Abstract
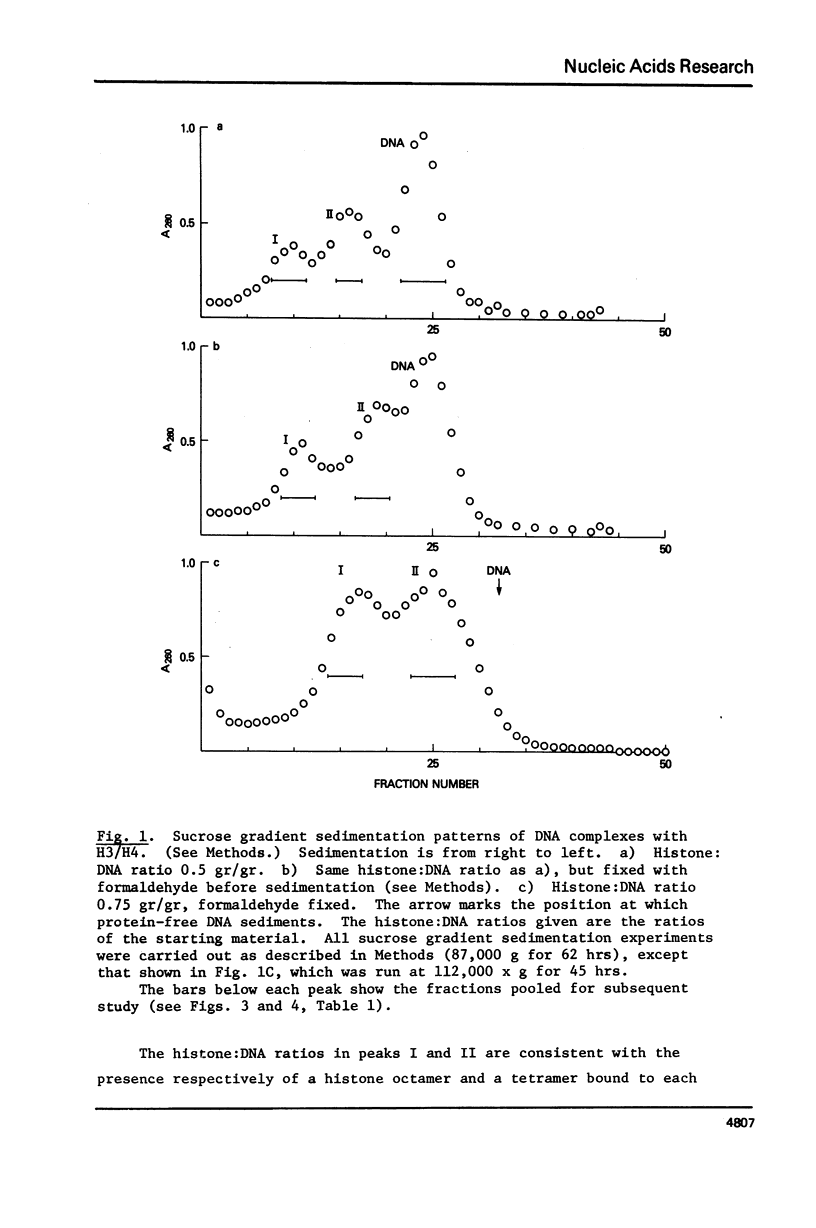
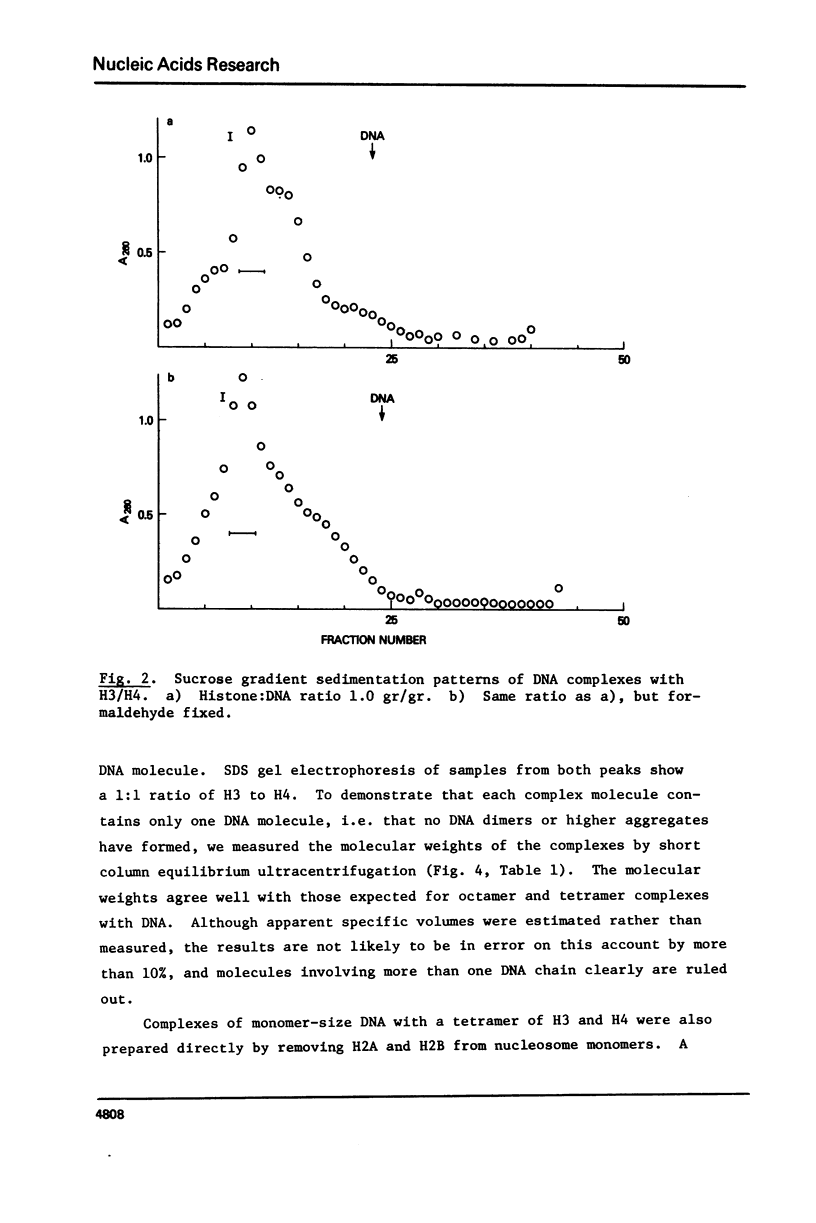
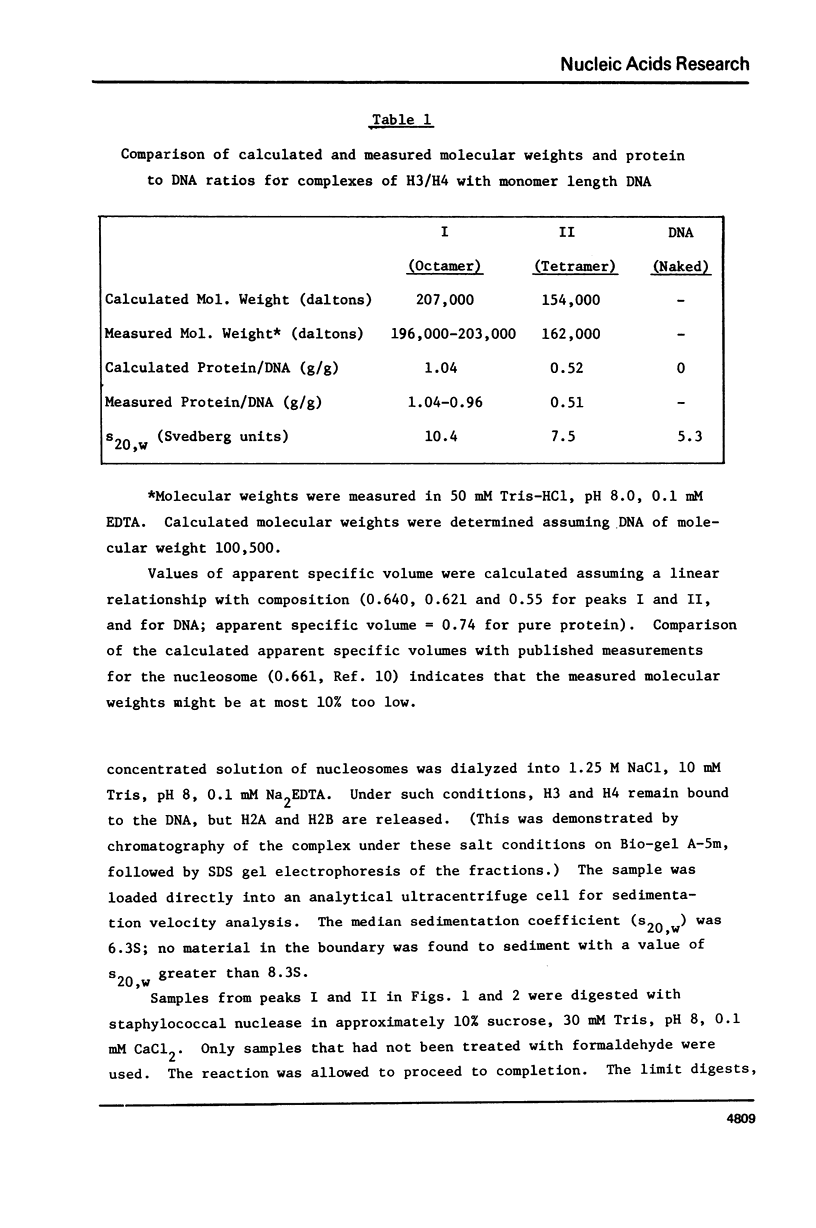
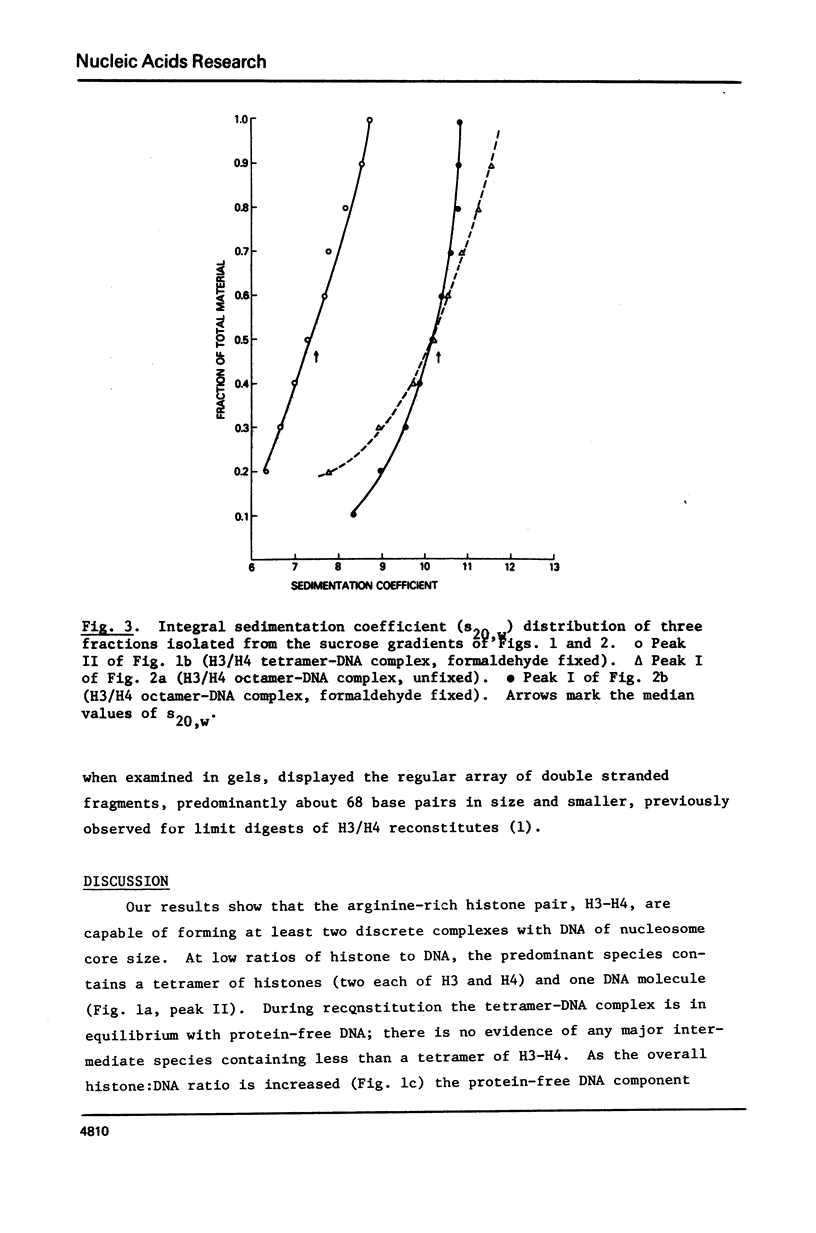
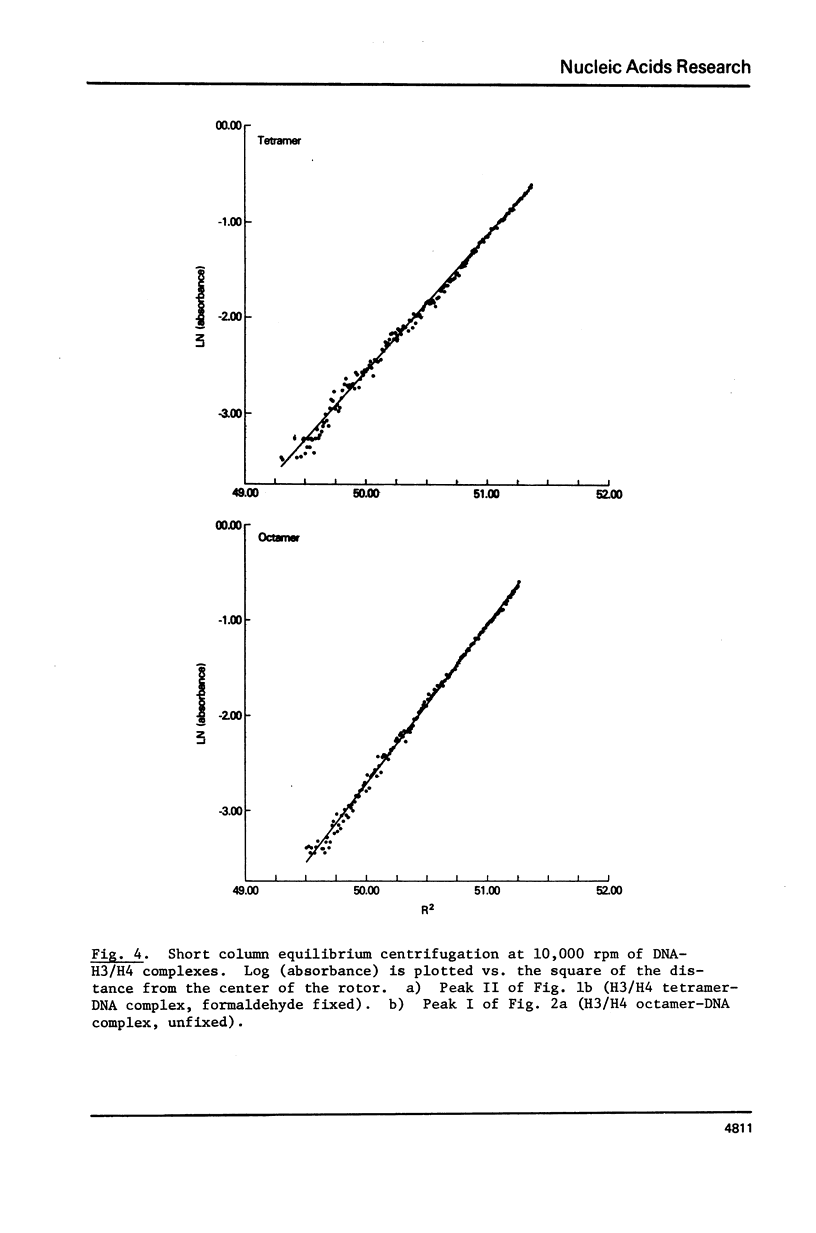
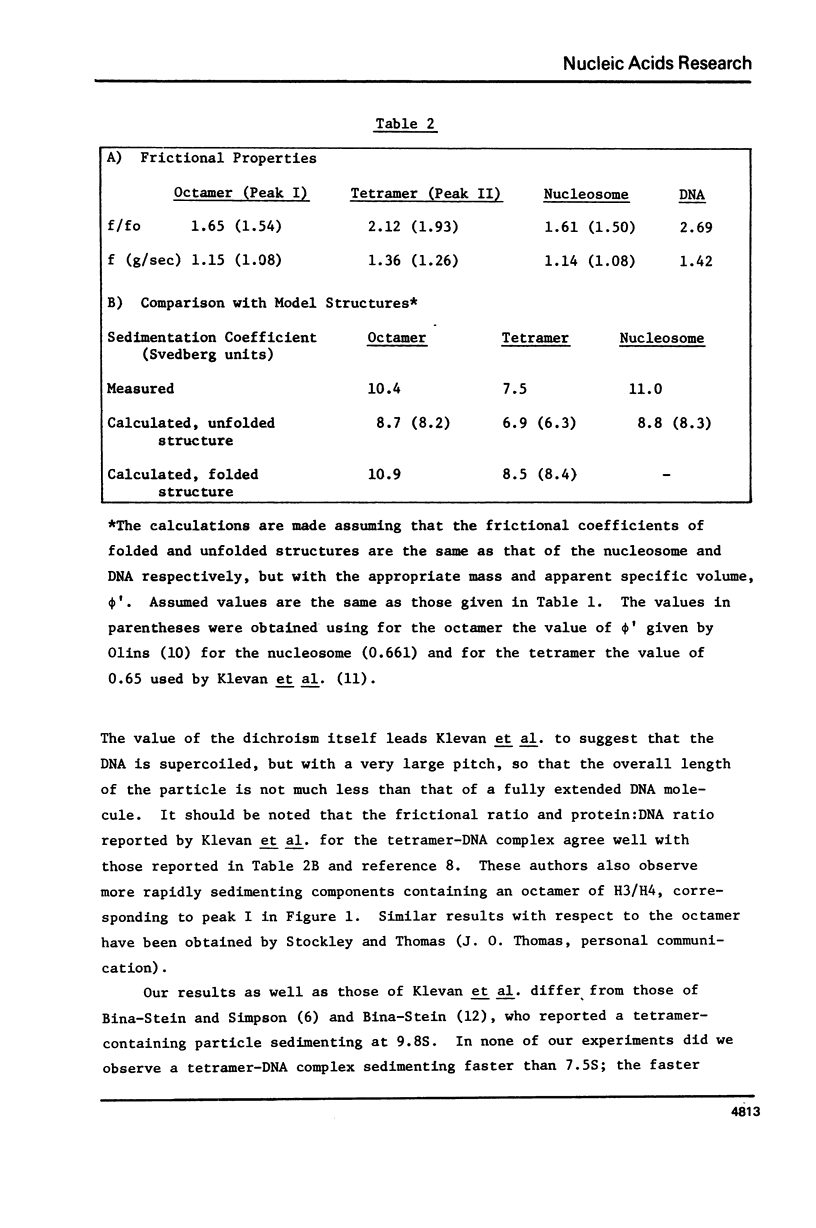
Equimolar mixtures of histones H3 and H4 have been reconstituted onto DNA of nucleosome core size. Two distinct complexes are formed in a relative abundance that depends on the starting ratio of H3 + H4 to DNA. One of these complexes contains two H3-H4 dimers for each DNA molecule, and has a sedimentation coefficient of 7.5S. The other complex contains an octamer consisting of four H3-H4 dimers, and has a sedimentation coefficient of 10.4S. On the basis of these measurements, we conclude that the octamer complex (but not the tetramer complex) is a fully folded, compact structure resembling the nucleosome.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M. Folding of 140-base pair length DNA by a core of arginine-rich histones. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):5213–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M., Simpson R. T. Specific folding and contraction of DNA by histones H3 and H4. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Butler-Browne G. S., Carpenter B. G., Stephens R. M. Physical studies of chromatin. The recombination of histones with DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):21–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Histone H3 disulfide dimers and nucleosome structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5519–5523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Supercoiling energy and nucleosome formation: the role of the arginine-rich histone kernel. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1159–1181. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. The organization of histones and DNA in chromatin: evidence for an arginine-rich histone kernel. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Sollner-Webb B., Simon R. H., Williamson P., Zasloff M., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure, DNA folding, and gene activity. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):57–75. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G., Eisenberg H. Deoxyribonucleate solutions: sedimentation in a density gradient, partial specific volumes, density and refractive index increments, and preferential interactions. Biopolymers. 1968;6(8):1077–1100. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Weintraub H. Chromosomal proteins and chromatin structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:725–774. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hnilica L. S. Methods for analysis of histones. Methods Enzymol. 1975;40:102–138. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)40011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevan L., Dattagupta N., Hogan M., Crothers D. M. Physical studies of nucleosome assemble. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4533–4540. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Stephens R. M., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. A nucleosome-like structure containing DNA and the arginine-rich histones H3 and H4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jul;4(7):2477–2485. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.7.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Carlson R. D., Wright E. B., Olins D. E. Chromatin nu bodies: isolation, subfractionation and physical characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Dec;3(12):3271–3291. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.12.3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Germond J. E., Sures M., Gallwitz D., Bellard M., Chambon P. Nucleosome structure I: all four histones, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4, are required to form a nucleosome, but an H3-H4 subnucleosomal particle is formed with H3-H4 alone. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):287–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure as probed by nucleases and proteases: evidence for the central role of histones H3 and H4. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Palter K., Van Lente F. Histones H2a, H2b, H3, and H4 form a tetrameric complex in solutions of high salt. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):85–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


