W., von Hippel P. H. Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 has two polynucleotide binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4786–4790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. E., von Hippel P. H. Interaction of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 with ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1040–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. E., von Hippel P. H. Nucleic acid binding properties of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1. I. Structure and interactions of binding site I. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 5;122(3):321–338. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper D. E., von Hippel P. H. Nucleic acid binding properties of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1. II. Co-operativity and specificity of binding site II. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 5;122(3):339–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Mackie G. A., Zimmermann R. A., Ebel J. P., Fellner P. Primary sequence of the 16S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Feb;2(2):265–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink T. R., Crothers D. M. Free energy of imperfect nucleic acid helices. I. The bulge defect. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiser I., Margaritella P., Kuechler E. Photoaffinity reaction between polyuridylic acid and protein S1 on the Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 1;52(2):281–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80825-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelz S., Steitz J. A. Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 recognizes two sites in bacteriophage Qbeta RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5177–5179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J., Crothers D. M. Free energy of imperfect nucleic acid helices. II. Small hairpin loops. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 5;73(4):497–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J., Steitz J. A., Crothers D. M. Direct physical evidence for secondary structure in an isolated fragment of R17 bacteriophage mRNA. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):204–208. doi: 10.1038/248204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Kaempfer R. Translational repression of a viral messenger RNA by a host protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5749–5755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Hermoso J. M., Thomas J. O., Szer W. Nucleic acid helix-unwinding properties of ribosomal protein S1 and the role of S1 in mRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde R., Quoc Khanh N., Lipecky R., Gassen H. G. On the function of the ribosomal protein S1 in the elongation cycle of bacterial protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 1;93(3):565–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipecky R., Kohlschein J., Gassen H. G. Complex formation between ribosomal protein S1, oligo-and polynucleotides: chain length dependence and base specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3627–3642. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Wahba A. J. Inhibition of synthetic and natural messenger translation. II. Specificity and mechanism of action of a protein isolated from Escherichia coli MRE 600 ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3808–3813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B. The preparation of deuterated ribosomal materials for neutron scattering. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:639–655. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Assembly of bacterial ribosomes. Science. 1973 Mar 2;179(4076):864–873. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4076.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senear A. W., Steitz J. A. Site-specific interaction of Qbeta host factor and ribosomal protein S1 with Qbeta and R17 bacteriophage RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1902–1912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobura J. E., Chowdhury M. R., Hawley D. A., Wahba A. J. Requirement of chain initiation factor 3 and ribosomal protein S1 in translation of synthetic and natural messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):17–29. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Steege D. A. Characterization of two mRNA-rRNA complexes implicated in the initiation of protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1977 Aug 25;114(4):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90177-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Wahba A. J., Laughrea M., Moore P. B. Differential requirements for polypeptide chain initiation complex formation at the three bacteriophage R17 initiator regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W., Hermoso J. M., Boublik M. Destabilization of the secondary structure of RNA by ribosomal protein S1 from Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):957–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90685-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W., Hermoso J. M., Leffler S. Ribosomal protein S1 and polypeptide chain initiation in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2325–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., Aviram M., Kanarek A., Weiss A. Polyuridylic acid binding and translating by Escherichia coli ribosomes: stimulation by protein I, inhibition by aurintricarboxylic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 27;281(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dieijen G., Van Der Laken C. J., Van Knippenberg P. H., Van Duin J. Function of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 in translation of natural and synthetic messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 15;93(3):351–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., van Knippenberg P. H., van Duin J. The specific role of ribosomal protein S1 in the recognition of native phage RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 1;64(2):511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin J., van Knippenberg P. H. Functional heterogeneity of the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. 3. Requirement of protein S1 for translation. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 25;84(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



