Abstract
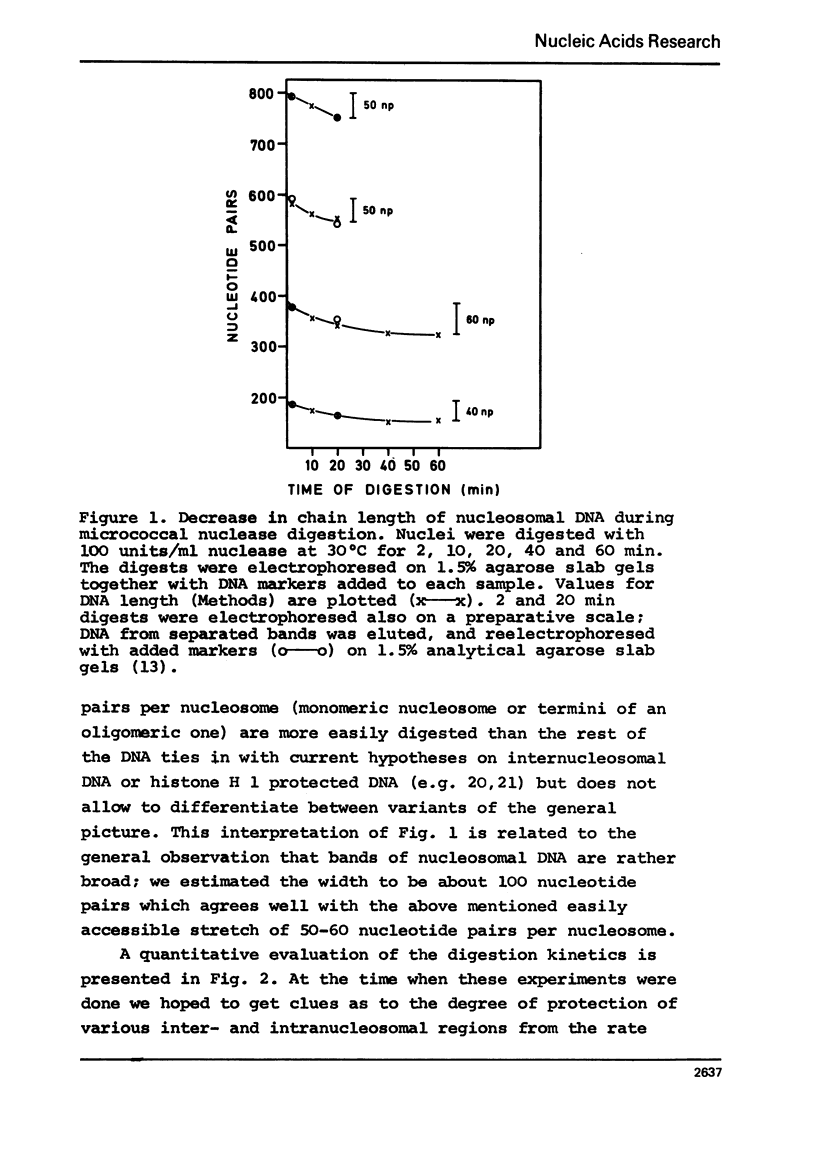
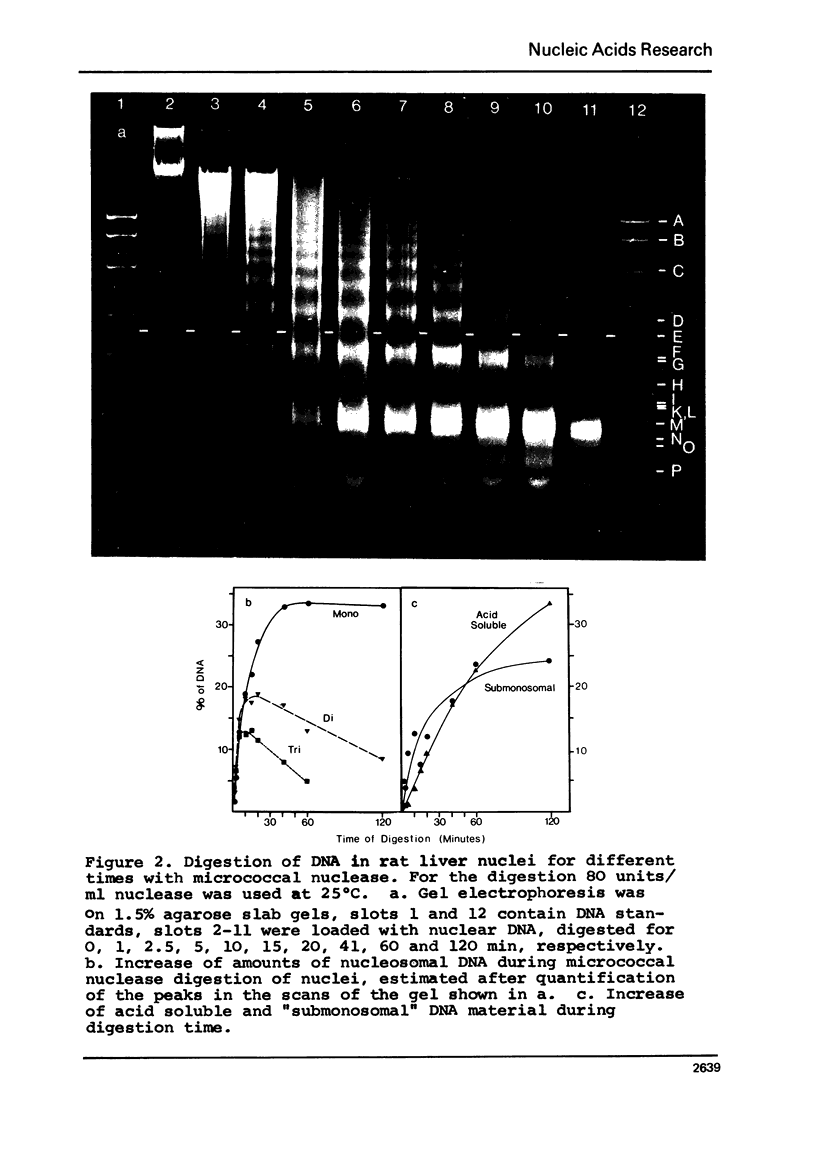
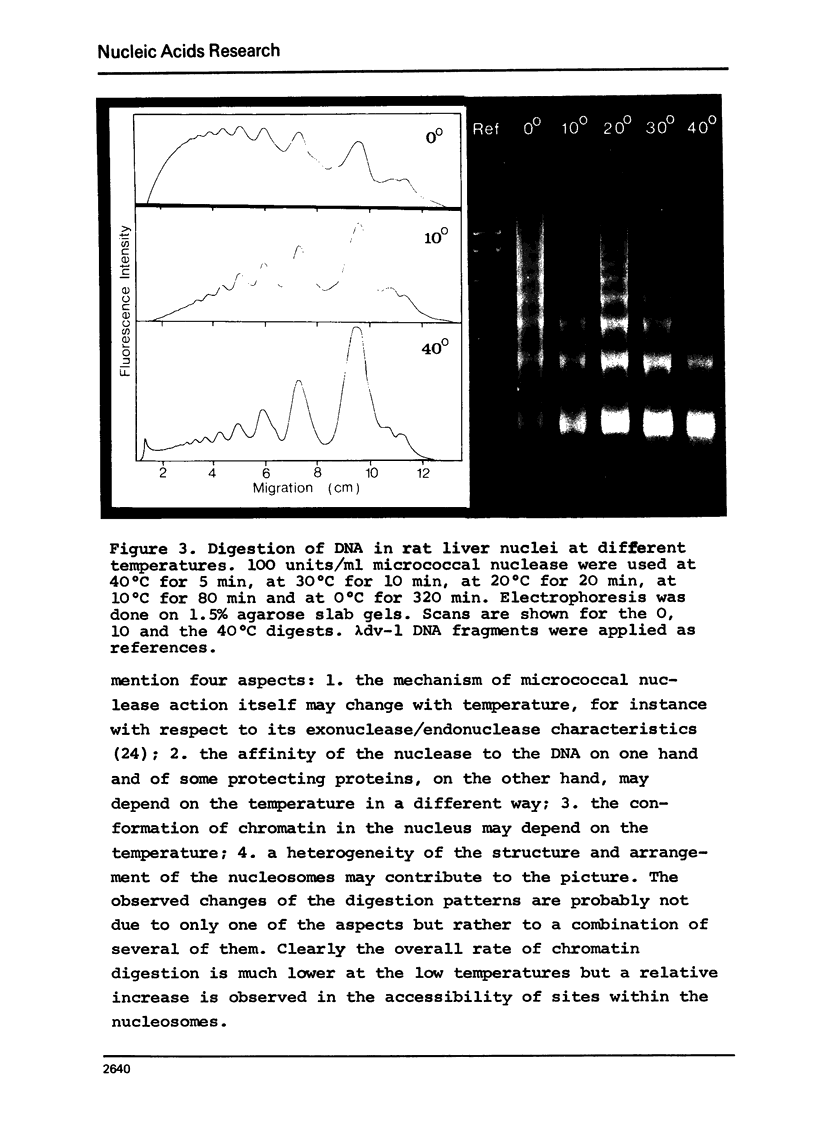
In the course of digestions of rat liver nuclei with micrococcal nuclease the size of the nucleosomal DNA is shortened by 50-60 nucleotide pairs from starting lengths of about 200, 400, 600, 800, etc. nucleotide pairs in the monomeric and oligomeric nucleosomes, respectively. Acid soluble DNA material is created relatively slowly as compared to the rate of formation of subnucleosomal material. More DNA with lengths in between the 200, 400, etc. nucleotide pairs of nucleosomal DNA is formed when digestions with micrococcal nuclease are carried out at 0 to 10 degrees C compared to 40 degrees C. With DNAase II, on the other hand, formation of a 200 nucleotide pair pattern is favoured at the low temperatures. Apparently, the accessibility of potential cleavage sites in between and within nucleosomes depends strongly on the conditions of digestion. Possible reasons for this dependence are discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R. Cleavage of DNA in nuclei and chromatin with staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2921–2925. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakayev V. V., Melnickov A. A., Osicka V. D., Varshausky A. J. Studies on chromatin. II. Isolation and characterization of chromatin subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Aug;2(8):1401–1419. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.8.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. P., Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Ibel K. The subunit structure of the eukaryotic chromosome. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):245–249. doi: 10.1038/253245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keichline L. D., Villee C. A., Wassarman P. M. Structure of eukaryotic chromatin. Evaluation of periodicity using endogenous and exogenous nucleases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 18;425(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. F., Donohue D. C., Finch L. R. New analytical procedure for the estimation of DNA with p-nitrophenylhydrazine. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):562–574. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterhof D. K., Hozier J. C., Rill R. L. Nucleas action on chromatin: evidence for discrete, repeated nucleoprotein units along chromatin fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):633–637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer W., Horz W., Igo-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Restriction nucleases as probes of chromatin structure. Nature. 1975 Dec 4;258(5534):450–452. doi: 10.1038/258450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. R., Herman T. M., Kovacic R. T., Beaudreau G. S., Van Holde K. E. Analysis of subunit organization in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Whitlock J. P., Jr Chemical evidence that chromatin DNA exists as 160 base pair beads interspersed with 40 base pair bridges. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jan;3(1):117–127. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. A comparison of the digestion of nuclei and chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2915–2920. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeck R. E., Hobom G. Mapping of cleavage sites for restriction endonucleases in lambdadv plasmids. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):595–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock C. L., Sweetman H. E., Frado L. L. Structural repeating units in chromatin. II. Their isolation and partial characterization. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:111–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90660-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bruggen E. F., Arnberg A. C., van Holde K. E., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Shaw B. R. Electron microscopy of chromatin subunit particles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1365–1370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]