Abstract
The zinc-responsive Zap1 transcription factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae controls many genes involved in zinc homeostasis. Zap1 has two activation domains, AD1 and AD2, which are independently regulated by zinc. While AD1 can fully activate most Zap1 target genes, AD2 is active only on a subset of those genes. One hypothesis explaining this promoter specificity was that AD1 and AD2 recruit different coactivators. To address this question, we carried out a genetic screen to identify coactivator complexes that are required for Zap1-mediated activation. SWI/SNF, SAGA, and Mediator complexes were implicated as playing major roles in Zap1 activation. Consistent with this conclusion, we found that these three complexes are recruited to Zap1 target promoters in a zinc-responsive and Zap1-dependent manner. Coactivator recruitment was highly interdependent such that mutations disrupting SAGA impaired recruitment of SWI/SNF and vice versa. Optimal Mediator recruitment was dependent on both SAGA and SWI/SNF. A comparison of the coactivators recruited by AD1 and AD2 found no obvious differences suggesting that recruitment of different coactivators is not likely the mechanism of AD specificity. Rather, our results suggest that AD2 recruits coactivators less effectively than AD1 and is therefore only functional on some promoters.
Keywords: Coactivators, homeostasis, regulation, yeast, Zap1 transcription, zinc
Introduction
Eukaryotic transcriptional activators function by recruiting proteins and protein complexes, termed “coactivators”, to target promoters. These coactivators facilitate transcription initiation through a variety of mechanisms. Some coactivators, such as the SWI/SNF, ISW1, and RSC complexes, have ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling activity and aid transcriptional activation by clearing promoter regions of inhibitory nucleosomes (Martens and Winston, 2003). Other coactivators, such as the SAGA, ADA, and NuA4 complexes, have acetyl transferase (HAT) activity and modify histones in nucleosomes to diminish their DNA packaging capacity (Sterner and Berger, 2000). Other coactivator complexes serve as bridging adaptors between activator proteins and RNA polymerase II. The Mediator and TFIID complexes are well-known examples of this type of coactivator (Biddick and Young, 2005; Bhaumik, 2011). Transcriptional activation often requires a combination of these factors to be recruited to a promoter (Biddick and Young, 2009).
In this report, we characterize the coactivator requirements of the zinc-responsive Zap1 transcription factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Zap1 is the central player in yeast zinc homeostasis because it activates expression of as many as 80 genes in zinc-limited cells (Eide, 2009). Genes induced by Zap1 encode proteins such as the plasma membrane zinc transporters Zrt1, Zrt2, and Fet4, the vacuolar zinc transporters Zrt3 and Zrc1, and other proteins important to adapting to zinc deficiency conditions (Lyons et al., 2000; Wu et al., 2008). Zap1 binds to one or more 11 bp zinc-responsive elements (ZRE) in the promoters of its target genes. The consensus sequence for the ZRE is 5′-ACCTTNAAGGT-3′.
Zinc regulates Zap1 activity through at least four mechanisms. First, Zap1 regulates its own transcription by positive transcriptional autoregulation (Zhao and Eide, 1997). Zinc-limited cells increase the level of Zap1 and this increase may facilitate activation of target genes with weaker ZREs (Wu et al., 2008). The Zap1 DNA-binding domain contains five C2H2 zinc fingers (Znf3-7), each of which is required for DNA-binding activity (Fig. 1A) (Evans-Galea et al., 2003). The interaction of this domain with ZREs in vivo is regulated by zinc status such that binding is reduced in zinc-replete cells (Frey et al., 2011). Although the mechanism of this regulation is not yet known, it does not appear to involve the direct binding of zinc to the DNA binding domain to disrupt Zap1 binding.
Figure 1.
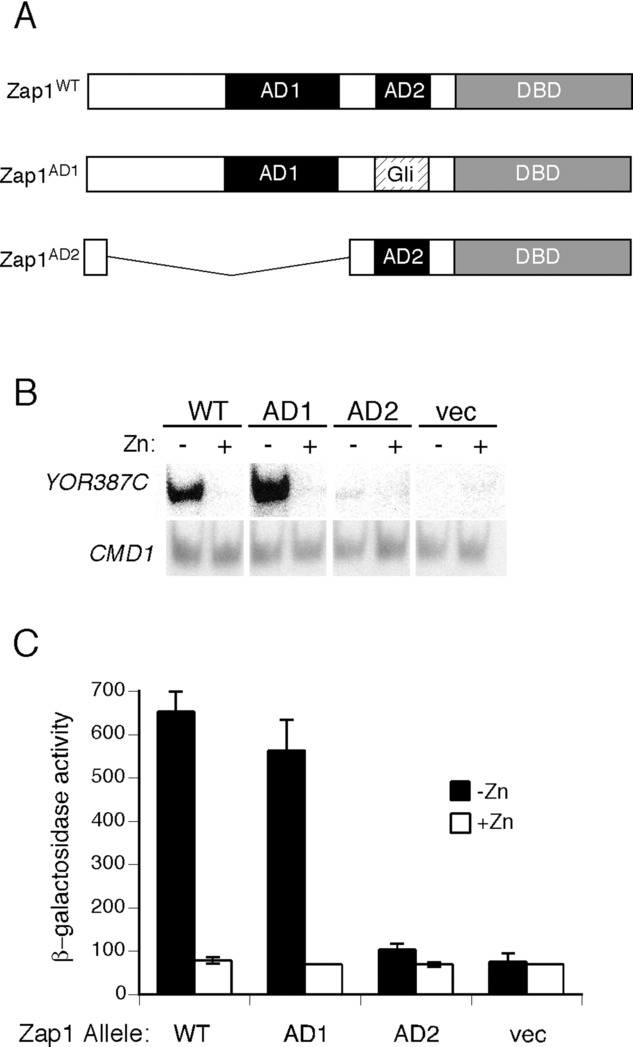
YOR387C induction by Zap1 is AD1 specific. (A) Zap1 alleles used in this study. (B) zap1Δ cells expressing either Zap1WT, Zap1AD1, Zap1AD2, or the empty vector were grown to mid-log phase in LZM supplemented with either 1 μM (−) or 1000 μM (+) ZnCl2. Total RNA was then isolated and YOR387C mRNA levels were measured by S1 nuclease protection assays. Expression of CMD1, which encodes calmodulin, was used as a loading control. (C) Cells as described in panel B bearing the YOR387C-lacZ reporter were grown to mid-log phase in LZM supplemented with either 1 μM (filled columns) or 1000 μM (open columns) ZnCl2. Cells were then harvested, and β-galactosidase assays were performed. The values shown are the means of three independent cultures and the error bars represent ±1 SD.
Zap1 also contains two activation domains whose functions are regulated by zinc. Activation domain 1 (AD1) was mapped to residues 207–402 (Fig. 1A) (Frey and Eide, 2011). This region is found within a larger zinc-responsive domain, ZRDAD1, which spans residues 182–502 (Herbig et al., 2005). Current evidence suggests that zinc binding to ZRDAD1 causes a conformational change in the protein that masks the ability of AD1 to activate transcription. A similar mechanism controls activation domain 2 (AD2). AD2 maps to residues 611–640 and is found within a second zinc-responsive domain (ZRDAD2) defined by two zinc fingers, Znf1 and Znf2 (Bird et al., 2003; Wang et al., 2006). Zinc binding to those zinc fingers represses AD2 function. We have previously proposed that zinc binding to ZRDAD1 and the zinc fingers of ZRDAD2 inhibits coactivator recruitment by AD1 and AD2 (Bird et al., 2003; Herbig et al., 2005).
A remarkable feature of Zap1's two activation domains is that they are regulated by zinc independently of each other. Moreover, both domains are evolutionarily conserved in Zap1 orthologs from widely divergent fungal species. These observations suggested that the two Zap1 activation domains play distinct roles in zinc-limited cells. We recently addressed those functions by examining Zap1 target gene expression in cells expressing wild-type Zap1 or Zap1 alleles with only AD1 or AD2 (Frey and Eide, 2011). Our results indicated that AD1 plays the primary role on all Zap1-regulated promoters. With respect to AD2 function, Zap1 target genes fall into two general classes, those genes that are efficiently activated by AD2 and those on which AD2 is inactive. To explain these results, one hypothesis we proposed was that AD1 and AD2 recruit different coactivators and thus their ability to activate a given promoter depends on the contribution that their respective coactivators can make to target gene induction. To test this model and better understand how Zap1 activates transcription in response to low zinc, we conducted a genetic screen to identify coactivators recruited by AD1 that are required for Zap1 activity. The results indicated that Zap1 recruits SWI/SNF, SAGA, and Mediator to its target promoters and that this recruitment is Zap1 dependent and zinc responsive. Both AD1 and AD2 showed similar coactivator requirements suggesting that these domains do not recruit different coactivators. Rather, our results indicate that AD2 is a weaker domain than AD1 and this may explain why it is less able to activate some promoters.
Results
A genetic screen to identify coactivator complexes required for Zap1 AD1 function
To characterize the coactivator requirements of Zap1, we focused initially on identifying those coactivator proteins and complexes specifically required for AD1 function. This approach was feasible because some genes are completely dependent on AD1 and AD2 does not contribute to their induction in low zinc. Our previous studies suggested that YOR387C is one such gene (Frey and Eide, 2011). The product of YOR387C is a cell wall protein of unknown function, but this gene is a highly induced Zap1 target.
The Zap1 alleles used to assess the AD specificity of YOR387C activation are depicted in Figure 1A. Each allele has six amino-terminal myc epitope tags and was expressed from a plasmid vector at a low constitutive level similar to that of chromosomally expressed Zap1 (Frey and Eide, 2011). The first allele, designated “Zap1WT”, contained full-length Zap1. In the second allele, referred to as “Zap1AD1”, the Znf1 and Znf2 zinc fingers of Zap1 (residues 581–641) were deleted and replaced with Znf1 and Znf2 from the human Gli protein. The Gli Znf1/Znf2 domain lacks any detectable activation domain function (Frey and Eide, 2011). Thus, this substitution removes all AD2 function by replacing that region with a structurally similar but transcriptionally inactive domain. The third allele was “Zap1AD2” in which amino acids 6–551 were deleted. Because the structure of AD1 is unknown, we knew of no structural ortholog of this domain and were unable to generate an allele analogous to the Gli substitution in Zap1AD1. Nonetheless, given the extent of the deletion, Zap1AD2 lacks all AD1 function.
A zap1Δ mutant expressing Zap1AD1 was capable of fully inducing chromosomal YOR387C mRNA expression in a low zinc culture medium while Zap1AD2 was unable to activate transcription of this gene (Fig. 1B). When the YOR387C promoter was fused to the lacZ reporter gene and assayed for expression using β-galactosidase activity assays, the plasmid-born YOR387C-lacZ reporter was regulated in the same manner as the chromosomal promoter (Fig. 1C).
Because the YOR387C-lacZ fusion showed the same specificity for AD1 function as the chromosomal gene, we used this reporter to test a large number of mutants disrupted for different coactivator subunits for their ability to drive its expression. Fifty-eight different coactivator mutant strains from the yeast deletion collection were transformed with the YOR387C-lacZ reporter, grown in low zinc, and then assayed for β-galactosidase activity (Table 1). Activities measured ranged from 6–181% of the activity observed in the isogenic wild-type strain. Several mutants showed decreased YOR387C-lacZ expression relative to the wild-type strain suggesting that the affected coactivators may be required for Zap1 function.
Table 1.
Effects of coactivator mutations on YOR387C-lacZ expression
| Strain | Coactivator complex | Percentage of WT expression1 |
|---|---|---|
| Wild-type (BY4743) | - | 100 |
| zap1Δ | - | 14 |
| ahc1Δ | ADA | 106 |
| ada2Δ | ADA, SAGA | 17 |
| ada3Δ | ADA, SAGA | 36 |
| ada1Δ | SAGA | NA2 |
| ada5Δ | SAGA | NA2 |
| spt3Δ | SAGA | 14 |
| spt7Δ | SAGA | 135 |
| spt8Δ | SAGA | 102 |
| chd1Δ | SAGA | 86 |
| yer049wΔ | NuA3 | 95 |
| sas3Δ | NuA3 | 113 |
| eaf3Δ | NuA4 | 149 |
| bdf1Δ | TFIID | 53 |
| bdf2Δ | TFIID | 95 |
| elp3Δ | HAT | 89 |
| ayt1Δ | HAT | 66 |
| hpa2Δ | HAT | 95 |
| hpa3Δ | HAT | 100 |
| sas2Δ | HAT | 111 |
| taf14Δ | TFIID, SWI/SNF, NuA3 | 102 |
| snf2Δ | SWI/SNF | 115 |
| swi3Δ | SWI/SNF | 21 |
| snf5Δ | SWI/SNF | 85 |
| snf6Δ | SWI/SNF | 24 |
| snf11Δ | SWI/SNF | 105 |
| rsc1Δ | RSC | 98 |
| rsc2Δ | RSC | 41 |
| isw1Δ | ISW1 | 92 |
| isw2Δ | ISW2 | 103 |
| itc1Δ | ISW2 | 89 |
| not3Δ | CCR4-NOT | 181 |
| not4Δ | CCR4-NOT | 115 |
| not5Δ | CCR4-NOT | 11 |
| caf1Δ | CCR4-NOT | 172 |
| caf4Δ | CCR4-NOT | 135 |
| caf16Δ | CCR4-NOT | 115 |
| caf40Δ | CCR4-NOT | 62 |
| caf130Δ | CCR4-NOT | 113 |
| dhh1Δ | CCR4-NOT | 6 |
| ssn3Δ | Mediator/SRB | 70 |
| ssn8Δ | Mediator/SRB | 78 |
| srb2Δ | Mediator/SRB | 131 |
| srb8Δ | Mediator/SRB | 157 |
| med1Δ | Mediator/SRB | 73 |
| nut1Δ | Mediator/SRB | 111 |
| pgd1Δ | Mediator/SRB | 117 |
| sin4Δ | Mediator/SRB | 68 |
| med15Δ | Mediator/SRB | NA2 |
| cdc73Δ | PAF1 | 93 |
| rtf1Δ | PAF1 | 87 |
| leo1Δ | PAF1 | 65 |
| paf1Δ | PAF1 | NA2 |
| ccr4Δ | CCR4-NOT, PAF1 | 24 |
| hpr1Δ | THO/TREX | 86 |
| mft1Δ | THO/TREX | 16 |
| tex1Δ | THO/TREX | 100 |
| thp2Δ | THO/TREX | 96 |
| dst1Δ | TFIIS | 119 |
Values below 50% of wild-type expression are shown in bold.
NA, not assayed due to poor growth in low zinc.
We chose an arbitrary cut-off value and focused on those mutants with more than a 50% decrease in expression relative to wild-type levels. We predicted that these subunits, and the complexes in which they are found, are most important for Zap1 AD1 function. As a result, we identified nine mutants with strong defects in YOR387C-lacZ expression. These mutations affected components of SAGA and related complexes (ada2Δ, ada3Δ, spt3Δ), SWI/SNF (swi3Δ, snf6Δ), RSC (rsc2Δ), CCR4-NOT (ccr4Δ, dhh1Δ, not5Δ), and THO-TREX (mft1Δ) complexes. In addition, we identified four other coactivator subunit mutants that grew very poorly in low zinc and therefore could not be assayed. Given that Zap1 activity is required for low zinc growth, these mutated genes may encode additional candidates for Zap1-recruited coactivators. The mutants that grew too poorly in low zinc to assay were ada1Δ and ada5Δ (SAGA complex), med15Δ (Mediator), and paf1Δ (PAF1 complex).
The results of this screen suggested that Zap1 directly or indirectly recruits ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes (SWI/SNF, RSC), the SAGA histone acetylating complex, and possibly the Mediator complex to activate the YOR387C promoter. An alternative hypothesis was that the defect in expression of YOR387C-lacZ was due to impaired activation of the ZAP1 promoter thereby depleting the cell of Zap1 and indirectly reducing YOR387C expression. To test this possibility, we assayed Zap1 levels in wild-type cells and coactivator mutants by immunoblotting. Levels of Zap1 protein similar to that of wild-type cells were observed in all coactivator mutants tested except ccr4Δ, ada1Δ, and ada5Δ (Fig. 2). The very low level of Zap1 in ada1Δ and ada5Δ strains provides a clear explanation for the inability of these cells to grow in zinc-limiting media where Zap1 activity is required. Notably, ccr4Δ mutants also grow poorly in low zinc (data not shown).
Figure 2.
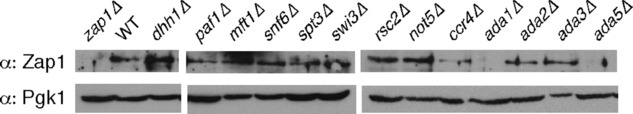
Zap1 protein accumulation is not affected in most coactivator mutant strains. Coactivator deletion mutants that affected YOR387C-lacZ expression were grown to mid-log phase in LZM supplemented with 1 μM ZnCl2. Protein extracts were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody raised against the DNA binding domain of Zap1. Pgk1 phosphoglycerate kinase was used as a loading control.
Coactivators required for activation of YOR387C-lacZ are not activation domain specific
To assess whether the coactivator subunits identified in the genetic screen were specifically required for AD1-activated transcription or might also mediate transcription activation by AD2, we assessed Zap1 activity in those coactivator mutants using two promoters that can be activated by either AD1 and AD2, that is DPP1 and ZRT1 (Frey and Eide, 2011). ZRT1 encodes a zinc uptake transporter and DPP1 encodes diacylglycerol pyrophosphate phosphatase that is induced in low zinc for unknown reasons. Coactivator mutant strains lacking chromosomal ZAP1 (zap1Δ) and expressing either Zap1WT, Zap1AD1, or ZapAD2 were transformed with DPP1-lacZ or ZRT1-lacZ reporters. These cells were grown in zinc-limiting conditions and assayed for β-galactosidase activity. Expression of the DPP1-lacZ reporter was reduced in all coactivator mutants tested relative to the corresponding wild-type control strain (Fig. 3A). Moreover, the effect of each coactivator mutation was similar in cells expressing Zap1WT, Zap1AD1, and Zap1AD2 alleles. This result suggests that on this promoter, AD1 and AD2 are similarly reliant on these coactivators. Most highly affected were mutants affecting subunits of the SWI/SNF (swi3Δ, snf6Δ) and SAGA (spt3Δ, ada2Δ, ada3Δ) complexes. Results obtained with the ZRT1-lacZ reporter were similar (Fig. 3B) although Zap1WT appeared to be more severely affected by loss of Ada3 and Dhh1 than either Zap1AD1 or Zap1AD2. The reason for this effect is unknown.
Figure 3.
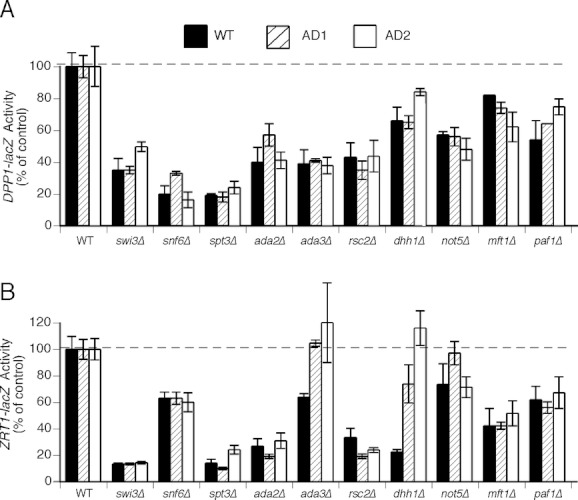
Coactivators required for activation of YOR387C-lacZ are not activation domain specific. The indicated coactivator mutant strains lacking chromosomal ZAP1 (zap1Δ) and expressing either Zap1WT (filled columns), Zap1AD1 (hatched columns), or Zap1AD2 (open columns) were transformed with DPP1-lacZ (A) or ZRT1-lacZ (B) reporters. These cells were grown to mid-log phase in LZM supplemented with 1 μM ZnCl2 and then assayed for β-galactosidase activity. The shown values are the means of three independent cultures and are expressed as a percentage of the isogenic zap1Δ strain expressing the corresponding Zap1 allele but lacking any coactivator mutation. The values shown are the means of three independent cultures and the error bars represent ±1 SD. The dashed line indicates 100% activity measured in the control strains.
Zinc- and Zap1-dependent recruitment of coactivator complexes
The results of Figure 3 suggested that AD1 and AD2 are both highly reliant on SWI/SNF and SAGA and may recruit those complexes to Zap1 target promoters in a Zap1-dependent and zinc-responsive manner. To test this hypothesis directly, we assayed recruitment of these complexes to the ZRT1 promoter in vivo using chromatin immunoprecipitation. Recruitment of Mediator complex was also tested because the med15Δ mutant was unable to grow in low zinc, thereby suggesting a role for Mediator in the Zap1 activation process. PCR analysis of input DNAs indicated similar levels of total chromatin were used in each immunoprecipitation and the quantitativeness of the assay was confirmed using serial dilutions of input DNA samples (Fig. 4). Immunoprecipitation of TAP-tagged Swi3 (SWI/SNF), Spt3 (SAGA), and Med15 (Mediator) from cross-linked chromatin isolated from zinc-limited cells all resulted in enrichment of the ZRT1 promoter (Fig. 4, lanes 1–4). These results indicate recruitment of these subunits and their complexes occurs in zinc-limited wild-type cells. This recruitment was zinc responsive as it was not observed in zinc-replete cells (Fig. 4, lanes 5–8). Moreover, this recruitment was Zap1 dependent because it was not observed in zap1Δ mutant cells grown in low zinc (Fig. 4, lanes 9–12). Similar results were obtained with the ZPS1 promoter; ZPS1 encodes a cell wall protein of unknown function and is also a Zap1 target gene. Chromatin immunoprecipitation of the CMD1 promoter was used as a negative control to confirm that the effects observed with the ZRT1 and ZPS1 promoters were specific. CMD1 is known to be dependent on TFIID recruitment and not dependent on the coactivators examined in this assay (Huisinga and Pugh, 2004). As expected, no enrichment of CMD1 promoter DNA was observed.
Figure 4.
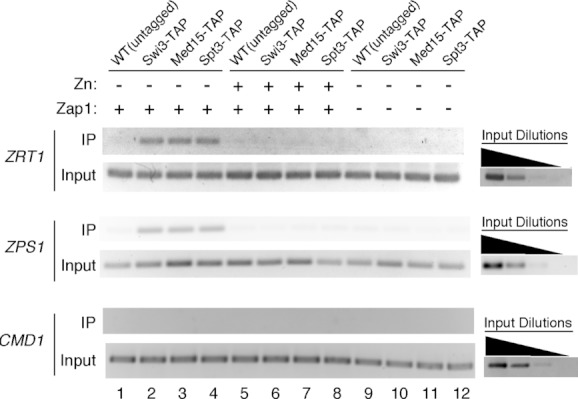
Recruitment of Swi3, Med15, and Spt3 is zinc responsive and Zap1 dependent. Untagged wild-type (BY4741), and isogenic Swi3-TAP, Med15-TAP, and Spt3-TAP tagged strains were grown in LZM supplemented with either 1 μM (−, lanes 1–4) or 1000 μM (+, lanes 5–8) ZnCl2. Isogenic zap1Δ cells grown in low zinc were used in lanes 9–12. The cells were cross-linked with formaldehyde, harvested, and chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis was performed using IgG-Sepharose to immunoprecipitate the TAP-tagged proteins. Coprecipitation of specific DNA fragments was then assessed by PCR using primers flanking the ZREs of the ZRT1 and ZPS1 promoters. Primers specific for the CMD1 promoter were used as a negative control. PCR amplification of 10-fold serial dilutions of input samples was used to confirm the quantitative nature of the assay.
Interdependence of coactivator recruitment by Zap1
Coactivator recruitment at promoters can be ordered such that disrupted recruitment at early steps can alter recruitment of other coactivators later in the assembly process (Biddick and Young, 2009). Alternatively, larger multi-coactivator super-complexes may be destabilized by the absence of one coactivator component regardless of the order of recruitment. To determine the possible interdependence of coactivator recruitment by Zap1, we examined whether disruption of one complex affected recruitment of other complexes. Chromatin immunoprecipitation of the ZRT1 promoter was used to assess the interdependency of coactivator recruitment. First, we found that lack of SWI/SNF complex subunit Swi3 disrupted recruitment of SAGA to ZRT1 when assayed using Ada2-TAP (Fig. 5A). This result was confirmed using chromatin immunoprecipitation of a second SAGA subunit, Spt3. Immunoprecipitation of the ZRT1 promoter with Spt3-TAP was reduced in the ada2Δ mutant, consistent with both Spt3 and Ada2 being components of SAGA (Fig. 5B). Spt3-TAP immunoprecipitation of the ZRT1 promoter was eliminated in the swi3Δ mutant indicating again that SAGA recruitment requires SWI/SNF function. The converse was also true. Swi3-TAP immunoprecipitation of the ZRT1 promoter was completely inhibited in the ada2Δ SAGA complex mutant (Fig. 5C). Similarly, recruitment of Mediator was impaired in both the swi3Δ and the ada2Δ mutants (Fig. 5D). These results suggest that efficient Mediator recruitment to ZRT1 is dependent on both SWI/SNF and SAGA. Thus, SWI/SNF, SAGA, and Mediator recruitment to the ZRT1 promoter appears to be highly interdependent.
Figure 5.
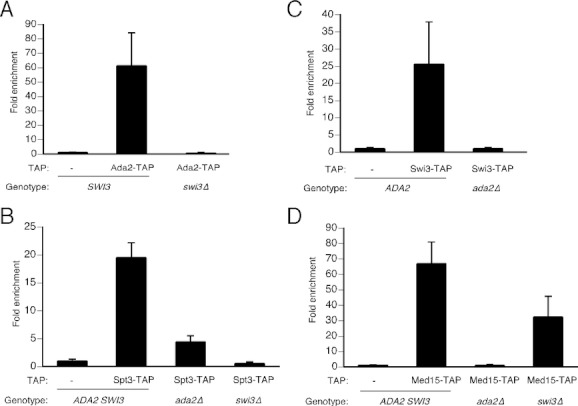
Coactivator recruitment by Zap1 is strongly interdependent. Results from chromatin immunoprecipitation of Ada2-TAP (A), Spt3-TAP (B), Swi3-TAP (C), and Med15-TAP (D) are shown. Isogenic ada2Δ and swi3Δ mutants were used to determine the effects of disrupting one complex on the recruitment of others. The indicated strains were grown to mid-log phase in LZM supplemented with 1 μM ZnCl2. Cells were then cross-linked with formaldehyde, harvested, and chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis was performed using IgG-Sepharose to immunoprecipitate TAP-tagged proteins. Coprecipitation of specific DNA fragments was then assessed by real-time PCR using primers flanking the ZREs of the ZRT1 promoter. The values shown are the means of three independent cultures and the error bars represent 1 SD.
Coactivator recruitment efficiency suggests that AD2 is weaker than AD1
The genetic results shown in Figure 3 suggest that AD1 and AD2 both recruit similar coactivators to Zap1-responsive promoters. To test this hypothesis directly, we examined coactivator recruitment by AD1 and AD2 alone using chromatin immunoprecipitation. On the chromosomal ZRT1 promoter, a promoter that is efficiently activated by either AD1 or AD2, we found that immunoprecipitation of Med15-TAP, Spt3-TAP, and Swi3-TAP resulted in enrichment of that promoter DNA from cells expressing Zap1 alleles bearing AD1 or AD2 alone (Fig. 6). Recruitment of Med15-TAP and Spt3-TAP by Zap1AD2 was lower than their recruitment by Zap1AD1 suggesting that AD2 is less able to recruit those factors than AD1. Both AD1 and AD2 were equally capable of Swi3-TAP recruitment. These results support the hypothesis that both AD1 and AD2 recruit SWI/SNF, SAGA, and Mediator, but suggest that AD2 is less effective in certain aspects of this recruitment than AD1.
Figure 6.
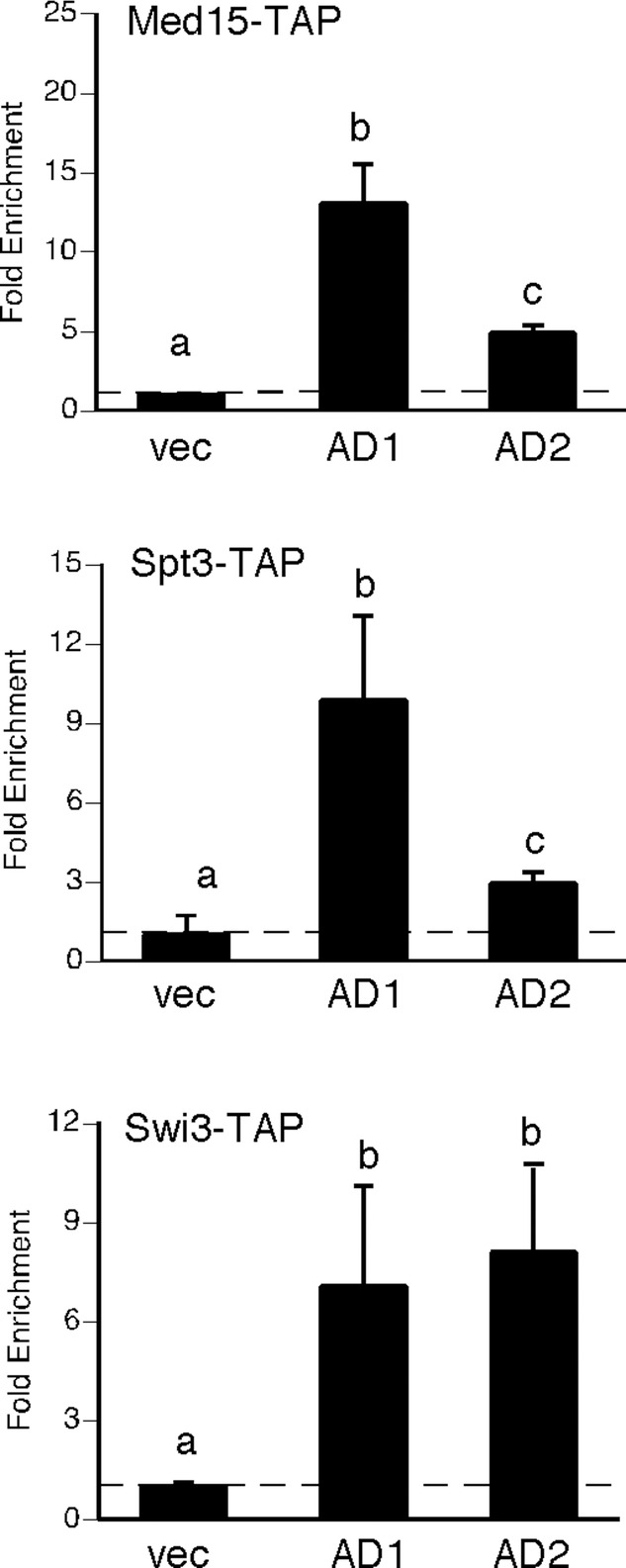
Coactivator recruitment by AD2 is weaker than AD1-mediated recruitment. Chromosomal ZAP1 was deleted from strains expressing Med15-TAP, Spt3-TAP, or Swi3-TAP. The resulting strains were transformed with Zap1AD1, Zap1AD2, or the empty vector and grown to mid-log phase in LZM supplemented with 1 μM ZnCl2. These cells were then cross-linked with formaldehyde, harvested, and chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis was performed using IgG-Sepharose to immunoprecipitate TAP-tagged proteins. Coprecipitation of the ZRT1 promoter was then assessed by real-time PCR using primers flanking the ZRT1 ZREs. The values shown are the means of three independent cultures and the error bars represent 1 SD. The letters denote values that are significantly different from each other (P < 0.05) as determined using ANOVA. The dashed lines mark the background level of recruitment observed in the vector-only cells.
Discussion
In this study, we initiated a characterization of the coactivator requirements of the Zap1 transcription factor. A genetic screen was used to identify coactivator complex subunits required for optimal expression of one Zap1 target gene, YOR387C, in low zinc. A similar approach was used previously to identify coactivators used by the Gcn4 transcription factor (Swanson et al., 2003). Among the approximately 60 coactivator mutants that we analyzed, 10 were found to have reduced YOR387C expression below an arbitrary threshold value of 50%. The identity of those mutants implicated SWI/SNF and SAGA complexes as being particularly important for Zap1-induced expression. In addition, given the very poor growth of the med15Δ mutant in low zinc, Mediator complex was also implicated. Other complexes that we identified that may play lesser roles on Zap1-regulated genes include CCR4-NOT, THO-TREX, and Paf1 complexes. These complexes play various roles in transcription initiation, transcription elongation, RNA export, and RNA degradation (Collart, 2003; Jaehning, 2010; Rondon et al., 2010).
We focused our attention on the SWI/SNF, SAGA, and Mediator complexes because of the strong effect mutations affecting those complexes had on YOR387C expression. It should be noted, however, that our genetic screen was not exhaustive and many more coactivator mutants await analysis. In addition, other coactivator mutants that we found to reduce YOR387C expression but not below our threshold value may also affect coactivator complexes that are recruited by Zap1 and contribute significantly to transcription. Thus, while we have identified coactivator complexes important for Zap1 function, other unrecognized coactivators may be involved as well.
Alternative approaches to identifying coactivators recruited by a given transcription factor include chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with mass spectrometry to identify interacting proteins. While this approach has been used successfully by others, we believe that the genetic approach we have used has a significant advantage. Our approach can identify coactivator complexes that are not only recruited to a promoter but must also play significant functional roles in the initiation process. While the genetic approach does not specifically identify coactivators that interact directly with Zap1, it does highlight those factors that are especially important for gene expression whether they are directly or indirectly recruited by the Zap1 activation domains.
The initial goal of our genetic screen was to identify those factors required for AD1 function. This was possible because YOR387C transcription is entirely dependent on AD1 and AD2 does not activate this promoter. Thus, mutations found to decrease YOR387C-lacZ expression are likely to affect AD1-mediated activation. Once identified, we could then test the role of these factors on other Zap1-regulated promoters. By analyzing the DPP1 and ZRT1 promoters, we found that the effects of the coactivator mutants were similar. These results suggest that at least for the YOR387C, DPP1, and ZRT1 promoters, Zap1-mediated activation has similar coactivator requirements. Because DPP1 and ZRT1 can be activated by either AD1 or AD2, we could also compare the effects of these mutations on either AD1 or AD2 function. We found that the effects of these mutations on these two activation domains were also similar. These results suggest that AD1 and AD2 have similar coactivator requirements. This hypothesis was supported by chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments showing that AD1 and AD2 can both recruit SWI/SNF, SAGA, and Mediator to a Zap1 target promoter.
We began this study with the hypothesis that, in zinc-replete cells, zinc binding to ligand residues within and flanking AD1 and AD2 blocks coactivator recruitment (Bird et al., 2003; Herbig et al., 2005). This was confirmed when we examined the zinc and Zap1 dependence of coactivator recruitment. Assembly of coactivators on Zap1 target promoters was also found to be highly interdependent with SAGA recruitment requiring SWI/SNF activity and vice versa. Optimal recruitment of Mediator complex was also dependent on both SWI/SNF and SAGA function. From our results, we cannot assess the order of recruitment as has been done previously with other promoters that can be quickly activated. This is not possible for Zap1 target promoters because it takes several hours to induce these promoters as a cell transitions from a zinc-replete to a zinc-limited state. On other promoters where these experiments have been done, it was found that assembly is a highly ordered process (Biddick and Young, 2009). On the HO promoter, for example, Mediator is recruited by the Swi5 activator following SWI/SNF and SAGA entry (Cosma, 2002). In contrast, Mediator is recruited by Gal4 to the GAL1 promoter after SAGA but before SWI/SNF (Bryant and Ptashne, 2003; Lemieux and Gaudreau, 2004). Zap1-mediated induction differs from that of Gal4 where SWI/SNF and SAGA are recruited by the activator independently of each other. Thus, our findings reflect the heterogeneity of coactivator interactions as observed in other coactivator recruitment studies.
If AD1 and AD2 require the same coactivators, as our data suggest, why are some promoters responsive to AD2 and other promoters are not responsive? As described above, our knowledge of what coactivators are required for function of AD1 and AD2 is still incomplete and there may be some key differences in the specific complexes recruited by these two domains. Continued analysis of coactivator recruitment by AD1 and AD2 may identify AD-specific coactivators. Our results do support a second hypothesis that is AD2 is a weaker-activation domain and may therefore be incapable of activating those genes that require a strong activation domain due to, for example, especially repressive nucleosome positioning. Promoters that are better poised for activation would then be responsive to either a strong activation domain (AD1) or a weaker domain like AD2. We showed previously that while AD1 is sufficient to activate transcription of the ZRT1 gene under normal conditions, it was not sufficient to activate transcription at 37°C where AD2 was also required (Frey and Eide, 2011). We suggested that AD2 may therefore be needed to aid AD1 when zinc deficiency is combined with other stresses such as heat stress. Now that we know some of the coactivators recruited by Zap1, we can further explore the novel roles of AD1 and AD2 in Zap1-mediated transcription.
Experimental Procedures
Growth conditions
Yeast strains were grown in either YP medium supplemented with 2% glucose (YPD) or synthetic defined medium with 2% glucose and the appropriate auxotrophic supplements. Limiting zinc medium (LZM) was prepared as previously described (Gitan et al., 1998) with 2% glucose as the carbon source and the indicated concentration of ZnCl2. LZM contains 1-mM EDTA and 20-mM citrate as metal buffers to limit zinc availability. Because of those metal buffers, the zinc available to cells in LZM is far lower than the total concentration.
Yeast strains and plasmids
Yeast strains used in this study included DY1457 (MATα ade6 can1 his3 leu2 trp1 ura3), ABY9 (DY1457 zap1Δ::KanMX4) (Zhao and Eide, 1997), BY4741 (MATa his3Δ leu2Δ met15Δ ura3Δ) and BY4743 (MATa/α met15Δ/+ lys2Δ/+ his3Δ/ his3Δ leu2Δ/ leu2Δ ura3Δ/ ura3Δ). All strains newly constructed for this study are listed in Table 2. The homozygous coactivator mutant strains (Open Biosystems) were all isogenic with BY4743 and contain the corresponding gene deleted and replaced with the KanMX4 cassette. The TAP-tagged coactivator strains (Open Biosystems) were isogenic with BY4741 and had the tandem affinity purification (TAP) tag inserted at the C-terminus of the indicated gene. To delete the ZAP1 gene in these strains, KanMX4 or HphMX4 cassettes flanked by 500 base pairs of the promoter and terminator regions of ZAP1 were generated by overlap PCR and the resulting fragment was transformed into recipient strains to generate isogenic zap1Δ mutants. The ZRT1-lacZ and DPP1-lacZ reporters were previously described (Lyons et al., 2000). The YOR387C-lacZ reporter was constructed by amplifying the 1000 base pair region upstream of the translational start site of the YOR387C gene using primers with 40 bp of homology to YEp353 (Myers et al., 1986). The resulting fragment was then inserted into BamHI-, EcoRI-digested YEp353 using homologous recombination. Plasmids pYef2L (vector), pYef2L-Zap1-6x-myc (Zap1WT), pYef2L-Zap1Δ6-551-6x-myc (Zap1AD2), and pYef2-Zap1ΔZnf1/2::GliZnf1/2-6x-myc (Zap1AD1) were previously described (Bird et al., 2000; Frey and Eide, 2011). These plasmids express ZAP1 from the GAL1 promoter. To normalize protein expression of the different myc-tagged Zap1 alleles to that of endogenous Zap1, cells were cotransformed with plasmid pGEV (Gao and Pinkham, 2000). GEV is a hybrid-activator protein containing the Gal4 DNA-binding domain, the hormone-responsive domain of the estrogen receptor, and VP16 activation domain. Treatment of GEV-containing cells with 10-nM β-estradiol resulted in expression of these Zap1 alleles at levels equal to chromosomally expressed Zap1 (Frey and Eide, 2011).
Table 2.
Strains generated in this study
| Strain | Relevant genotype1 |
|---|---|
| AFY101 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 ada2Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY102 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 ada3Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY103 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 spt3Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY104 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 swi3Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY105 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 snf6Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY106 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 rsc2Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY107 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 dhh1Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY108 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 paf1Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY109 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 ccr4Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY110 | zap1Δ::hphMX4 not5Δ::kanMX4 |
| AFY111 | swi3Δ::kanMX4 ADA2-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY112 | ada2Δ::kanMX4 SPT3-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY113 | swi3Δ::KanMX4 SPT3-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY114 | ada2Δ::kanMX4 SWI3-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY115 | ada2Δ::kanMX4 MED15-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY116 | swi3Δ::kanMX4 MED15-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY118 | zap1Δ::kanMX4 MED15-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY119 | zap1Δ::kanMX4 SPT3-TAP::HIS3 |
| AFY120 | zap1Δ::kanMX4 SWI3-TAP::HIS3 |
All of these strains were derived from BY4741.
S1 nuclease protection assays
RNA was extracted from cells using hot acid phenol extraction and S1 analysis was performed as previously described (Dohrmann et al., 1992). Thirty micrograms of total RNA was hybridized to a 32P end-labeled oligonucleotide probe before digestion by S1 nuclease and separation on an 8% polyacrylamide/8 M urea gel. Probes are listed in Table 3.
Table 3.
Oligonucleotides used in this study
| Gene | Purpose | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| YOR387C | S1 nuclease assay | 5′-TTATTACAAGTGACGTTAGTCAAATCAAA TCTGACGGCTGCCATGGT-3′ |
| ZRT1 | SQ-PCR/ChIP1 | 5′-CAATACACCCGTACTCTCTTGCCTGT-3′ |
| ZRT1 | SQ-PCR/ChIP | 5′-TGCTCTCAACCTACTTTCCATGAC-3′ |
| CMD1 | SQ-PCR/ChIP | 5′-CCTCCAATCTTACCGAAGA-3′ |
| CMD1 | SQ-PCR/ChIP | 5′-GCGGGAGCAAAAAATCACA-3′ |
| ZPS1 | SQ-PCR/ChIP | 5′-GCCGTTTCTTTTTGGGCAGTA-3′ |
| ZPS1 | SQ-PCR/ChIP | 5′-GCCTTTAAAAACAGCGCTTCC-3′ |
| ZRT1 | RT-PCR/ChIP2 | 5′-CGCGCGCCAGATAACTAAAA-3′ |
| ZRT1 | RT-PCR/ChIP | 5′-ACCGCACAGATGAGAACCTTG-3′ |
β-galactosidase assays
Cells were grown for 15–20 h to mid-log phase (A600 = 0.3–0.7) in LZM supplemented with the indicated amount of ZnCl2. β-galactosidase activity was measured as described (Guarente, 1983) and activity units were calculated as follows: (ΔA420 × 1000)/(min × mL of culture × absorbance of the culture at 595 nm).
Immunoblot analysis
Protein extracts for immunoblots were prepared by cell disruption in the presence of trichloroacetic acid (Peter et al., 1993). Immunoblots were performed essentially as described (Harlow and Lane, 1988). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (7.5% acrylamide) and then transferred to nitrocellulose. Blots were probed with anti-Zap1 (Evans-Galea et al., 2003), anti-c-myc (monoclonal 9E10, Roche), or anti-Pgk1 (Molecular Probes) antibodies, washed, and then incubated with either goat anti-mouse or goat anti-rabbit IgG antibodies coupled to horseradish peroxidase. TAP-tagged proteins were detected using goat anti-rabbit IgG antibodies. Detection was by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL; Amersham).
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed as described (Kanin et al., 2007). Wild-type BY4741 cells or isogenic strains with TAP tag insertions (Open Biosystems) in ADA2, MED15, SPT3, or SWI3 were grown to an A600 ∼ 0.5 and then treated with 1% formaldehyde to cross-link protein-DNA complexes. The cross-linking reaction was quenched by adding 125-mM glycine. After two washes with ice-cold PBS, the cells were lysed with glass beads in buffer containing Complete Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Roche), 1-mM PMSF, and 2 mM-benzamidine. Following centrifugation for 10 min at 16,000 × g, the supernatants were incubated with IgG-Sepharose (GE Healthcare) at 4°C for 1 h. The cross-links were reversed in TES and coprecipitation of specific promoter fragments with the TAP-tagged coactivator was assessed by PCR using primers flanking the ZRT1 ZREs (Table 3). Primers specific to the CMD1 promoter were used as a negative control because this housekeeping gene relies on TFIID for activation and not the coactivators assayed in these experiments. Quantitative analysis of chromatin immunoprecipitation fractions was performed using real-time PCR. The relative amount of coprecipitated DNA was calculated from input DNA and is reported as a fold-increase relative to zap1Δ cells containing an empty vector.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant GM56285 to D. E. The authors thank Audrey Gasch for providing strains, the members of the Eide laboratory for helpful discussions, and for critical reading of the manuscript.
References
- Bhaumik SR. Distinct regulatory mechanisms of eukaryotic transcriptional activation by SAGA and TFIID. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1809:97–108. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.08.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddick R, Young ET. Yeast mediator and its role in transcriptional regulation. C.R. Biol. 2005;328:773–782. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2005.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddick R, Young ET. The disorderly study of ordered recruitment. Yeast. 2009;26:205–220. doi: 10.1002/yea.1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A, McCall K, Kramer M, Blankman E, Winge D, Eide D. Zinc fingers can act as Zn(II) sensors to regulate transcriptional activation domain function. EMBO J. 2003;22:5137–5146. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird AJ, Zhao H, Luo H, Jensen LT, Srinivasan C, Evans-Galea M, Winge DR, Eide DJ. A dual role for zinc fingers in both DNA binding and zinc sensing by the Zap1 transcriptional activator. EMBO J. 2000;19:3704–3713. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.14.3704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant GO, Ptashne M. Independent recruitment in vivo by Gal4 of two complexes required for transcription. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:1301–1309. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart MA. Global control of gene expression in yeast by the Ccr4-Not complex. Gene. 2003;313:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00672-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosma MP. Ordered recruitment: gene-specific mechanism of transcription activation. Mol. Cell. 2002;10:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00604-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohrmann PR, Butler G, Tamai K, Dorland S, Greene JR, Thiele DJ, Stillman DJ. Parallel pathways of gene regulation: homologous regulators SWI5 and ACE2 differentially control transcription of HO and chitinase. Gene. Dev. 1992;6:93–104. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide DJ. Homeostatic and adaptive responses to zinc deficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:18565–18569. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R900014200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans-Galea MV, Blankman E, Myszka DG, Bird AJ, Eide DJ, Winge DR. Two of the five zinc fingers in the Zap1 transcription factor DNA binding domain dominate site-specific DNA binding. Biochemistry. 2003;42:1053–1061. doi: 10.1021/bi0263199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey AG, Eide DJ. Roles of two activation domains in Zap1 in the response to zinc deficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:6844–6854. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.203927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey AG, Bird AJ, V. Evans-Galea M, Blankman E, Winge DR, Eide DJ. Zinc-regulated DNA binding of the yeast Zap1 zinc-responsive activator. PLoS One. 2011;6:e22535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao CY, Pinkham JL. Tightly regulated, beta-estradiol dose-dependent expression system for yeast. Biotechniques. 2000;29:1226–1231. doi: 10.2144/00296st02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitan RS, Luo H, Rodgers J, Broderius M, Eide D. Zinc-induced inactivation of the yeast ZRT1 zinc transporter occurs through endocytosis and vacuolar degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:28617–28624. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.44.28617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E, Lane D. Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Press; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Herbig A, Bird AJ, Swierczek S, McCall K, Mooney M, Wu CY, Winge DR, Eide DJ. Zap1 activation domain 1 and its role in controlling gene expression in response to cellular zinc status. Mol. Microbiol. 2005;57:834–846. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisinga KL, Pugh BF. A genome-wide housekeeping role for TFIID and a highly regulated stress-related role for SAGA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. 2004;13:573–585. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaehning JA. The Paf1 complex: platform or player in RNA polymerase II transcription? Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1799:379–388. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanin EI, Kipp RT, Kung C, Slattery M, Viale A, Hahn S, Shokat KM, Ansari AZ. Chemical inhibition of the TFIIH-associated kinase Cdk7/Kin28 does not impair global mRNA synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:5812–5817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611505104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux K, Gaudreau L. Targeting of Swi/Snf to the yeast GAL1 UAS G requires the Mediator, TAF IIs, and RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004;23:4040–4050. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons TJ, Gasch AP, Gaither LA, Botstein D, Brown PO, Eide DJ. Genome-wide characterization of the Zap1p zinc-responsive regulon in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:7957–7962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.14.7957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens JA, Winston F. Recent advances in understanding chromatin remodeling by Swi/Snf complexes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2003;13:136–142. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(03)00022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers AM, Tzagoloff A, Kinney DM, Lusty CJ. Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene. 1986;45:299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M, Gartner A, Horecka J, Ammerer G, Herskowitz I. FAR1 links the signal transduction pathway to the cell cycle machinery in yeast. Cell. 1993;73:747–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90254-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondon AG, Jimeno S, Aguilera A. The interface between transcription and mRNP export: from THO to THSC/TREX-2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1799:533–538. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterner DE, Berger SL. Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000;64:435–459. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.64.2.435-459.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson MJ, Qiu H, Sumibcay L, Krueger A, Kim SJ, Natarajan K, Yoon S, Hinnebusch AG. A multiplicity of coactivators is required by Gcn4p at individual promoters in vivo. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;23:2800–2820. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.8.2800-2820.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z, Feng LS, Matskevich V, Venkataraman K, Parasuram P, Laity JH. Solution structure of a Zap1 zinc-responsive domain provides insights into metalloregulatory transcriptional repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Mol. Biol. 2006;357:1167–1183. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu CY, Bird AJ, Chung LM, Newton MA, Winge DR, Eide DJ. Differential control of Zap1-regulated genes in response to zinc deficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:370. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H, Eide DJ. Zap1p, a metalloregulatory protein involved in zinc-responsive transcriptional regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997;17:5044–5052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.9.5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


