Abstract
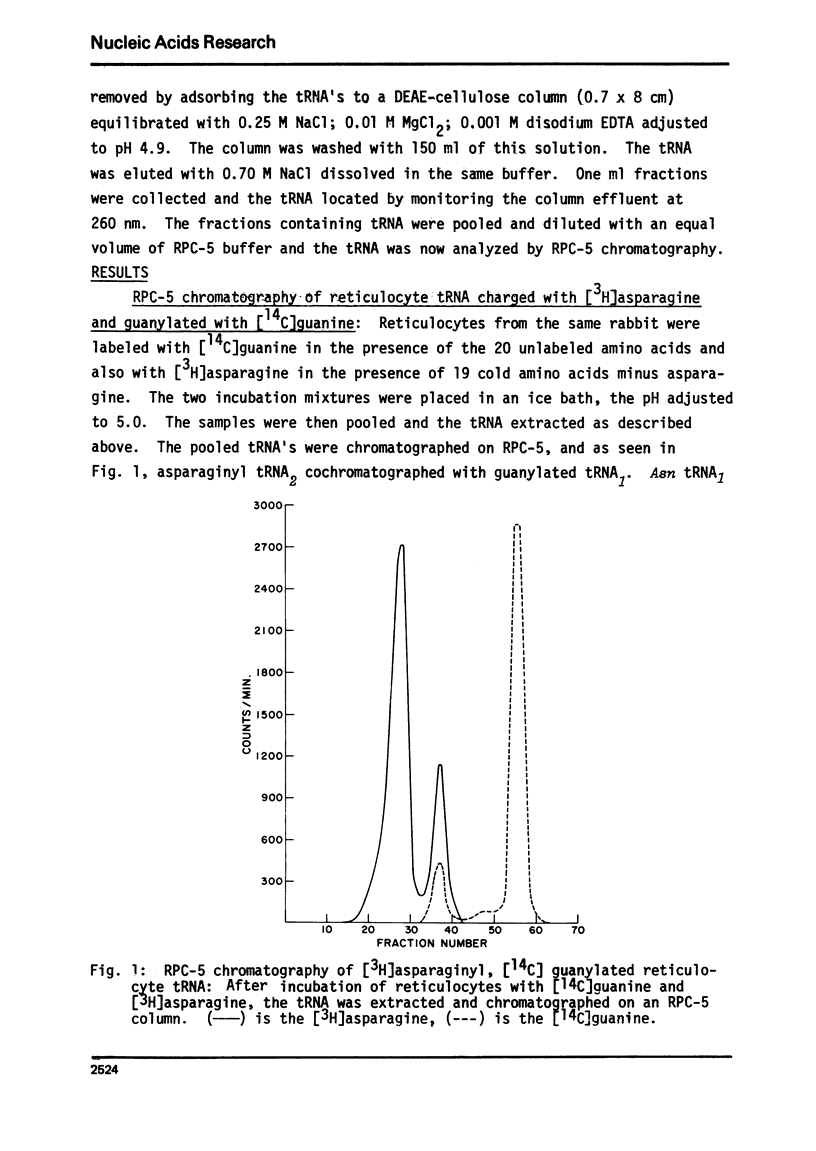
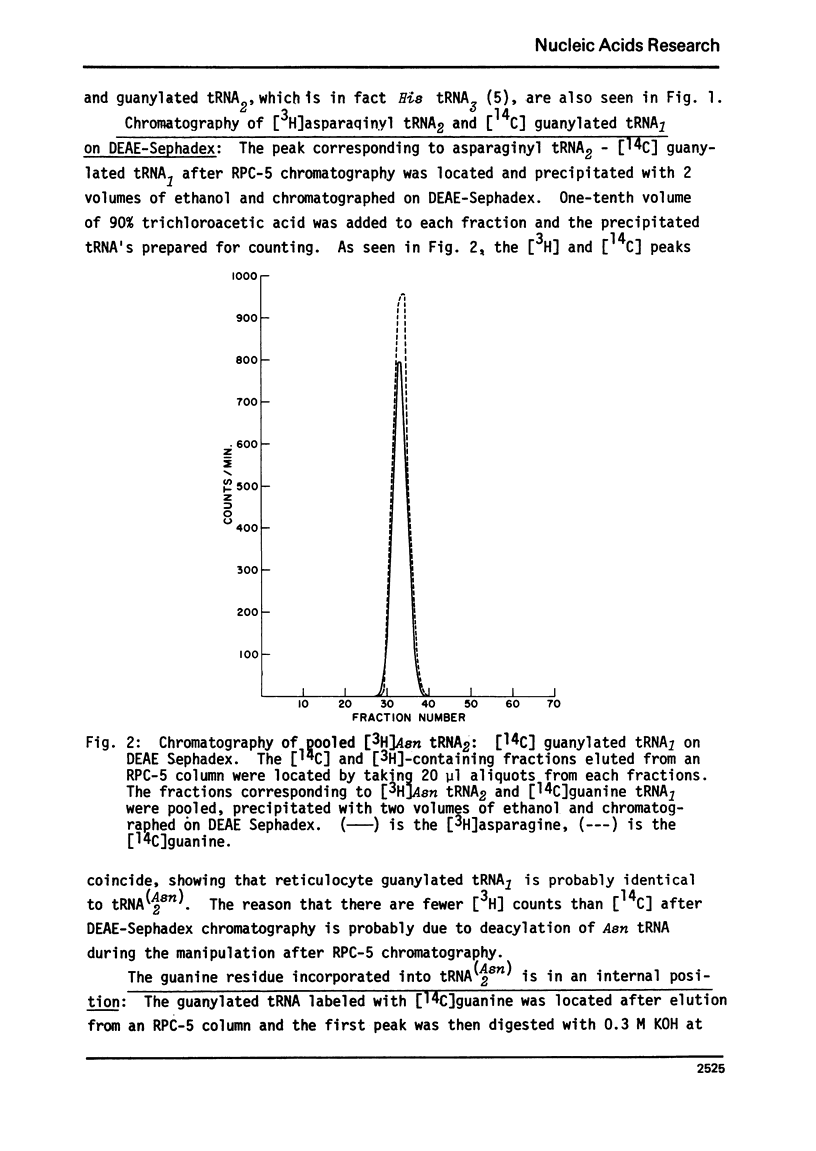
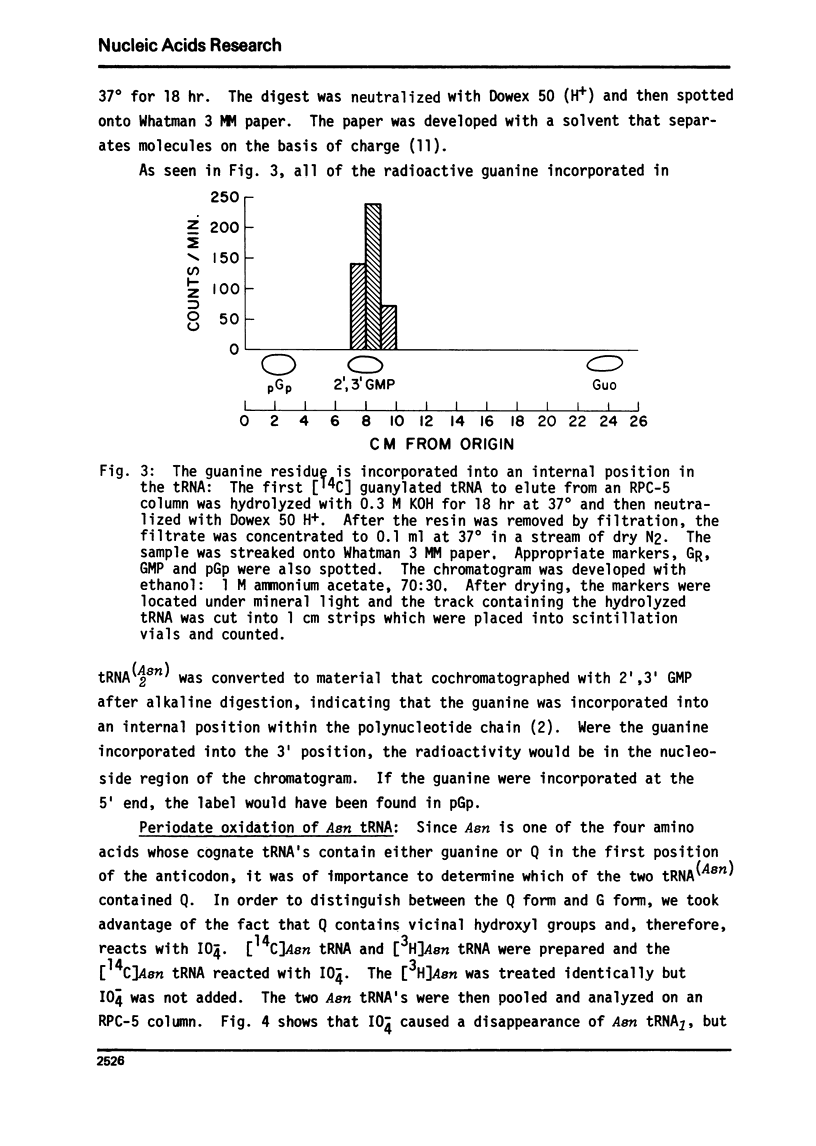
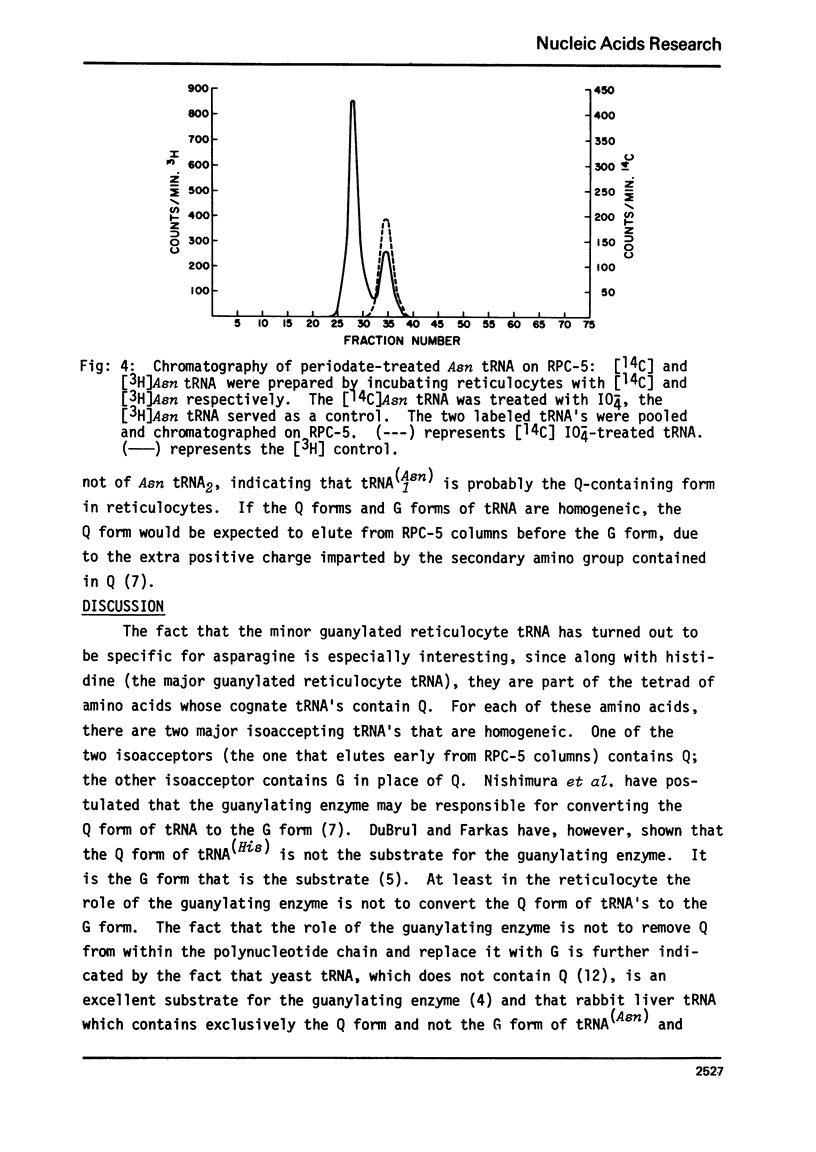
Two of the tRNA's found in rabbit reticulocytes are substrates for a post-transcriptional modification leading to the incorporation of guanine into the polynucleotide chain. The major guanylated tRNA was previously identified as tRNA(H3is). In the present report we show that the minor guanylated tRNA is tRNA(A2sn), and that just as in the case of tRNA(His), the guanine is located in an internal position. There are only two tRNA(Asn) in reticulocytes. We further show that one of these, the one that is not labeled with guanine, contains the hypermodified base known as Q. tRNA(A2sn) does not contain Q.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DEBELLIS R. H., GLUCK N., MARKS P. A. SYNTHESIS OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN RABBIT BLOOD CELLS IN VIVO. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1329–1337. doi: 10.1172/JCI105008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas W. R., Singh R. D. Guanylation of transfer ribonucleic acid by a cell-free lysate of rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7780–7785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankins W. D., Farkas W. R. Guanylation of transfer RNA by rabbit reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 16;213(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Kuchino Y., Nihei K., Nishimura S. Distribution of the modified nucleoside Q and its derivatives in animal and plant transfer RNA's. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1931–1939. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Oashi Z., Harada F., Nishimura S., Oppenheimer N. J., Crain P. F., Liehr J. G., von Minden D. L., McCloskey J. A. Structure of the modified nucleoside Q isolated from Escherichia coli transfer ribonucleic acid. 7-(4,5-cis-Dihydroxy-1-cyclopenten-3-ylaminomethyl)-7-deazaguanosine. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4198–4208. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelmers A. D., Heatherly D. E. Columns for rapid chromatographic separation of small amounts of tracer-labeled transfer ribonucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):486–495. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Caskey C. T., Nirenberg M. Fine structure of RNA codewords recognized by bacterial, amphibian, and mammalian transfer RNA. Science. 1967 Feb 17;155(3764):820–826. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3764.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAHR P. F. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF RIBONUCLEASE II FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3716–3726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Meltzer V. N., McNamara A. L. A comparison of rabbit liver and reticulocyte transfer RNA: evidence of unique species in reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 31;349(3):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


