Abstract
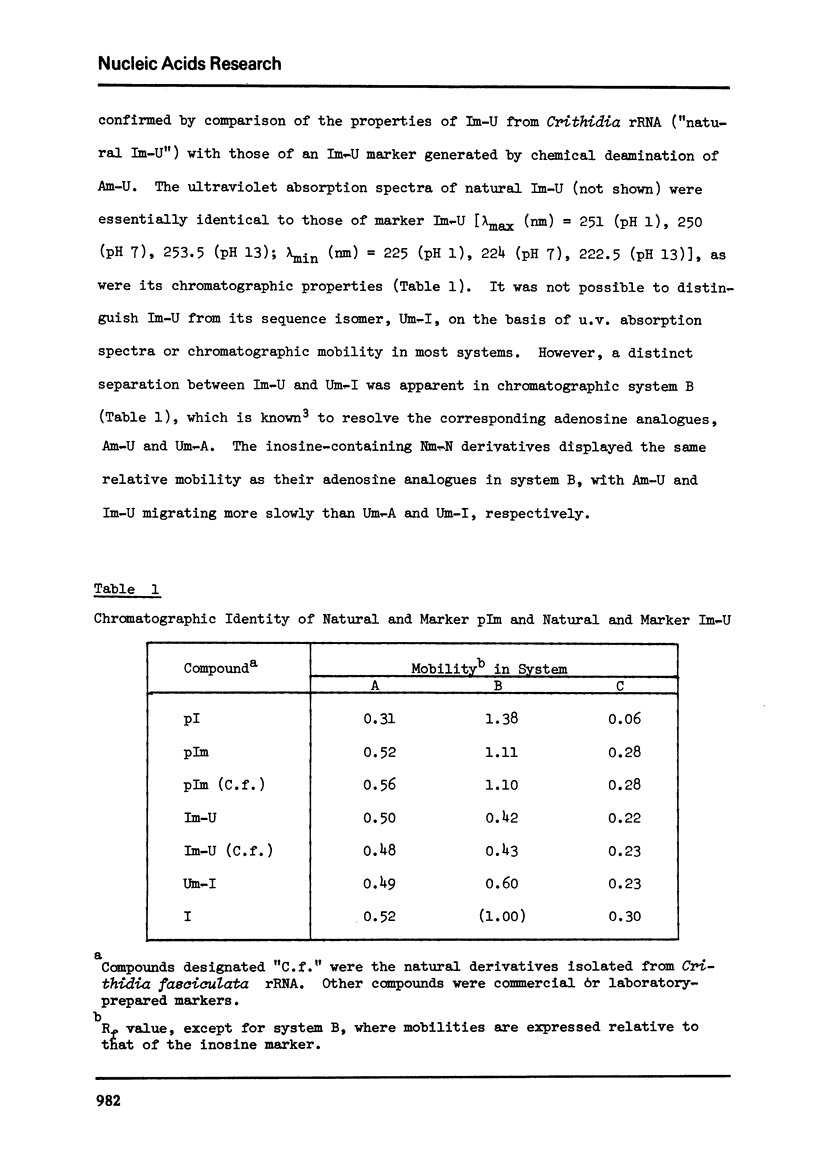
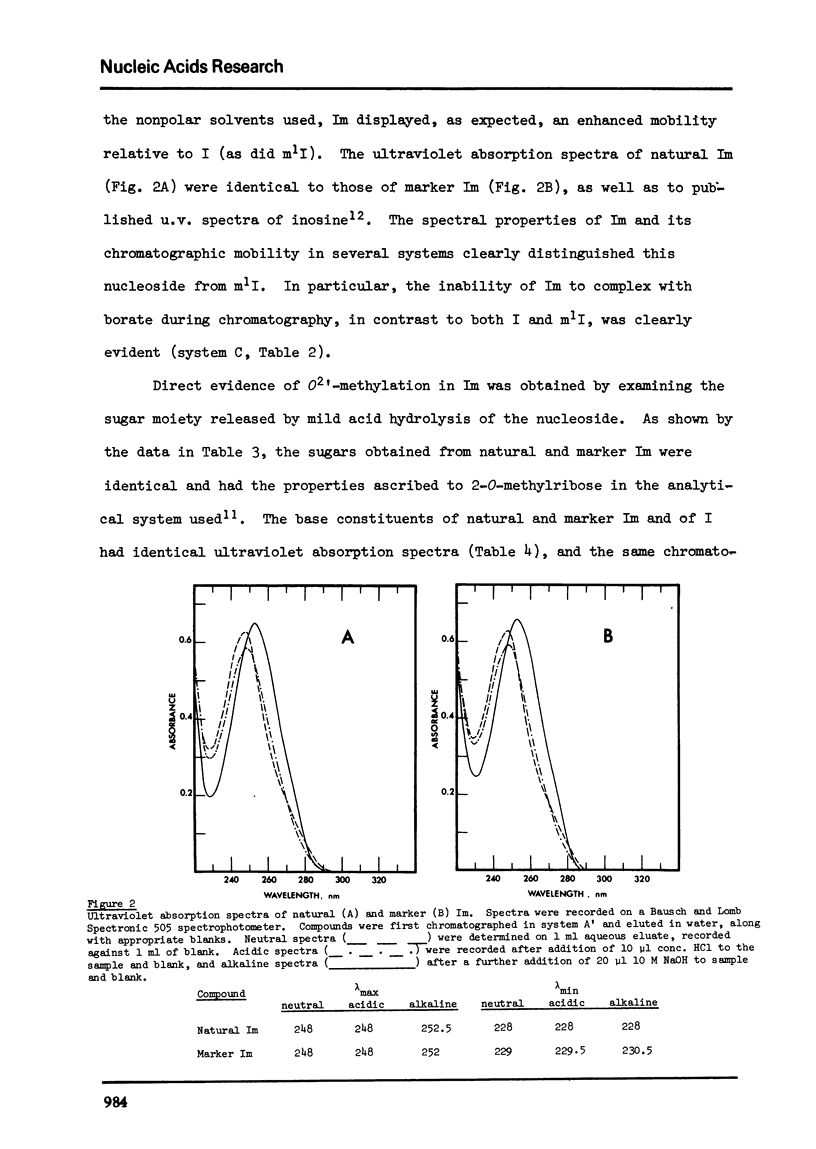
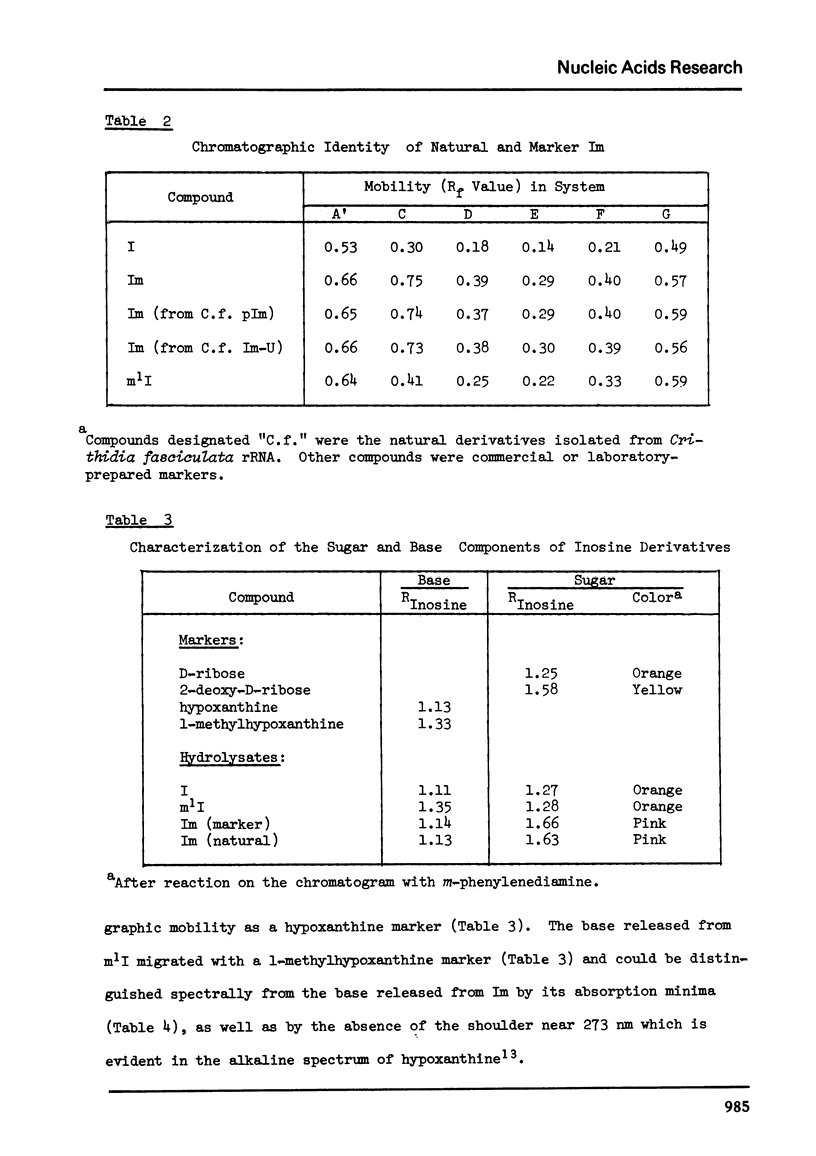
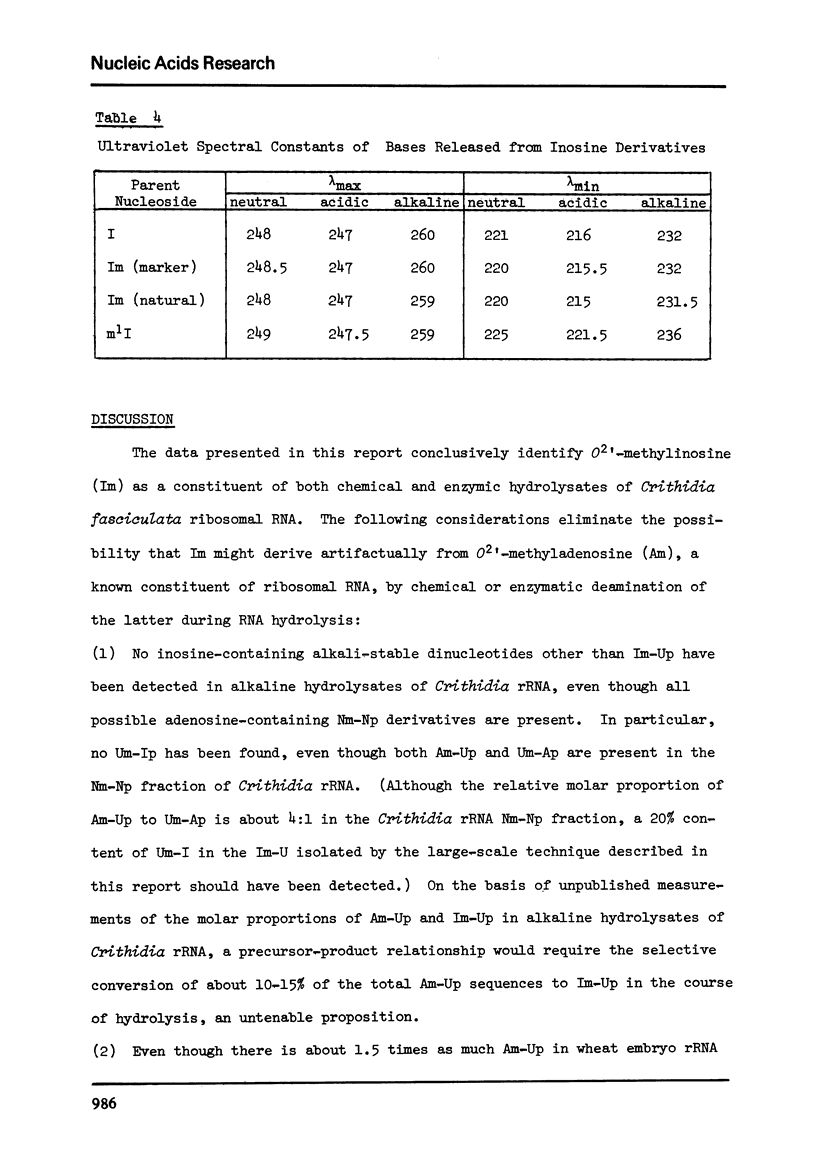
A novel nucleoside, O2'-methylinosine (Im), has been identified as a constituent of the ribosomal RNA of Crithidia fasciculata, a hemoflaggelate protozoan. The nucleoside is released as part of an alkali-stable dinucleotide, Im-Up, by alkaline hydrolysis of Crithidia rRNA, and as a 5'-nucleotide, pIm, by snake venom hydrolysis of the same RNA. The Im-containing derivatives isolated from Crithidia rRNA were characterized by comparison with marker compounds prepared by chemical deamination of the corresponding adenosine analogues. O2'-Methylinosine prepared from either natural Im-Up or natural pIm had the same ultraviolet absorption spectra and chromatographic properties as marker Im. Characterization of the base and sugar components of Im as hypoxanthine and 2-O-methylribose, respectively, provided final confimration of structure. Control experiments have eliminated the possibility that Im arises from O2'-methyladenosine (Am), a known constituent of ribosomal RNA, by chemical or enzymatic deamination during hydrolysis of Crithidia rRNA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cunningham R. S., Gray M. W. Derivatives of N-(N-(9-beta-D-ribofuranosylpurin-6-yl)carbamoyl)threonine in phosphodiesterase hydrolysates of wheat embryo transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):543–553. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. Analysis of O2'-methylnucleoside 5'-phosphates in snake venom hydrolysates of RNA: identification of O2'-methyl-5-carboxymethyluridine as a constituent of yeast transfer RNA. Can J Biochem. 1975 Jul;53(7):735–746. doi: 10.1139/o75-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
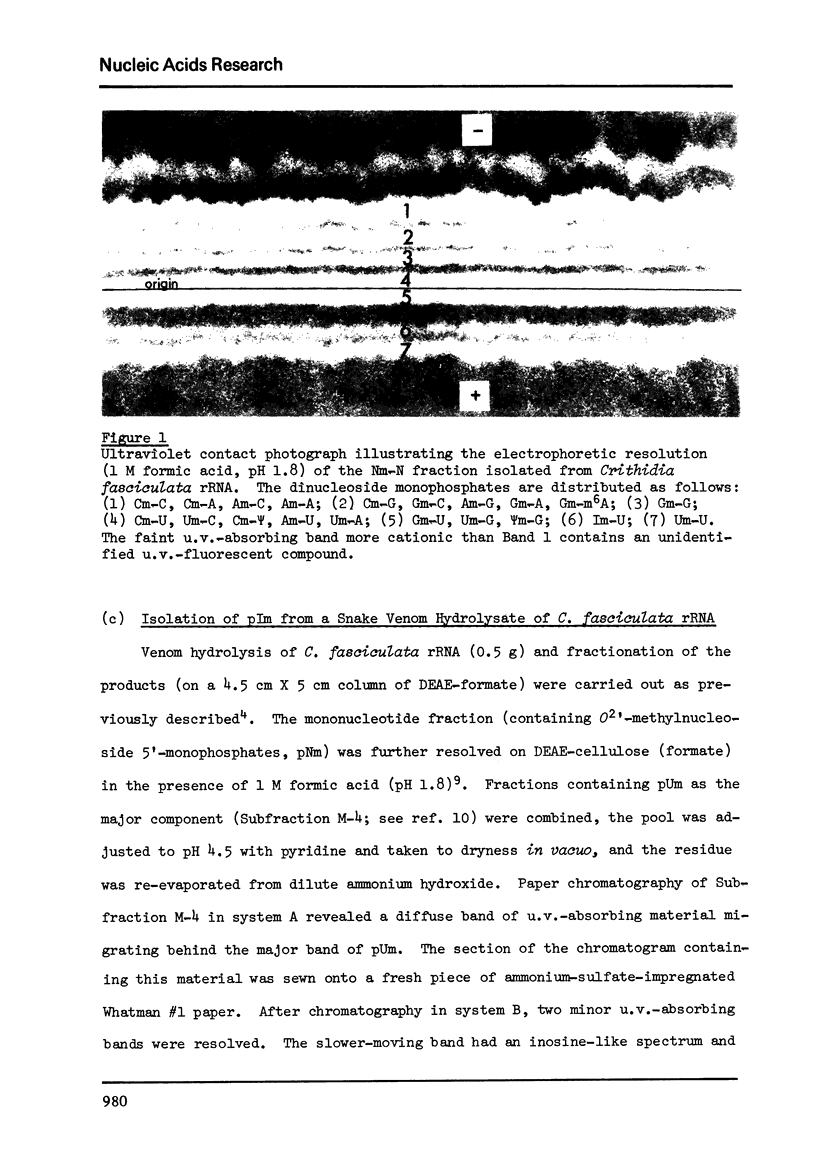
- Gray M. W. Dinucleotide sequences containing both base and sugar modifications in the ribosomal RNA of Crithidia fasciculata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 6;374(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. The presence of O-2'-methylpseudouridine in the 18S + 26S ribosomal ribonucleates of wheat embryo. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5453–5463. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE B. G., ALLEN F. W. The isolation of dinucleotides from alkali hydrolyzates of ribonucleates. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Apr;39:721–728. doi: 10.1139/o61-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE B. G. The separation of adenosine, guanosine, cytidine and uridine by one-dimensional filter-paper chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 28;72:110–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Forbes J., de Jonge P., Klootwijk J. Presence of a hypermodified nucleotide in HeLa cell 18 S and Saccharomyces carlsbergensis 17 S ribosomal RNAs. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):60–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. L., Lane B. G. Characterization of N4,O2'-dimethylcytidine, a rare nucleoside constituent of Escherichia coli 16-S RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 29;166(3):605–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGH H., LANE B. G. THE ALKALI-STABLE DINUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCES IN 18S+28S RIBONUCLEATES FROM WHEAT GERM. Can J Biochem. 1964 Jul;42:1011–1021. doi: 10.1139/o64-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saponara A. G., Enger M. D. The isolation from ribonucleic acid of substituted uridines containing alpha-aminobutyrate moieties derived from methionine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 27;349(1):61–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazawa I., Tazawa S., Alderfer J. L., Ts'o P. O. A novel procedure for the synthesis of 2'-O-alkyl nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4931–4937. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



