Abstract
Background
Transcriptomic studies in clinical research are essential tools for deciphering the functional elements of the genome and unraveling underlying disease mechanisms. Various technologies have been developed to deduce and quantify the transcriptome including hybridization and sequencing-based approaches. Recently, high density exon microarrays have been successfully employed for detecting differentially expressed genes and alternative splicing events for biomarker discovery and disease diagnostics. The field of transcriptomics is currently being revolutionized by high throughput DNA sequencing methodologies to map, characterize, and quantify the transcriptome.
Methods
In an effort to understand the merits and limitations of each of these tools, we undertook a study of the transcriptome in sickle cell disease, a monogenic disease comparing the Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST microarray (Exon array) and Illumina’s deep sequencing technology (RNA-seq) on whole blood clinical specimens.
Results
Analysis indicated a strong concordance (R = 0.64) between Exon array and RNA-seq data at both gene level and exon level transcript expression. The magnitude of differential expression was found to be generally higher in RNA-seq than in the Exon microarrays. We also demonstrate for the first time the ability of RNA-seq technology to discover novel transcript variants and differential expression in previously unannotated genomic regions in sickle cell disease. In addition to detecting expression level changes, RNA-seq technology was also able to identify sequence variation in the expressed transcripts.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that microarrays remain useful and accurate for transcriptomic analysis of clinical samples with low input requirements, while RNA-seq technology complements and extends microarray measurements for novel discoveries.
Keywords: Sickle cell disease, RNA-Seq, Exon arrays, Transcriptome, Clinical genomics
Background
With the completion of the human genome project, the monitoring of changes in the entire human transcriptome is an increasingly attractive method for dissecting the molecular basis of disease processes [1,2]. In this regard, the ability to utilize a patient’s transcriptome to detect the onset of disease, monitor its progression, and even to suggest treatment modalities with the highest probability of success would greatly enhance the quality of medical care and treatment [3-6]. Peripheral whole blood is a nucleic acid-rich and inflammatory cell-rich information reservoir. Analytical methodologies to detect transcriptomic changes in these cells may reveal novel biomarkers for disease diagnosis and treatment.
Until recently, high throughput microarray technologies have been the method of choice in clinical studies with limited amounts of RNA from blood samples, biopsy specimens, or enriched cell populations, to obtain gene expression profiles. The high density Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST array (Exon array) with 1.2 million probesets targeting every known and predicted exon in the entire genome has been successfully employed in clinical investigations for obtaining gene expression profiles and associated alternative splicing events in disease processes [7-9]. Despite these successes, inherent limitations in the dynamic range of arrays and the lack of complete coverage for detecting alternative splicing events have constrained the application of this technology.
With the advent of next-generation sequencing technologies, RNA-seq has emerged as a powerful tool for transcriptome analysis [10-12]. By mapping millions of RNA-seq reads to individual transcripts, estimation of expression levels of individual exons and whole transcripts can be performed. It is likely that the microarray-based (analog) gene-expression profiling technology will be replaced by digital sequencing based gene-expression profiling (RNA-seq) [8,13,14]. The purported advantages of RNA-seq include generation of expression data for individual annotated genes with nearly unlimited dynamic range; ability to comprehensively detect novel transcripts and mRNA variants resulting from alternative promoter usages, splicing, polyadenylation and sequence variation; and lowered background. However, the technology also brings with it new issues such as the requirement for large amounts of starting material, cumbersome library preparation; novel systematic biases during sample preparation and sequencing that must be accounted for when analyzing the data. Additionally, data processing of multireads and splice junctions have been problematic when mapping the sequences back to a genome.
Considering the merits and limitations of each of the technologies, we undertook the current study using complex whole blood specimens from patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) and matched healthy controls to address the following major questions:
(1). How do the technologies compare with regard to sensitivity, specificity, and variability of gene expression data? (2). Do the differentially expressed transcripts and alternatively spliced exons in SCD correlate well between RNA-seq and Exon arrays? (3). Does the abundant expression of globin transcripts in SCD interfere with RNA-seq analysis? (4). Are we able to discover novel differentially expressed transcripts in SCD using RNA-seq? (5). Can we detect sequence variants in the expressed transcripts?
Although previous comparative studies [15,16] have reported the advantages of RNA-Seq and microarrays, to our knowledge, our study is the first to use a human monogenic disease model to compare RNA-Seq and microarrays. We report here our observations on the SCD transcriptome from RNA-seq and Exon arrays with the belief that our findings will be useful to clinical investigators in choosing the appropriate genomic technique for understanding molecular mechanism of diseases for diagnosis and the development of novel therapeutics.
Methods
Subjects
The study was approved by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases institutional review board (NIH protocol 03-CC-0015) and written informed consents were obtained from study participants. Patients selected for this study included patients (n = 6) with sickle cell disease of mean age 41.6 ± 10.1 and the control group (n = 4) of self-identified African American subjects of mean age 42.2 ± 8.9, without sickle cell disease. The biosamples were collected in steady state condition and none of the individuals was receiving anti-platelet medication.
Isolation of RNA from whole blood specimens
Blood specimens (2.5 ml) collected in PAXgene™ tubes from each subject were incubated at room temperature for 4 h for RNA stabilization and then stored at − 80 °C. RNA was extracted from whole blood using the PAXgene™ Blood RNA System Kit following the manufacturer's guidelines. Briefly, samples were removed from −80 °C and incubated at room temperature for 2 hours to ensure complete lysis. Following lysis, the tubes were centrifuged for 10 min at 5,000 × g the supernatant was discarded and 500 μL of RNase-free water added to the pellet. The tube was vortexed thoroughly to re-suspend the pellet, centrifuged for 10 min at 5000 × g and the entire supernatant was discarded. The pellet was re-suspended in 360 μL of buffer BR1 by vortexing and further purification of RNA was done following the manufacturer's protocol with on-column DNase digestion. Quality of the purified RNA from was verified on an Agilent® 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA); RNA concentrations were determined using a NanoDrop® ND-1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE).
Total RNA from six SCD patients and four healthy controls were used for detailed analysis on RNA-seq and exon array platforms. Data analysis was carried out on 6 SCD and 3 healthy controls after removing a control sample which was identified to be an outlier based on principal component analysis (PCA) of the transformed data from RNA-seq.
Depletion of globin transcripts
Globin mRNA was depleted from a portion of each total RNA sample isolated from PAXgene tubes using the GLOBINclear™-Human kit (Ambion, Austin, TX). In brief 2 μg of total RNA from human whole blood was mixed with a biotinylated Capture Oligo Mix in hybridization buffer. The mixture was incubated for 15 minutes to allow the biotinylated oligonucleotides to hybridize with the globin mRNA species. Streptavidin magnetic beads were then added, to capture the globin mRNA and the magnetic beads were then pulled to the side of the tube with a magnet and the RNA, depleted of the globin mRNA, was transferred to a fresh tube. The RNA was further purified using a rapid magnetic bead-based purification method [17].
Preparation of biotinylated cDNA targets for exon array hybridizations in GCAS
50 ng RNA samples were amplified using the WT-Ovation™ Pico RNA Amplification System (NuGEN, San Carlos, CA) in a 3 step process as recommended by the manufacturer. All processes were performed in an automated manner using the genechip array station (GCAS). In brief, first strand cDNA was prepared using a unique first strand DNA/RNA chimeric primer mix and reverse transcriptase. In the second step, DNA/RNA Heteroduplex Double Stranded cDNA was generated which serves as the substrate for SPIA amplification - a linear isothermal DNA amplification process developed by NuGEN. RNase H degrades the RNA in the DNA/RNA heteroduplex at the 5´ end of the first cDNA strand exposing part of the unique priming site for the initiation of the next round of cDNA synthesis. The process of SPIA DNA/RNA primer binding, DNA replication, strand displacement and RNA cleavage is repeated, resulting in rapid accumulation of SPIA cDNA. Following amplification and purification, 3 μg of the amplified cDNA were processed with the WT-Ovation Exon Module to produce sense strand ST-cDNA. Following purification and quantitation, 5 μg ST-cDNA was fragmented and labeled with the FL-Ovation™ cDNA Biotin Module using a proprietary two-step fragmentation and labeling process. The first step is a combined chemical and enzymatic fragmentation process that yields single-stranded cDNA products in the 50 to 100 base range. In the second step, this fragmented product is labeled via enzymatic attachment of a biotin-labeled nucleotide to the 3-hydroxyl end of the fragmented cDNA generated in the first step. Hybridization, washing and laser scanning of Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST microarrays were performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA). Hybridization was performed at 45 °C overnight, followed by washing and staining using FS450 fluidics station. Scanning was carried out using the 7 G GCS3000 scanner.
Microarray data collection and annotation
Exon-level core RMA-sketch intensity values for each of the chips were collected using Affymetrix Expression Console (EC) Software (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA). The 284,258 core probesets were annotated using the Affymetrix annotation file from Netaffx (http://www.netaffx.com, HuEx-1_0-st-v2.na29.hg18.probeset.csv).
Analysis of exon arrays
Gene level intensity values were obtained by taking the average RMA values over probesets for each transcript cluster. A two sample t-test (SCD N1 = 6 and control N2 = 3) was computed on 9 samples in order to determine differential gene expression between SCD and controls. Microarray RMA values for each transcript cluster for each of 9 samples were submitted to a Principal Component Analysis in order to detect possible outliers. Alternative splicing analysis was computed using the ExonANOVA available from software developed by two of the authors, J.B and P.J.M (http://affylims.cit.nih.gov/MSCLtoolbox). The ExonANOVA model fits the following formula
| (1) |
to the data.
In the above formula, yijk is the log 2 expression intensity, i is treatment, j is replicate within treatment and k indexes exons. The μ is the mean and the two fixed factors are the treatment effect (A) and exon effect (C). The random factor (β) is the sample within treatment effect and (ϵ) is the error. The fixed interaction between treatment and exon (AC) models the alternative splicing event. In this study, the treatment effect is sickle cell or control. The significance of a detected alternatively spliced event is denoted p-AC. Alternatively spliced events are declared if p-AC < = 10^-8 and the maximum absolute interaction effect (maxik|ACik|) is greater than or equal to 2. A p-AC < = 10^-8 corresponds to less than 1% false discovery rate (FDR) using the method of Benjamini and Hochberg [18].
Library construction for RNA-seq
High quality total RNA at 1.5 μg was used for analysis on the Illumina GAII analyzer on six SCD samples and four healthy controls. cDNA library preparation and sequencing reactions were carried out using Illumina library prep, clustering and sequencing reagents following the manufacturer's recommendations (http://www.illumina.com). Briefly, mRNAs were purified using poly-T oligo-attached magnetic beads and then fragmented. The first and the second strand cDNAs were synthesized and end repaired. Adaptors were ligated after adenylation at the 3'-ends. After gel purification, cDNA templates were enriched by PCR. cDNA libraries were validated using a High Sensitivity Chip on the Agilent2100 Bioanalyzer™ (Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA). The samples were clustered on a flow cell using the cBOT. After clustering, the samples were loaded on the Illumina GA-II machine. The samples were sequenced using a single lane with 36 cycles. Initial base calling and quality filtering of the Illumina GA-II image data were performed using the default parameters of the Illumina GA Pipeline GERALD stage (http://www.illumina.com).
Mapping and analysis of RNA-seq data
The raw data Fastq sequence files obtained from GAII were mapped to the human genome (build HG18) to get genomic addresses using Bowtie/Tophat [19] allowing up to two mismatches. Reads that mapped to more than 10 locations were discarded. We obtained ~15.1 million reads per sample. We mapped reads both to exons of known RefSeq transcripts (human genome build 18) and to Affymetrix probe selection region coordinates. Reads mapped to Refseq exons and to Affymetrix probeset selection regions were counted using the CoverageBed method in BedTools [20]. Reads were counted for exons within each RefSeq transcript. In order to compare RNA-seq data fairly to the Exon microarray, we counted reads mapped to each probeset selection region (or probeset) within each exon.
Transcript cluster level reads were counted per probeset within each transcript cluster. Very low count transcript clusters (fewer than 6 samples with 6 or more counts) were ignored. This filtered out a total of 7,146 transcript clusters leaving 11,562 for further statistical analysis. In order to normalize the data, transcript cluster counts were divided by the median transcript cluster count for that sample, and logarithm base 10 transformed, yielding transformed, normalized counts. After principal component analysis (PCA) of the transformed data, one outlier, a control sample was detected and disregarded from further analysis leaving 9 samples. A two sample t-test (sickle cell N1 = 6, control N2 = 3) was used on the normalized, transformed data to test for differential expression. Alternative splicing analysis was computed using the ExonANOVA as with the microarrays data. A conservative and reasonable background limit at 4.5 RMA units was applied for Exon arrays and 1.0 in RPKM units as recommended by Mortazavi et al. [21] was applied for RNA_seq. The RMA level of 4.5 is slightly above the median RMA for detected exons (Affymetrix DABG value p < 0.01, Affymetrix’s recommendation for a conservative detection of exons).
In order to identify novel transcription events, we counted reads mapping to each 200 base pair region of the genome. Only populated bins (5 or more samples had 6 or more reads) bins were considered further. This filter retained 187,764 bins for analysis. We disregarded bins that fell within annotated RefSeq exons. The remaining 48,462 bins, describe novel, unannotated transcription events. To normalize these data, counts were divided by the 90th percentile of counts for that sample and base 10 logarithm transformed. p-values were required to be 0.0005 or less (corresponding to FDR < 0.15), and the fold-change was required to be 2-fold or greater. If differential expression was found, it was classified as a novel transcript.
Real time Q-PCR analysis
First-strand cDNA was synthesized using 500 ng of RNA and random primers in a 20 μl reverse transcriptase reaction mixture using Invitrogen’s Superscript cDNA synthesis kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) following the manufacturer’s directions. Quantitative real-time PCR assays were carried out on 11 differentially expressed genes from both the platforms with the use of gene-specific double fluorescently labeled probes in a 7900 Sequence Detector (PE Applied Biosystems, Norwalk, CT). Probes and primers were obtained from Applied Biosystems. In brief, PCR amplification was performed in a 384 well plate with a 20-μl reaction mixture containing 300 nm of each primer, 200 nm probe, 200 nm dNTP in 1x real time PCR buffer and passive reference (ROX) fluorochrome. The thermal cycling conditions were 2 min at 50° C and 10 min at 95° C, followed by 40 cycles of 15 sec denaturation at 95° C and 1 min annealing and extension at 60° C. Samples were analyzed in duplicate and the Ct values obtained were normalized to the housekeeping gene ß actin. The comparative CT (ΔΔ CT) method [22] which compares the differences in CT values between groups was used to achieve the relative fold change in gene expression between SCD and Controls.
Results
Principal component analysis
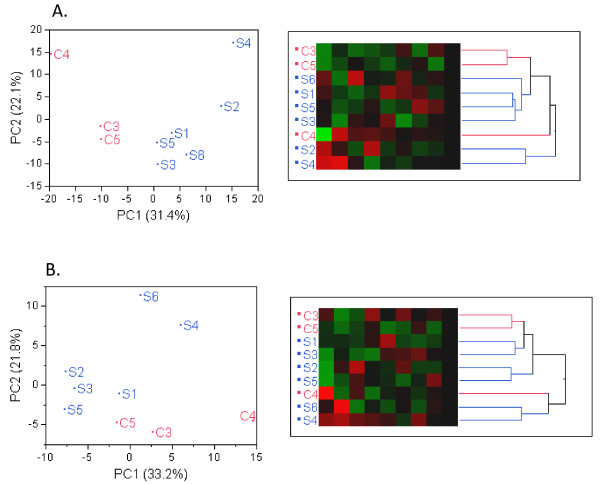
Principal component analysis was first used to identify outliers within the SCD and healthy controls groups. Figure 1A for RNA-seq data showed a clear segregation and clustering of SCD and healthy controls. Similarly with the Exon array analysis on the same set of samples, a clear separation of SCD patients and healthy controls was observed as depicted in Figure 1B. The first principal component (PC1) accounted for 31% of total variability in the RNA-seq data and 33% of total variability of Exon array data, and also fully separated the sickle cell group from the controls. Sample S6 displayed the largest value for the Affymetrix QC parameter all_probesets_rle_mean, a measure of hybridization quality, where larger values indicate lesser quality. This fact may explain the divergence of patterns observed in the two dendrograms
Figure 1 .
Principal component analysis and hierarchical clustering (A) RNA-seq data. Principal Component 1 (PC1, x-axis) represents 31.4% and PC2 (y-axis) represents 22.1% of total variation in the data. Hierarchical cluster of 9 samples with heatmap representing all 9 PCs in left-to-right order. (B). Exon array data. PC1 vs. PC2 on Exon array data together representing 33.2% and 21.8% of the data variability. Hierarchical clustering shows similarities to that in A, e.g. sample C4 departs strongly from remaining data, samples C3, C5 appear to be neighbors in both data sets.
Evaluation of dynamic range, within platform reproducibility - coefficient of variation and sensitivity
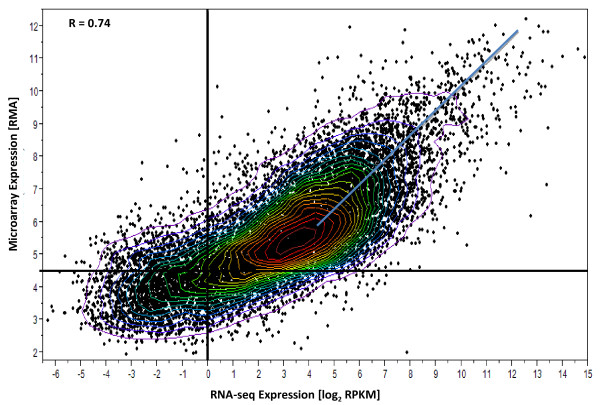
To assess the dynamic range (the ratio of the largest observable value to the background expression level (over all genes) of each platform, a scatter plot (Figure 2) was constructed using the results on control samples for each method. The base 10 logarithm of the RPKM values from RNA-seq (normalized for gene length) is plotted versus the base 10 logarithm of signal intensity values for Exon array. As can be seen from the figure, RNA-seq shows a larger dynamic range of expression when compared to the Exon array and the magnitude of this increased dynamic range varied from 4 to 16 fold according to the expression levels of differentially expressed genes.
Figure 2 .
Comparison of Gene Expression Measurements by Two Methods. Gene Microarray expression level (RMA) vs. RNA-seq expression level (log2 RPKM) for subject C3. Both axes are expressed in base 2 logarithmic scale. The dynamic range (ratio of largest observable value to apparent background value) of the RNA-seq data is clearly larger than that of Exon array data. Bivariate density contours indicate a strong but nonlinear correlation between the two measurements. The two methods yield nearly proportional results above the median expression levels (Blue line). Solid Black lines are detection limits for microarray (RMA = 4.5) and RNA-seq (log2RPKM =0). Refer Methods for the description of detection limits.
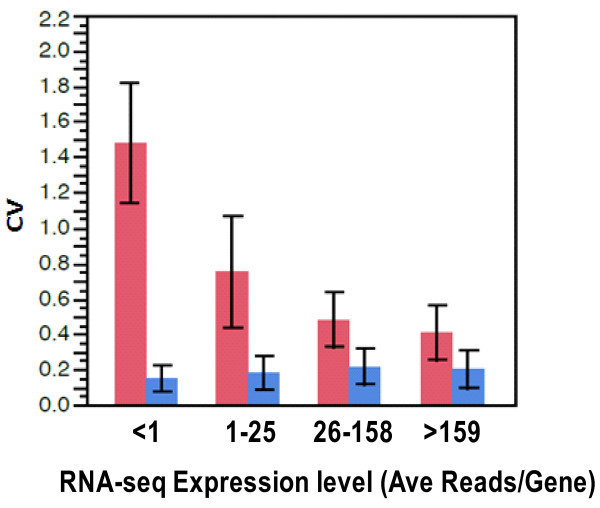
The technical reproducibility and coefficient of variation of the array and RNA-seq platforms at both the gene and exon levels was examined using the mean expression levels over all samples. The pooled coefficient of variation calculated over all samples were broken up into 4 bins (see Figure 3 legend) Figure 3 clearly shows that the coefficient of variation for exon array is much lower than that for RNA-seq and is also independent of the number of counts for each transcript suggesting that technical variability within group is higher in the RNA-seq platform than the arrays, especially for genes with low-expression thereby demonstrating the potential advantage of microarray in cases where the RNA-seq counts are very small. The RNA-seq CV drops to 40% for highly expressed genes while for the exon array the CV rises slightly, to about 20% . This difference is partly a consequence of the extended dynamic range for RNA-seq (or equivalently, the compressed dynamic range observed in microarray).
Figure 3 .
Coefficient of Variation (CV) versus expression level for microarray and RNA-seq. RNA-seq expression level is grouped inot 4 bins according to RNA-seq average number of reads per gene lesser than1, 1–25, 26–158, 159 or higher. CV is calculated as sample standard deviation of expression level within group (SCD and control), pooled and dvidied by mean expression level for RNA-seq (Red). For microarray (Blue), the expression values (RMA units) are first divided by ln (2) = 0.693 to convert them to a natural log scale. Then the CV is calculated as the pooled standard deviation of natural log of the expression levels.
With the expectation that deeper sequencing and large amounts of starting material are needed to adequately cover low abundance transcripts, we tested the sensitivity of each of the platforms by examining the expression of transcripts above background. With the application of conservative and reasonable background limits at 4.5 RMA units for Exon arrays and 1.0 in RPKM units for RNA_seq to one sample for a control subject C3 (Figure 2), we were able to detect 6% more transcripts (12,310/11,662 = 1.06) above background in exon arrays than in RNA-seq.
Differentially expressed genes in SCD
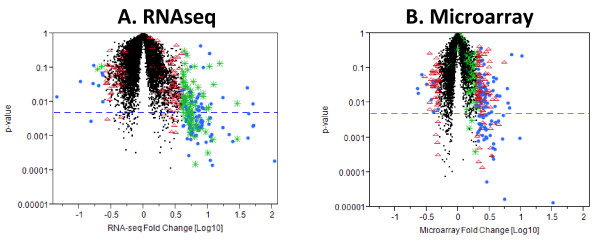
Global gene level expression analysis for each platform is shown in volcano plots (Figure 4). The fold changes from RNA-seq have generally larger magnitude than those from the arrays, with RNA-seq values ranging up to 100 fold, while with microarrays, we observed fold changes up to 31 fold. The relative magnitude of log fold changes can be clearly observed in Figure 4 and Figure 5, with RNA-seq reporting generally twice the log fold change compared with Exon array. In order to perform an unbiased comparative analysis of the two platforms and knowing that the microarrays have a compressed fold change, we chose two different conservative filters to select differentially expressed transcripts. We selected transcripts using different criteria for each method, specifically, requiring at least a 2-fold change in microarray data or a greater than 4-fold change in RNA-seq data. Altogether, 331 transcripts were found to be differentially expressed one or the other method, by these criteria. Many of these genes fell into pathways related to SCD including inflammatory response, oxidoreductase pathways, stress response, cell signaling and apoptosis (Table 1).
Figure 4 .
Volcano plots for RNA-seq and Exon array. (A). p-value vs. log10 fold change (SCD vs. control) for RNA-seq data.(B). p-value vs. log10 fold change for Affymetrix human Exon array data. Points in the lower right and lower left hand corners of the plots represent transcript clusters that are significant and differentially expressed. ●Blue circles represent transcripts with a FC greater or equal to 4 in RNA-seq and Δ Red triangles represent FC greater or equal to 2 in Exon arrays. *Green asterisks represent transcripts with a FC greater than or equal to 4 on RNA-seq only.
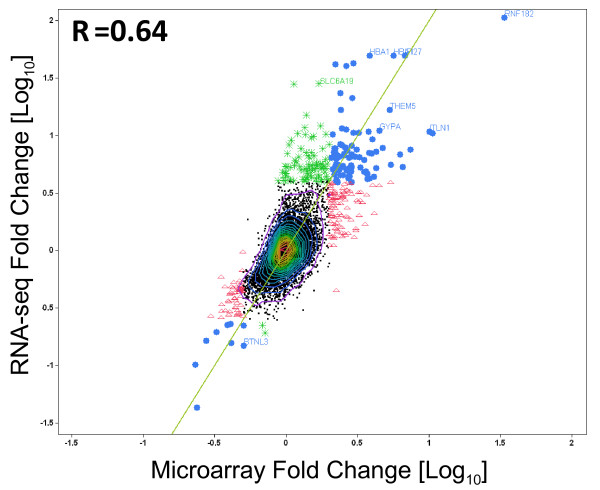
Figure 5 .
Fold change for RNA-seq vs. fold change for Exon array (SCD vs Control). A total of 331 transcript clusters are highlighted in the figure. The 96 blue circles ● represent transcripts with a FC greater than or equal to 4 in RNA-seq and a FC greater than or equal to 2 in microarray. The 151 red triangles ▴ represent transcripts with a fold change greater than or equal to 2 on microarray only. The 84 green asterisks * represent transcripts with a fold change greater than or equal to 4 in RNA-seq only. Correlation coefficient, R = 0.64. Genes showing greater than 4 fold change in expression levels were selected as differentially expressed in RNA-seq and genes showing greater than 2 fold change in expression levels were selected as differentially expressed in microarrays.
Table 1.
Selected Differentially Expressed Genes Grouped by Pathways of Interest
| Genes | Symbol | Gene Title |
FC RNA-seq |
FC MA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Apoptosis/cell cycle regulation | ||||
|
NM_005581 |
BCAM |
basal cell adhesion molecule |
12.27 |
1.73 |
|
NM_138578 |
BCL2L1 |
BCL2-like 1 |
5.44 |
1.45 |
|
NM_198892 |
BMP2K |
BMP2 inducible kinase |
4.09 |
1.93 |
|
NM_004331 |
BNIP3L |
BCL2 |
4.98 |
1.37 |
|
NM_014326 |
DAPK2 |
death-associated protein kinase 2 |
0.33 |
0.48 |
|
NM_001923 |
DDB1 |
damage-specific DNA binding protein 1, 127 kDa |
2.82 |
2.23 |
|
NM_001122665 |
DDX3Y |
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 3, Y |
1.29 |
3.00 |
|
NM_017631 |
DDX60 |
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 60 |
1.51 |
2.25 |
|
NM_019030 |
DHX29 |
DEAH (Asp-Glu-Ala-His) box polypeptide 29 |
1.29 |
2.07 |
|
NM_024940 |
DOCK5 |
dedicator of cytokinesis 5 |
0.43 |
0.50 |
|
NM_004864 |
GDF15 |
growth differentiation factor 15 |
4.77 |
0.99 |
|
NM_002094 |
GSPT1 |
G1 to S phase transition 1 |
4.03 |
1.34 |
|
Cell-signaling | ||||
|
NM_017436 |
A4GALT |
alpha 1,4-galactosyltransferase |
4.70 |
0.98 |
|
NR_024080 |
ACP1 |
acid phosphatase 1, soluble |
2.79 |
2.41 |
|
NM_015256 |
ACSL6 |
acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 6 |
6.96 |
2.24 |
|
NM_005622 |
ACSM3 |
acyl-CoA synthetase medium-chain family member 3 |
3.90 |
2.72 |
|
NM_001629 |
ALOX5AP |
arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein |
0.39 |
0.48 |
|
NM_020980 |
AQP9 |
aquaporin 9 |
0.48 |
0.37 |
|
NM_015313 |
ARHGEF12 |
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 12 |
3.42 |
2.49 |
|
NM_015994 |
ATP6V1D |
ATPase, H + transporting, V1 subunit D |
1.54 |
2.21 |
|
NM_199186 |
BPGM |
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase |
11.03 |
2.89 |
|
NM_020850 |
RANBP10 |
RAN binding protein 10 |
5.70 |
2.31 |
|
NM_001145657 |
RAP1GAP |
RAP1 GTPase activating protein |
42.05 |
2.58 |
|
NM_014737 |
RASSF2 |
Ras association (RalGDS |
0.45 |
0.47 |
|
NM_002923 |
RGS2 |
regulator of G-protein signaling 2, 24 kDa |
0.32 |
0.44 |
|
NM_000062 |
SERPING1 |
serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade G (C1 inhibitor) |
3.58 |
2.03 |
|
NM_001122752 |
SERPINI1 |
serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade I (neuroserpin), 1 |
1.47 |
3.07 |
|
NM_007111 |
TFDP1 |
transcription factor Dp-1 |
5.69 |
2.45 |
|
NM_003227 |
TFR2 |
transferrin receptor 2 |
5.67 |
1.42 |
|
NM_173804 |
TMEM86B |
transmembrane protein 86B |
5.22 |
1.39 |
|
NM_015049 |
TRAK2 |
trafficking protein, kinesin binding 2 |
5.51 |
3.24 |
|
NM_022066 |
UBE2O |
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2O |
7.13 |
2.83 |
|
Oxidative stress/antioxidants/Stress Response | ||||
|
NM_000032 |
ALAS2 |
aminolevulinate, delta-, synthase 2 |
4.36 |
1.66 |
|
NM_001128829 |
CA1 |
carbonic anhydrase I |
10.68 |
2.07 |
|
NM_000067 |
CA2 |
carbonic anhydrase II |
5.03 |
3.45 |
|
NM_016417 |
GLRX5 |
glutaredoxin 5 |
5.24 |
1.59 |
|
NM_201397 |
GPX1 |
glutathione peroxidase 1 |
8.02 |
2.16 |
|
NM_001145260 |
NCOA4 |
nuclear receptor coactivator 4 |
4.77 |
2.12 |
|
NM_002501 |
NFIX |
nuclear factor I |
5.73 |
1.73 |
|
NM_000274 |
OAT |
ornithine aminotransferase (gyrate atrophy) |
1.30 |
2.19 |
|
NM_030758 |
OSBP2 |
oxysterol binding protein 2 |
11.80 |
2.57 |
|
NM_032523 |
OSBPL6 |
oxysterol binding protein-like 6 |
4.70 |
2.45 |
|
NM_005809 |
PRDX2 |
peroxiredoxin 2 |
4.10 |
1.12 |
|
NM_006745 |
SC4MOL |
sterol-C4-methyl oxidase-like |
1.31 |
2.47 |
|
NM_138432 |
SDSL |
serine dehydratase-like |
6.58 |
1.21 |
|
NM_003944 |
SELENBP1 |
selenium binding protein 1 |
5.76 |
1.92 |
|
NM_175839 |
SMOX |
spermine oxidase |
5.09 |
2.78 |
|
NM_003794 |
SNX4 |
sorting nexin 4 |
1.43 |
2.29 |
|
NM_003105 |
SORL1 |
sortilin-related receptor, L(DLR class) A repeats |
0.48 |
0.41 |
|
NM_003227 |
TFR2 |
transferrin receptor 2 |
5.67 |
1.42 |
|
NM_022648 |
TNS1 |
tensin 1 |
4.21 |
1.05 |
|
Inflammatory Response | ||||
|
NM_005581 |
BCAM |
basal cell adhesion molecule (Lutheran blood group) |
12.27 |
1.73 |
|
NM_003965 |
CCRL2 |
chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 2 |
2.00 |
2.28 |
|
NM_012120 |
CD2AP |
CD2-associated protein |
2.30 |
2.20 |
|
NM_001001548 |
CD36 |
CD36 molecule (thrombospondin receptor) |
1.68 |
2.11 |
|
NM_152243 |
CDC42EP1 |
CDC42 effector protein (Rho GTPase binding) 1 |
8.43 |
1.04 |
|
NM_004344 |
CETN2 |
centrin, EF-hand protein, 2 |
2.85 |
2.46 |
|
NM_001008388 |
CISD2 |
CDGSH iron sulfur domain 2 |
7.29 |
3.91 |
|
NM_033554 |
HLA-DPA1 |
major histocompatibility complex, DP alpha 1 |
1.32 |
2.11 |
|
NM_002125 |
HLA-DRB5 |
major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 5 |
1.96 |
2.09 |
|
NM_001130080 |
IFI27 |
interferon, alpha-inducible protein 27 |
51.57 |
6.64 |
|
NM_006417 |
IFI44 |
interferon-induced protein 44 |
3.14 |
3.21 |
|
NM_006820 |
IFI44L |
interferon-induced protein 44-like |
3.86 |
5.37 |
|
NM_001548 |
IFIT1 |
interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide 1 |
3.04 |
2.62 |
|
NM_000576 |
IL1B |
interleukin 1, beta |
0.43 |
0.41 |
|
NM_004633 |
IL1R2 |
interleukin 1 receptor, type II |
0.17 |
0.27 |
|
NM_002182 |
IL1RAP |
interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein |
0.29 |
0.40 |
|
NM_002183 |
IL3RA |
interleukin 3 receptor, alpha (low affinity) |
0.52 |
0.49 |
|
NM_003024 |
ITSN1 |
intersectin 1 (SH3 domain protein) |
6.28 |
1.87 |
|
NM_003189 |
TAL1 |
T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 |
5.37 |
1.76 |
|
NM_017772 |
TBC1D22B |
TBC1 domain family, member 22B |
3.78 |
2.82 |
|
NM_152772 |
TCP11L2 |
t-complex 11 (mouse)-like 2 |
3.32 |
2.64 |
|
Red Cell genes | ||||
|
NM_020476 |
ANK1 |
ankyrin 1, erythrocytic |
4.04 |
1.62 |
|
NM_152326 |
ANKRD9 |
ankyrin repeat domain 9 |
9.23 |
1.08 |
|
NM_001728 |
BSG |
basigin (Ok blood group) |
5.01 |
1.50 |
|
NM_016633 |
ERAF |
erythroid associated factor |
9.64 |
3.91 |
|
NM_001017922 |
ERMAP |
erythroblast membrane-associated protein |
3.86 |
2.05 |
|
NM_001012515 |
FECH |
ferrochelatase (protoporphyria) |
8.10 |
2.56 |
|
NM_002099 |
GYPA |
glycophorin A (MNS blood group) |
11.49 |
4.40 |
|
NM_002100 |
GYPB |
glycophorin B (MNS blood group) |
7.43 |
2.11 |
|
NM_198682 |
GYPE |
glycophorin E |
6.67 |
2.70 |
|
NM_000558 |
HBA1 |
hemoglobin, alpha 1 |
51.86 |
5.54 |
|
NM_000518 |
HBB |
hemoglobin, beta |
28.47 |
1.12 |
|
NM_000519 |
HBD |
hemoglobin, delta |
44.50 |
2.88 |
|
NM_005330 |
HBE1 |
hemoglobin, epsilon 1 |
24.48 |
2.34 |
|
NM_000559 |
HBG1 |
hemoglobin, gamma A |
43.18 |
2.17 |
|
NM_001003938 |
HBM |
hemoglobin, mu |
3.75 |
2.04 |
|
NM_005332 |
HBZ |
hemoglobin, zeta |
8.72 |
2.34 |
|
NM_018437 |
HEMGN |
hemogen |
5.83 |
2.18 |
|
NM_000420 |
KEL |
Kell blood group, metallo-endopeptidase |
4.59 |
1.67 |
|
NM_006563 |
KLF1 |
Kruppel-like factor 1 (erythroid) |
6.76 |
1.41 |
|
Novel Genes | ||||
|
NM_007021 |
C10orf10 |
chromosome 10 open reading frame 10 |
10.26 |
1.35 |
|
NM_001009894 |
C12orf29 |
chromosome 12 open reading frame 29 |
1.39 |
2.71 |
|
NM_014059 |
C13orf15 |
chromosome 13 open reading frame 15 |
2.22 |
2.03 |
|
NM_025057 |
C14orf45 |
chromosome 14 open reading frame 45 |
4.54 |
4.02 |
|
AK303128 |
C17orf99 |
chromosome 17 open reading frame 99 |
5.43 |
1.24 |
|
BC038410 |
C1orf105 |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 105 |
6.00 |
1.16 |
|
NM_020362 |
C1orf128 |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 128 |
5.23 |
2.58 |
|
NM_015680 |
C2orf24 |
chromosome 2 open reading frame 24 |
4.06 |
1.75 |
|
NM_001042521 |
C2orf88 |
chromosome 2 open reading frame 88 |
5.41 |
2.19 |
|
NM_001002029 |
C4B |
complement component 4B |
4.22 |
1.37 |
|
NM_000715 |
C4BPA |
complement component 4 binding protein, alpha |
0.04 |
0.23 |
|
NM_001128424 |
C4orf18 |
chromosome 4 open reading frame 18 |
1.35 |
2.60 |
|
NM_032412 |
C5orf32 |
chromosome 5 open reading frame 32 |
3.04 |
2.12 |
|
NM_032385 |
C5orf4 |
chromosome 5 open reading frame 4 |
7.20 |
2.18 |
|
NM_052831 |
C6orf192 |
chromosome 6 open reading frame 192 |
2.08 |
2.36 |
| NR_027330 | C7orf54 | chromosome 7 open reading frame 54 | 0.67 | 0.49 |
* Differentially expressed genes were selected if they showed greater than 4-fold change (SCD v Control) in RNAseq or greater than 2-fold change in Microarray.
Of the 331 selected transcripts, 84 transcripts pass only the RNA-seq filter, 151 transcripts pass only the exon array filter and 96 transcripts pass both (Figure 6). Of the 331 transcripts, only 11 (3.3%) were discordant in their direction of change as measured by the two methods and none of these were among the 96 passing both filters. The cross platform correlation for the differential expression (Figure 5) was substantial (r = 0.64), indicating that the two methods give highly similar results overall. With the additional requirement of statistical significance p < 0.005 corresponding to FDR <24% for RNA-seq and FDR < 35% for Exon array, only 112 transcripts showed changes in one or both methods. Of these, 54 showed differential expression only in RNA-seq, 27 showed differential expression in only Exon array, and 31 showed differential expression in both methods.
Figure 6 .
Venn diagram showing the 331 differentially expressed genes between SCD and Healthy Controls for RNA-seq and microarray. Gene selection Criteria for RNA-Seq -FC greater than or equal to 4; Exon array -FC greater than or equal to 2.
Genes identified as differentially expressed in SCD were subjected to gene ontology enrichment analysis to determine their molecular functions. This analysis selected 10 highly significant functional pathways including cell cycle regulators, apoptosis, oxidative stress response, inflammation and immune response, free radical scavenging, protein modification, and hematopoiesis. (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Examination of these pathways suggests that these differentially regulated genes are consistent with the homeostatic response to known pathobiological stresses in SCD, including oxidative and hemolytic stress, vascular injury, and participation in repair. We also observed upregulated expression of several reticulocyte specific genes such as ankyrin1, erythroid associated factor, hemoglobins, nuclear associated factor, glycophorin, transferrin receptor, and selenium binding protein, as expected with prominent reticulocytosis in SCD, thereby validating the performance of the two technologies in identifying biological alterations in the sickle cell disease model.
Effect of globin reduction on RNA-seq data quality
Currently, RNA-seq requires enrichment steps to select Poly A RNA for library construction from total RNA. Since ribosomal RNA represents over 90% of the RNA within a given cell, studies have shown that its removal increases the sensitivity to retrieve data from the remaining portion of the transcriptome. In large clinical studies where whole blood PAXgene RNA is used, there is an additional interference by the high levels of globins in whole blood RNA. This is further complicated in hematologic diseases such as sickle cell where globins account for more than 70% of mRNA.
In order to determine if globins interfere with the sequence reads and affect the sensitivity of transcriptome analysis on RNA-seq platform, we reduced the globins on one sickle cell patient sample and compared the globin reduced and non-reduced samples on RNA-seq. Scatter plot analysis of the normalized transcript read counts for these two samples showed a high correlation (R = 0.93, Additional file 2: Figure S2). This suggests that the globin transcripts in the sickle cell sample do not affect the sequence reads and do not introduce much bias in the analysis.
Validation by QPCR analysis
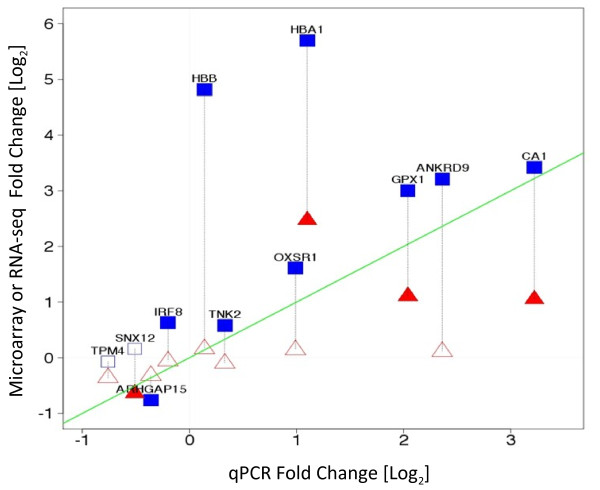
Taqman analysis was used to validate 11 selected differentially expressed genes identified by one or both the microarray and RNA-seq platforms. The concordance of each platform with QPCR analysis was measured by Pearson’s correlation on the fold changes. A good degree of correlation was observed for most of the genes across the three platforms (Additional file 3: Table S2). RNA-seq and QPCR showed a correlation R = 0.6; while QPCR and Exon array revealed a correlation of R = 0.58. The line of identity shown in Figure 7 illustrates the concordance between the platforms. The most highly correlated genes between the platforms are those that lie closest to the line of identity in the figure. Genes IRF8, SNX12, and TPM 4 showed directional discrepancy between microarray and RNA-seq, however QPCR analysis corroborated the microarray data for those genes. Conversely, QPCR analysis of gene TNK2, which was found to be up-regulated by RNA-seq and down regulated by Exon array, corroborated the RNA-seq analysis.
Figure 7 .
Validation by QPCR - Log2 expression fold change (SCD vs. Control) measured by microarray (Red) or RNA-seq (Blue) vs. qPCR on selected genes. Closed symbols represent significant changes, open signals are not significant. The green line is the line of identity. Symbols closer to the line of identity are in better agreement with QPCR. ▴Significantly differentially expressed genes by microarray, ■Significantly differentially expressed genes by RNA-seq; Δ No significance in microarray; □No significance in RNA-seq.
Detection of alternatively spliced exons
Using ExonAnova analysis and filtering criteria as set forth in the Methods section, we were able to identify 16 genes displaying alternative splicing using the RNA-seq platform including ATF6B, BCL6, CARM1, CCNDBP1, COX4I1, DCTN2, HPS1, INPP5D, INSIG1, NUDT, NUDT4P1, RHCE, RHD, TNXA, TNXB, and UNC13D as shown in Table 2. Exon array, on the other hand was able to identify only HBA1 as a significantly alternatively spliced gene while the other genes did not meet the statistical filter for splicing.
Table 2.
Highly Significant Alternatively Spliced Genes
| Symbol | GeneTitle | Molecular Functions | RNAseq | MA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Splicing Index |
|
| ATF6B* |
activating transcription factor 6 beta |
Cell Death/Immune Response |
0.49* |
0.17 |
| BCL6* |
B-cell CLL |
Apoptosis/Immune Response |
0.68* |
0.07 |
| CARM* |
coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 |
Cell Development/Differentiation |
0.40* |
0.12 |
| CCND* |
cyclin D-type binding-protein 1 |
Cell Cycle |
0.63* |
0.13 |
| COX4I* |
cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV iso1 |
Cellular Development/Compromise |
0.89* |
0.04 |
| DCTN* |
dynactin 2 (p50) |
Cellular Movement |
0.47* |
0.08 |
| HPS1* |
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 1 |
Inflammatory Response; Cell Signaling |
0.39* |
0.15 |
| INPP5* |
inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase |
Cell-Cell Signaling |
0.49* |
0.07 |
| INSIG1* |
insulin induced gene 1 |
Lipid metabolism, Molecular Transport |
0.52* |
0.09 |
| NUDT* |
nudix type motif 4 |
Cell signaling; Hematopoiesis |
0.37* |
0.16 |
| NUDT* |
nudix motif 4 pseudogene |
Cell signaling; Hematopoiesis |
0.37* |
0.16 |
| RHCE* |
Rh blood group, CcEe antigens |
Agglutination of red blood cells |
0.54* |
0.18 |
| RHD* |
Rh blood group, D antigen |
Agglutination of red blood cells |
0.54* |
0.18 |
| TNXA* |
tenascin XA (pseudogene) |
Cellular Assembly |
0.49* |
0.17 |
| TNXB* |
tenascin XB |
Cellular Assembly |
0.49* |
0.17 |
| UNC13* |
unc-13 homolog D |
Cell Signaling |
0.76* |
0.10 |
| HBA1** | hemoglobin, alpha 1 | Transport of oxygen | 0.09 | 0.57** |
* Selected genes from RNA-Seq with P < 0.00000001.
** Selected Genes from Microarray with P < 0.00000001.
Discovery of novel transcripts to be differentially expressed in SCD
RNA-seq technology is capable of discovering novel transcripts and novel isoforms as it is not constrained to measure only pre-defined transcripts, as is the microarray. Instead of mapping reads to known transcripts, we mapped reads to the entire genome, and collected them into 200 base pair bins (see Methods) to identify such novel transcripts. We identified 86 novel regions that manifest a significant (p < 0.005; 15% FDR), greater than 2-fold change between sickle cell disease and control groups (Table 3).
Table 3.
Highly Significant Novel Differentially Expressed 200 bp Regions
| Chromosome | Start-Base −1 | End- Base 200 | Fold Change | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr1 |
203465800 |
203465999 |
18.69 |
0.00005 |
| chr1 |
246094400 |
246094599 |
12.84 |
0.00018 |
| chr1 |
144990000 |
144990199 |
4.96 |
0.00016 |
| chr1 |
209819000 |
209819199 |
4.93 |
0.00022 |
| chr1 |
554400 |
554599 |
0.44 |
0.00050 |
| chr1 |
91770600 |
91770799 |
0.43 |
0.00030 |
| chr1 |
157083400 |
157083599 |
0.33 |
0.00034 |
| chr1 |
159838000 |
159838199 |
0.26 |
0.00025 |
| chr2 |
177785200 |
177785399 |
9.45 |
0.00049 |
| chr2 |
128992200 |
128992399 |
5.46 |
0.00038 |
| chr2 |
91411400 |
91411599 |
3.38 |
0.00037 |
| chr2 |
175293200 |
175293399 |
0.50 |
0.00037 |
| chr2 |
207652800 |
207652999 |
0.35 |
0.00012 |
| chr3 |
76567600 |
76567799 |
0.49 |
0.00029 |
| chr4 |
154075400 |
154075599 |
10.11 |
0.00029 |
| chr4 |
38368600 |
38368799 |
9.62 |
0.00004 |
| chr4 |
154075800 |
154075999 |
7.75 |
0.00005 |
| chr4 |
146763600 |
146763799 |
4.91 |
0.00035 |
| chr4 |
146765600 |
146765799 |
4.82 |
0.00018 |
| chr4 |
111338400 |
111338599 |
4.66 |
0.00028 |
| chr4 |
146516600 |
146516799 |
0.39 |
0.00014 |
| chr4 |
26043400 |
26043599 |
0.38 |
0.00045 |
| chr5 |
176439200 |
176439399 |
5.84 |
0.00048 |
| chr5 |
138854200 |
138854399 |
5.30 |
0.00014 |
| chr5 |
138856400 |
138856599 |
3.34 |
0.00006 |
| chr5 |
177142200 |
177142399 |
3.10 |
0.00046 |
| chr5 |
43623000 |
43623199 |
0.46 |
0.00018 |
| chr5 |
99410000 |
99410199 |
0.26 |
0.00010 |
| chr6 |
53038000 |
53038199 |
10.59 |
0.00015 |
| chr6 |
151297600 |
151297799 |
5.46 |
0.00021 |
| chr6 |
28212400 |
28212599 |
2.43 |
0.00004 |
| chr7 |
55681200 |
55681399 |
3.73 |
0.00047 |
| chr7 |
5567000 |
5567199 |
0.48 |
0.00041 |
| chr7 |
139365000 |
139365199 |
0.35 |
0.00034 |
| chr8 |
41761600 |
41761799 |
8.49 |
0.00001 |
| chr8 |
41762200 |
41762399 |
6.42 |
0.00046 |
| chr8 |
130922200 |
130922399 |
0.34 |
0.00033 |
| chr9 |
35101200 |
35101399 |
22.26 |
0.00009 |
| chr9 |
35101400 |
35101599 |
18.75 |
0.00019 |
| chr9 |
5101000 |
5101199 |
3.04 |
0.00020 |
| chr9 |
79521600 |
79521799 |
0.38 |
0.00020 |
| chr9 |
79523600 |
79523799 |
0.36 |
0.00014 |
| chr10 |
13766600 |
13766799 |
12.54 |
0.00002 |
| chr10 |
91112400 |
91112599 |
11.27 |
0.00042 |
| chr10 |
75248600 |
75248799 |
0.37 |
0.00000 |
| chr10 |
81901200 |
81901399 |
0.35 |
0.00036 |
| chr11 |
5225800 |
5225999 |
24.75 |
0.00001 |
| chr11 |
94542200 |
94542399 |
2.35 |
0.00002 |
| chr11 |
117571400 |
117571599 |
0.37 |
0.00034 |
| chr11 |
6193200 |
6193399 |
0.34 |
0.00012 |
| chr12 |
111304400 |
111304599 |
9.16 |
0.00022 |
| chr12 |
105247200 |
105247399 |
7.71 |
0.00033 |
| chr12 |
88443200 |
88443399 |
3.83 |
0.00014 |
| chr12 |
62331800 |
62331999 |
0.47 |
0.00032 |
| chr13 |
74302000 |
74302199 |
7.60 |
0.00014 |
| chr13 |
18137800 |
18137999 |
3.88 |
0.00013 |
| chr14 |
65417400 |
65417599 |
6.12 |
0.00029 |
| chr14 |
65417000 |
65417199 |
5.15 |
0.00033 |
| chr14 |
52176600 |
52176799 |
0.36 |
0.00046 |
| chr15 |
72689200 |
72689399 |
11.91 |
0.00011 |
| chr15 |
72678200 |
72678399 |
6.26 |
0.00018 |
| chr15 |
72688400 |
72688599 |
6.17 |
0.00014 |
| chr15 |
72687200 |
72687399 |
5.89 |
0.00028 |
| chr15 |
79393000 |
79393199 |
0.43 |
0.00002 |
| chr17 |
39736800 |
39736999 |
9.65 |
0.00025 |
| chr17 |
39632800 |
39632999 |
3.77 |
0.00047 |
| chr17 |
35692200 |
35692399 |
0.43 |
0.00047 |
| chr18 |
14383400 |
14383599 |
3.15 |
0.00016 |
| chr19 |
51317000 |
51317199 |
7.49 |
0.00019 |
| chr19 |
56938000 |
56938199 |
0.31 |
0.00035 |
| chr20 |
55405400 |
55405599 |
13.85 |
0.00012 |
| chr20 |
30909600 |
30909799 |
0.44 |
0.00014 |
| chr20 |
1403000 |
1403199 |
0.29 |
0.00036 |
| chr21 |
14058800 |
14058999 |
4.92 |
0.00006 |
| chr22 |
29607600 |
29607799 |
12.14 |
0.00048 |
| chr22 |
35263200 |
35263399 |
6.35 |
0.00047 |
| chr22 |
43511000 |
43511199 |
2.97 |
0.00018 |
| chr22 |
20569800 |
20569999 |
0.45 |
0.00029 |
| chr22 |
22898800 |
22898999 |
0.34 |
0.00010 |
| chrM |
12600 |
12799 |
0.44 |
0.00026 |
| chrX |
55067400 |
55067599 |
5.80 |
0.00033 |
| chrX |
125434800 |
125434999 |
0.50 |
0.00005 |
| chrX |
143984400 |
143984599 |
0.41 |
0.00005 |
| chrX |
1389000 |
1389199 |
0.34 |
0.00037 |
| chrY |
3611200 |
3611399 |
8.93 |
0.00011 |
| chrY | 1389000 | 1389199 | 0.34 | 0.00037 |
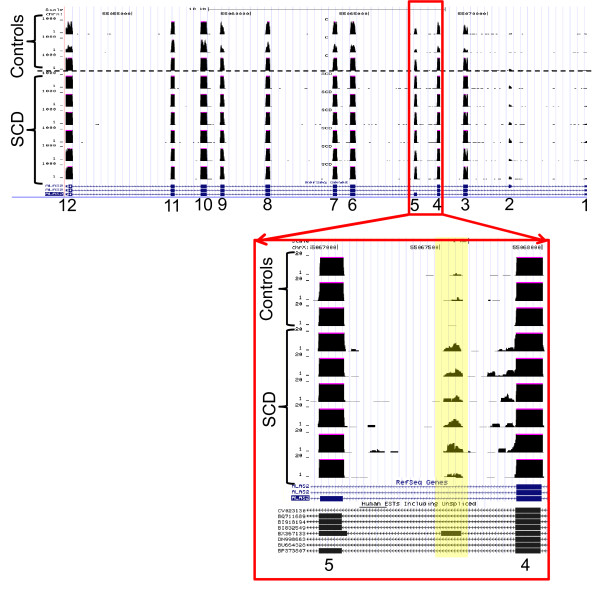
One novel region was found within the differentially expressed ALAS2 gene. Figure 8A shows the high expression levels detected for each exon of that gene. Based on the known exons, the computed expression change was 4 fold. One 200 bp region (Table 3, chrX:55067400–55067599) falls between exons 4 and 5, and showed a significant (P < 0.0003), 6 fold expression change, but with expression levels that are nearly invisible in the context of the surrounding exons (Figure 8). Figure 8 and the Additional file 4: Figure S3 (zoomedin exon 4A) show that expression is in fact present in this region for the SCD patients but nearly completely absent in controls. Curiously, expression in this apparently novel region has been previously observed in a single EST derived from T-cells (EST BX367133). It is likely that this represents a rarely used, alternative exon for the ALAS2 gene with greater expression in SCD (6-fold vs 2-fold). Similarly, 200 bp bin analysis showed several differentially expressed regions in chromosomes X, Y, M, 1–12, 19, 20 and 22 and these regions mapped to mitochondrial genes with some regions representing psuedogenes. These results are shown in Table 3. Additional file 5: Table S1 shows few examples of the alignment of sequences by BLAST.
Figure 8 .
Coverage Plot of RNA-seq data forALAS2 gene RNA-seq reads forALAS2 gene are shown in genomic context (chrX:55,051,744-55,074,222). An apparently novel exon dubbed 4a, between exons 4 and 5 is expressed significantly more in SCD compared with controls (p = 0.0003). This exon has been previously observed as human EST BX367133, in a clone derived from T cells. The inset shows the region bounded by exons 4 and 5 with the coverage range expanded and truncated to 20 for each track.
Analysis for sequence variation in expressed transcripts
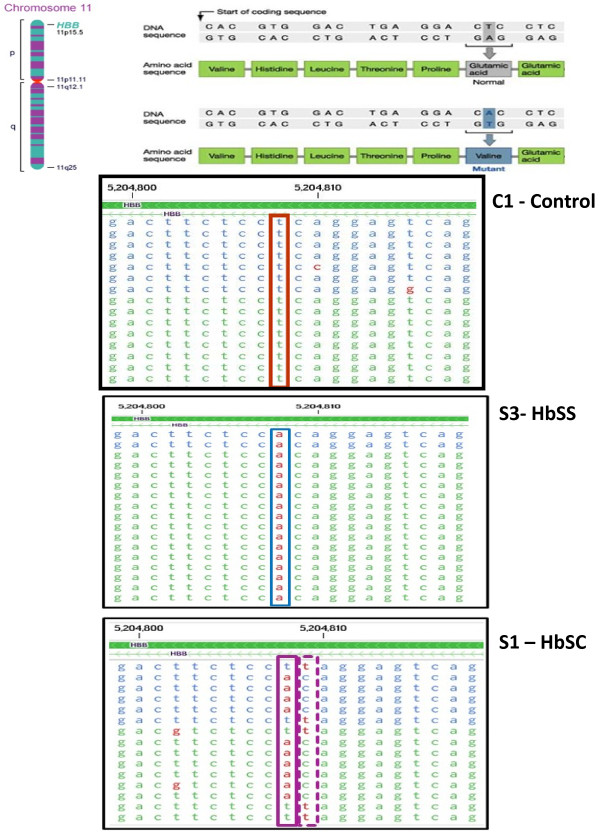
RNA-seq is an attractive method that enables the identification of sequence variations in expressed transcripts. To illustrate the feasibility of identifying sequence variation in expressed genes, we visualized the sequence of reads from the beta globin gene (DNAnexus, https://dnanexus.com/) for SCD and control subjects in the neighborhood of the known single mutation driving sickle cell disease. In SCD, glutamic acid (coded by CTC) is replaced by Valine (coded by CAC). Figure 9 clearly identifies this mutation in the sickle cell sample as compared to the controls. Interestingly, one of our sickle cell patients (S1) was a compound heterozygous hemoglobin SC patient and the heterozygosity in this patient is clearly seen in Figure 9. This demonstrates the ability of the RNA-seq technology to identify sequence variation in the expressed transcripts that would not be detected in the microarray analysis.
Figure 9 .
Analysis of sequence variants in the expressed hemoglobin transcript in a Healthy Control – (C1), and Homozygous (S3-HbSS) and Heterozygous (S1-HbSC) Sickle Cell Patients Observed sequences of HBB (hemoglobin B) gene in the region including the known sickle cell mutation, which causes a substituion of valine (coded by CAC) for glutamic acid (coded by CTC). The box for the reads from sample C1 - control, show the observed sequences (on the coding strand, but in reversed order) and are consistently T at the mutation position. The box for sample S3 - HbSS shows the consistent substitution of A at this same position. The box for sample S1 - HbSC show approximately 50% substitution of A for T at this position, and an additional mutation at the neighboring postion C- > T. This sample was revealed to be from a compound heterozygous hemoglobin SC patient.
Discussion
Whole transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) is a powerful transcriptional profiling technology using next generation sequencing platforms [4,23-25] and has signaled a new age in clinical genomics. Several recent studies have indicated that RNA-seq will be more useful than the current microarray technology due to the increased dynamic range of signal of sequencing [4,26-28] and its ability to identify the exact location of transcription boundaries at single base resolution. RNA-seq also provides the sequence information needed to identify single nucleotide variants, map variant transcription start sites, and detect novel transcript splicing. These features make RNA-seq particularly useful for studying complex transcriptomes, such as those found in the clinical blood samples.
Although attractive, clinical application of RNA-seq is feasible only if the tool can demonstrate high specificity, sensitivity and reproducibility with limited amount of starting material. Although current technology for transcriptome sequencing requires at least 100 ng total RNA (tens of thousands of cell equivalents), along with additional enrichment steps to select for poly(A) + RNA and/or to reduce the content of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) prior to NGS library construction, to minimize the loss of input material researchers tend to start with a minimum of 1 microgram total RNA. The utility of RNA-seq data generated is believed to be sensitive to read length, mapping and assembly of reads and statistical and computational challenges. However, with the current availability of substantially improved mapping software, these challenges are expected to be well tackled. Microarrays, on the other hand, are known to suffer from reduced dynamic range of signals due to saturation biases and high background, and non-specific or cross-hybridization resulting in false-positive signals, especially for transcripts that have low expression levels.
Considering these challenges inherent to each of the high throughput platforms, we undertook this comparative study in an attempt to better understand the relative merits of high density exon microarrays and RNA-seq for biomarker discovery in the clinical setting. We chose the sickle cell disease because strong differential expression has been previously observed, and the phenotype of the disease is in manifested in blood, an accessible tissue for study. Sampling whole blood, a globin abundant tissue, allowed us to examine the potential interference of high abundant globin transcripts during sequencing and also to potentially discover novel genes that are associated with sickle cell disease from cell types such as nucleated red cells in addition to the conventional peripheral blood mononuclear cells. We believe that this is the first study that has compared the 2 platforms on a monogenic human disease model using easily accessible whole blood clinical specimens mimicking a large scale clinical research project.
In this study we used 50 ng of total RNA on exon arrays without any globin reduction or poly(A) + enrichment to identify differentially expressed genes and alternative splicing events in sickle cell disease. The same samples were also analyzed by RNA-seq using 1.5 micrograms of total RNA. RNA-seq analysis generated an average of 83% mappable reads from the whole blood samples after poly(A) + enrichment. The globin reduction process had insignificant effect on the mappable read count, even for sickle cells samples which have high levels of globin RNA suggetsing that it is not necessary to reduce the globins while analyzing whole blood samples by RNA-seq.
As expected, comparison of the dynamic range of the two platforms confirmed that RNA-seq has a dramatically larger range varying from 4 to 16 fold. This enticing feature of RNA-seq effectively removes the saturation biases inherent to the array platform. Examination of the technical reproducibility and coefficient of variation of the array and RNA-seq platforms at the gene and exon levels, as a function of the mean expression level, indicated that the coefficient of variation for microarray is much lower than that for RNA-seq and is also independent of the expression level for each transcript, suggesting that technical variability within group is higher in the RNA-seq platform than the arrays. A similar observation has been reported by Marioni et al. [15]. They observed extremely high CVs when the read counts were low, a domain where Poisson counting error dominates in RNA-seq. In this domain, microarray produces moderately low CV (20%), suggesting that microarray may in fact be more effective at detecting expression changes for low-abundance genes.
Our comparative analysis of detection sensitivity with material from clinical samples revealed that even with the usage of 30 times less starting material (50 ng vs 1.5 micrograms) Exon arrays could detect as many transcripts above background as in RNA-seq. It should be noted that the sequencing depth in this study (~10 million reads) is comparable with most published RNA-seq studies. Xu and others [29] from their comparative study using GG Exon arrays to RNA-seq reported that although both platforms detect similar expression changes at the gene level, the Exon array is more sensitive at the exon level and deeper sequencing is required to adequately cover low abundance transcripts [29]. It should be mentioned here that with the latest much improved sequencing instruments, it would be easier to generate ~ 80 million reads and this would substantially increase the sensitivity of detection in RNA-seq platform.
We found 331 transcripts with differentially expressed transcripts in SCD. These included genes involved in pathways related to sickle cell disease such as inflammatory response, oxidoreductase pathways, stress response, cell signaling and apoptosis. Of these 331 transcripts which showed a high degree of correlation (R = 0.64), 96 genes were identified by both the technologies. A similar observation has also been reported by correlating gene expression arrays and RNA-seq on their study on differentially expressed liver and kidney tissues [15]. Only 11 genes out of the 331 genes from the current study showed an opposite trend in differential expression in sickle cell disease, suggesting that the number of false positives was small, using either method.
Gene ontology analysis of these genes helped to classify their molecular functions into ten highly significant functional pathway such as cellular cycle regulators, apoptosis, oxidative stress response, inflammation and immune response, free radical scavenging, protein modification, and hematopoiesis. Examination of these pathways suggests that differentially regulation may be in response to oxidant and hemolytic stress, vascular injury and participation in repair and homeostasis [17,30-34]. Interestingly, GDF15 expression was upregulated, which also has been observed in thalassemia intermedia, and associated with repression of hepcidin, an important mediator of the inflammatory response on erythropoiesis [35].
We also observed upregulated expression of several reticulocyte specific genes as expected in SCD where a higher proportion of reticulocytes are observed. This finding validates the performance of both technologies in identifying alterations relevant to sickle cell disease. From a biological perspective, the whole blood expression profile provided a window into real time erythrocyte expression profiles. Insights into the transcription profile of these red blood cells may contribute greatly to our understanding of mechanism of disease, prognosis, and responses to therapeutics.
Using ExonAnova analysis on RNA-seq data, we identified 16 alternatively spliced genes. While further validation of these splice variants is needed, it is interesting to note that both RHCE and RHD are components of the important Rh antigen system on red cells. However the potential implications of altered Rh splicing in SCD is still unclear. Deficiency of UNC13D is known to result in defective exocytosis of cytolytic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, causing immune dysregulation [36]. Whether altered expression of UNC13D in SCD could contribute to the relative immune compromise of SCD may merit future investigation.
To illustrate the power of RNA-seq in detecting differential transcription not associated with known genes, we scanned the entire genome for novel differential expression focusing only on unannotated genomic regions. By doing so, we found an interesting region to include an apparently novel, minor exon between exons 4 and 5 in the ALAS2 gene with SCD patients showing at least six times higher expression levels compared to the control subjects (p = 0.003). This could suggest alternative splicing in SCD which might serve as an ALAS2 transcription regulator. Follow up of this suggestion would require a functional analysis of this newly identified region of ALAS2 but is beyond the scope of the current study but is planned for the future. ALAS2 gene expression is restricted to the erythroid lineage [37] and plays a pivotal role in heme synthesis. In addition to heme-mediated feedback inhibition of enzymatic function, ALAS-2, a member of a small family of genes is modulated by iron [38]. This ability of RNA-seq to identify regions in detail holds great promise for the future discovery of novel transcripts and biomarkers in clinical genomic studies.
Another key advantage of RNA-seq over existing technologies for transcriptomic studies is its ability to identify sequence variations in expressed transcripts. To illustrate the feasibility of identifying sequence variation in expressed genes, we focused on the known single nucleotide mutation in SCD in which glutamic acid-6 is replaced by valine (GAG replaced by GTG). We were able to successfully detect this mutation in all the sickle cell patients. Interestingly, we were also able to identify, that same mutation in heterozygous combination with a hemoglobin C beta globin variant having glutamic acid replaced by lysine (GAG replaced by AAG) in one compound heterozygous sickle cell patient, thereby demonstrating the ability of RNA-seq to reliably identify heterozygous single base mutations in the expressed transcripts.
In conclusion, our study clearly illustrates a high level of concordance between the array platform and the RNA-seq technology, and suggests that the high density Exon array still remains a powerful tool to generate meaningful data when the amount of material is limited. Although RNA-seq is still in the early stages of use in clinical studies, it has clear advantages over the array based transcriptomic methods, based on its ability to discover novel transcripts, identify sequence variants, and increased dynamic range of signals leading to increase fold change in measured expression levels. With the rapid evolution of NGS instruments and library preparation methods with multiplexing barcodes, longer read lengths and large number of paired end reads associated with reduced cost per lane is highly feasible in the near future. The use of picogram to few nanogram amounts to total RNA for RNAseq still needs to be optimized in order to capture low abundance transcripts.
We believe that the results from this study provide guidelines on the choice of tools in the form of arrays or RNA-seq for clinical transcriptomic studies using limited amount of starting material. We believe that the selection of an appropriate tool for clinical genomic studies is mostly driven by the biological question underlying the study: whether a formal hypothesis is being tested or is the study intended to better describe the complete transcriptome and discover novel transcripts. An emerging approach is to apply both RNA-seq and arrays in combination, in large scale clinical studies, where RNA-seq is used first to define the transcriptome elements associated with the disease in question, followed by high throughput and reliable screening of these elements on thousands of patient samples using the arrays. Integrating data from both microarray and RNA-seq experiments may open up new possibilities for creating meaningful informational networks which will aid our understanding of disease pathology and development of novel therapeutics.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
NR designed the study, wrote the manuscript, NR, PL, KW, performed the experiments. YY helped in mapping the NGS data. JB, PJM performed data analysis and edited the manuscript. GK initiated the NIH protocol for patient recruitment, sample collection and edited the manuscript. DL and CJO funded the study and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
Supplementary Material
Figure S1. Gene Ontology analysis on the differentially expressed genes. The top 13 highly significant classification/functions of genes are shown in the figure.
Figure S2. Effect of Globin Reduction on RNA-seq expression. Y-axis: Read counts per transcript, normalized by median for globin reduced sample; X-axis: Read counts normalized by median for same sample using standard preparation. Correlation coefficient is 0.93.
Table S2. Validation of few differentially expressed genes by QPCR.
Figure S3. Putative Exon 4A . UCSC Genome Browser view of the BAM files for each sample showing genomic region chromosome X: 55067500–5506725. The first 3 aligned tracks show the control samples, the following 5 tracks show the sickle cell disease samples. Aligned reads are Red if to the negative strands and blue if to the positive strands. The total reads per sample is: C3: 15,715,705, C4: 15,131,360, C5: 15,730,372, S6: 16,570,843, S1: 13,481,528, S2: 16,707,788, S3: 14,650,161, S4: 18,580,778 and S5: 16,460,443. S6: 16570843, S1.
Table S1. Complete List of differentially expressed genes (n = 331).
Contributor Information
Nalini Raghavachari, Email: nraghavachari@nhlbi.nih.gov.
Jennifer Barb, Email: barbj@mail.nih.gov.
Yanqin Yang, Email: Yanqin.yang@mail.nih.gov.
Poching Liu, Email: pcliu@nhlbi.nih.gov.
Kimberly Woodhouse, Email: kwoodhous@nhlbi.nih.gov.
Daniel Levy, Email: levyd@nhlbi.nih.gov.
Christopher J O‘Donnell, Email: odonnellc@nhlbi.nih.gov.
Peter J Munson, Email: munson@mail.nih.gov.
Gregory J Kato, Email: gkato@nhlbi.nih.gov.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Drs. Kairong Cui and Keji Zhao for their help in library construction and sequencing. We thank Dr. Shurjo Sen NHGRI for his valuable time and advice in analyzing the sequence data. We acknowledge the help of Ms. Marlene Peters-Lawrence for her assistance in collecting these specimens from volunteers and thank the sickle cell and healthy control subjects who participated in this study. This work was funded by the NHLBI Division of Intramural Research (1 ZIA HL006013-03) and by the CIT Division of Computational Bioscience.
References
- Melton SD, Genta RM, Souza RF. Biomarkers and molecular diagnosis of gastrointestinal and pancreatic neoplasms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(11):620–628. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudan I. New technologies provide insights into genetic basis of psychiatric disorders and explain their co-morbidity. Psychiatr Danub. 2010;22(2):190–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzel JN, Blazer KR, Macdonald DJ, Culver JO, Offit K. Genetics, genomics, and cancer risk assessment: State of the Art and Future Directions in the Era of Personalized Medicine. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(5):327–359. doi: 10.3322/caac.20128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X, Jiao R, Yang L, Wu LP, Li YR, Wang J. New-generation high-throughput technologies based 'omics' research strategy in human disease. Yi Chuan. 2011;33(8):829–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit K. Personalized medicine: new genomics, old lessons. Hum Genet. 2011;130(1):3–14. doi: 10.1007/s00439-011-1028-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam CW, Lau KC, Tong SF. Microarrays for personalized genomic medicine. Adv Clin Chem. 2011;52:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(10)52001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdueva D, Wing MR, Schaub B, Triche TJ. Experimental comparison and evaluation of the Affymetrix exon and U133Plus2 GeneChip arrays. PLoS One. 2007;2(9):e913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford JR, Hey Y, Yates T, Li Y, Pepper SD, Miller CJ. A comparison of massively parallel nucleotide sequencing with oligonucleotide microarrays for global transcription profiling. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:282. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu JM, Camilli A. Discovery of bacterial sRNAs by high-throughput sequencing. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;733:63–79. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-089-8_5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirulli ET, Singh A, Shianna KV, Ge D, Smith JP, Maia JM, Heinzen EL, Goedert JJ, Goldstein DB. Screening the human exome: a comparison of whole genome and whole transcriptome sequencing. Genome Biol. 2010;11(5):R57. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-r57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang F, Barbacioru C, Nordman E, Li B, Xu N, Bashkirov VI, Lao K, Surani MA. RNA-Seq analysis to capture the transcriptome landscape of a single cell. Nat Protoc. 2010;5(3):516–535. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagalakshmi U, Waern K, Snyder M. RNA-Seq: a method for comprehensive transcriptome analysis. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2010;Chapter 4:11–13. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb0411s89. Unit 4 11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tariq MA, Kim HJ, Jejelowo O, Pourmand N. Whole-transcriptome RNAseq analysis from minute amount of total RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(18):e120. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J, Grant SF. Advances in whole genome sequencing technology. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010;12(2):293–305. doi: 10.2174/138920111794295729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marioni JC, Mason CE, Mane SM, Stephens M, Gilad Y. RNA-seq: an assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays. Genome Res. 2008;18(9):1509–1517. doi: 10.1101/gr.079558.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu GE. Recent Applications of DNA Sequencing Technologies in Food, Nutrition and Agriculture. Recent Pat Food Nutr Agric. 2011;3(3):187–195. doi: 10.2174/2212798411103030187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghavachari N, Xu X, Munson PJ, Gladwin MT. Characterization of whole blood gene expression profiles as a sequel to globin mRNA reduction in patients with sickle cell disease. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6484. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological) 1995;57(1):289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL. TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(9):1105–1111. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan AR, Hall IM. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(6):841–842. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5(7):621–628. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieche I, Parfait B, Tozlu S, Lidereau R, Vidaud M. Quantitation of androgen receptor gene expression in sporadic breast tumors by real-time RT-PCR: evidence that MYC is an AR-regulated gene. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22(9):1521–1526. doi: 10.1093/carcin/22.9.1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Q, Lu AY. Pharmacogenetics, pharmacogenomics, and individualized medicine. Pharmacol Rev. 2011;63(2):437–459. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardis ER. A decade's perspective on DNA sequencing technology. Nature. 2011;470(7333):198–203. doi: 10.1038/nature09796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor BS, Ladanyi M. Clinical cancer genomics: how soon is now? J Pathol. 2010;223(2):318–326. doi: 10.1002/path.2794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommasi S, Danza K, Pilato B, De Summa S. Innovative technology for cancer risk analysis. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(Suppl 1):i37–43. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger MR, Kerick M, Timmermann B, Isau M. The power of NGS technologies to delineate the genome organization in cancer: from mutations to structural variations and epigenetic alterations. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011;30(2):199–210. doi: 10.1007/s10555-011-9278-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settle SH, Sulman EP. Tumor profiling: development of prognostic and predictive factors to guide brain tumor treatment. Curr Oncol Rep. 2010;13(1):26–36. doi: 10.1007/s11912-010-0138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu W, Seok J, Mindrinos MN, Schweitzer AC, Jiang H, Wilhelmy J, Clark TA, Kapur K, Xing Y, Faham M. et al. Human transcriptome array for high-throughput clinical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(9):3707–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019753108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris CR. Mechanisms of vasculopathy in sickle cell disease and thalassemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2008. pp. 177–185. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jison ML, Munson PJ, Barb JJ, Suffredini AF, Talwar S, Logun C, Raghavachari N, Beigel JH, Shelhamer JH, Danner RL, Gladwin MT. Blood mononuclear cell gene expression profiles characterize the oxidant, hemolytic, and inflammatory stress of sickle cell disease. Blood. 2004;104(1):270–280. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-08-2760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg MH, Brugnara C. Pathophysiological-based approaches to treatment of sickle cell disease. Annu Rev Med. 2003;54:89–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.54.101601.152439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghavachari N, Xu X, Harris A, Villagra J, Logun C, Barb J, Solomon MA, Suffredini AF, Danner RL, Kato G. et al. Amplified expression profiling of platelet transcriptome reveals changes in arginine metabolic pathways in patients with sickle cell disease. Circulation. 2007;115(12):1551–1562. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.658641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato GJ, Hebbel RP, Steinberg MH, Gladwin MT. Vasculopathy in sickle cell disease: Biology, pathophysiology, genetics, translational medicine, and new research directions. Am J Hematol. 2009;84(9):618–625. doi: 10.1002/ajh.21475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanno T, Bhanu NV, Oneal PA, Goh SH, Staker P, Lee YT, Moroney JW, Reed CH, Luban NL, Wang RH. et al. High levels of GDF15 in thalassemia suppress expression of the iron regulatory protein hepcidin. Nat Med. 2007;13(9):1096–1101. doi: 10.1038/nm1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann J, Callebaut I, Raposo G, Certain S, Bacq D, Dumont C, Lambert N, Ouachee-Chardin M, Chedeville G, Tamary H. et al. Munc13-4 is essential for cytolytic granules fusion and is mutated in a form of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL3) Cell. 2003;115(4):461–473. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00855-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter PD, Willard HF, Gorski JL, Bishop DF. Assignment of human erythroid delta-aminolevulinate synthase (ALAS2) to a distal subregion of band Xp11.21 by PCR analysis of somatic cell hybrids containing X; autosome translocations. Genomics. 1992;13(1):211–212. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90223-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox TC, Bawden MJ, Martin A, May BK. Human erythroid 5-aminolevulinate synthase: promoter analysis and identification of an iron-responsive element in the mRNA. The EMBO journal. 1991;10(7):1891–1902. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Gene Ontology analysis on the differentially expressed genes. The top 13 highly significant classification/functions of genes are shown in the figure.
Figure S2. Effect of Globin Reduction on RNA-seq expression. Y-axis: Read counts per transcript, normalized by median for globin reduced sample; X-axis: Read counts normalized by median for same sample using standard preparation. Correlation coefficient is 0.93.
Table S2. Validation of few differentially expressed genes by QPCR.
Figure S3. Putative Exon 4A . UCSC Genome Browser view of the BAM files for each sample showing genomic region chromosome X: 55067500–5506725. The first 3 aligned tracks show the control samples, the following 5 tracks show the sickle cell disease samples. Aligned reads are Red if to the negative strands and blue if to the positive strands. The total reads per sample is: C3: 15,715,705, C4: 15,131,360, C5: 15,730,372, S6: 16,570,843, S1: 13,481,528, S2: 16,707,788, S3: 14,650,161, S4: 18,580,778 and S5: 16,460,443. S6: 16570843, S1.
Table S1. Complete List of differentially expressed genes (n = 331).