Abstract
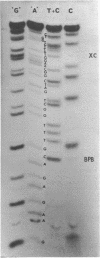
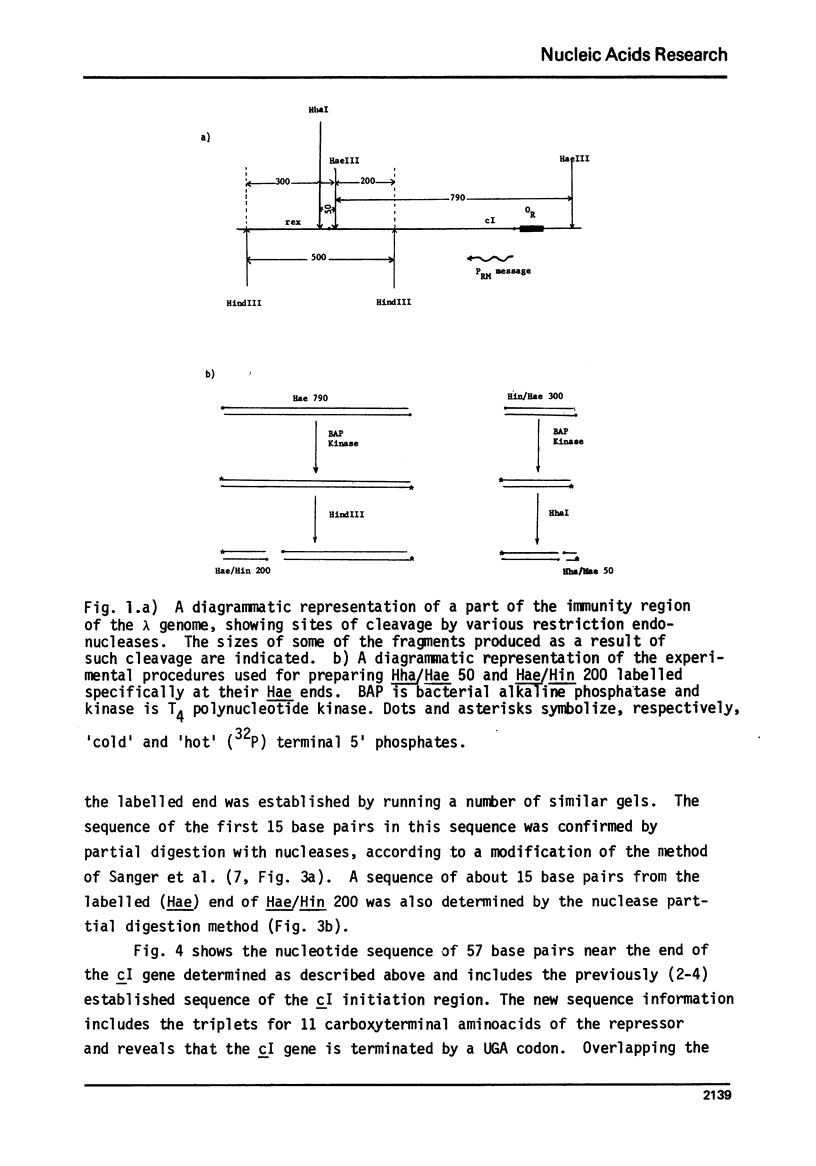
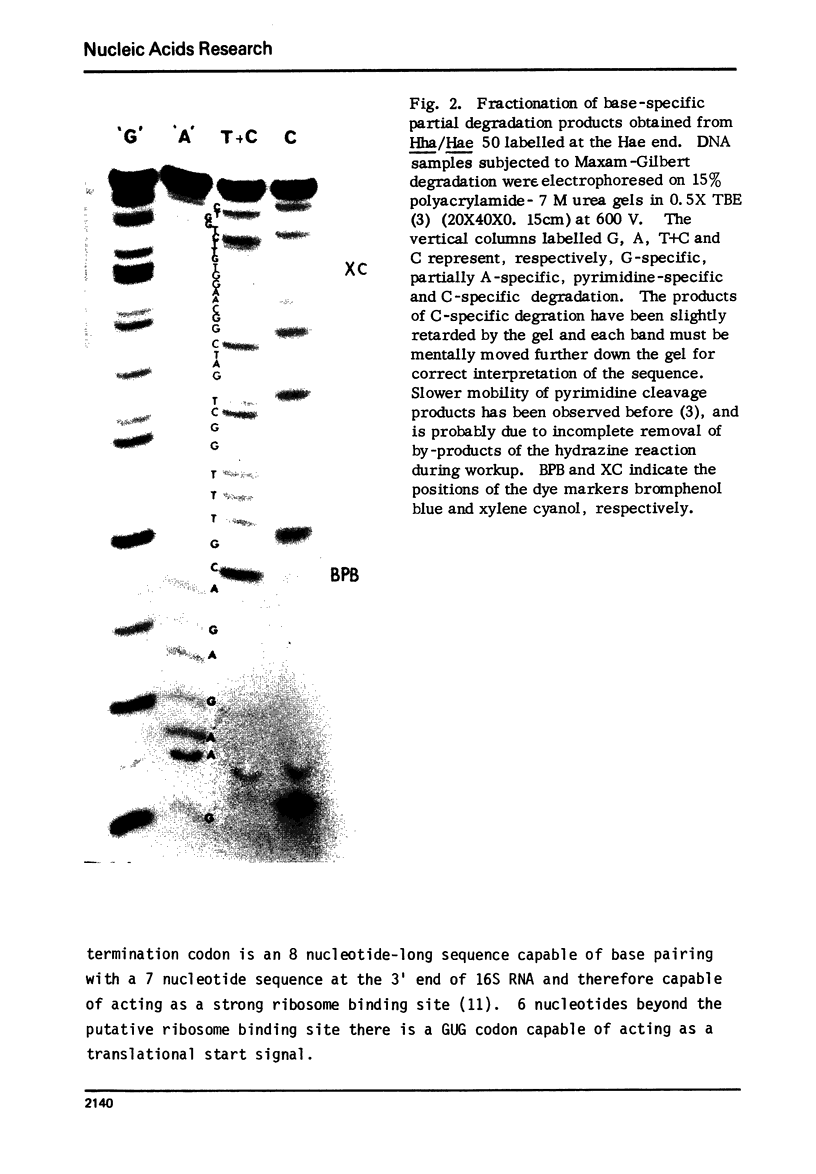
The nucleotide sequence of 57 base pairs near the end of the cI gene in phage lambda is presented. This sequence was determined by direct sequencing techniques and includes the codons for 11 carboxyterminal aminoacids of the cI product, the lambda repressor. The sequence reveals that the cI gene, which has recently been shown to have a unique initiation region, is terminated by a UGA codon. A GUG triplet, which could act as a translation start signal for the rex gene occurs 8 base pairs beyond the cI termination codon. This GUG triplet is preceded by a sequence that could serve as a strong ribosome binding site for the rex message.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jay E., Bambara R., Padmanabhan R., Wu R. DNA sequence analysis: a general, simple and rapid method for sequencing large oligodeoxyribonucleotide fragments by mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):331–353. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton J. H., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Specific fragments of phi X174 deoxyribonucleic acid produced by a restriction enzyme from Haemophilus aegyptius, endonuclease Z. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.42-50.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old R., Murray K., Boizes G. Recognition sequence of restriction endonuclease III from Hemophilus influenzae. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):331–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Donelson J. E., Coulson A. R., Kössel H., Fischer D. Use of DNA polymerase I primed by a synthetic oligonucleotide to determine a nucleotide sequence in phage fl DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1209–1213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Wilcox K. W. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. I. Purification and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Pirrotta V., Ineichen K. Lambda repressor regulates the switch between PR and Prm promoters. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):665–669. doi: 10.1038/262665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gussin G. N. Genetic characterization of a prm- mutant of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):300–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]