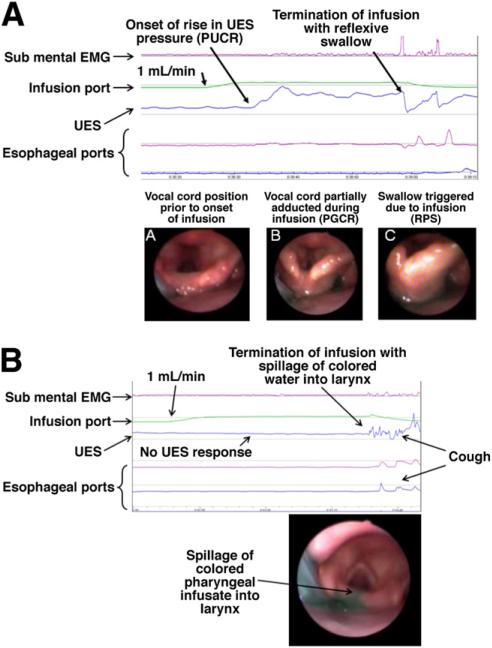
Figure 2.
(A) PUCR, PGCR, and RPS: infusion of water at 1 mL/min into the pharynx of a nonsmoker subject resulted in a more than 100% increase in UES pressure above the baseline (PUCR) after 5.4 seconds (0.1 mL) from the onset of infusion. This was not associated with any submental electromyographic changes. At 37.3 seconds after the onset of water infusion (0.6 mL) an irrepressible swallow was triggered (RPS). Infusion of water into the pharynx also resulted in adduction (incomplete closure) of vocal cords (PGCR). (a) Vocal cord position before pharyngeal infusion of water. (b) Adduction (incomplete closure) of vocal cords during the infusion (PGCR). This response was not associated with any submental electromyographic activity. (c) Onset of swallow. (B) Unlike the nonsmoker subject in A, infusion of water at 1 mL/min into the pharynx of a smoker subject did not induce any UES pressure changes (no PUCR) and did not induce RPS. At 30.6 seconds after onset of pharyngeal infusion, video endoscopic views of the larynx showed colored water rising up to the superior margin of the interarytenoid fold with spillage into the larynx. This resulted in a cough response. EMG, electromyography.