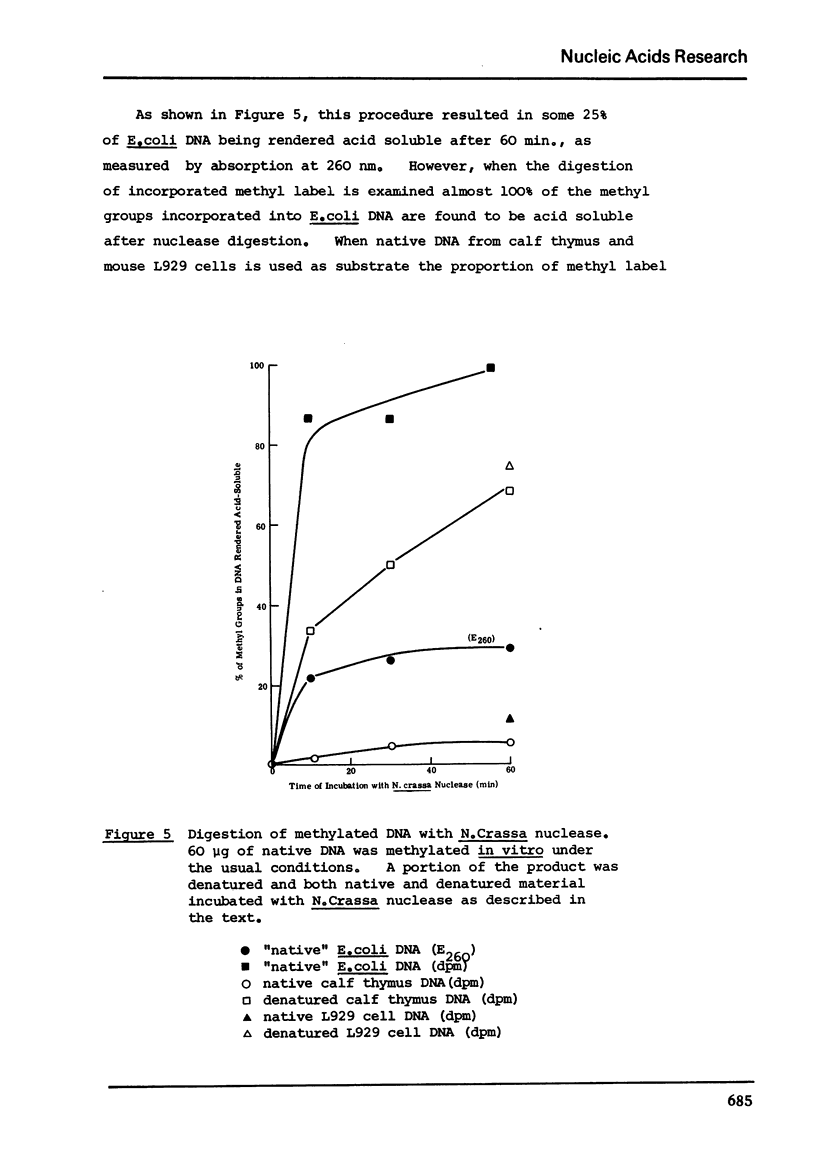
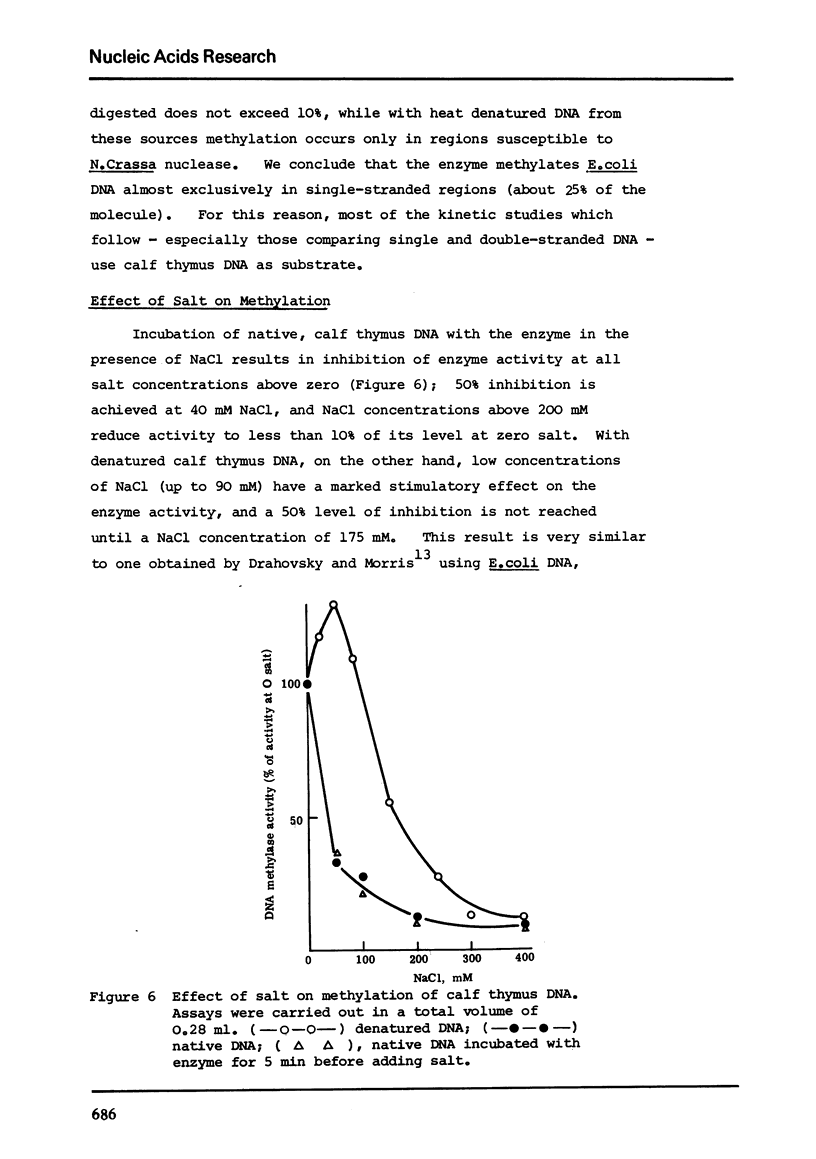
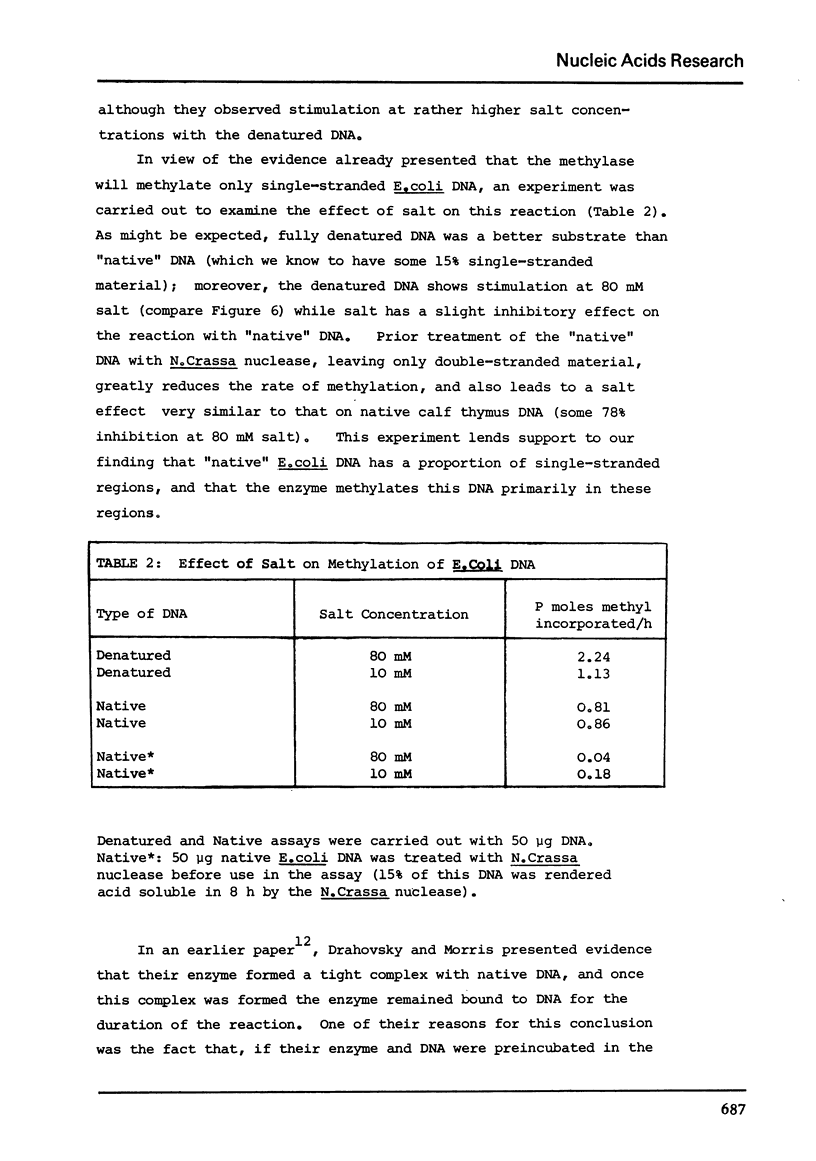
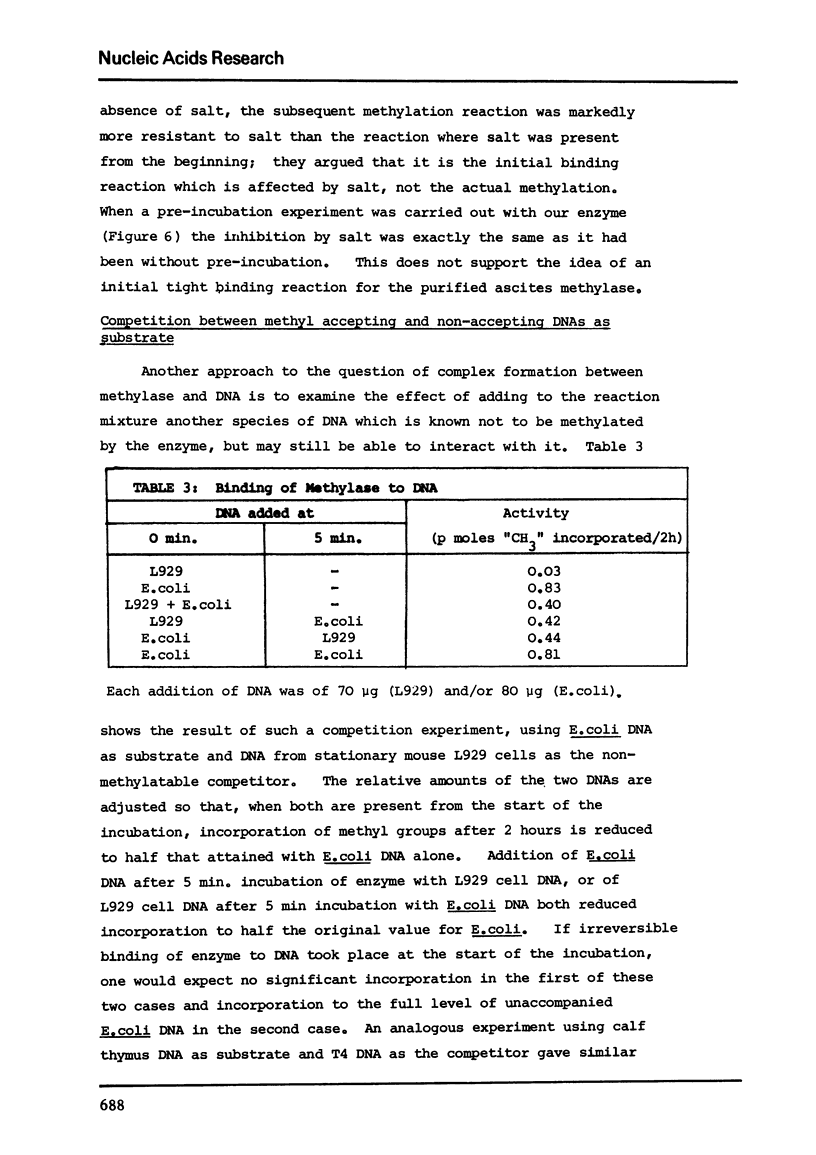
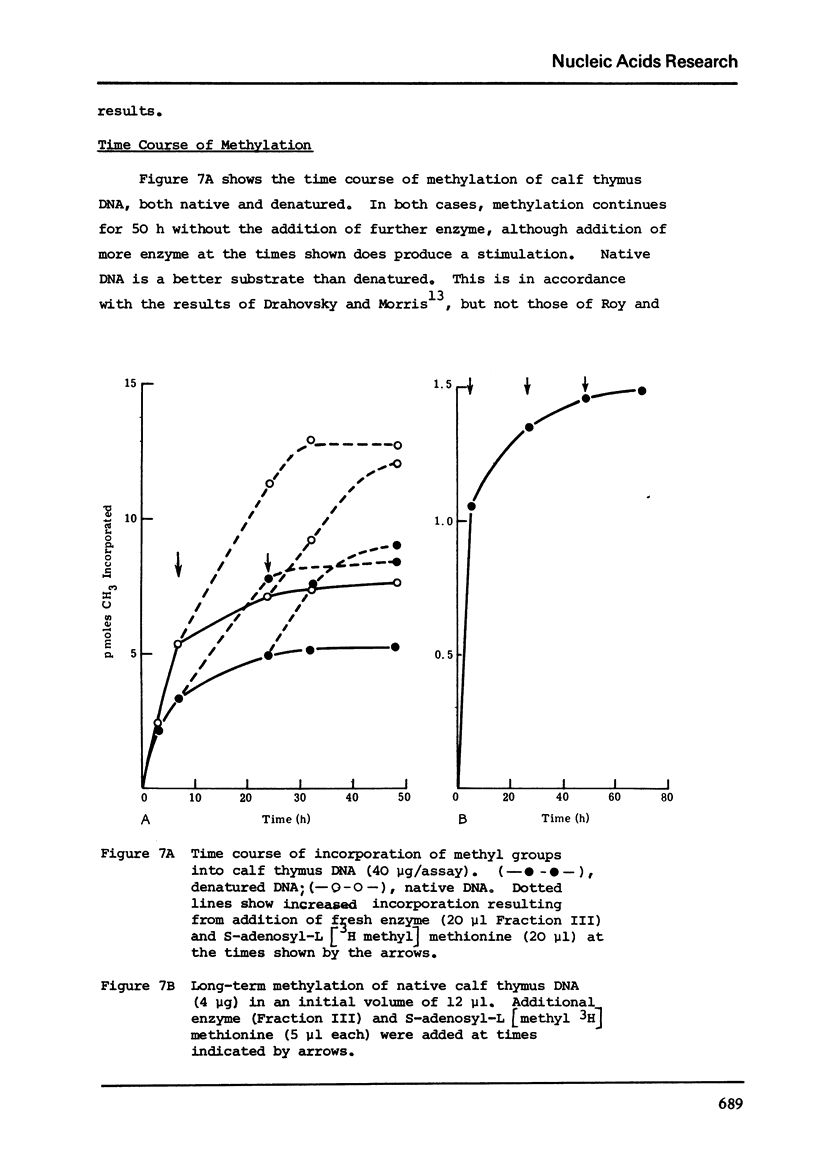
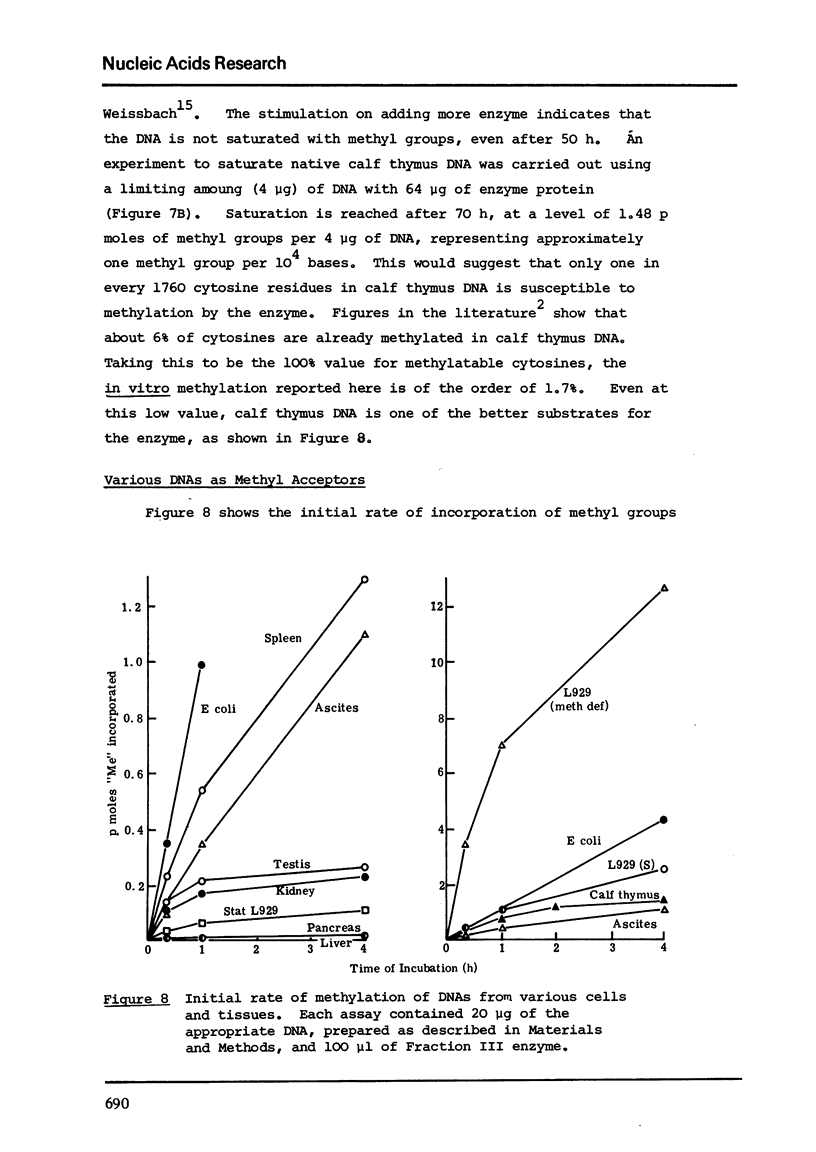
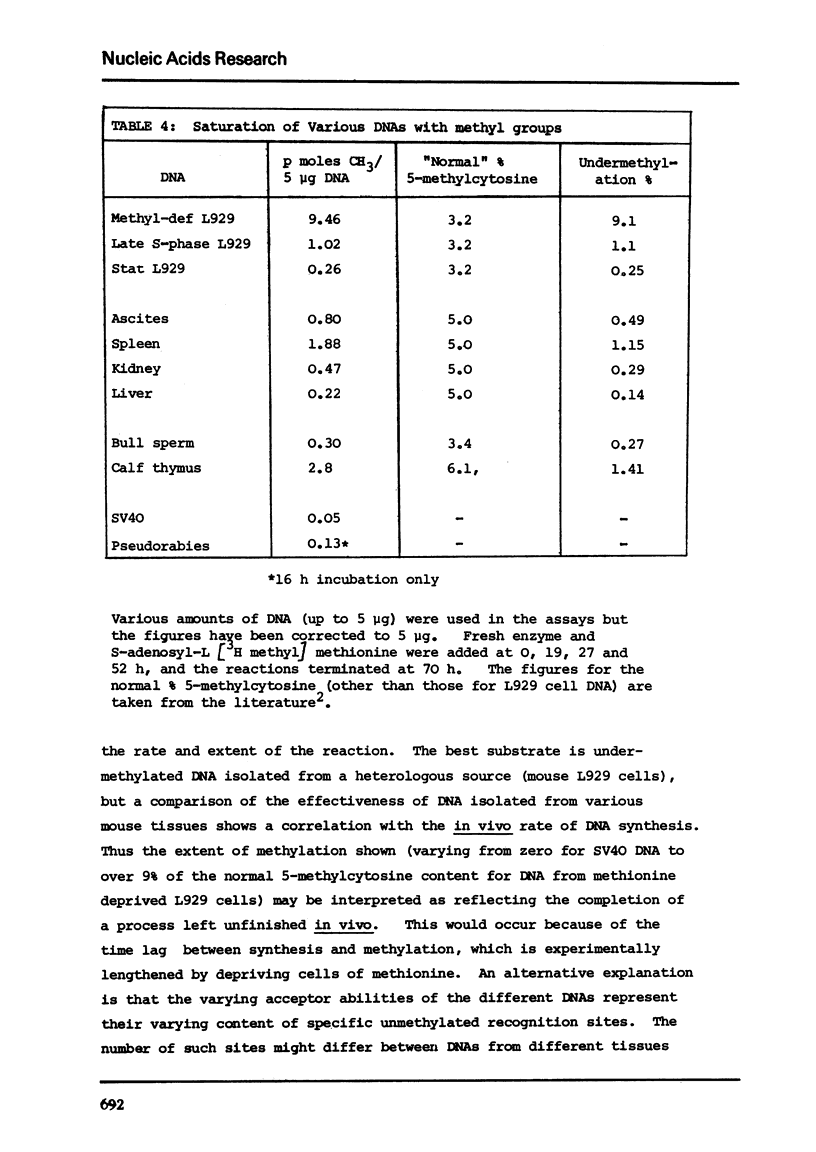
Abstract
DNA methylase has been purified 405-fold from Krebs II ascites cells. The purified enzyme is homogeneous on SDS-poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis (molecular weight about 80,000) and the only product of the reaction with DNA is 5-methyl cytosine. Both native and denatured DNA are methylated by the enzyme; with calf thymus DNA the double stranded form is the better substrate but the enzyme preferentially methylates single stranded E.coli DNA even in "native" preparations. Our results do not support a mechanism whereby the enzyme methylates DNA by binding irreversibly and "walking" along it. By measuring maximum levels of methylation of DNAs from different sources we have estimated the proportion of unmethylated sites present in them. Homologous ascites DNA can be methylated, but only to about 5% of the level of the best substrate, undermethylated mouse L929 cell DNA. DNA isolated from growing cells or tissues is a better substrate than DNA from normal liver or pancreas, or from stationary cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L., Hogarth C. DNA methylation in isolated nuclei: old and new DNAs are methylated. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 7;331(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90434-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. L. The effect of endogenous pools of thymidylate on the apparent rate of DNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Jul;56(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. L. The relationship between synthesis and methylation of DNA in mouse fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 16;254(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90829-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arber W., Linn S. DNA modification and restriction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:467–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon R. H., Adams R. L. The in vivo methylation of DNA in mouse fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):322–329. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon R. H. Enzymic modification of chromosomal macromolecules. I. DNA and protein methylation in mouse tumour cell chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 11;232(2):359–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahovsky D., Morris N. R. The mechanism of action of rat liver DNA methylase. 3. Nucleotide requirements for binding and methylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 25;277(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahovský D., Morris N. R. Mechanism of action of rat liver DNA methylase. I. Interaction with double-stranded methyl-acceptor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):475–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahovský D., Morris N. R. Mechanism of action of rat liver DNA methylase. II. Interaction with single-stranded methyl-acceptor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90384-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalousek F., Morris N. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid methylase activity in rat spleen. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2440–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalousek F., Morris N. R. The purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid methylase from rat spleen. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1157–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W. The 5-methylcytosine content of DNA: tissue specificity. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Aug;78(1):33–36. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. R., Pih K. D. The preparation of soluble DNA methylase from normal and regenerating rat liver. Cancer Res. 1971 Apr;31(4):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Marmur J. Purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid methylase from Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):761–773. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P. H., Weissbach A. DNA methylase from HeLa cell nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1669–1684. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheid B., Srinivasan P. R., Borek E. Deoxyribonucleic acid methylase of mammalian tissues. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):280–285. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneider T. W., Teague W. M., Rogachevsky L. M. S-adenosylmethionine: DNA-cytosine 5-methyltransferase from a Novikoff rat hepatoma cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1685–1700. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi L., Granieri A., Scarano E. Enzymatic DNA modifications in isolated nuclei from developing sea urchin embryos. Exp Cell Res. 1972 May;72(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90588-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanyushin B. F., Mazin A. L., Vasilyev V. K., Belozersky A. N. The content of 5-methylcytosine in animal DNA: the species and tissue specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 28;299(3):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanyushin B. F., Tkacheva S. G., Belozersky A. N. Rare bases in animal DNA. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):948–949. doi: 10.1038/225948a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




