Abstract
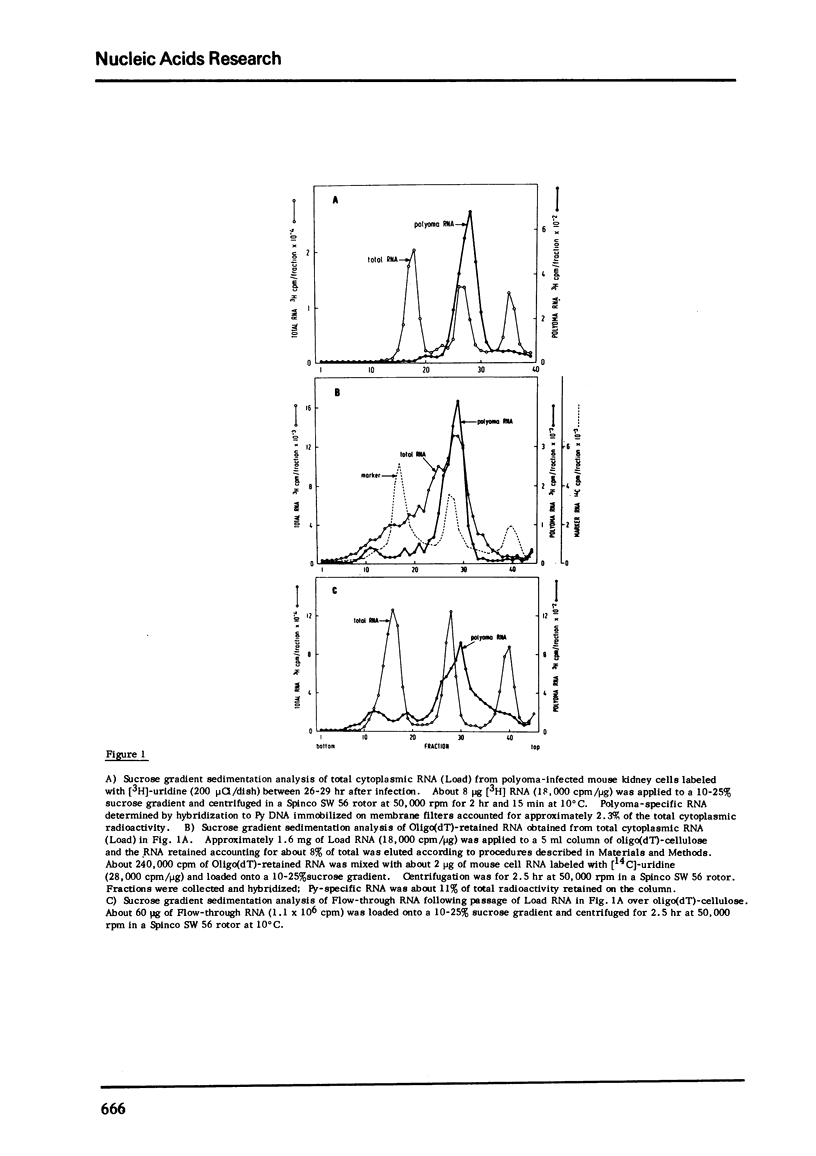
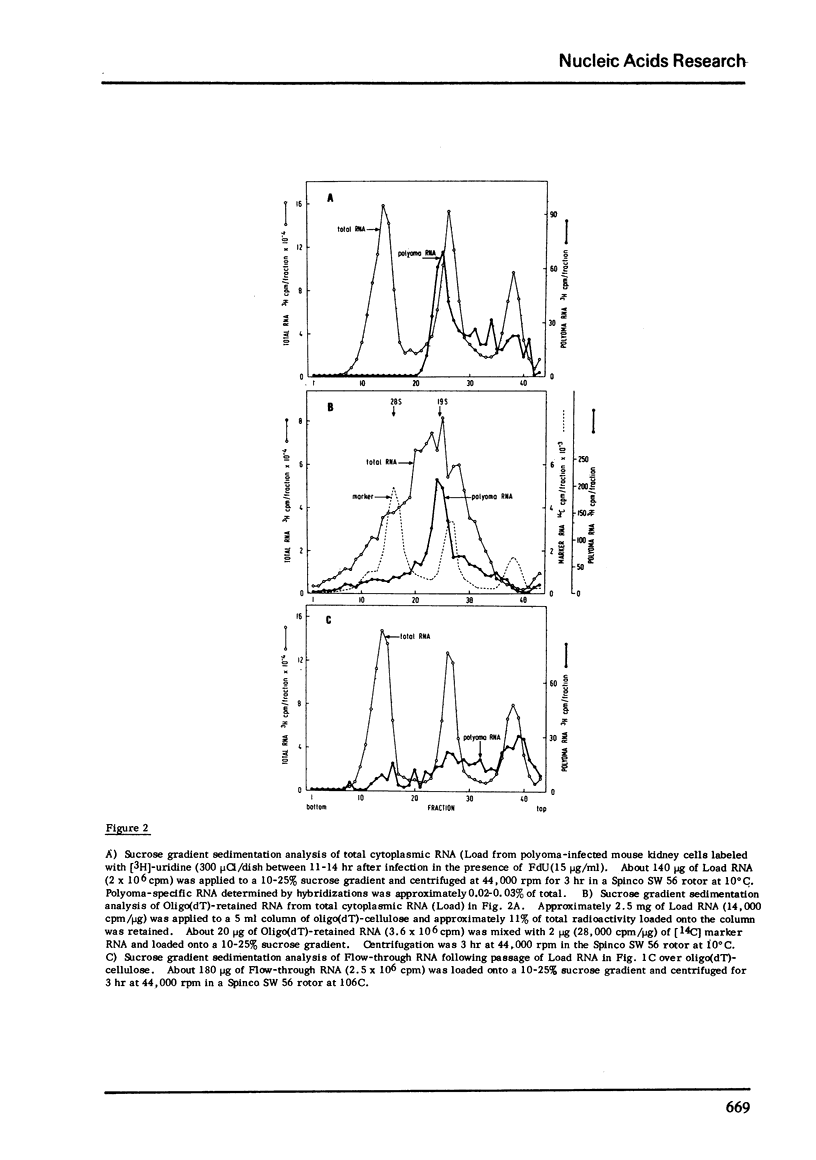
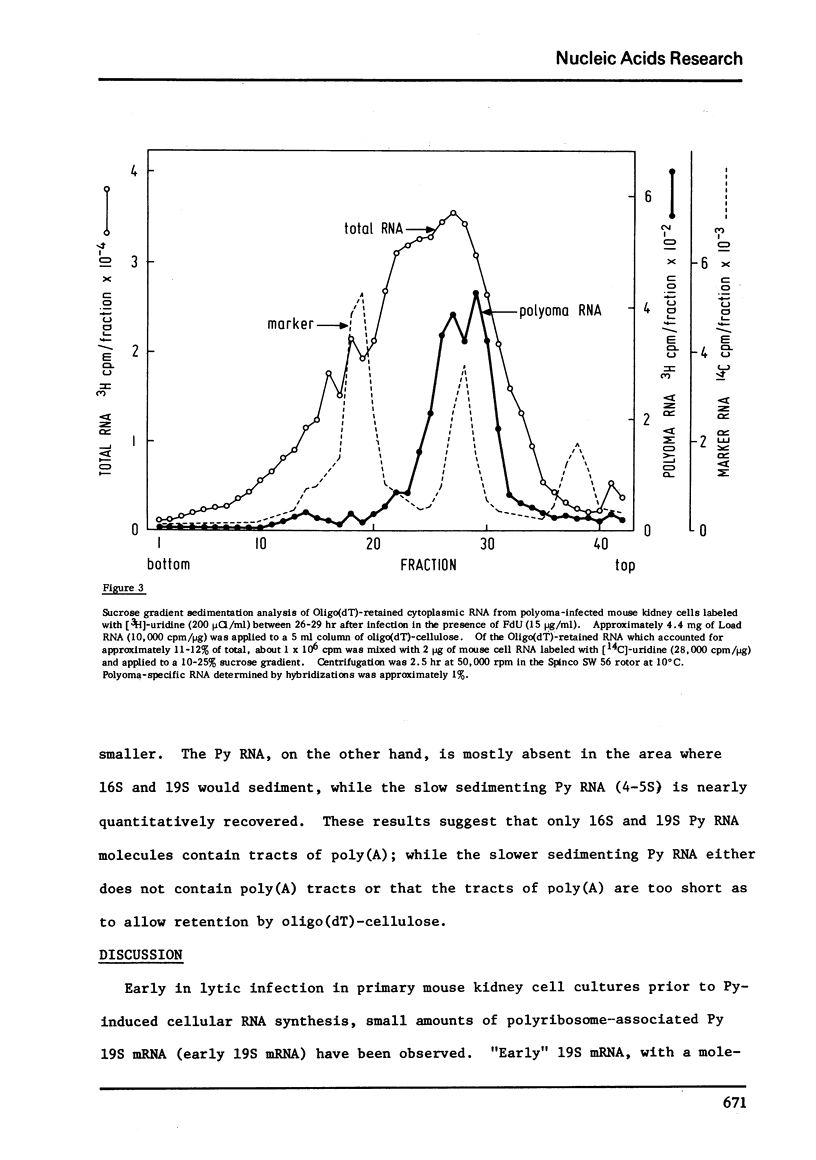
During late lytic infection of mouse kidney cell cultures polyoma 16S and 19S (late 19S RNA) were isolated by oligo(dT)-cellulose chromatography. Approximately 60-80% of total cytoplasmic polyoma RNA contained tracts of poly(A) which were retained by oligo(dT)-cellulose. Early in lytic infection when viral DNA synthesis and the production of capsid protein are blocked by the addition of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine, approximately 100% of polyoma "early" 19S RNA was quantitatively retained by oligo(dT)-cellulose indicating the presence of poly(A) tracts on most 19S mRNA molecules. In addition, 2 classes polyoma RNA, synthesized after the onset of cellular RNA synthesis under conditions where DNA synthesis is inhibited with 5-fluorodeoxyuridine, were found to contain tracts of poly(A). These species sedimenting at 16S and 19S in aqueous sucrose density gradients were also quantitatively retained by oligo (dT)-cellulose.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Buetti E., Scherrer K., Weil R. Transcription of the polyoma virus genome: synthesis and cleavage of giant late polyoma-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2231–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):359–373. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Scharff M. D., Robbins E. Preparation of mammalian polyribosomes with the detergent Nonidet P-40. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 21;149(1):302–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90715-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E. Characterization of late polyoma mRNA. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):249–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.249-260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Philipson L., Wall R., Adesnik M. Polyadenylic acid sequences: role in conversion of nuclear RNA into messenger RNA. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):507–510. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust C. H., Jr, Diggelmann H., Mach B. Isolation of poly(adenylic acid)-rich ribonucleic acid from mouse myeloma and synthesis of complementary deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):925–931. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Perry R. P. The isolation and characterization of steady-state labeled messenger RNA from L-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J., Goldstein D., Weil R. A study on the transcription of the polyoma viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):226–233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Lindstrom D. M., Shure H., Old R. W. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):187–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Weinberg R., Ozer H. L. Translation of mRNA from simian virus 40-infected cells into simian virus 40 capsid protein by cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.590-595.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., May P., Weil R. "Early" virus-specific RNA may contain information necessary for chromosome replication and mitosis induced by Simian Virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1654–1658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendecki J., Lee S. Y., Brawerman G. Characteristics of the polyadenylic acid segment associated with messenger ribonucleic acid in mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):792–798. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. L., Aviv H., Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Rozenblatt S., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA of simian virus 40: synthesis of the major capsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pétursson G., Weil R. A study on the mechanism of polyoma-induced activation of the cellular DNA-synthesizing apparatus. Synchronization by FUdR of virus-induced DNA synthesis. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;24(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01242898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Weil R. Polyoma viral DNA replicated as a nucleoprotein complex in close association with the host cell chromatin. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):567–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.567-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Darnell J. E. Polyadenylic acid segment in mRNA becomes shorter with age. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):265–268. doi: 10.1038/newbio241265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E. Purification of polyoma virus. Virology. 1963 Feb;19:158–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Kára J. Polyoma "tumor antigen": an activator of chromosome replication? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):1011–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R., Salomon E., May E., May P. A simplifying concept in tumor virology: virus-specific "pleiotropic effectors". Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):381–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Ben-Ishai Z., Newbold J. E. Simian virus 40 transcription in productively infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1263–1273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1263-1273.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Warnaar S. O., Winocour E. Isolation and characterization of simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.193-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



