Abstract
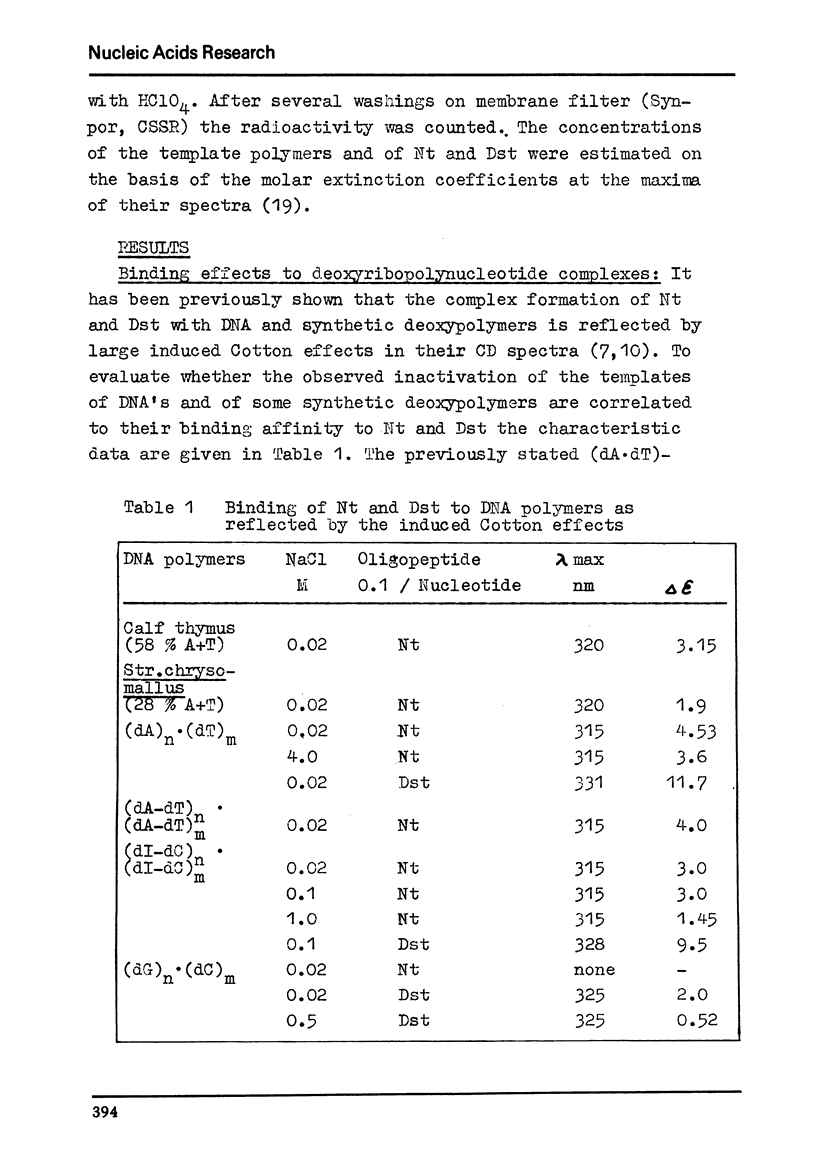
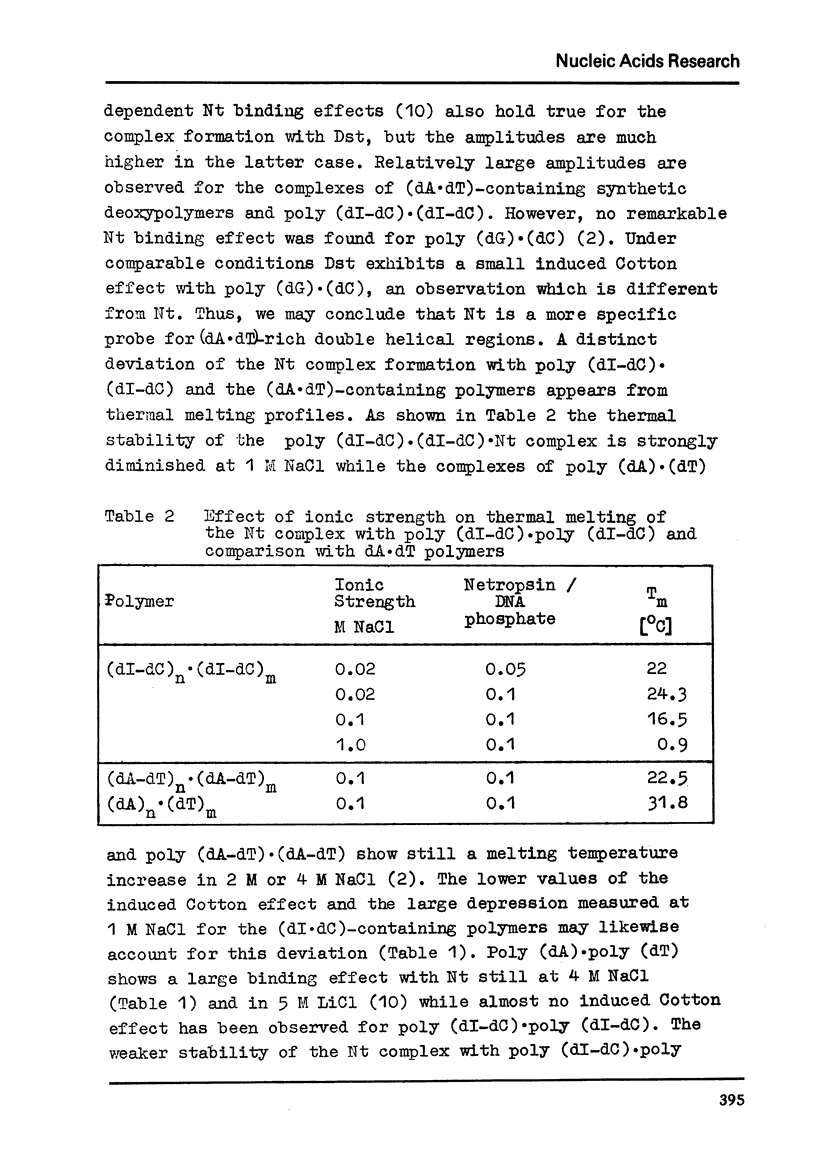
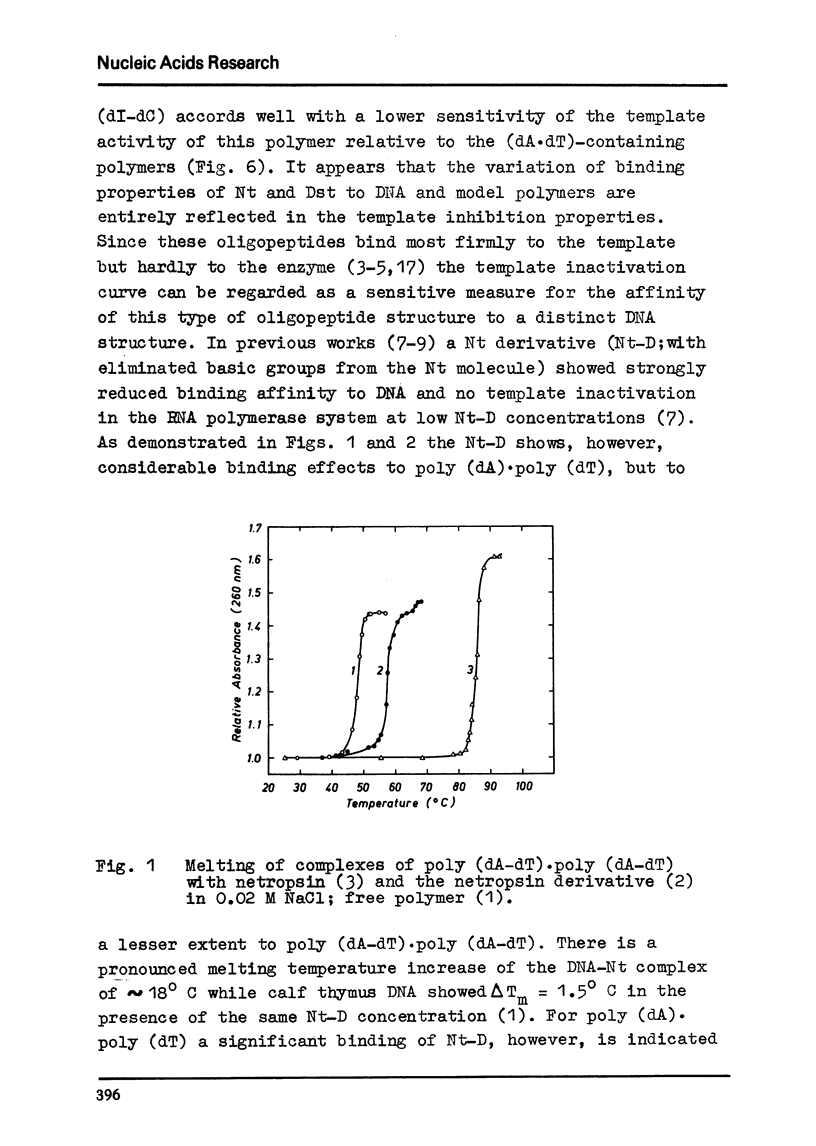
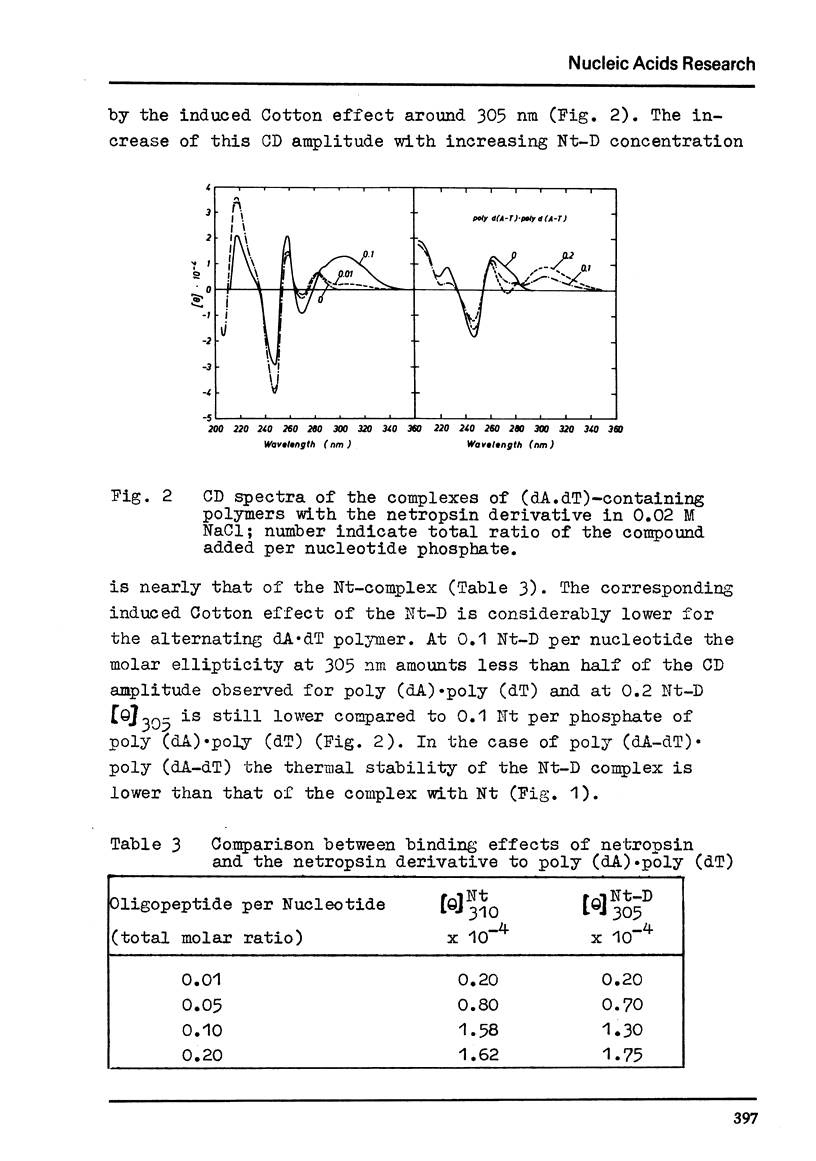
The inhibitory effect of the polypeptide antibiotics netropsin and distamycin A on DNA dependent nucleic acid synthesis has been shown to be related to the base composition of the template DNA. A number of natural DNA's of quite different dA·dT content as well as poly (dI-dC)·poly (dI-dC), poly (dA-dT)·poly (dA-dT), poly (dA) · poly (dT) and poly (dG)·poly(dC) has been studied as templates in DNA and in part in RNA polymerase reaction. The highest binding efficiency of netropsin existing for (dA·dT)-containing DNA polymers and the less pronounced interaction with the (dI·dC)-containing polymer shown by the melting and CD spectral behaviour of the complexes are entirely reflected in the template inactivation. The same is evident for distamycin A. However, in contrast to netropsin the antibiotic distamycin A exhibits some binding tendency to poly (dG)·poly (dC). Binding effects of a netropsin derivative to DNA and (dA·dT)-containing polymers suggest the importance of hydrogen bonds of the peptide groups in the complex formation.
Full text
PDF


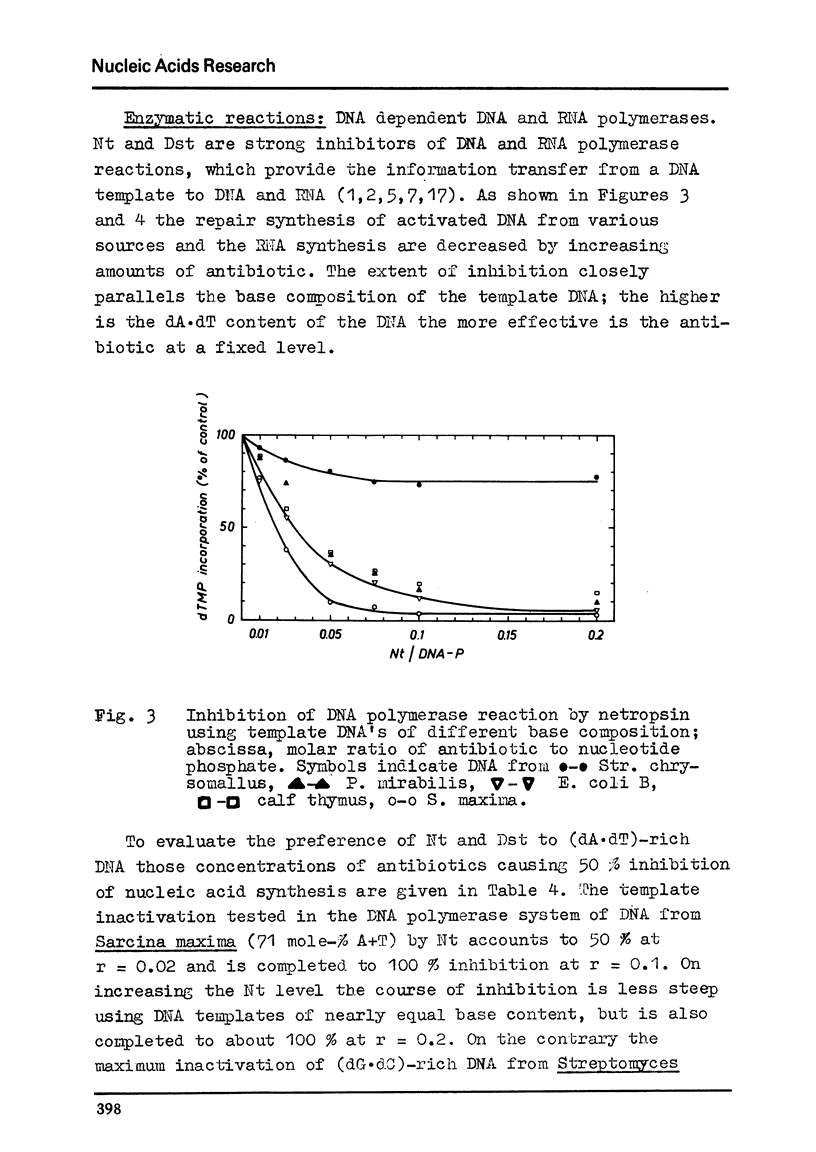
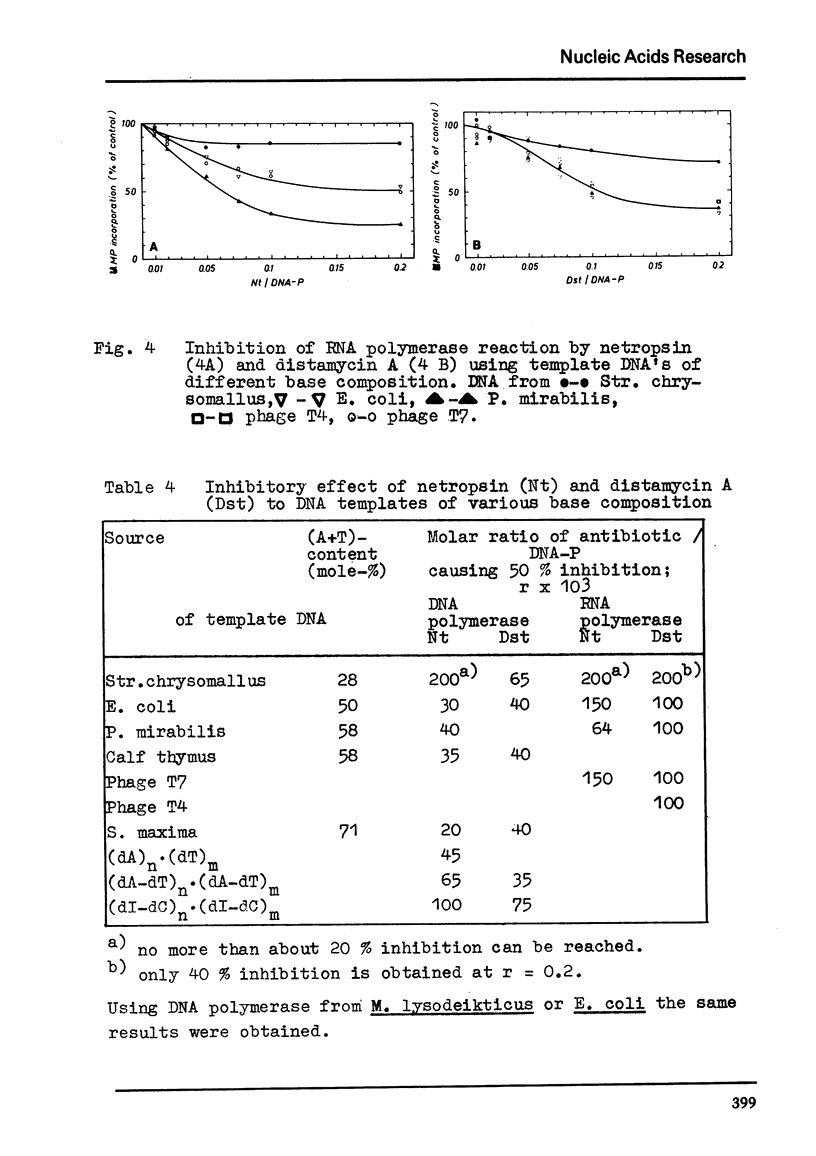
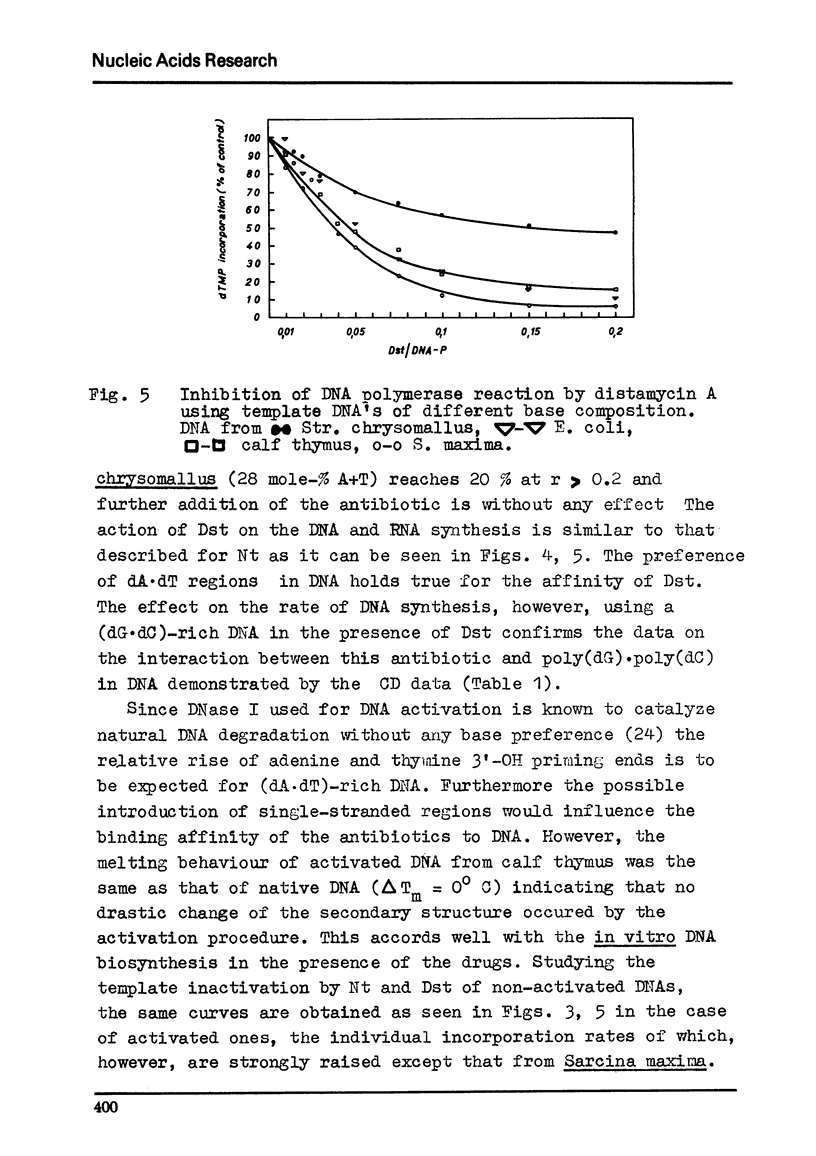
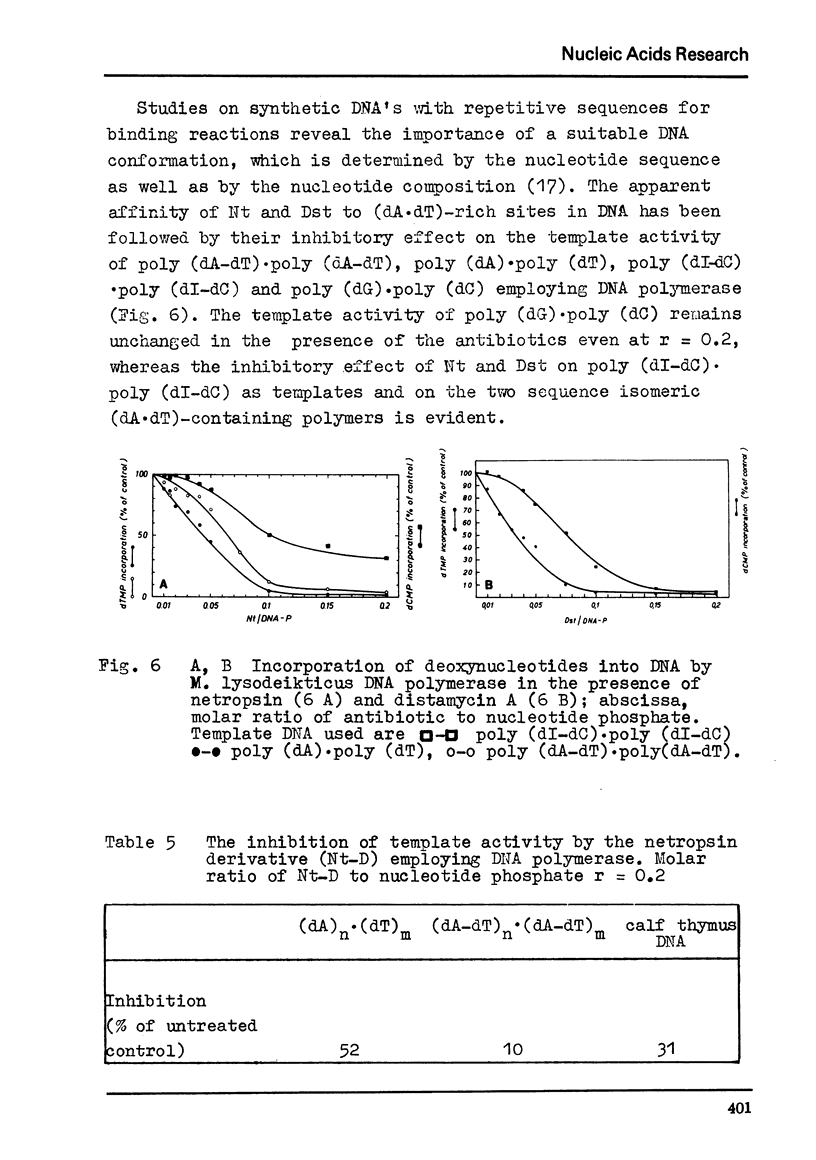



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Le Talaer J. Y., Jeanteur P. Preferential binding of E. coli RNA-polymerase to A-T rich sequences of bacteriophage lambda DNA. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jan 30;12(5):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck G., Triebel H., Waring M., Zimmer C. Conformation dependent binding of netropsin and distamycin to DNA and DNA model polymers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):503–530. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Obermeier J., Maidhof A., Zahn R. K. Distamycin: an inhibitor of DNA-dependent nucleic acid synthesis. Chem Biol Interact. 1974 Mar;8(3):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(74)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puschendorf B., Grunicke H. Effect of Distamycin A on the template activity of DNA in a DNA polymerase system. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(4):355–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puschendorf B., Petersen E., Wolf H., Werchau H., Grunicke H. Studies on the effect of distamycin A on the DNA dependent RNA polymerase system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90659-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishido K., Ikeda Y. Preferential binding of RNA polymerase to the thymidylic acid-rich fragments obtained from bacteriophage fl DNA. J Biochem. 1970 Dec;68(6):881–884. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasedatelev A. S., Gursky G. V., Zimmer C., Thrum H. Binding of netropsin to DNA and synthetic polynucleotides. Mol Biol Rep. 1974 Mar;1(6):337–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00309567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Puschendorf B., Grunicke H., Chandra P., Venner H. Influence of netropsin and distamycin A on the secondary structure and template activity of DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 29;21(2):269–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman B. K. Purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 10;241(9):2035–2041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



