Abstract
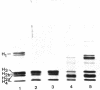
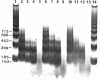
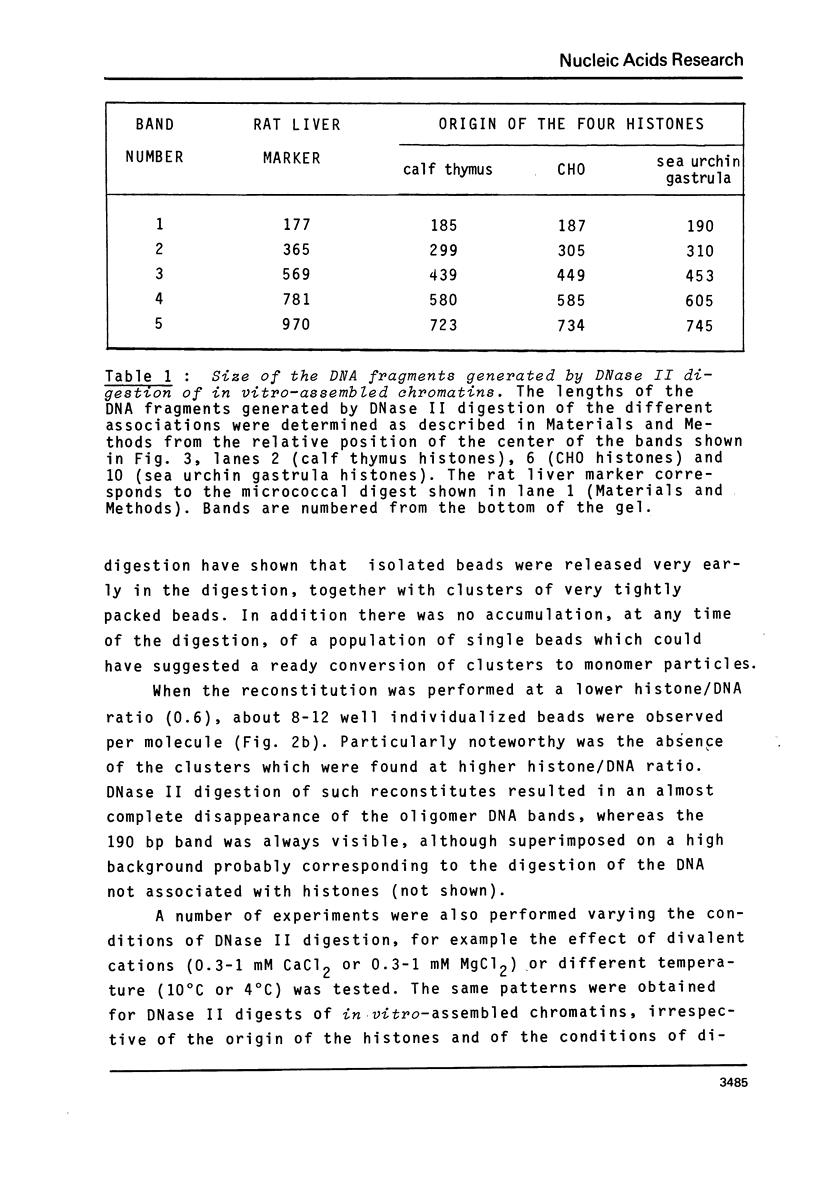
The four histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 from calf thymus, CHO and sea urchin gastrula cells were associated by stepwise dialysis from 2 M NaCl with SV40 DNA Form I. The in vitro-assembled chromatins were visualized by electron microscopy and the size of the DNA fragments generated by digestion with DNase II was determined. Irrespective of the origin of the histones, the size of the smallest DNA band generated at early times of digestion was about 190 base pairs, whereas oligomeric DNA bands were multiples of 140 bp. These results support our previous proposal that the four histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are able to organize more than 140 bp of DNA, but do not provide any evidence that the variability of histones H2A and H2B plays a role in the variability of the DNA repeat length of native chromatins.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellard M., Oudet P., Germond J. E., Chambon P. Subunit structure of simian-virus-40 minichromosome. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):543–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Bernardi A., Chersi A. Studies on acid hydrolases. I. A procedure for the preparation of acid deoxyribonuclease and other acid hydrolases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 24;129(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Hewish D. R., Mobbs J. Mammalian chromatin substructure studies with the calcium-magnesium endonuclease and two-dimensional polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):67–72. doi: 10.1042/bj1430067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Stability of nucleosomes in native and reconstituted chromatins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3173–3192. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D., Morris N. R. Assembly of SV40 chromatin in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. R. A comparison of the structure of chicken erythrocyte and chicken liver chromatin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Differences and similarities in chromatin structure of Neurospora crassa and higher eucaryotes. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Germond J. E., Bellard M., Spadafora C., Chambon P. Nucleosome structure. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 May 11;283(997):241–258. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1978.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadafora C., Bellard M., Compton J. L., Chambon P. The DNA repeat lengths in chromatins from sea urchin sperm and gastrule cells are markedly different. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Streeck R. E., Zachau H. G. Closely spaced nucleosome cores in reconstituted histone.DNA complexes and histone-H1-depleted chromatin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):615–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Thompson R. J. Variation in chromatin structure in two cell types from the same tissue: a short DNA repeat length in cerebral cortex neurons. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):633–640. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]