Abstract
Sequence for the leader RNA Synthesized by the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus is presented and its complementary sequence representing the 3'-terminal sequence of the genome RNA is deduced. Comparison with the leader RNA sequence of the serologically distinct Indiana strain reveals that the 3'-terminal region of the genomes of two viruses is highly conserved.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. D., Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus: mode of transcription. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):1–8. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Moyer S. A., Rhodes D. P. Studies on the in vitro adenylation of RNA by vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):547–558. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Emerson S. U., Flamand A. Reconstitution of infectivity and transcriptase activity of homologous and heterologous viruses: vesicular stomatitis (Indiana serotype), Chandipura, vesicular stomatitis (New Jersey serotype), and Cocal viruses. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):139–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.139-144.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. Translation and identification of the mRNA species synthesized in vitro by the virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):274–278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. A unique RNA species involved in initiation of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcription in vitro. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
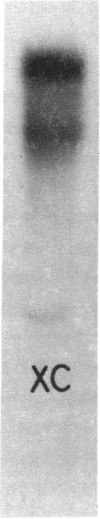
- Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K. In vitro RNA transcription by the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Characterization of the leader RNA. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):188–194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.188-194.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Stone H. O. Methylation of messenger RNA of Newcastle disease virus in vitro by a virion-associated enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Yu Y. Both NS and L proteins are required for in vitro RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1348–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1348-1356.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Gumport R. I., Uhlenbeck O. C. Dinucleoside pyrophosphate are substrates for T4-induced RNA ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4839–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franze-Fernandez M. T., Banerjee A. K. In vitro RNA transcription by the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Characterization of the mRNA species. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):179–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.179-187.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legault D., Takayesu D., Prevec L. Heterotypic exclusion between vesicular stomatitis viruses of the New Jersey and Indiana serotypes. J Gen Virol. 1977 Apr;35(1):53–65. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. Messenger RNA species synthesized in vitro by the virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Ishihama A. Function and structure of RNA polymerase from vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4307–4314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Flamand A., Bishop D. H. Synthesis of RNA by mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) and the ability of wild-type VSV New Jersey to complement the VSV Indiana ts G I-114 transcription defect. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):157–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.157-169.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Flamand A., Clark H. F., Obijeski J. F., Roy P., Bishop D. H. Detection of homologous RNA sequences among six rhabdovirus genomes. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):250–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.250-252.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]