Abstract
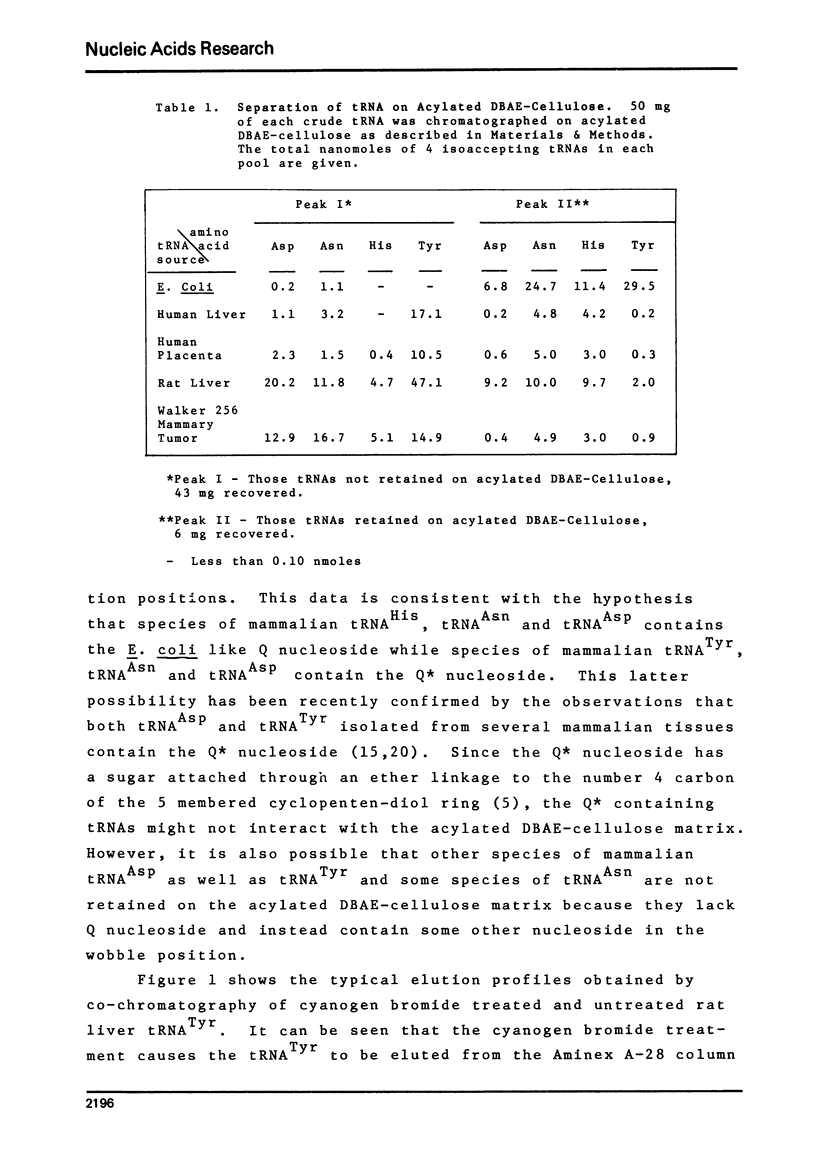
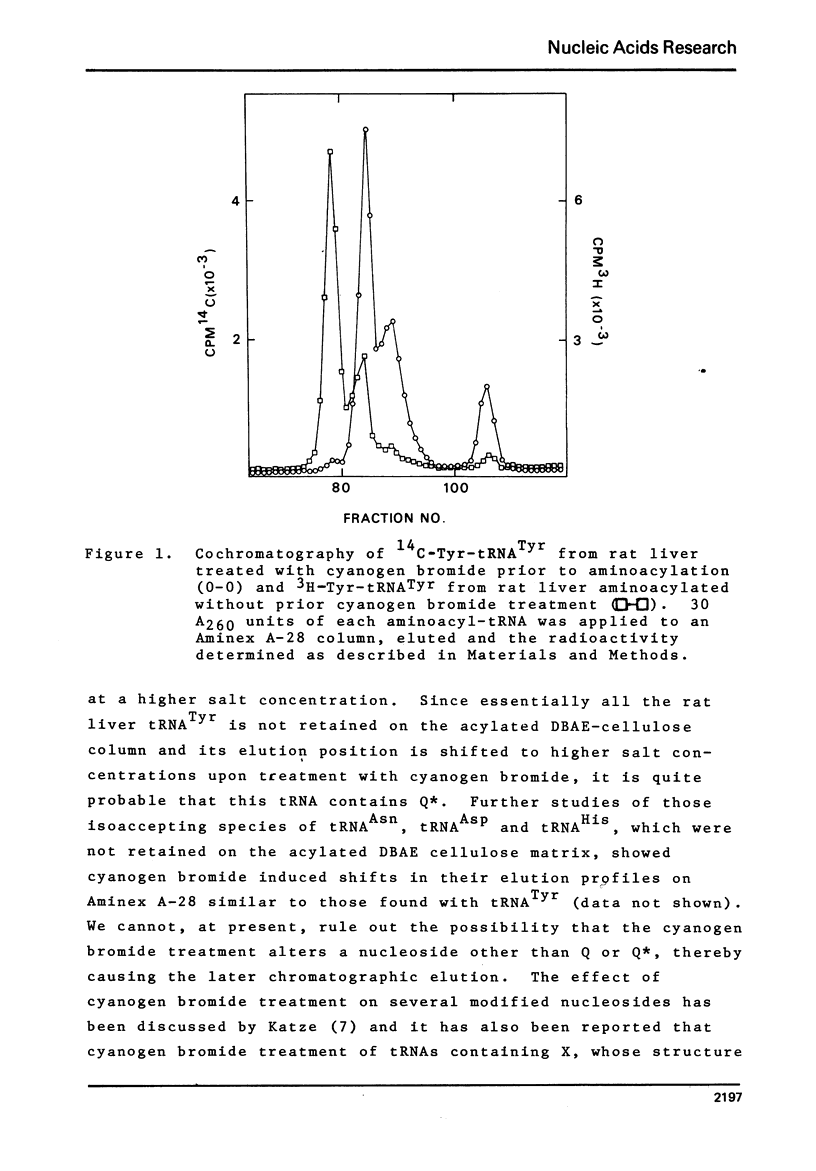
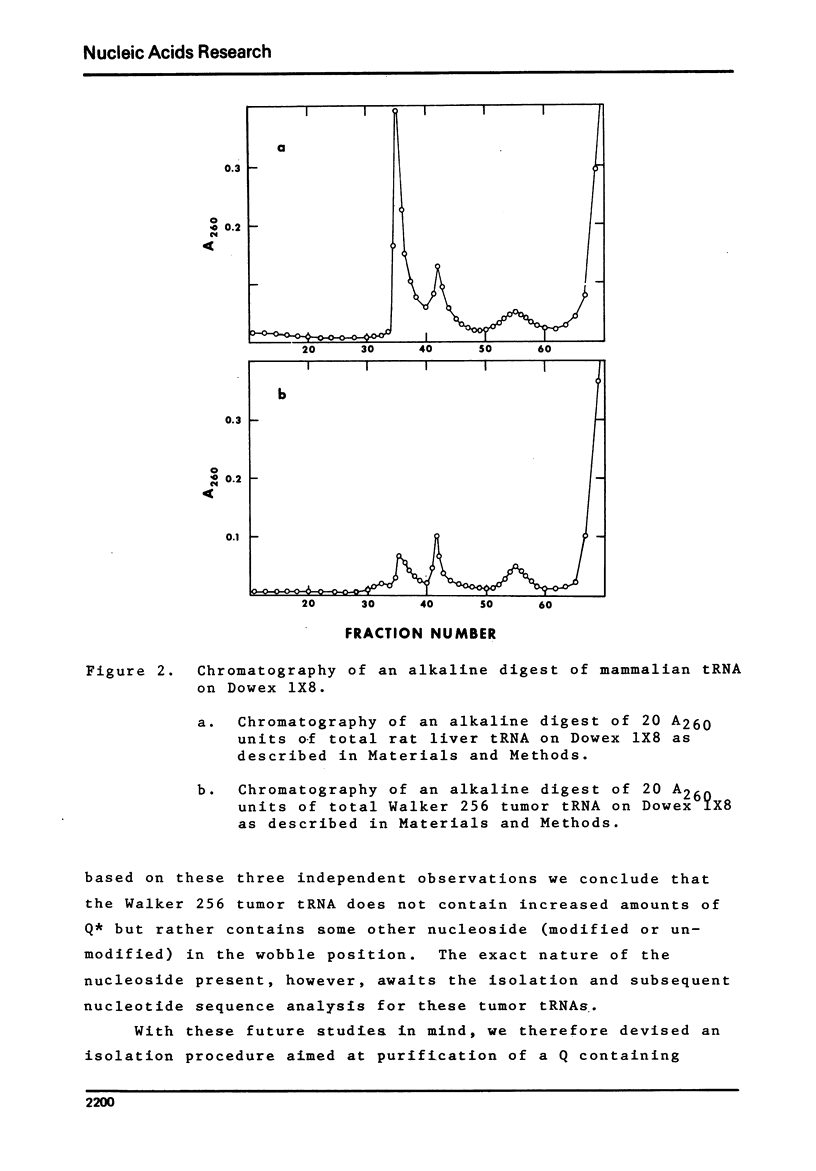
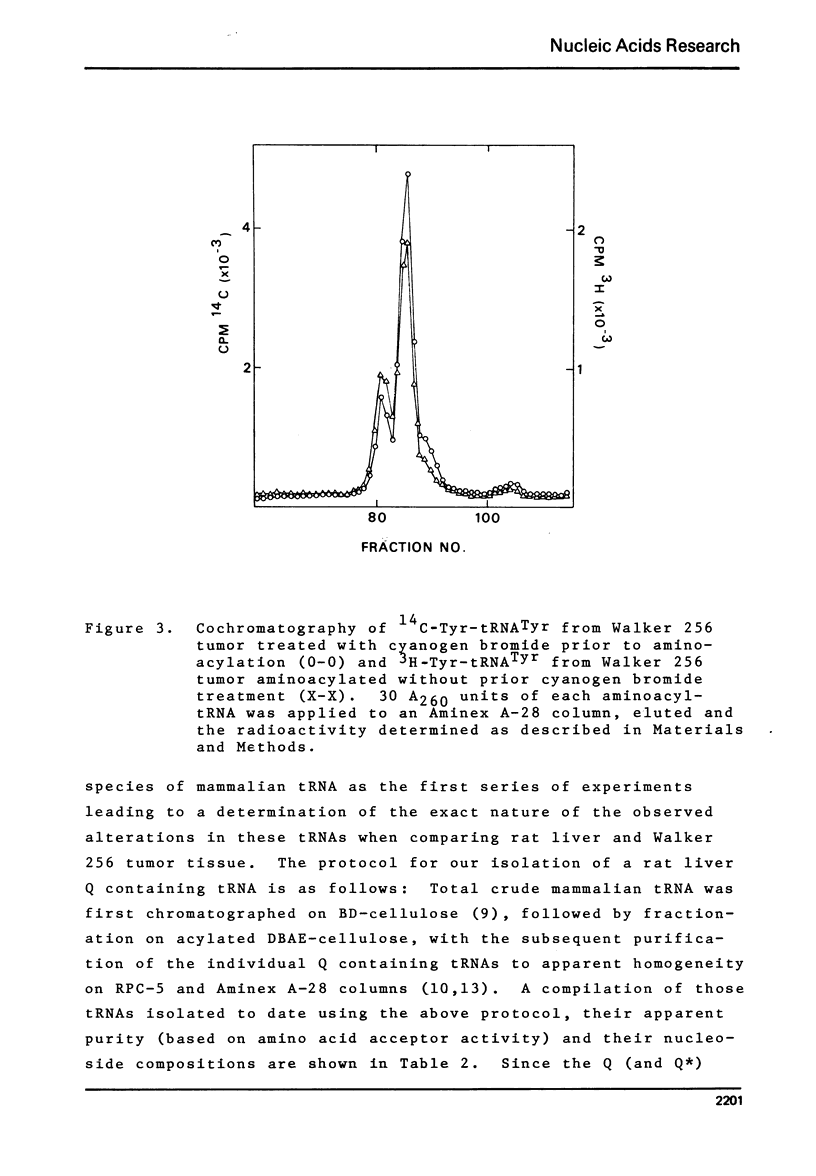
Studies of the chromatographic behavior of mammalian tRNAs, from several sources, on acylated DBAE-cellulose indicate that species of tRNA Asn , tRNA Asp and tRNA His can be retained on this matrix, while species of tRNA Tyr, tRNA Asn and tRNA Asp are not retained. Treatment of total rat liver tRNA with cyanogen bromide and subsequent chromatography on Aminex A-28 columns demonstrated that these tRNA species might contain Q (or Q*) nucleoside. However, comparable studies of the tRNA isolated from Walker 256 rat mammary tumor tissue demonstrated that this tumor tRNA almost totally lacks the hypermodified nucleosides Q and Q*. In addition, we have found that at least the major species of rat liver tRNA Asn contains the Q nucleoside. These studies indicate that chromatography on the acylated DBAE-cellulose matrix, couple with the analytical ion-exchange chromatography of cyanogen bromide treated and untreated amino-acyl-tRNA can be a valuable technique for the determination of alterations in the Q (or Q*) nucleoside content of the tRNAs isolated from normal and tumor tissues.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amandaraj M. P., Roe B. A. Purification of human placenta phenylalanine, valine, methionine, glucine, and serine transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5068–5073. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe W. T., Griffin A. C., McBride C., Bowen J. M. The distribution and properties of aspartyl transfer RNA in human and animal tumors. Cancer Res. 1975 Sep;35(9):2586–2593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinault A. C., Tan K. H., Hassur S. M., Hecht S. M. Initial position of aminoacylation of individual Escherichia coli, yeast, and calf liver transfer RNAs. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):766–776. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S., Li H. J., Nakanishi K., Van Lear G. 3-(3-amino-3-carboxy-n-propyl)uridine. The structure of the nucleoside in Escherichia coli transfer ribonucleic acid that reacts with phenoxyacetoxysuccinimide. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2932–2937. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Roe B. A., Anandaraj M. P., RajBhandary U. L. Nucleotide sequence of human placenta cytoplasmic initiator tRNA. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Kuchino Y., Nihei K., Nishimura S. Distribution of the modified nucleoside Q and its derivatives in animal and plant transfer RNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1931–1939. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Nakanishi K., Macfarlane R. D., Torgerson D. F., Ohashi Z., McCloskey J. A., Gross H. J., Nishimura S. Letter: The structure of Q* nucleoside isolated from rabbit liver transfer ribonucleic acid. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Aug 4;98(16):5044–5046. doi: 10.1021/ja00432a071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Oashi Z., Harada F., Nishimura S., Oppenheimer N. J., Crain P. F., Liehr J. G., von Minden D. L., McCloskey J. A. Structure of the modified nucleoside Q isolated from Escherichia coli transfer ribonucleic acid. 7-(4,5-cis-Dihydroxy-1-cyclopenten-3-ylaminomethyl)-7-deazaguanosine. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4198–4208. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze J. R. Alterations in SVT2 cell transfer RNAs in response to cell density and serum type. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 10;383(2):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90254-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Mignery R., Reszelbach R., Roe B., Sirover M., Dudock B. The absence of ribothymidine in specific eukaryotic transfer RNAs. I. Glycine and threonine tRNAs of wheat embryo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Gilham P. T., Söll D. An improved method for the purification of tRNA by chromatography on dihydroxyboryl substituted cellulose. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jun;2(6):853–864. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Harada F., Nishimura S. Specific replacement of Q base in the anticodon of tRNA by guanine catalyzed by a cell-free extract of rabbit reticulocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2593–2603. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Shindo-Okada N., Nishimura S. Isolation of mammalian tRNAAsp and tRNATyr by lectin-Sepharose affinity column chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Feb;4(2):415–423. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Randerath E., Chia L. S., Nowak B. J. Base analysis of ribopolynucleotides by chemical tritium labeling: an improved mapping procedure for nucleoside trialcohols. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B. A., Anandaraj M. P., Chia L. S., Randerath E., Gupta R. C., Randerath K. Sequence studies on tRNAPhe from placenta: comparison with known sequences of tRNAPhe from other normal mammalian tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B. A. Studies on human tRNA. I. The rapid, large scale isolation and partial fractionation of placenta and liver tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jan;2(1):21–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B., Marcu K., Dudock B. The isolation and sequence analysis of transfer RNA: the use of plaskon chromatography (RPC-5). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 10;319(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saneyoshi M., Nishimura S. Selective inactivation of amino acid acceptor and ribosome-binding activities of Escherichia coli tRNA by modification with cyanogen bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 12;246(1):123–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. N. Chromatographic changes in specific tRNAs after reaction with cyanogen bromide and sodium periodate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 11;353(3):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. N., Tener G. M. Activity of a transfer RNA modifying enzyme during the development of Drosophila and its relationship to the su(s) locus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):635–651. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


