Abstract
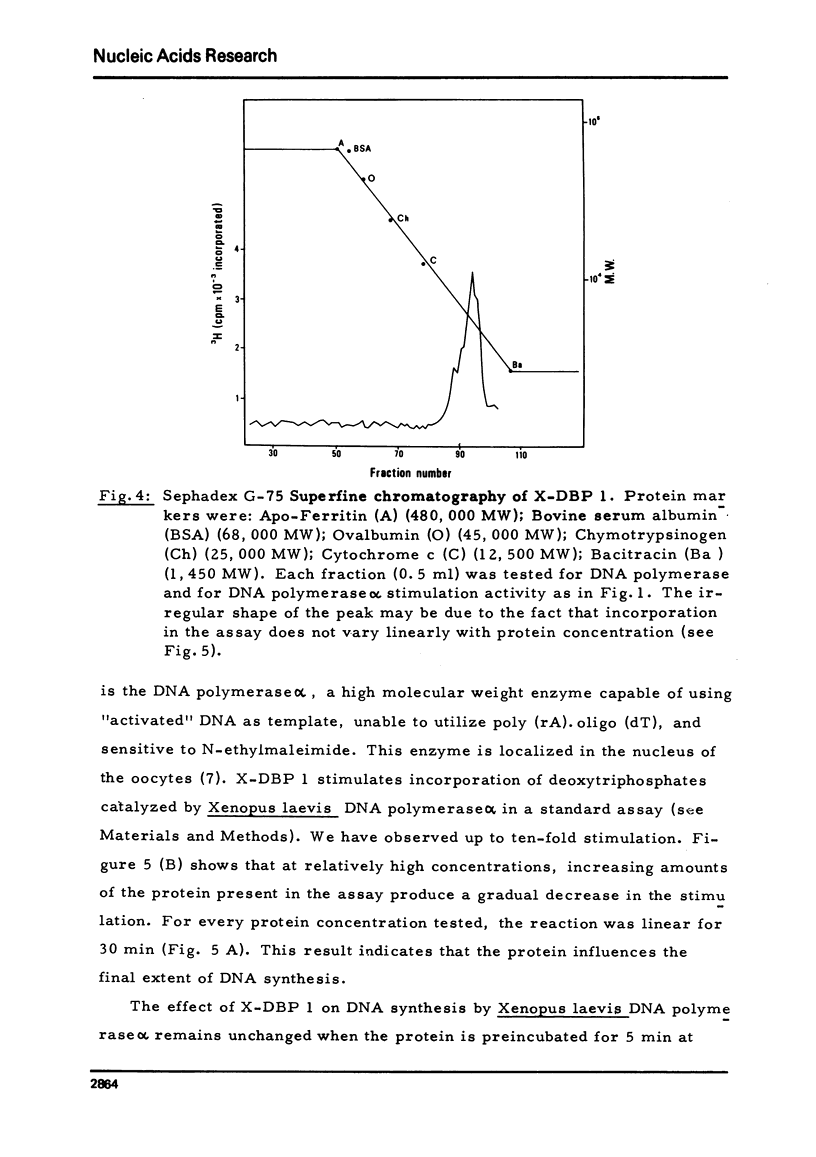
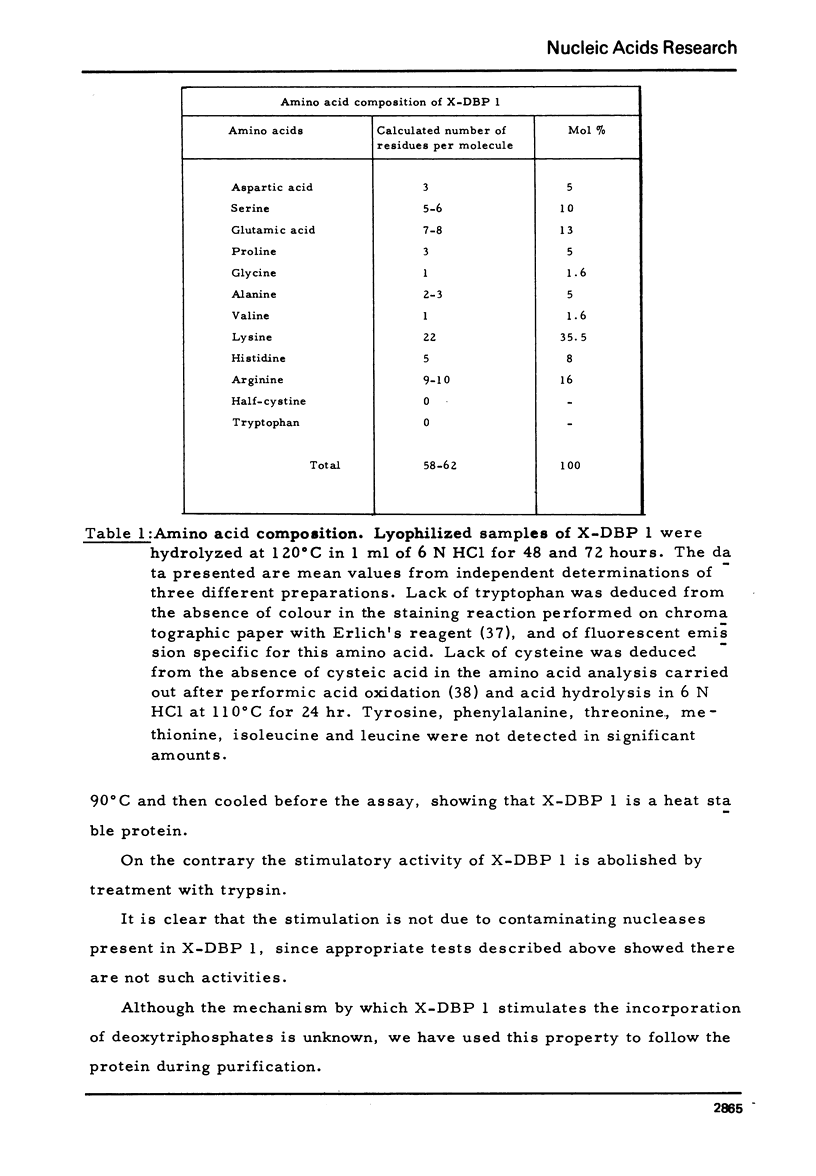
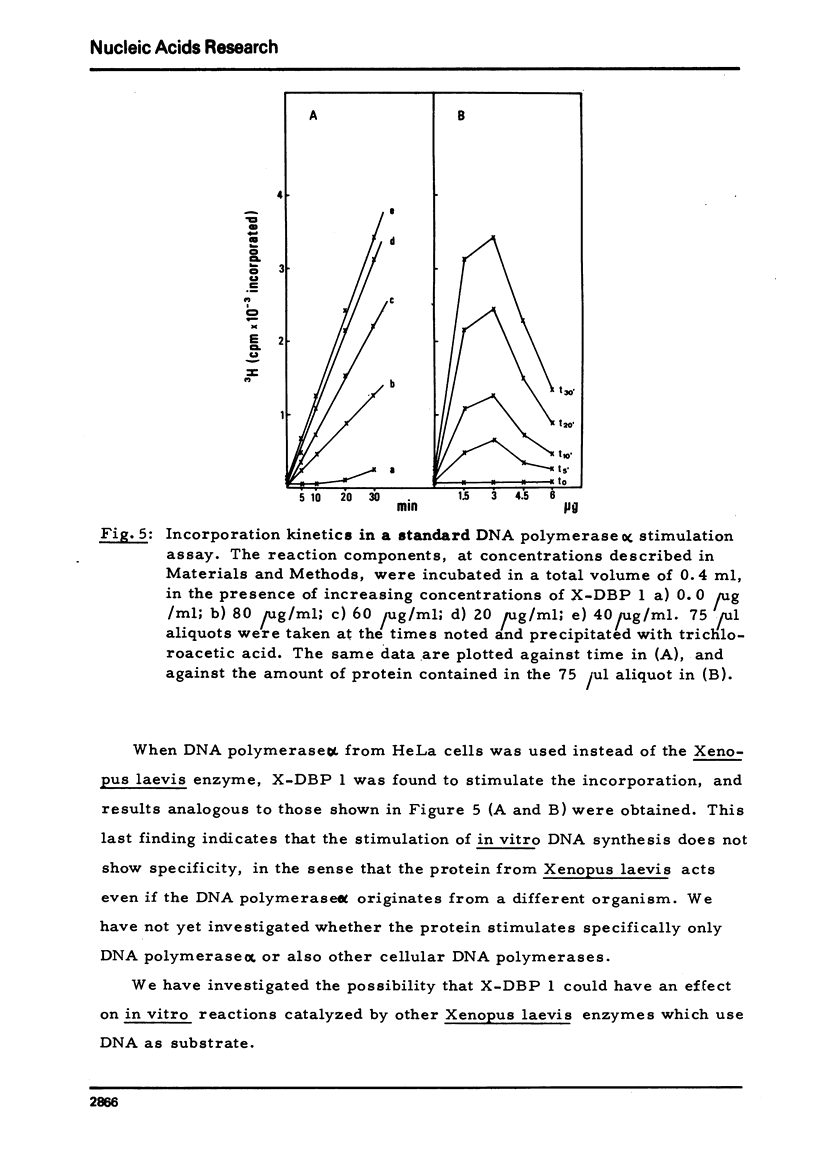
A DNA-binding protein from Xenopus laevis unfertilized eggs has been purified to apparent homogeneity. It is a heat stable, lysine-rich protein and has a molecular weight corresponding to 8,200 daltons, measured by sodium dodecyl sulphate gel electrophoresis. The protein, which is active in a monomeric form, stimulates DNA polymerase alpha, and binds to single and double stranded DNA. One egg contains about 4 x 10(12) molecules (minimum estimate) of the protein; since we calculate that 4 x 10(8) molecules are sufficient to cover the entire genome (haploid complement), there is much more protein than is needed to cover chromosomal DNA.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D., Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis in early amphibian development: histone and DNA syntheses are not co-ordinated. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):263–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts B., Frey L., Delius H. Isolation and characterization of gene 5 protein of filamentous bacterial viruses. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldi M. I., Bazzicalupo P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Particulate DNA polymerase from the cytoplasm of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):985–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks G. R., Spanos A. The isolation and properties of a DNA-unwinding protein from Ustilago maydis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 25;93(1):63–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Dawid I. B. Specific gene amplification in oocytes. Oocyte nuclei contain extrachromosomal replicas of the genes for ribosomal RNA. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):272–280. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G. Replication of DNA in eukaryotic chromosomes. Br Med Bull. 1973 Sep;29(3):192–195. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B. Deoxyribonucleic acid in amphibian eggs. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):581–599. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandini Attardi D., Martini G., Mattoccia E., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Effect of Xenopus laevis oocyte extract on supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA: formation of complex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., O'Farrell P. Z., Russel M. Regulation of gene 32 expression during bacteriophage T4 infection of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7251–7262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Speight V. A. The appearance of cytoplasmic DNA polymerase activity during the maturation of amphibian oocytes into eggs. Exp Cell Res. 1969 May;55(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90488-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G., Alberts B. Nucleic acid helix-coil transitions mediated by helix-unwinding proteins from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick G., Delius H., Alberts B. Single-stranded DNA structure and DNA polymerase activity in the presence of nucleic acid helix-unwinding proteins from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2142–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Stern H. A DNA-binding protein in meiotic cells of Lilium. Dev Biol. 1971 Sep;26(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H. Histone messengers and histone genes. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Characterization of purified DNA-relaxing enzyme from human tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2550–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman R. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus) isolated on deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6222–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G., Tato F., Gandini Attardi D., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Nuclear localization of DNA polymerase alpha in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):875–879. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoccia E., Attardi D. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. DNA-relaxing activity and endonuclease activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4551–4554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oey J. L., Knippers R. Properties of the isolated gene 5 protein of bacteriophage fd. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkowska E., Macgregor H. C., Birnstiel M. L. Gene amplification in the oocyte nucleus of mutant and wild-type Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):649–650. doi: 10.1038/217649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben R. C., Gefter M. L. A DNA-binding protein induced by bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1846–1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben R. C., Gefter M. L. A deoxyribonucleic acid-binding protein induced by bacteriophage T7. Purification and properties of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3843–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherzinger E., Litfin F., Jost E. Stimulation of T7 DNA polymerase by a new phage-coded protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Jul 2;123(3):247–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00271243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N., Delius H., Kornberg T., Gefter M. L., Alberts B. A DNA-unwinding protein isolated from Escherichia coli: its interaction with DNA and with DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Weissbach A. HeLa cell R-deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. Separation and characterization of two enzymatic activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5809–5815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatò F., Gandini D. A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Major DNA polymerases common to different Xenopus laevis cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3706–3710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A. Vertebrate DNA polymerases. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]