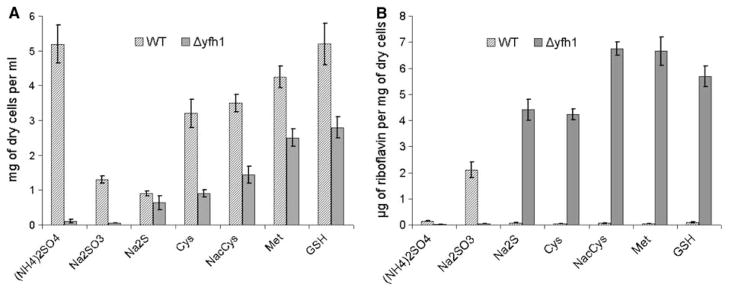
Fig. 1.
Growth (a) and riboflavin productivity (b) of P. guilliermondii WT and Δyfh1 mutant in synthetic sulfur free medium B supplemented with different sulfur containing compounds. Cultures of P. guilliermondii wild-type strain R-66 (WT) and Δyfh1 mutant were grown aerobically in YPS medium for 16 h. Cells were pelleted, washed with water and resuspended in water to an optical density OD600 of 0.2. Aliquots of 0.3 ml were inoculated in 100 ml Erlenmeyer flasks containing 20 ml of the synthetic medium B containing 3.6 μM of iron added as ammonium ferrous sulfate and supplemented with: (NH4)2SO4—40 mM of ammonium sulfate, Na2SO3—2.5 mM of sodium sulfite, Met—0.2 mM of methionine, GSH—0.2 mM of glutathione, Cys—0.2 mM of cysteine, NACys—0.1 mM N-Acetyl-L-cysteine, Na2S—5 mM sodium sulfide. Cell density and concentration of riboflavin were determined after 5 days of incubation at 30°C on gyro shaker at 200 rpm. Values are means ± SE of three independent experiments