Abstract
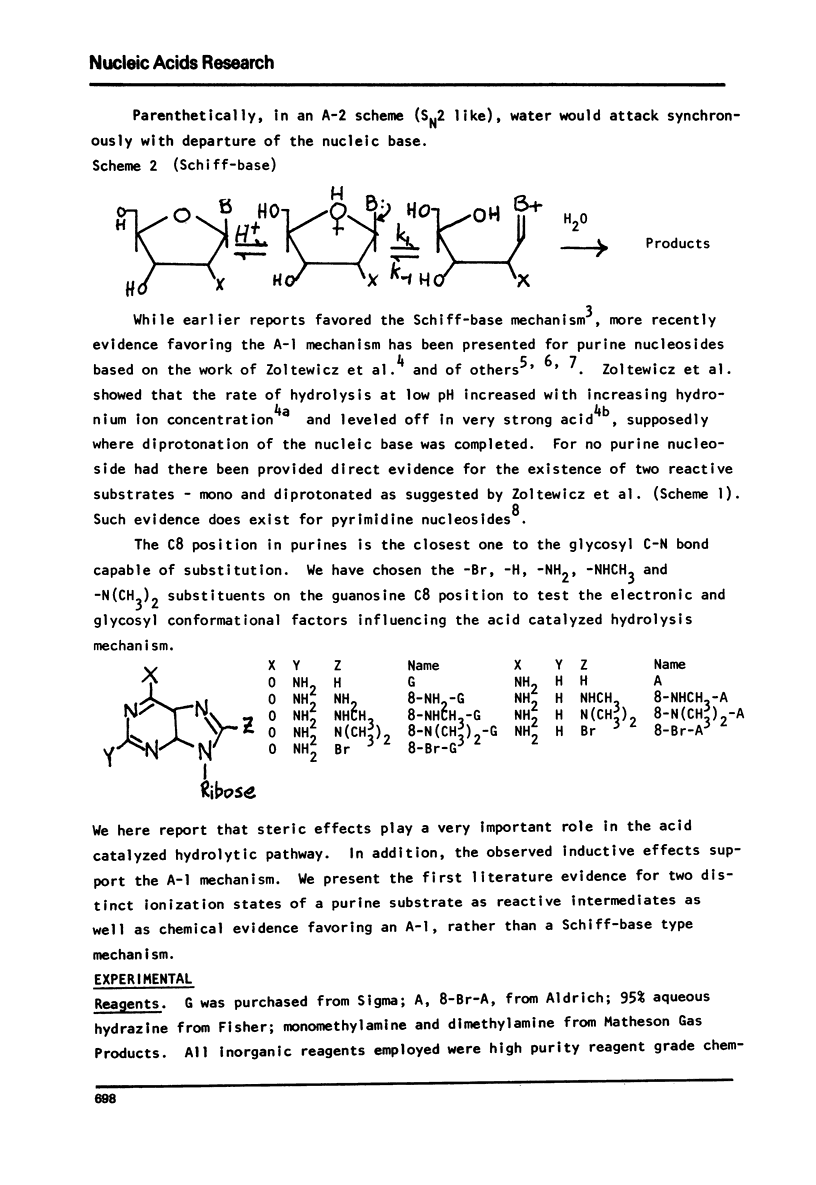
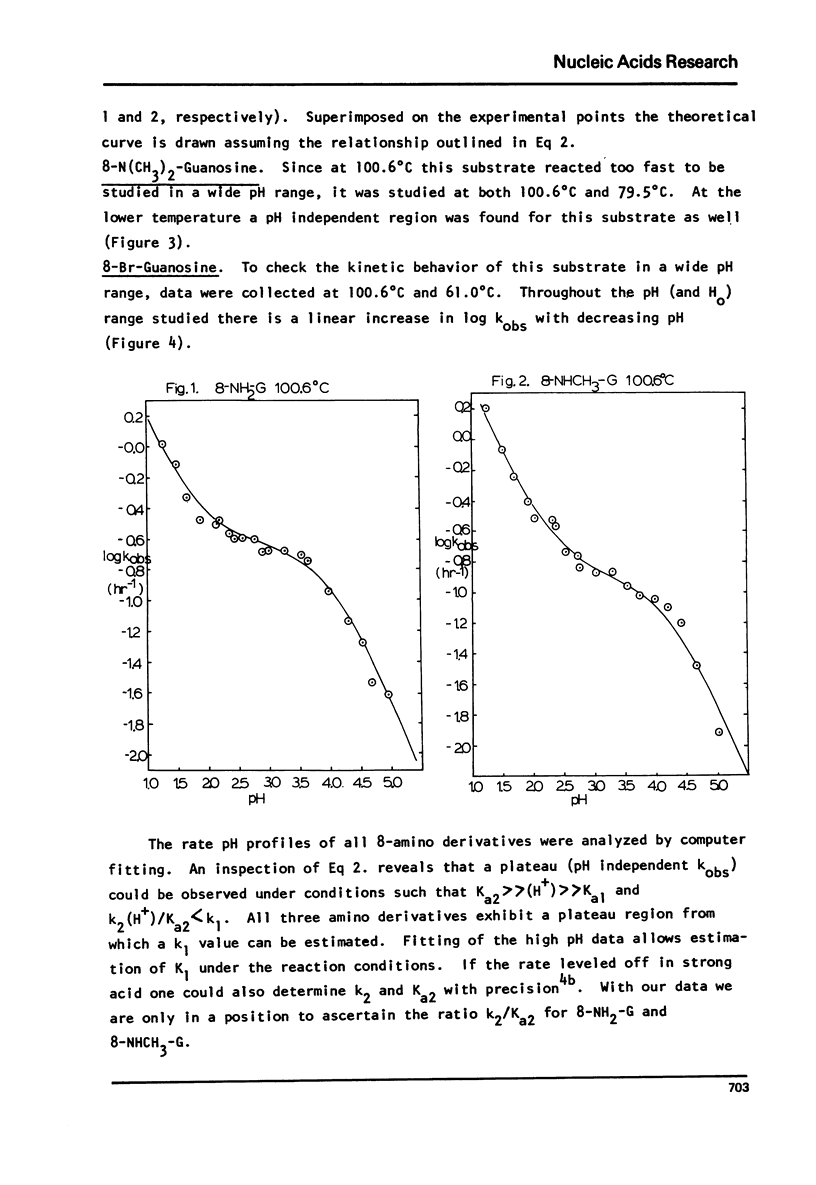
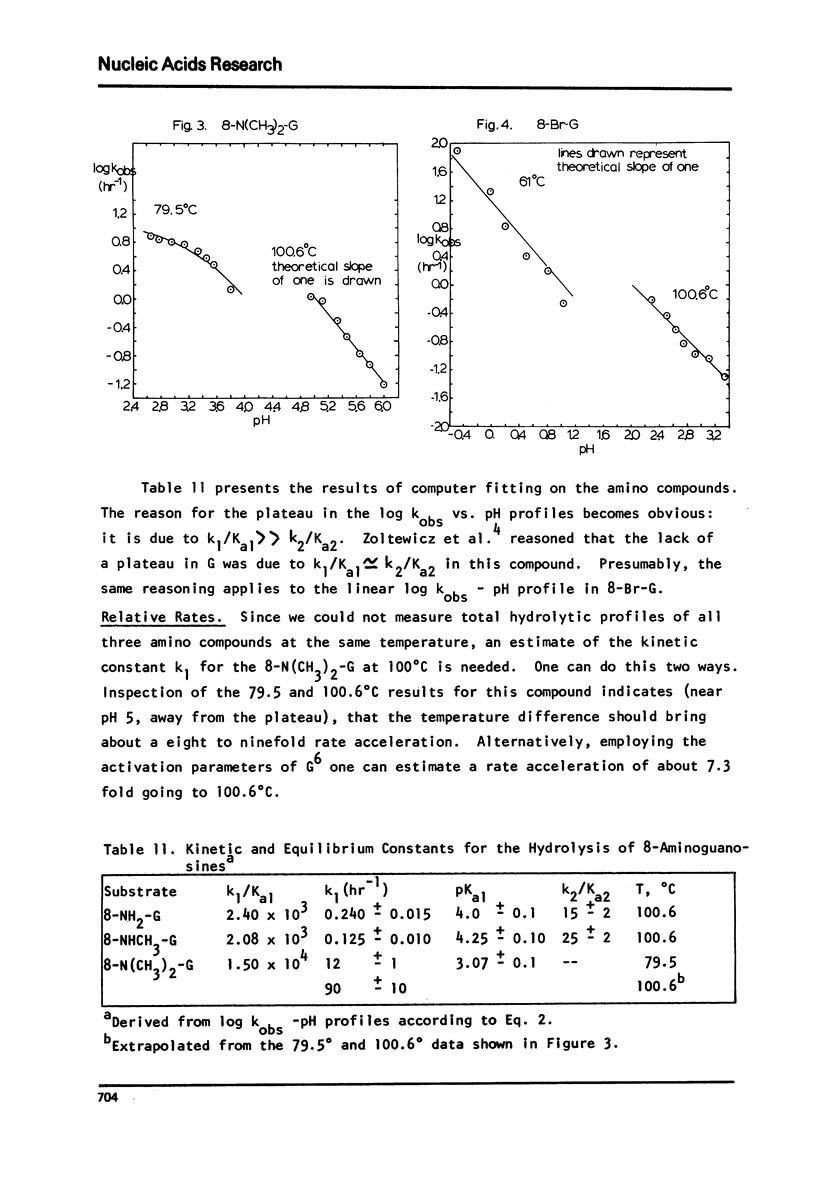
The log kobs vs. pH profiles were determined in the intermediate acidity region for the glycosyl hydrolysis of guanosine and its 8-amino, 8-monomethylamino, 8-dimethylamino and 8-bromo derivatives. The decreased rate of the 8-amino and enhanced rate of the 8-bromo compound compared to guanosine support an A type mechanism: base protonation followed by glycosyl bond cleavage. All three 8-amino guanosines exhibited log kobs - pH profiles clearly showing that both mono and di-base protonated nucleosides undergo hydrolysis. The 700 fold rate acceleration of 8-N(CH3)-guanosine compared to 8-NHCH3-guanosine and the 110 fold rate acceleration of 8-N(CH3)2-adenosine compared to 8-NHCH3-adenosine could be unequivocally attributed to the fixed syn glycosyl conformation of both 8-dimethylamino compounds and relief of steric compression upon hydrolysis in these molecules. The lack of anomerization of all substrates during the course of the reaction supports an A rather than a Schiff-base mechanism.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cadet J., Teoule R. Letter: Nucleic acid hydrolysis. I. Isomerization and anomerization of pyrimidic deoxyribonucleosides in an acidic medium. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Oct 2;96(20):6517–6519. doi: 10.1021/ja00827a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. R., Mehta P. J. Solvolysis of adenine nucleosides. I. Effects of sugars and adenine substituents on acid solvolyses. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Nov 29;94(24):8532–8541. doi: 10.1021/ja00779a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett E. R., Mehta P. J. Solvolysis of adenine nucleosides. II. Effects of sugars and adenine substituents on alkaline solvolyses. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Nov 29;94(24):8542–8547. doi: 10.1021/ja00779a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES R. E., ROBINS R. K. PURINE NUCLEOSIDES. IX. THE SYNTHESIS OF 9-BETA-D-RIBOFURANOSYL URIC ACID AND OTHER RELATED 8-SUBSTITUTED PURINE RIBONUCLEOSIDES. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Apr 20;87:1772–1776. doi: 10.1021/ja01086a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevesi L., Wolfson-Davidson E., Nagy J. B., Nagy O. B., Bruylants A. Contribution to the mechanism of the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of purine nucleosides. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 28;94(13):4715–4720. doi: 10.1021/ja00768a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara M., Muneyama K. Studies of nucleosides and nucleotides. 30. Syntheses of 8-substituted guanosine derivatives. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1966 Jan;14(1):46–49. doi: 10.1248/cpb.14.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara M., Uesugi S., Yoshida K. Studies on the conformation of purine nucleosides and their 5'-phosphates. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):830–836. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan F. Lennard-Jones potential calculations of the barrier to rotation around the glycosidic C-N linkage in selected purine nucleosides and nucleotides. A direct comparison of the results of 6-12 potential calculations with results of semiempirical molecular orbital studies. J Theor Biol. 1973 Sep 21;41(2):375–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan F. Purine carbon-8 substituent as probe of the electronic structures of adenine and guanine. A computational study. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Sep 4;96(18):5911–5917. doi: 10.1021/ja00825a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3610–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long R. A., Robins R. K., Townsend L. B. Purine nucleosides. XV. The synthesis of 8-aminoand 8-substituted aminopurine nucleosides. J Org Chem. 1967 Sep;32(9):2751–2756. doi: 10.1021/jo01284a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzica R. P., Rousseau R. J., Robins R. K., Townsend L. B. A study on the relative stability and a quantitative appraoch to the reaction mechanism of the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of certain7-and9- -D-ribofuranosylpurines. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 28;94(13):4708–4714. doi: 10.1021/ja00768a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins M. J., Khwaja T. A., Robins R. K. Purine nucleosides. XXIX. The synthesis of 2'-deoxy-L-adenosine and 2'-deoxy-L-guanosine and their alpha anomers. J Org Chem. 1970 Mar;35(3):636–639. doi: 10.1021/jo00828a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Danzig M. Acidic hydrolysis of deoxycytidine and deoxyuridine derivatives. The general mechanism of deoxyribonucleoside hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 4;11(1):23–29. doi: 10.1021/bi00751a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Kang S. Uncatalyzed hydrolysis of deoxyuridine, thymidine, and 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):1806–1810. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., von Philipsborn W. Protonierung von Purin, Adenin und Guanin. NMR Spektren und Strukturen der Mono-, Di- und Tri-Kationen. Helv Chim Acta. 1971;54(6):1543–1558. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19710540604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoltewicz J. A., Clark D. F. Kinetics and mechanism of the hydrolysis of guanosine and 7-methylguanosine nucleosides in perchloric acid. J Org Chem. 1972 Apr 21;37(8):1193–1197. doi: 10.1021/jo00973a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoltewicz J. A., Clark D. F., Sharpless T. W., Grahe G. Kinetics and mechanism of the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of some purine nucleosides. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Mar 25;92(6):1741–1749. doi: 10.1021/ja00709a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



