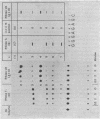
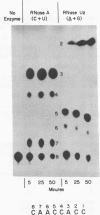
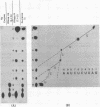
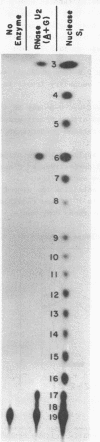
Abstract
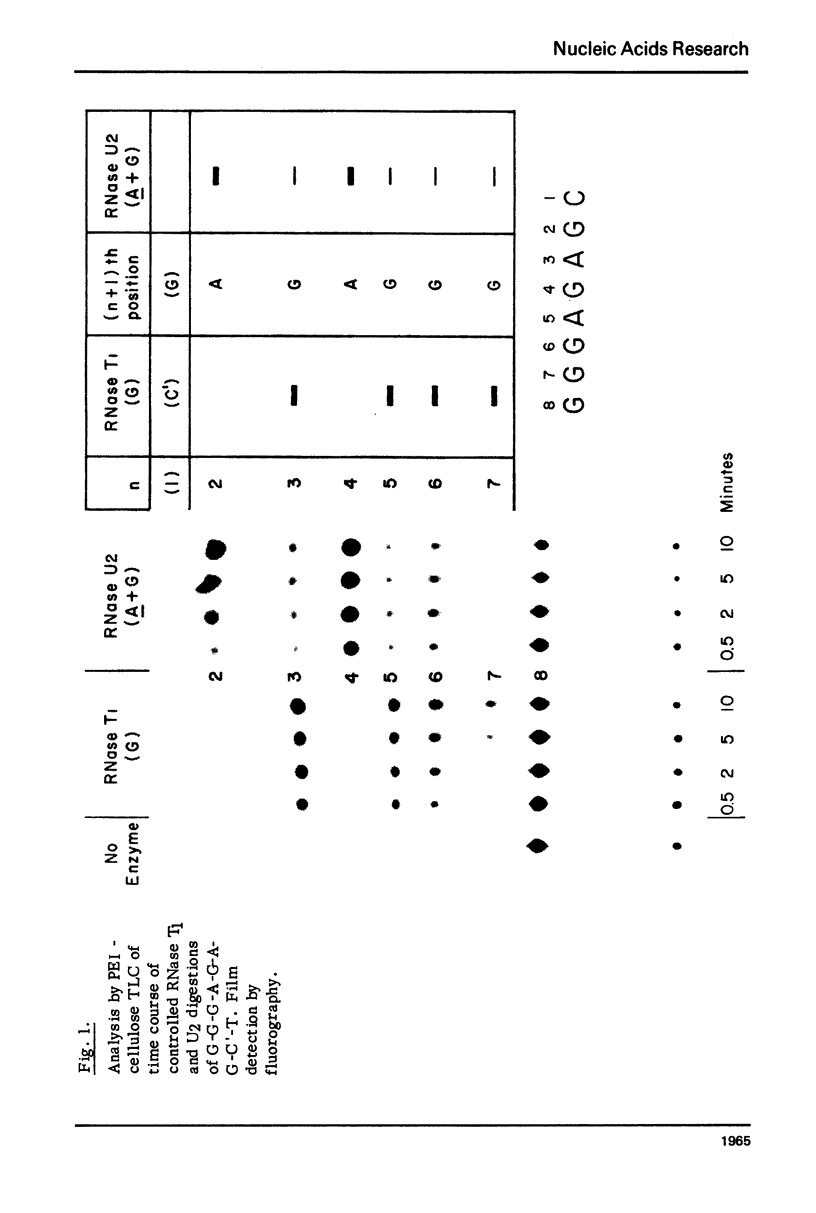
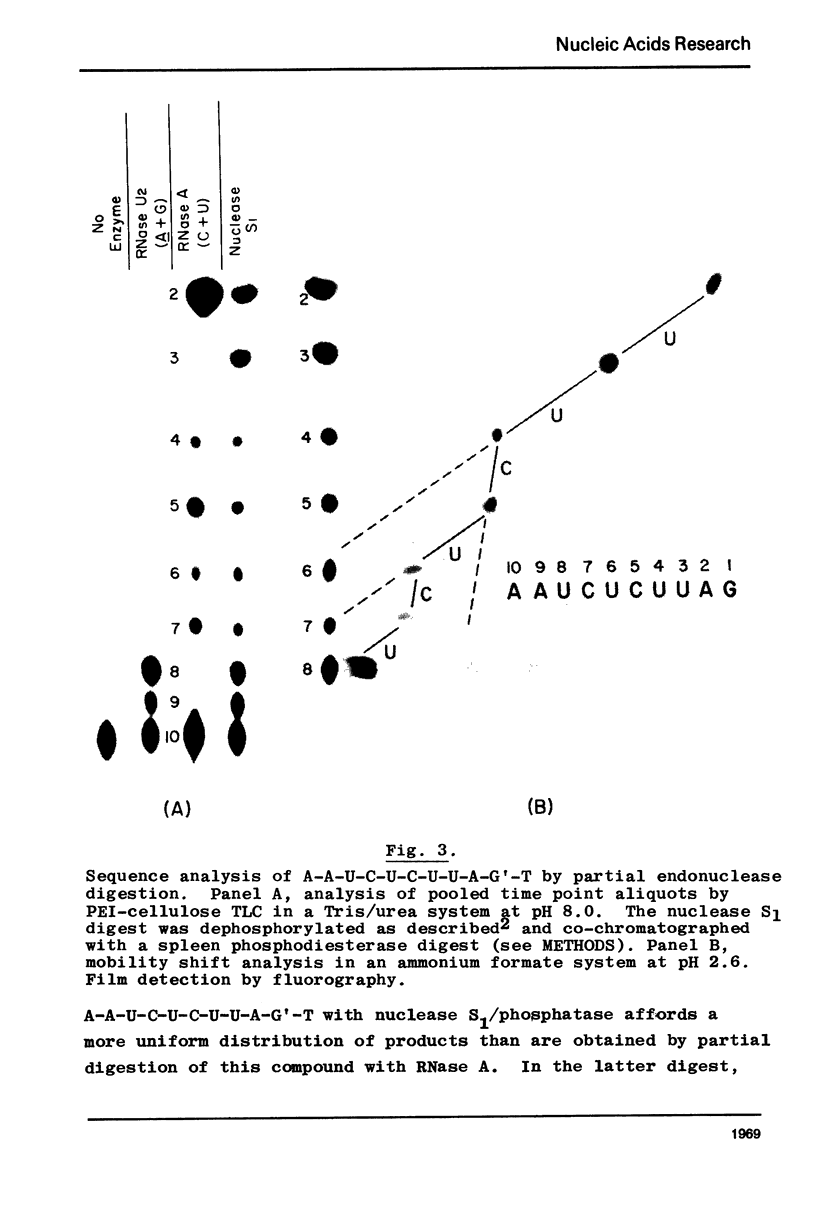
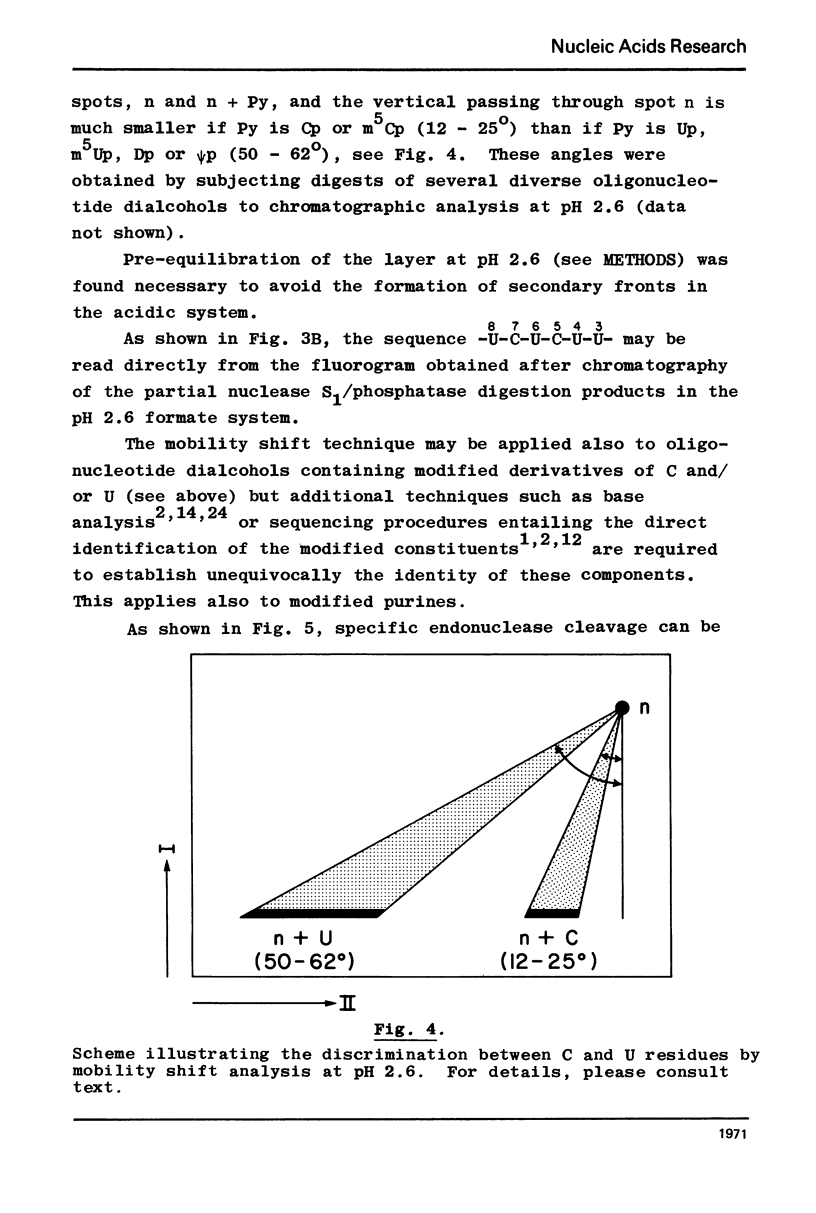
Nonradioactive RNA fragments may be sequenced by incorporation of (3H)-label into 3'-terminal positions, controlled digestion with specific ribonucleases, and separation according to size of the digestion products on polyethyleneimine- (PEI-) cellulose thin layers. This combination of techniques allows one to measure accurately distances of specific cleavage sites from the labeled terminal positions. The cleavage specificities of RNases T1, U2, and A are utilized to identify the positions of G, A, and pyrimidine residues respectively. C and U may be distinguished by mobility differences on PEI-cellulose thin layers at ph 2.6. The procedure is simple, rapid, and highly sensitive; as little as 0.5 - 1 microgram of a RNA of the size of tRNA will be needed to sequence all fragments in a complete RNase digest.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima T., Uchida T., Egami F. Studies on extracellular ribonucleases of Ustilago sphaerogena. Characterization of substrate specificity with special reference to purine-specific ribonucleases. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(3):609–613. doi: 10.1042/bj1060609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R., Behrens K. A ribonuclease from Physarum. Biochemical properties and synthesis in the mitotic cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 19;195(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90605-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne J. K., Paddock G. V., Liu A., Clarke P., Heindell H. C., Salser W. Nucleotide sequences from the rabbit beta globin gene inserted into Escherichia coli plasmids. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):389–391. doi: 10.1126/science.318762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Chromatography of 32P-labelled oligonucleotides on thin layers of DEAE-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. H., Brum C. K., Siberklang M., RajBhandary U. L., Hecker L. I., Barnett W. E. The first nucleotide sequence of an organelle transfer RNA: chloroplastic tRNAphe. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. H., Kuo S., Hawkins E., Miller N. R. The corrected nucleotide sequence of yeast leucine transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):951–955. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Fiers W. A method for the isolation of cytidylate series from ribonuclease T1-oligonucleotides. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doctor B. P., Loebel J. E., Sodd M. A., Winter D. B. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., Abelson J. N., Landy A., Zadrazil S., Smith J. D. The nucleotide sequences of tyrosine transfer RNAs of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Apr;13(3):461–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Randerath E., Randerath K. A double-labeling procedure for sequence analysis of picomole amounts of nonradioactive RNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):2895–2914. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. C., Randerath K., Randerath E. Sequence analysis of small amounts of nonradioactive oligoribonucleotides containing ribose-methylated nucleosides by a combination of 3H- and 32P-labeling techniques. Anal Biochem. 1976 Nov;76(50):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramaru M., Uchida T., Egami F. Studies on ribonucleases from Physarum polycephalum. Purification and characterization of substrate specificity. J Biochem. 1969 May;65(5):693–700. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski S., Yamane T., Fresco J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the "denaturable" leucine transfer RNA from yeast. Science. 1971 Apr 23;172(3981):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3981.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhard R. E., Rajbhandary U. L. Nucleotide sequences at the 5'termini of rabbit alpha and beta globin mRNA. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):747–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RajBhandary U. L., Chang S. H. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXXII. Yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid: partial digestion with ribonuclease T-1 and derivation of the total primary structure. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):598–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RajBhandary U. L., Faulkner R. D., Stuart A. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXIX. Yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid: products obtained by degradation with pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):575–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RajBhandary U. L. Studies on polynucleotides. LXXVII. The labeling of end groups in polynucleotide chains: the selective modification of diol end groups in ribonucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):556–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath E., Yu C. T., Randerath K. Base analysis of ribopolynucleotides by chemical tritium labeling: a methodological study with model nucleosides and purified tRNA species. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jul;48(1):172–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K. An evaluation of film detection methods for weak beta-emitters, particularly tritium. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:188–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Randerath E., Chia L. S., Gupta R. C., Sivarajan M. Sequence analysis of nonradioactive RNA fragments by periodate-phosphatase digestion and chemical tritium labeling: characterization of large oligonucleotides and oligonucleotides containing modified nucleosides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Sep;1(9):1121–1141. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.9.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Randerath E. Ion-exchange thin-layer chromatography. XV. Preparation, properties and applications of paper-like PEI-cellulose sheets. J Chromatogr. 1966 Apr;22(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)97076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmukler M., Jewett P. B., Levy C. C. The effects of polyamines on a residue-specific human plasma ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2206–2212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simsek M., Ziegenmeyer J., Heckman J., Rajbhandary U. L. Absence of the sequence G-T-psi-C-G(A)- in several eukaryotic cytoplasmic initiator transfer RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1041–1045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivarajan M., Gupta R. C., Chia L. L., Randerath E., Randerath K. Tritium sequence analysis of oligoribonucleotides: a combination of post-labeling and thin-layer chromatographic techniques for the analysis of partial snake venom phosphodiesterase digests. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Oct;1(10):1329–1341. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.10.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto K. S., Söll D. Fingerprinting nonradioactive ribonucleic acid with the aid of polynucleotide phosphorylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Jan;1(1):171–181. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Székely M., Sanger F. Use of polynucleotide kinase in fingerprinting non-radioactive nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 14;43(3):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMLINSON R. V., TENER G. M. THE EFFECT OF UREA, FORMAMIDE, AND GLYCOLS ON THE SECONDARY BINDING FORCES IN THE ION-EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY OF POLYNUCLEOTIDES OF DEAE-CELLULOSE. Biochemistry. 1963 Jul-Aug;2:697–702. doi: 10.1021/bi00904a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]